Article Directory
Preface
Linux's firewall system mainly works at the network layer, filtering and restricting TCP/IP data packets, which is a typical packet filtering firewall (or called a network layer firewall). The protective wall system of Linux system is based on kernel coding. With very stable performance and extremely high efficiency, it has been widely used.
1. Overview of Firewalld
Firewalld
- A dynamic firewall management tool that supports network links and interface security levels defined by the network area
- Support IPv4, IPv6 firewall settings and Ethernet bridge
- Support services or applications directly add firewall rules interface
- Has two configuration modes
◆Runtime configuration
◆Permanent configuration
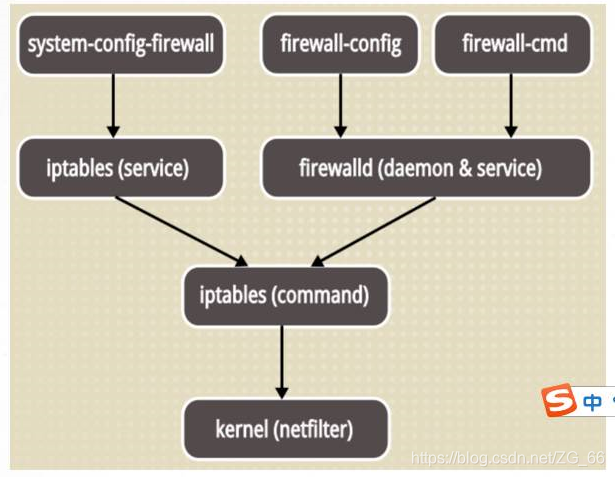
Second, the relationship between Firewalld and iptables
netfilter
- The packet filtering function system in the Linux kernel
- Known as the "kernel mode" of the Linux firewall
Firewalld/iptables
- CentOS7 default tool for managing firewall rules (Firewalld)
- Called the "user mode" of the Linux firewall
3. Firewalld network area
1. Regional introduction
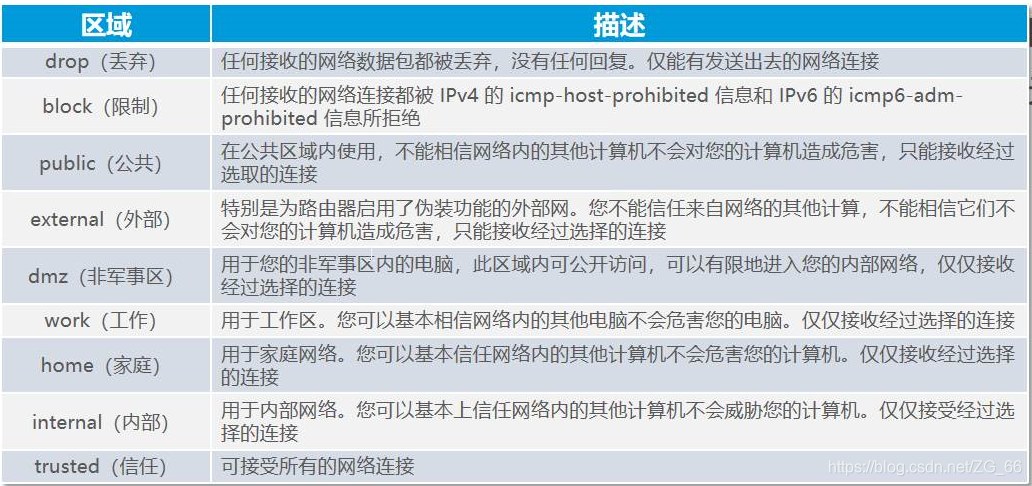
- The area is like a security door to enter the host, each area has different restriction rules
- One or more areas can be used, but any active area needs to be associated with at least the source address or interface
- By default, the public area is the default area, including all interfaces (network cards)
2. Firewalld data processing flow
Check the source address of the data source
- If the source address is associated with a specific area, the rules specified by the area are executed
- If the source address is not associated with a specific area, use the area of the incoming network interface and execute the rules specified by the area
- If the network interface is not associated with a specific area, the default area is used and the rules specified by the area are executed
Fourth, the configuration method of Firewalld firewall
1. Runtime configuration
- Take effect in real time, and continue until Firewalld restarts or reloads the configuration
- Do not interrupt existing connections
- Cannot modify service configuration
2. Permanent configuration
- Does not take effect immediately, unless Firewalld restarts or reloads the configuration
- Disconnect existing connection
- Can modify the service configuration
3. Firewall-config graphical tool
4. Firewall-cmd command line tool
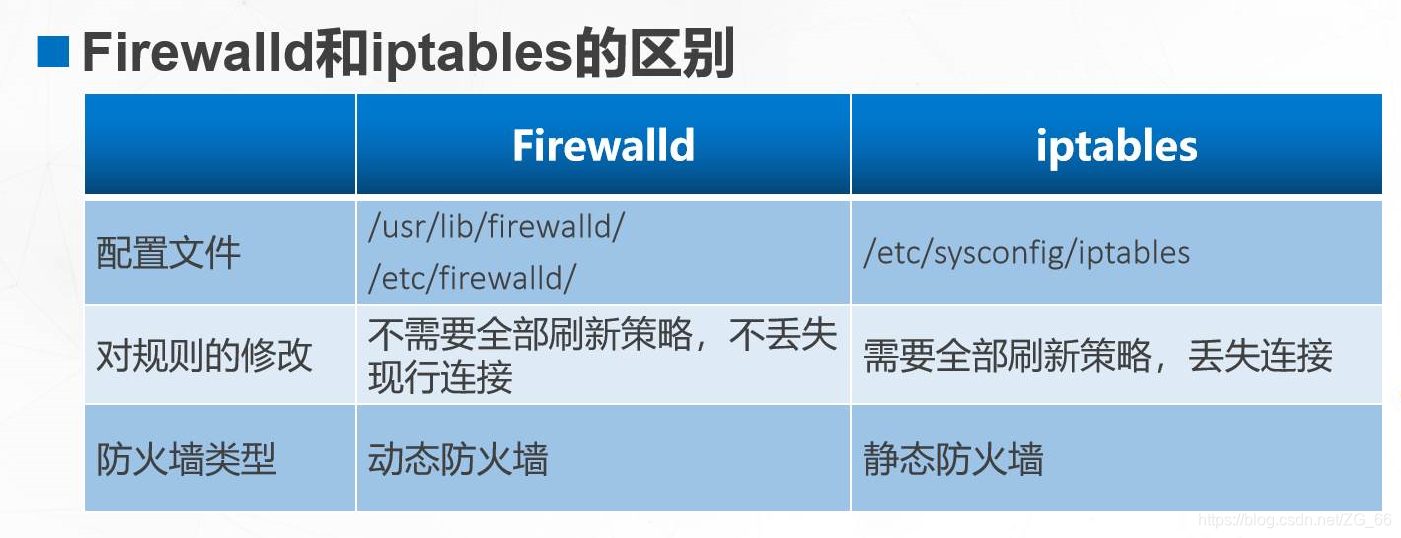
5. Configuration files in /etc/firewalld/
- Firewalld will give priority to the configuration in /etc/Firewalld/. If there is no configuration file, the configuration in /usr/lib/firewalld/ will be used.
◆/etc/firewalld/: User-defined configuration file. Copy in usr/lib/firewalld/
◆/usr/lib/firewalld/: The default configuration file, it is not recommended to modify, if you restore to the default configuration, you can directly delete the configuration in /etc/firewalld/
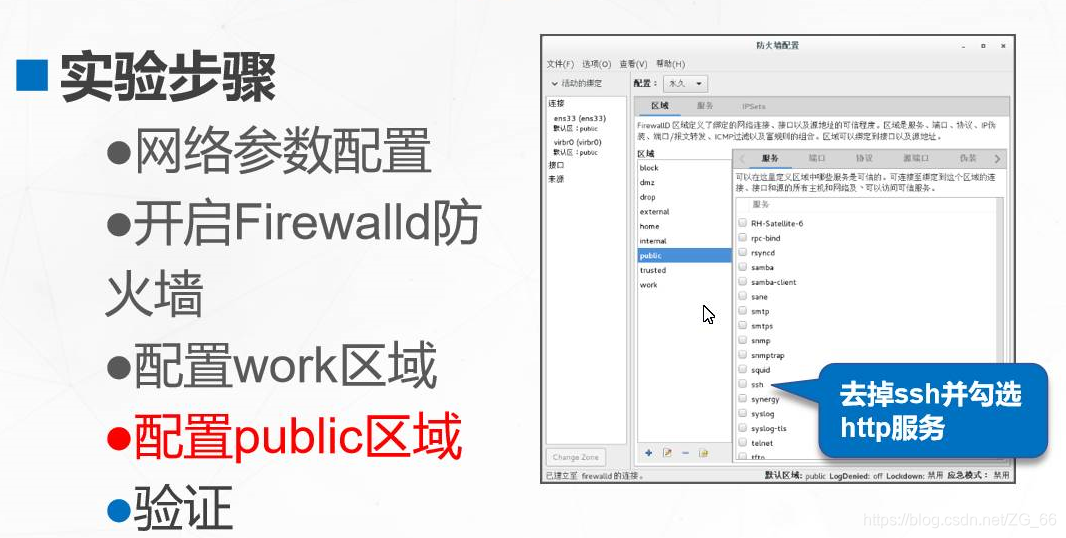
Five, Firewall-config graphical tool
First of all, you must turn on the firewall, and secondly, you can only enter in the terminal firewall-config, not remotely.
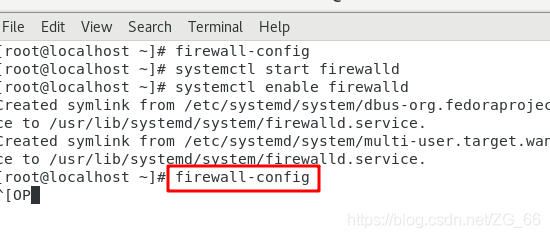
1. Runtime configuration/permanent configuration

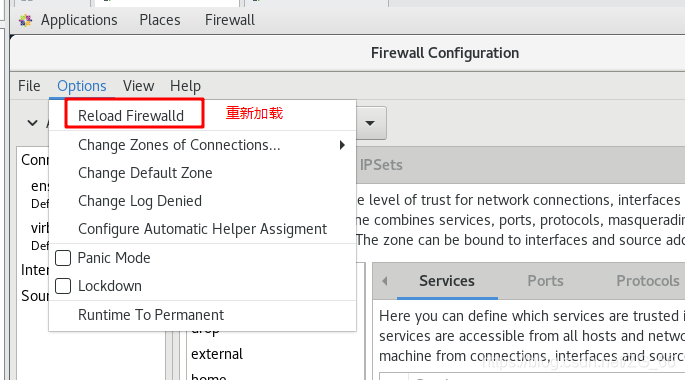
2. Reload the firewall
- Change permanent configuration and take effect
3. Associate the network card to the designated area
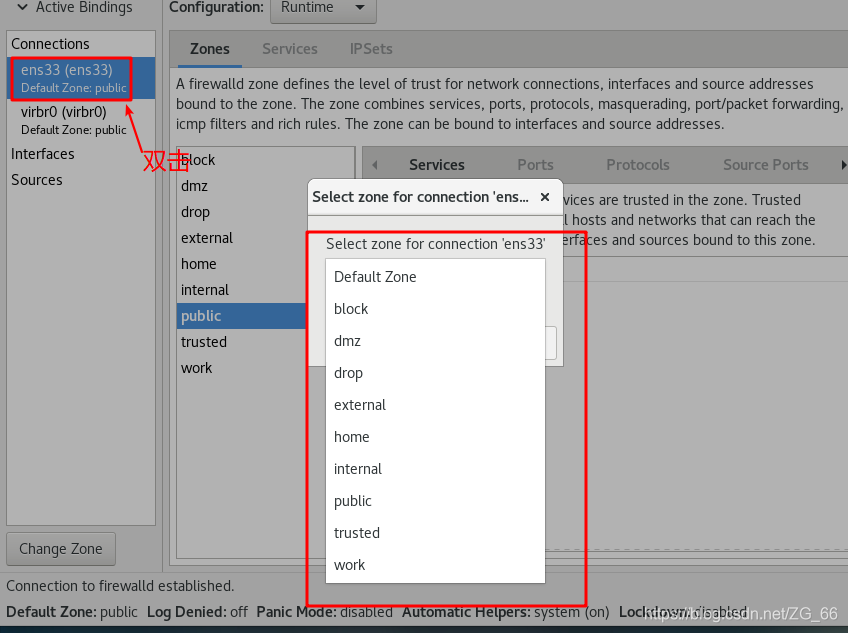
4. Modify the default area
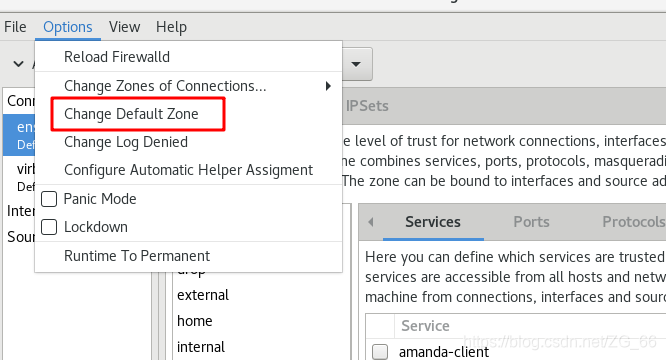
5. Connection status

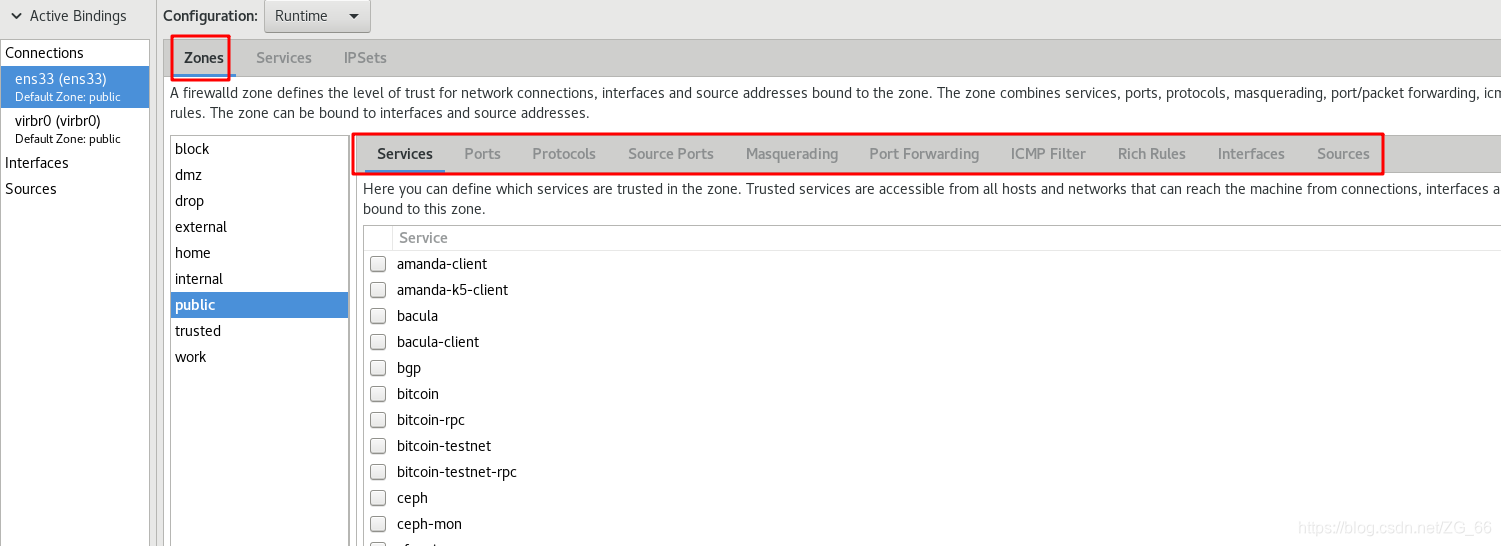
6. "Region" tab
- "Services" sub-tab
- "Port" sub-tab
- "Agreement" sub-tab
- "Source Port" sub-tab
