题目描述
面试题45.输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。例如输入数组{3,32,321},则打印出这三个数字能排成的最小数字为321323。
思路分析
自定义一个比较大小的函数,比较两个字符串s1, s2大小的时候,先将它们拼接起来,比较s1+s2,和s2+s1那个大,如果s1+s2大,那说明s2应该放前面,所以按这个规则,s2就应该排在s1前面
/*对vector容器内的数据进行排序,按照 将a和b转为string后
若 a+b<b+a a排在在前 的规则排序,
如 2 21 因为 212 < 221 所以 排序后为 21 2
to_string() 可以将int 转化为string
*/
class Solution {
public:
string PrintMinNumber(vector<int> numbers) {
//string result;
string result = ""; //string result = " ";""中间有空格会出错
if(numbers.empty())
return result;
sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.end(),cmp); //sort第三个参数设置排序规则
for(int i=0;i<numbers.size();i++){
result += to_string(numbers[i]);
}
return result;
}
private:
static bool cmp(int a,int b){ //排序规则,//cmp为全局函数,必须加static,否则报错
//string A="";
//string B="";
string A,B;
A+=to_string(a);
A+=to_string(b);
B+=to_string(b);
B+=to_string(a);
return A<B;
}
};
sort用法
1.sort函数包含在头文件为#include的c++标准库中,调用标准库里的排序方法可以实现对数据的排序,但是sort函数是如何实现的,我们不用考虑!
2.sort函数的模板有三个参数:
void sort (RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, Compare comp);
(1)第一个参数first:是要排序的数组的起始地址。
(2)第二个参数last:是结束的地址(最后一个数据的后一个数据的地址)
(3)第三个参数comp是排序的方法:可以是从升序也可是降序。如果第三个参数不写,则默认的排序方法是从小到大排序。
(1) 从小到大排序
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
main()
{
//sort函数第三个参数采用默认从小到大
int a[]={45,12,34,77,90,11,2,4,5,55};
sort(a,a+10);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
(2)从大到小排序
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a,int b);
main(){
//sort函数第三个参数自己定义,实现从大到小
int a[]={45,12,34,77,90,11,2,4,5,55};
sort(a,a+10,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
//自定义函数
bool cmp(int a,int b){
return a>b;
}
(3)指定排序规则
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include"cstring"
using namespace std;
typedef struct student{
char name[20];
int math;
int english;
}Student;
bool cmp(Student a,Student b);
main(){
//先按math从小到大排序,math相等,按english从大到小排序
Student a[4]={{"apple",67,89},{"limei",90,56},{"apple",90,99}};
sort(a,a+3,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
cout<<a[i].name <<" "<<a[i].math <<" "<<a[i].english <<endl;
}
bool cmp(Student a,Student b){
if(a.math >b.math )
return a.math <b.math ;//按math从小到大排序
else if(a.math ==b.math )
return a.english>b.english ; //math相等,按endlish从大到小排序23
}

(4).对于容器,容器中的数据类型可以多样化
1) 元素自身包含了比较关系,如int,double等基础类型,可以直接进行比较greater() 递减, less() 递增(省略)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include"vector"
using namespace std;
typedef struct student{
char name[20];
int math;
int english;
}Student;
bool cmp(Student a,Student b);
main(){
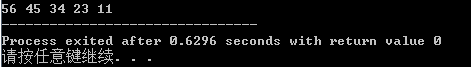
int s[]={34,56,11,23,45};
vector<int>arr(s,s+5);
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end(),greater<int>());
for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
2)元素本身为class或者struct,类内部需要重载< 运算符,实现元素的比较;
注意事项:bool operator<(const className & rhs) const; 如何参数为引用,需要加const,这样临时变量可以赋值;重载operator<为常成员函数,可以被常变量调用;
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include"vector"
using namespace std;
typedef struct student{
char name[20];
int math;
//按math从大到小排序
inline bool operator < (const student &x) const {
return math>x.math ;
}
}Student;
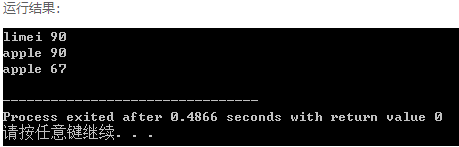
main(){
Student a[4]={{"apple",67},{"limei",90},{"apple",90}};
sort(a,a+3);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
cout<<a[i].name <<" "<<a[i].math <<" " <<endl;
}
重载<也可以定义为如下格式:
struct Cmp{
bool operator()(Info a1,Info a2) const {
return a1.val > a2.val;
}
};
