Original link: http://www.yiidian.com/struts2/struts2-ognl.html
1 Introduction to OGNL
OGNLThe full name of is Object-Graph Navigation Language (Object-Graph Navigation Language), which is a powerful open source expression language. Using this expression language, you can store any attributes of Java objects through a certain expression syntax and call The methods of Java objects can also automatically implement the necessary type conversion. If the expression is regarded as a string with semantics, then OGNL has undoubtedly become the communication bridge between this semantic string and Java objects.
2 OGNL data structure
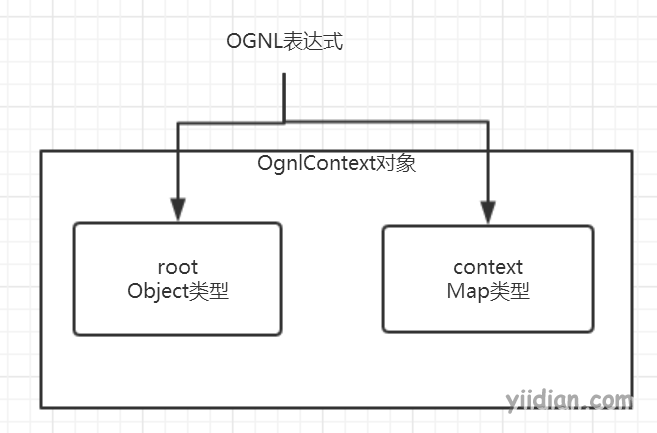
OGNL expressions operate on an OgnlContextobject called . This object contains two properties:
- root: root object, any object can be stored as a Root object
- context: Context object, this is a Map structure, any key-value key-value pair can be stored in this Map
Both of the above two attributes of the OgnlContext object, we can use the OGNL expression for data access.
3 OGNL expression syntax
Ognl expression basic rules:
-
To take the value of the root object, just pass the root object properties directly
-
To get the value of the context object, you must take it through the #key. Attribute in the specified context container
3.1 Environmental preparation
First import the ognl package to the project
Design a User class for storing data
package com.yiidian.ognl;
/**
* @author 一点教程(yiidian.com)
*/
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public User() {
super();
}
public User(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
3.2 Basic values
/**
* 基本取值
*/
@Test
// 取出root中的属性值
public void test1() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// ====使用OGNL表达式取出属性====
// 取出root中user对象的name属性
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 取出context中键为user1对象的name属性
String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user2.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age1 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user2.age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name1);
System.out.println(name2);
System.out.println(age1);
}
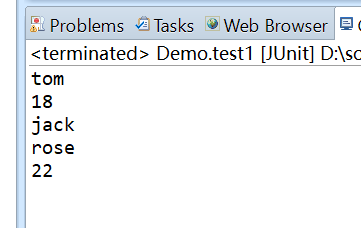
The result is:
3.3 Assignment
/**
* 赋值
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// 编写OGNL表达式
// 将root中的user对象的name属性赋值
Ognl.getValue("name='jerry'", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='张三',#user1.name",oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
}
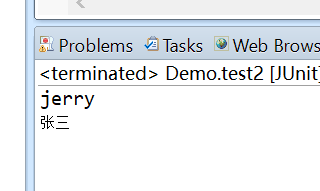
The result is:
3.4 Calling methods
/**
* 调用方法
*/
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// 编写OGNL表达式
// 调用root中user对象的setName方法
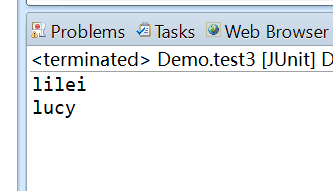
Ognl.getValue("setName('lilei')", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.setName('lucy'),#user1.getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
}
The result is:
3.5 Calling a static method
1) Design an OgnlUtil class with a static method sayHello
package com.yiidian.ognl;
/**
* @author 一点教程(yiidian.com)
*/
public class OgnlUtil {
public static String sayHello(String name){
return "你好,"+name;
}
}
使用Ognl表达式调用sayHello静态方法
/**
* 调用静态方法
*/
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// 编写OGNL表达式
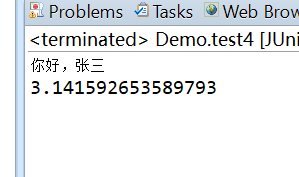
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("@com.yiidian.ognl.OgnlUtil@sayHello('张三')", oc,oc.getRoot());
Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(pi);
}
3.6 Create objects (List, Map)
/**
* 创建对象(List、Map)
*/
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// 编写OGNL表达式
// 创建list对象
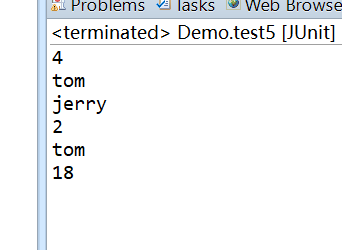
Integer size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}[0]", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.get(1)", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
// 创建Map对象
Integer size2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name3 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}['name']", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.get('age')", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(size2);
System.out.println(name3);
System.out.println(age);
}
The result is:
Source code download: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1lD59FmfQLsG1h1Yvx55WUg
Welcome to pay attention to my public number :: a little tutorial. Get exclusive collated learning resources and daily dry goods push.
If you are interested in my series of tutorials, you can also follow my website: yiidian.com