- "Disguise" sub-tab
- "Port Forwarding" sub-tab
- "ICMP Filter" sub-tab
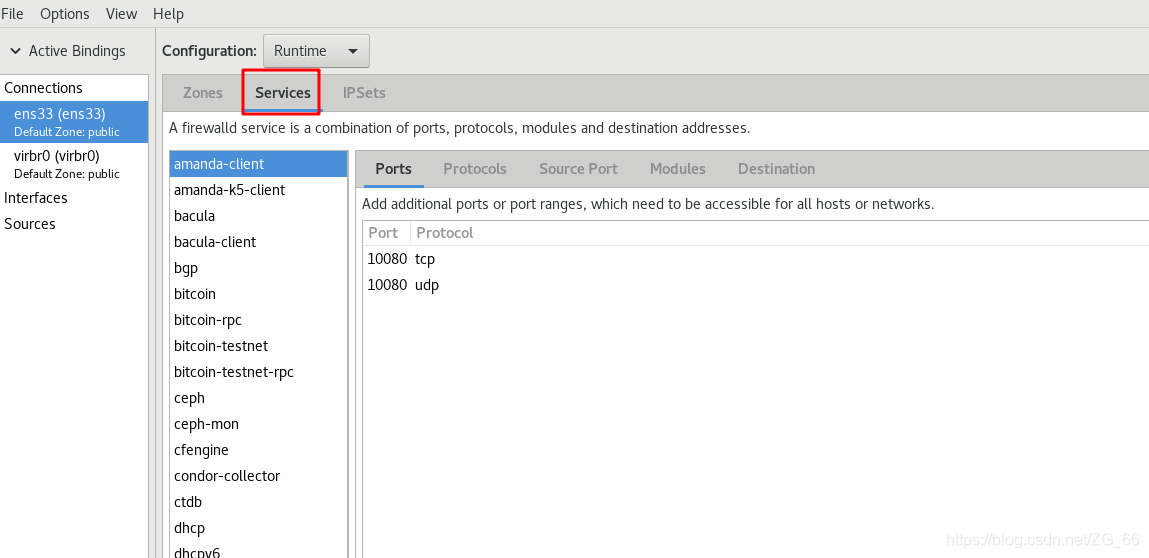
7. "Service" tab
- "Module" sub-tab
- "Destination Address" sub-tab
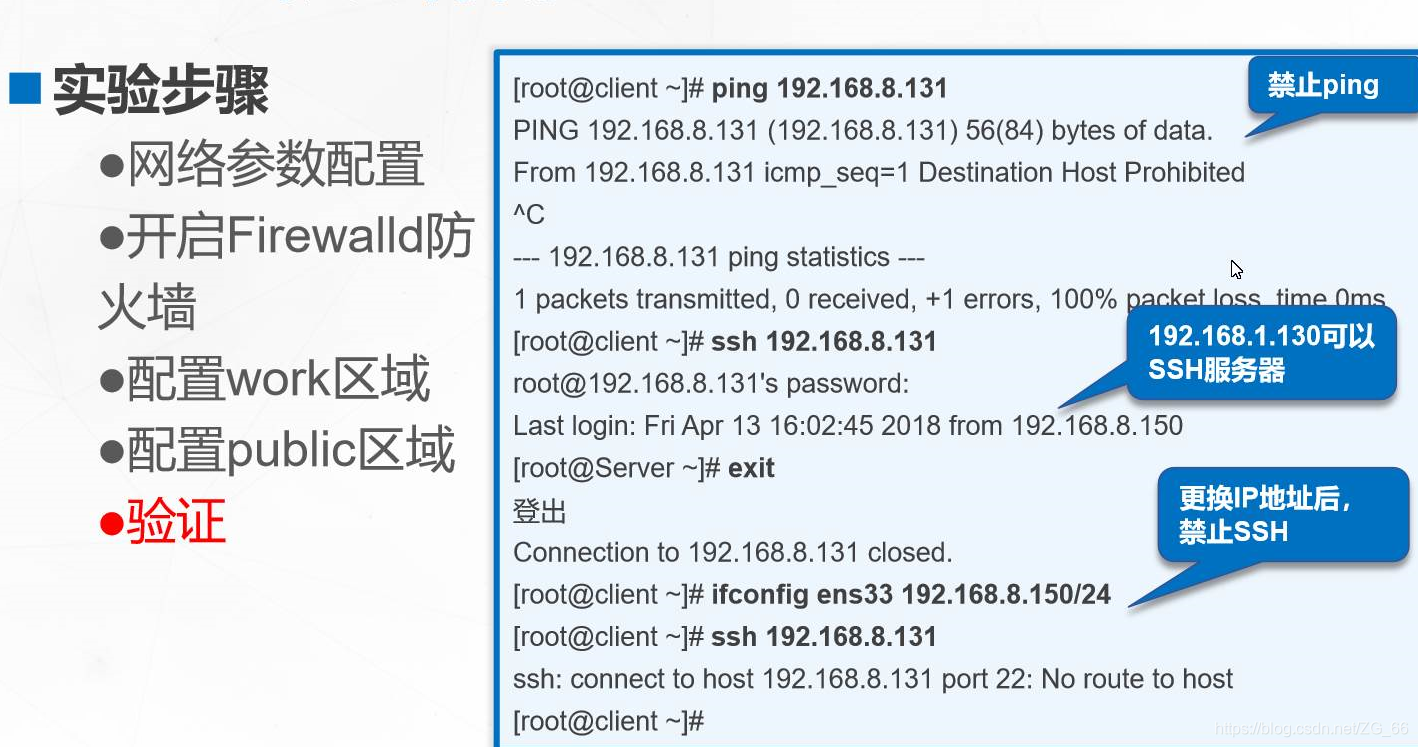
Six, Firewalld firewall case