Floating-point number is floating decimal point, but because a binary representation having a computer, of different lengths have different accuracy.
Three common floating point format: a half-precision (float16), single precision (float32), double precision (float64)
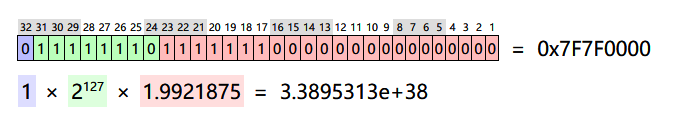
- Value=sign*exponent*fraction
- Value = sign bit * * decimal exponent
- It represents a negative sign bit
- Index indicates power
- Decimal place precision representation
Except that the difference index and fractional bits length; this representation is an approximation actually rational numbers;
Half-precision representation π, maximum and minimum values:
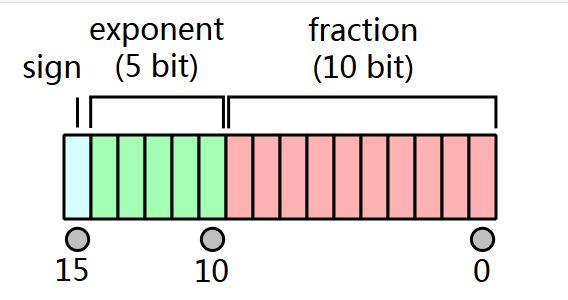
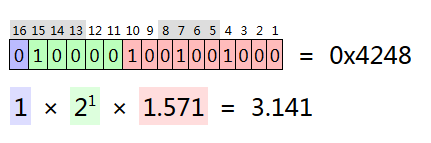


It represents single-precision π, maximum and minimum values:



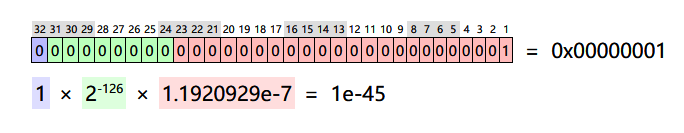

It represents a double π, maximum and minimum values:





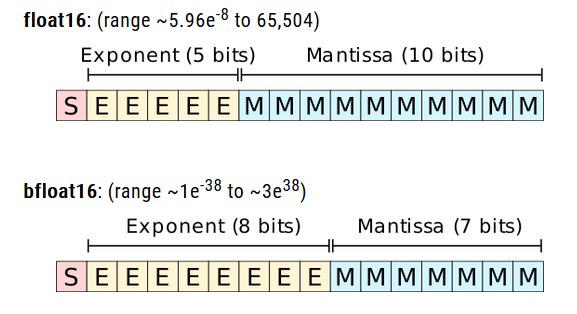
Bfloat16
Recently gave birth to a way of Bfloat16 count of using the same number of bits and semi-precision, single-precision and realized to keep the same index that is 8-bit exponent bits, can represent single-precision and the same number range, but at the expense of decimal place is accuracy.

references: