Article Directory
When we needed some individuals of the same structure together, you can consider using a collection.
Collections Framework
- Java framework provides a set of a high performance, easy to use interfaces and classes that are located java.util package

- Simplified diagram
- Orange for the interface, implementation class in blue.
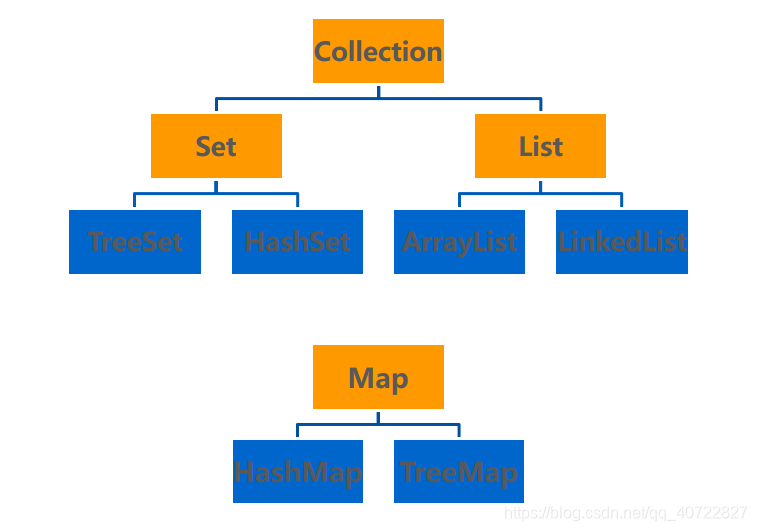
- Orange for the interface, implementation class in blue.
- Collection storing a set of interfaces is not unique, the object disordered
- Storing a set of Interface List is not unique, ordered (the sequence index) object
- Set interface to store a set of unique, unordered objects
- Map interface storing a set of key objects, there is provided the key to value mappings
- Key unique disorder
- value is not unique disorder
Collection
Collection Methods
| method | Explanation |
|---|---|
| boolean add(Object o) | Add objects to the collection |
| boolean remove(Object o) | Delete the specified object |
| int size() | Returns the number of elements in the current collection |
| boolean contains(Object o) | Is there a specified set of objects to find |
| boolean isEmpty() | Determining whether the set is empty |
| Iterator iterator() | Returns an iterator |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | Add the c set to all elements in the set |
| boolean containsAll(Collection c) | Are there elements of the collection c lookup collection |
| void clear() | Delete all the elements in the collection |
| void removeAll(Collection c) | C deleted from the collection in the collection and some elements |
| void retainAll(Collection c) | C delete elements in the collection that are not included from the collection |
Iterator -Iterator
In java, a lot of data containers, these operations have many similarities. Java uses iterators to provide a common user interface for a variety of containers. This makes its traversal operation specific implementation of the underlying container isolated from achieve decoupling.
- Note: iterator () method is java.lang.Iterable interface is inherited Collection.
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
| boolean hasNext() | If the iteration has more elements, it returns true. |
| E next() | Returns the next element iteration. |
| void remove() | Removes the last element (optional operation) iterator returned from the collection the iterator. |
- Use iterates over the collection ArrayList
List list = new ArrayList<>();
//集合
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
//Iterator迭代器
//1、获取迭代器
Iterator iter = list.iterator();
//2、通过循环迭代
//hasNext():判断是否存在下一个元素
while(iter.hasNext()){
//如果存在,则调用next实现迭代
//Object-->Integer-->int
int j=(int)iter.next(); //把Object型强转成int型
System.out.println(j);
}
- Note: In the iterative process of the collection, the collection is not allowed to directly modify the structure. If forced changes occur
并发修改异常. If you want to delete an element, you can use the built-in Iterator remove () method. 什么是并发修改异常?- In the course of the iterative collection, the collection is not allowed to directly modify the structure. Such as adding, deleting elements (changing number) if changed, it will cause concurrent modification exception.
并发修改异常原因?- When acquiring the iterator will set and associate consistent data held on both sides, there is an inner
modCountandexpectedModCount. By default the two of them are equal. When we take the elements, we will do a judgment as follows: modCount and default expectedModCount two are equal, and will determine whether modCount expectedModCount equal, if not equal to not throw a concurrent modification exception. modCount: Recording a collection of modified frequencyexpectedModCount: Review set number of times among the recording iterator
- When acquiring the iterator will set and associate consistent data held on both sides, there is an inner
List
- List java is one of the important data structures. It is inherited
java.util.Collectioninterfaces, mainlyArrayList,LinkedList,Vectorthree.ArrayList: Dynamic Array implementation, support random access.Vector: ArrayList and similar, but it is thread safe.LinkedList: Based on a doubly linked list to achieve, can only sequential access, but can quickly in the middle of a linked list insert and delete elements. Not only that, LinkedList can also be used as stacks, queues, and two-way queue.
- note:
- The collection is an object store
- List which can add duplicate elements, Set among not add duplicate elements
- List among the add return values are true
- Through the collection: the first set into an array, through the array
- List of methods
| List of methods | effect |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | Adds the specified element (optional operation) to the end of the list. |
| void add(int index, E element) | Inserting specified position in the list of the specified element (optional operation). |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | Appends all of the elements in the specified collection of this list, the order is specified collection returned by the iterator order of these elements (optional operation). |
| boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) | All the elements in the specified collection are inserted into the specified position (optional operation) list. |
| void clear() | Removes all elements from the list (optional operation). |
| boolean contains(Object o) | If the list contains the specified element, it returns true. |
| boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) | If the list contains all of the elements of the specified collection, it returns true. |
| boolean equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this list for equality. |
| E get(int index) | Returns the position of the elements specified in the list. |
| int hashCode() | Returns the hash code value list. |
| int indexOf(Object o) | Returns the index of the specified element in this list of the first occurrence; if this list does not contain the element, or -1. |
| boolean isEmpty() | If the list does not contain the element, it returns true. |
| Iterator iterator() | Proper sequence returns an iterator over the elements in the list. |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | Returns the index of the specified element in this list of the last occurrence; if the list does not contain this element, or -1. |
| ListIterator listIterator () | Iterator returns a list of elements in this list (in proper sequence). |
| ListIterator listIterator (int index) | Returns a list of elements in this list iterators (in proper sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. |
| E remove(int index) | Removed (optional operation) of the location specified in the list. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | Removed from this list the first occurrence of the specified element (if present) (optional). |
| boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) | Removes the specified collection contains all elements (optional operation) from the list. |
| boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) | Retain only the specified element (optional operation) Collection included in the list. |
| E set(int index, E element) | Location specified element (optional operation) replacing the list with the specified element. |
| int size() | Returns the number of elements in the list. |
| List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Returns a list view of the portion between the specified fromIndex (inclusive) and toIndex (exclusive). |
| Object[] toArray() | Returns the proper sequence, all array elements in the list (from the last element to the first element). |
| T[] toArray(T[] a) | Returns the proper order (from the first element to the last element), all array elements in the list comprising; when returned array of the specified type is the type of array operation. |
ListIterator
List接口提供了特殊的迭代器,称为 ListIterator ,除了允许Iterator 接口提供的正常操作外,该迭代器还允许元素插入和替换,以及双向访问。
ListIterator方法
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| void add(E e) | 将指定的元素插入列表(可选操作)。 |
| boolean hasNext() | 以正向遍历列表时,如果列表迭代器有多个元素,则返回 true(换句话说,如果 next 返回一个元素而不是抛出异常,则返回 true)。 |
| boolean hasPrevious() | 如果以逆向遍历列表,列表迭代器有多个元素,则返回 true。 |
| E next() | 返回列表中的下一个元素。 |
| int nextIndex() | 返回对 next 的后续调用所返回元素的索引。 |
| E previous() | 返回列表中的前一个元素。 |
| int previousIndex() | 返回对 previous 的后续调用所返回元素的索引。 |
| void remove() | 从列表中移除由 next 或 previous 返回的最后一个元素(可选操作)。 |
| void set(E e) | 用指定元素替换 next 或 previous 返回的最后一个元素(可选操作)。 |
ArrayList
ArrayList 使用连续的内存单元存储数据元素,是一个其容量能够动态增长的动态数组。当添加或删除数据元素时(最后位置除外),ArrayList 需要移动其被添加(或删除)元素后面的所有元素。所以插入和删除元素时较慢,查询较快。同时,ArrayList线程是不安全的!
- 一般单线程使用ArrayList ,而在多线程一般使用 Vector 和 CopyOnWriteArrayList。
ArrayList遍历方式
- 迭代器遍历
Iterator<Integer> it = arrayList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
- 索引值遍历
for(int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++){
System.out.print(arrayList.get(i) + " ");
}
- for循环遍历
for(Integer number : arrayList){
System.out.print(number + " ");
}
遍历ArrayList时,通过索引值遍历效率最高,for循环遍历次之,迭代器遍历最低。
LinkedList
LinkedList 是一个继承于 AbstractSequentialList 双向链表。它也可以被当做堆栈、队列或双端队列来进行操作。
LinkedList 实现 List 接口,能进行队列操作。
LinkedList 实现 Deque 接口,能将 LinkedList 当作双端队列使用。
ArrayList底层是由数组支持,而LinkedList 是由双向链表实现的,其中的每个对象包含数据的同时还包含指向链表中前一个与后一个元素的引用。
LinkedList 遍历方式
- 迭代器遍历
Iterator<Integer> iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
iterator.next();
}
- for循环get()遍历
for(int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++){
linkedList.get(i);
}
- Foreach循环遍历
for(Integer i : linkedList);
- 通过pollFirst()或pollLast()遍历
while(linkedList.size() != 0){
linkedList.pollFirst();
}
- 通过removeFirst()或removeLast()遍历
while(linkedList.size() != 0){
linkedList.removeFirst();
}
- 注意:遍历LinkedList时,使用removeFirst()或removeLast()效率最高,而for循环get()效率最低,应避免使用这种方式进行。应当注意的是,使用pollFirst()或pollLast()或removeFirst()或removeLast()遍历时,会删除原始数据,若只单纯的读取,应当选用第一种或第三种方式。
ArrayList 与 LinkedList 区别
- 因为 Array 是基于索引(index)的数据结构,它使用索引在数组中搜索和读取数据是很快的。Array 获取数据的时间复杂度是 O(1),但是要删除数据却是开销很大的,因为这需要重排数组中的所有数据。
- 相对于 ArrayList,LinkedList 插入是更快的。因为 LinkedList 不像 ArrayList 一样,不需要改变数组的大小,也不需要在数组装满的时候要将所有的数据重新装入一个新的数组,这是 ArrayList 最坏的一种情况,时间复杂度是 O(n),而 LinkedList 中插入或删除的时间复杂度仅为 O(1)。ArrayList 在插入数据时还需要更新索引(除了插入数组的尾部)。
- 类似于插入数据,删除数据时,LinkedList 也优于 ArrayList。
- LinkedList 需要更多的内存,因为 ArrayList 的每个索引的位置是实际的数据,而 LinkedList 中的每个节点中存储的是实际的数据和前后节点的位置。
- 你的应用不会随机访问数据。因为如果你需要 LinkedList 中的第 n 个元素的时候,你需要从第一个元素顺序数到第 n 个数据,然后读取数据。
- 你的应用更多的插入和删除元素,更少的读取数据。因为插入和删除元素不涉及重排数据,所以它要比 ArrayList 要快。
Vector
-
Vector 类实现了一个动态数组。和 ArrayList 很相似,但是两者是不同的。
-
Vector 主要用在事先不知道数组的大小,或者只是需要一个可以改变大小的数组的情况。
-
关于ArrayList和Vector区别如下:
- ArrayList在内存不够时默认是扩展50% + 1个,Vector是默认扩展1倍。
- Vector提供indexOf(obj, start)接口,ArrayList没有。
- Vector属于线程安全级别的,但是大多数情况下不使用Vector,因为线程安全需要更大的系统开销。
ArrayList 与 Vector 区别
- 同步性:Vector 是线程安全的,也就是说是同步的 ,而 ArrayList 是线程不安全的,不是同步的。
- 数据增长:当需要增长时,Vector 默认增长为原来一倍 ,而 ArrayList 却是原来的 50% ,这样 ArrayList 就有利于节约内存空间。
- 说明:如果涉及到堆栈,队列等操作,应该考虑用 Vector,如果需要快速随机访问元素,应该使用 ArrayList
Set
- Set继承于Collection接口,是一个不允许出现重复元素,并且无序的集合,主要有
HashSet和TreeSet两大实现类。HashSet:它是哈希表的结构,主要利用HashMap 的Key 来存储元素,计算插入元素的hashcode 来获取元素的集合中的位置。TreeSet:它是红黑树结构,每一个元素都是树中的一个节点,插入的元素都会进行排序。
- 如果自定义对象,属性完全相同,那么就判定你是同一个对象。
- 在判断重复元素的时候,Set集合会调用hashCode()和 equal() 方法来实现。
- 集合存和取的顺序不一样。
- Set方法摘要
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 如果 set 中尚未存在指定的元素,则添加此元素(可选操作)。 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 如果 set 中没有指定 collection 中的所有元素,则将其添加到此 set 中(可选操作)。 |
| void clear() | 移除此 set 中的所有元素(可选操作)。 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 如果 set 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。 |
| boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) | 如果此 set 包含指定 collection 的所有元素,则返回 true。 |
| boolean equals(Object o) | 比较指定对象与此 set 的相等性。 |
| int hashCode() | 返回 set 的哈希码值。 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 如果 set 不包含元素,则返回 true。 |
| Iterator iterator() | 返回在此 set 中的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 如果 set 中存在指定的元素,则将其移除(可选操作)。 |
| boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) | 移除 set 中那些包含在指定 collection 中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) | 仅保留 set 中那些包含在指定 collection 中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| int size() | 返回 set 中的元素数(其容量)。 |
| Object[] toArray() | 返回一个包含 set 中所有元素的数组。 |
| T[] toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含此 set 中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
HashSet
HashSet实现Set接口,底层由HashMap 实例的默认初始容量是 16 来实现,为哈希表结构,新增元素相当于HashMap的key,value默认为一个固定的Object。当有元素插入的时候,会计算元素的hashCode值,将元素插入到哈希表对应的位置中来,由于Set集合中并没有角标的概念,所以并没有像List一样提供get()方法。当获取HashSet中某个元素时,只能通过遍历集合的方式进行equals()比较来实现;它继承于AbstractSet,实现了Set, Cloneable, Serializable接口。
- 不允许出现重复因素;
- 允许插入Null值;
- 元素无序(添加顺序和遍历顺序不一致);
- 线程不安全,若2个线程同时操作HashSet,必须通过代码实现同步;
- 每一个对象都会有一个唯一的hashCode值,再添加对象时,会调用hashCode
- hashCode就是跟内存地址对应的编号,编号就是对应你内存的地址
LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet集合同样是根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,但是它同时使用链表维护元素的次序。这样使得元素看起 来像是以插入顺序保存的,也就是说,当遍历该集合时候,LinkedHashSet将会以元素的添加顺序访问集合的元素。
LinkedHashSet在迭代访问Set中的全部元素时,性能比HashSet好,但是插入时性能稍微逊色于HashSet。LinkedHashSet 它是 HashSet 的子类。它底层 是使用链表实现的,是Set 集合当中,唯一的一个保证元素怎么存怎么出。HashSet 能够保证元素的唯一,LinkedHashSet 性能相对于 HashSet 低。
TreeSet
Treeset 是 SortSet 接口的唯一实现类,TreeSet 可以确保结合元素处于排序状态。
- TreeSet支持两种排序方式,
自然排序和定制排序,其中自然排序为默认的排序方式。 - TreeSet 它也是无序的(这儿所说的无序是指:不是按照添加顺序展示)
- TreeSet 对添加的元素进行排序(从小到大),用来对元素进行排序,可以保证元素的唯一性
- (数字)按数字大小排序,(字母)按字母顺序排序,(汉字)按Unicode码排序
- TreeSet 当中存放的类型必须得是同一类型(同一个类的对象)
- 自定义的对象不能直接添加到TreeSet,先要添加到TreeSet中,必须要实现Comparable接口,并实现里面的campareTo方法。
- 方法摘要
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 将指定的元素添加到此 set(如果该元素尚未存在于 set 中)。 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 将指定 collection 中的所有元素添加到此 set 中。 |
| E ceiling(E e) | 返回此 set 中大于等于给定元素的最小元素;如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。 |
| void clear() | 移除此 set 中的所有元素。 |
| Object clone() | 返回 TreeSet 实例的浅表副本。 |
| Comparator<? super E> comparator() | 返回对此 set 中的元素进行排序的比较器;如果此 set 使用其元素的自然顺序,则返回 null。 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 如果此 set 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。 |
| Iterator descendingIterator() | 返回在此 set 元素上按降序进行迭代的迭代器。 |
| NavigableSet descendingSet() | 返回此 set 中所包含元素的逆序视图。 |
| E first() | 返回此 set 中当前第一个(最低)元素。 |
| E floor(E e) | 返回此 set 中小于等于给定元素的最大元素;如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。 |
| E higher(E e) | 返回此 set 中严格大于给定元素的最小元素;如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 如果此 set 不包含任何元素,则返回 true。 |
| Iterator iterator() | 返回在此 set 中的元素上按升序进行迭代的迭代器。 |
| E last() | 返回此 set 中当前最后一个(最高)元素。 |
| E lower(E e) | 返回此 set 中严格小于给定元素的最大元素;如果不存在这样的元素,则返回 null。 |
| E pollFirst() | 获取并移除第一个(最低)元素;如果此 set 为空,则返回 null。 |
| E pollLast() | 获取并移除最后一个(最高)元素;如果此 set 为空,则返回 null。 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 将指定的元素从 set 中移除(如果该元素存在于此 set 中)。 |
| int size() | 返回 set 中的元素数(set 的容量)。 |
List 和 Set 区别
- List, Set 都是继承自 Collection 接口
- List 特点:元素有放入顺序,元素可重复。Set 特点:元素无放入顺序,元素不可重复(注意:元素虽然无放入顺序,但是元素在 set 中的位置是有该元素的 HashCode 决定的,其位置其实是固定的)
- List 接口有三个实现类:LinkedList,ArrayList,Vector。Set 接口有两个实现类:HashSet(底层由 HashMap 实现),LinkedHashSet
Map
Map集合中存储的是键值对,键不能重复,值可以重复。根据键得到值,对map集合遍历时先得到键的set集合,对set集合进行遍历,得到相应的值。
HashMap
- 数组方式存储key/value,线程非安全,允许null作为key和value,key不可以重复,value允许重复,不保证元素迭代顺序是按照插入时的顺序,key的hash值是先计算key的hashcode值,然后再进行计算,每次容量扩容会重新计算所以key的hash值,会消耗资源,要求key必须重写equals和hashcode方法
HashMap 的工作原理
- HashMap 基于 hashing 原理,我们通过 put() 和 get() 方法储存和获取对象。当我们将键值对传递给 put() 方法时,它调用键对象的 hashCode() 方法来计算 hashcode,让后找到 bucket 位置来储存值对象。当获取对象时,通过键对象的 equals() 方法找到正确的键值对,然后返回值对象。HashMap 使用链表来解决碰撞问题,当发生碰撞了,对象将会储存在链表的下一个节点中。 HashMap 在每个链表节点中储存键值对对象。
LinkedHashMap
- LinkedHashMap保存了记录的插入顺序,在用Iteraor遍历LinkedHashMap时,先得到的记录肯定是先插入的,在遍历的时候会比HashMap慢,有HashMap的全部特性。
HashMap 和 HashTable 的区别
- HashMap 几乎可以等价于 HashTable,除了 HashMap 是非 synchronized 的,并可以接受 null(HashMap 可以接受为 null 的键值 (key) 和值 (value),而 HashTable 则不行)。
- HashMap 是非 synchronized,而 HashTable 是 synchronized,这意味着 HashTable 是线程安全的,多个线程可以共享一个 HashTable;而如果没有正确的同步的话,多个线程是不能共享 HashMap 的。Java 5 提供了 ConcurrentHashMap,它是 HashTable 的替代,比 HashTable 的扩展性更好。
- 另一个区别是 HashMap 的迭代器 (Iterator) 是 fail-fast 迭代器,而 HashTable 的 enumerator 迭代器不是 fail-fast 的。所以当有其它线程改变了 HashMap 的结构(增加或者移除元素),将会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException,但迭代器本身的 remove() 方法移除元素则不会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。但这并不是一个一定发生的行为,要看 JVM。这条同样也是 Enumeration 和 Iterator 的区别。
- 由于 HashTable 是线程安全的也是 synchronized,所以在单线程环境下它比 HashMap 要慢。如果你不需要同步,只需要单一线程,那么使用 HashMap 性能要好过 HashTable。
- HashMap 不能保证随着时间的推移 Map 中的元素次序是不变的。
HashSet 和 HashMap 区别
| HashMap | HashSet |
|---|---|
| HashMap | 实现了 Map 接口 HashSet 实现了 Set 接口 |
| HashMap | 储存键值对 HashSet 仅仅存储对象 |
| 使用 put() 方法将元素放入 map 中 | 使用 add() 方法将元素放入 set 中 |
| HashMap 中使用键对象来计算 hashcode 值 | HashSet 使用成员对象来计算 hashcode 值,对于两个对象来说 hashcode 可能相同,所以 equals() 方法用来判断对象的相等性,如果两个对象不同的话,那么返回 false |
| HashMap 比较快,因为是使用唯一的键来获取对象 | HashSet 较 HashMap 来说比较慢 |
TreeMap
- 基于红黑二叉树的NavigableMap的实现,线程非安全,不允许null,key不可以重复,value允许重复,存入TreeMap的元素应当实现Comparable接口或者实现Comparator接口,会按照排序后的顺序迭代元素,两个相比较的key不得抛出classCastException。主要用于存入元素的时候对元素进行自动排序,迭代输出的时候就按排序顺序输出
List 和 Map 区别
- List 特点:元素有放入顺序,元素可重复;
- Map 特点:元素按键值对存储,无放入顺序 ;
- List 接口有三个实现类:LinkedList,ArrayList,Vector;
- LinkedList:底层基于链表实现,链表内存是散乱的,每一个元素存储本身内存地址的同时还存储下一个元素的地址。链表增删快,查找慢;
- Map 接口有三个实现类:HashMap,HashTable,LinkedHashMap
- Map 相当于和 Collection 一个级别的;Map 集合存储键值对,且要求保持键的唯一性;
Collection和Collections的区别
- Collection是Java提供的集合接口,存储一组不唯一,无序的对象。它有两个子接口 List和Set。
- Java中还有一个Collections类,专门用来操作集合类 ,它提供一系列静态方法实现对 各种集合的搜索、排序、线程安全化等操作。
集合总结


The more you know, the more you do not know.
Proper way without surgery, patients can still seek, there is no way to surgery, ending surgery.
If you have other questions, welcome message, we can discuss, learn together and progress together
