Prefácio
Escrevi um artigo quando estava lendo o Transformer antes. O artigo inteiro foi quase traduzido do jornal. Recentemente, tive tempo de olhar o código do Transformer e a introdução de artigos de outras pessoas. Gravei aqui por conveniência. Confira. você mesmo mais tarde.
Link para o artigo anterior apresentando o transformador:
(4 mensagens) Blog do Transformer_Mr___WQ - blog CSDN ![]() https://blog.csdn.net/Mr___WQ/article/details/126629883?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502 A seguir, daremos uma breve introdução ao código do transformador.
https://blog.csdn.net/Mr___WQ/article/details/126629883?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502 A seguir, daremos uma breve introdução ao código do transformador.
Transformador
1 parâmetros do modelo
# Transformer Parameters
d_model = 512 # Embedding Size(词嵌入维度,此处设为512)
# FeedForward dimension (两次线性层中的隐藏层 512->2048->512,
#线性层是用来做特征提取的),当然最后会再接一个projection层
d_ff = 2048 # Feed Forward 层隐藏神经元个数
d_k = d_v = 64 # dimension of K(=Q), V(Q和K的维度需要相同,这里为了方便让K=V)
n_layers = 6 # number of Encoder of Decoder Layer(Block的个数)
n_heads = 8 # number of heads in Multi-Head Attention(有几个头)
2 camadas de incorporação
A função da camada Embedding é converter os dados de entrada em um determinado formato, como texto, em uma representação vetorial que pode ser processada pelo modelo para descrever as informações contidas nos dados originais.
A saída da camada de incorporação pode ser entendida como os recursos da etapa de tempo atual. Se for uma tarefa de texto, pode ser incorporação de palavras. Se forem outras tarefas, podem ser recursos extraídos por qualquer método razoável.
O código para construir a camada Embedding é muito simples. O núcleo é usar nn.Embedding fornecido pelo torch, como segue:
class Embeddings(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, vocab):
"""
类的初始化函数
d_model:指词嵌入的维度
vocab:指词表的大小
"""
super(Embeddings, self).__init__()
#之后就是调用nn中的预定义层Embedding,获得一个词嵌入对象self.lut
self.lut = nn.Embedding(vocab, d_model)
#最后就是将d_model传入类中
self.d_model =d_model
def forward(self, x):
"""
Embedding层的前向传播逻辑
参数x:这里代表输入给模型的单词文本通过词表映射后的one-hot向量
将x传给self.lut并与根号下self.d_model相乘作为结果返回
"""
embedds = self.lut(x)
return embedds * math.sqrt(self.d_model)Para testes simples aqui, codificamos e carregamos os dados manualmente. O código é o seguinte:
entences = [
# 中文和英语的单词个数不要求相同
# enc_input dec_input dec_output
['我 有 一 个 好 朋 友 P', 'S I have a good friend .', 'I have a good friend . E'],
['我 有 零 个 女 朋 友 P', 'S I have zero girl friend .', 'I have zero girl friend . E'],
['我 有 一 个 男 朋 友 P', 'S I have a boy friend .', 'I have a boy friend . E']
]
# 测试集(希望transformer能达到的效果)
# 输入:"我 有 一 个 女 朋 友"
# 输出:"i have a girlfriend"
# 中文和英语的单词要分开建立词库
# Padding Should be Zero
src_vocab = {'P': 0, '我': 1, '有': 2, '一': 3,
'个': 4, '好': 5, '朋': 6, '友': 7, '零': 8, '女': 9, '男': 10}
src_idx2word = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(src_vocab)}
src_vocab_size = len(src_vocab)
tgt_vocab = {'P': 0, 'I': 1, 'have': 2, 'a': 3, 'good': 4,
'friend': 5, 'zero': 6, 'girl': 7, 'boy': 8, 'S': 9, 'E': 10, '.': 11}
idx2word = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(tgt_vocab)}
tgt_vocab_size = len(tgt_vocab)
src_len = 8 # (源句子的长度)enc_input max sequence length
tgt_len = 7 # dec_input(=dec_output) max sequence length
def make_data(sentences):
"""把单词序列转换为数字序列"""
enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs = [], [], []
for i in range(len(sentences)):
enc_input = [[src_vocab[n] for n in sentences[i][0].split()]]
dec_input = [[tgt_vocab[n] for n in sentences[i][1].split()]]
dec_output = [[tgt_vocab[n] for n in sentences[i][2].split()]]
#[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0], [1, 2, 8, 4, 9, 6, 7, 0], [1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 6, 7, 0]]
enc_inputs.extend(enc_input)
#[[9, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 11], [9, 1, 2, 6, 7, 5, 11], [9, 1, 2, 3, 8, 5, 11]]
dec_inputs.extend(dec_input)
#[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 11, 10], [1, 2, 6, 7, 5, 11, 10], [1, 2, 3, 8, 5, 11, 10]]
dec_outputs.extend(dec_output)
return torch.LongTensor(enc_inputs), torch.LongTensor(dec_inputs), torch.LongTensor(dec_outputs)
class MyDataSet(Data.Dataset):
"""自定义DataLoader"""
def __init__(self, enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs):
super(MyDataSet, self).__init__()
self.enc_inputs = enc_inputs
self.dec_inputs = dec_inputs
self.dec_outputs = dec_outputs
def __len__(self):
return self.enc_inputs.shape[0]
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.enc_inputs[idx], self.dec_inputs[idx], self.dec_outputs[idx]
loader = Data.DataLoader(
MyDataSet(enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs), 2, True)
3 Codificação PosicionalCodificação Posicional
A fórmula de cálculo da codificação posicional é a seguinte:
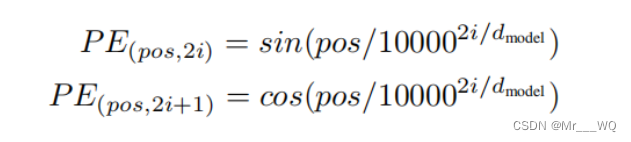
Para saber por que a fórmula de cálculo acima é usada, consulte Codificação posicional no Transformer - mathor (wmathor.com) ![]() https://wmathor.com/index.php/archives/1453/ . O sen e o cos na fórmula correspondem ao Dimensão embedding_dimension.Um conjunto de dimensões ordinais pares e ímpares. Por exemplo, um grupo de 0,1 e um grupo de 2,3 são processados pelas funções sin e cos acima, respectivamente, para produzir diferentes alterações periódicas. A posição é incorporada na dimensão embedding_dimension. À medida que o número da dimensão aumenta, as alterações
https://wmathor.com/index.php/archives/1453/ . O sen e o cos na fórmula correspondem ao Dimensão embedding_dimension.Um conjunto de dimensões ordinais pares e ímpares. Por exemplo, um grupo de 0,1 e um grupo de 2,3 são processados pelas funções sin e cos acima, respectivamente, para produzir diferentes alterações periódicas. A posição é incorporada na dimensão embedding_dimension. À medida que o número da dimensão aumenta, as alterações
periódicas se tornará cada vez mais. Quanto mais lento.

código mostrado abaixo:
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import math
def get_positional_encoding(max_seq_len, embed_dim):
# 初始化一个positional encoding
# embed_dim: 字嵌入的维度
# max_seq_len: 最大的序列长度
positional_encoding = np.array([
[pos / np.power(10000, 2 * i / embed_dim) for i in range(embed_dim)]
if pos != 0 else np.zeros(embed_dim) for pos in range(max_seq_len)])
positional_encoding[1:, 0::2] = np.sin(positional_encoding[1:, 0::2]) # dim 2i 偶数
positional_encoding[1:, 1::2] = np.cos(positional_encoding[1:, 1::2]) # dim 2i+1 奇数
return positional_encoding
4 Máscara
Existem duas partes no Transformer que usam máscara: a primeira é que durante o processo de treinamento da rede, o mesmo lote conterá várias sequências de texto e os comprimentos das diferentes sequências não são consistentes. Portanto, durante o processo de geração do conjunto de dados, é necessário preencher as sequências do mesmo lote com o mesmo comprimento. Porém, isso fará com que as informações sobre a posição do Padding sejam levadas em consideração no processo de cálculo da atenção. A parte expandida não deve ser notada, portanto é necessária uma operação de Máscara l, chamada Padding Mask; a segunda é que durante o processo de treinamento, é necessária uma tal matriz simétrica para cada amostra para mascarar todas as posições após o momento atual. , chamado Máscara de Atenção.
código mostrado abaixo:
def get_attn_pad_mask(seq_q, seq_k):
# pad mask的作用:在对value向量加权平均的时候,可以让pad对应的alpha_ij=0,这样注意力就不会考虑到pad向量
"""这里的q,k表示的是两个序列(跟注意力机制的q,k没有关系),例如encoder_inputs (x1,x2,..xm)和encoder_inputs (x1,x2..xm)
encoder和decoder都可能调用这个函数,所以seq_len视情况而定
seq_q: [batch_size, seq_len]
seq_k: [batch_size, seq_len]
seq_len could be src_len or it could be tgt_len
seq_len in seq_q and seq_len in seq_k maybe not equal
"""
batch_size, len_q = seq_q.size() # 这个seq_q只是用来expand维度的
batch_size, len_k = seq_k.size()
# eq(zero) is PAD token
# 例如:seq_k = [[1,2,3,4,0], [1,2,3,5,0]]
# [batch_size, 1, len_k], True is masked
pad_attn_mask = seq_k.data.eq(0).unsqueeze(1)
# [batch_size, len_q, len_k] 构成一个立方体(batch_size个这样的矩阵)
return pad_attn_mask.expand(batch_size, len_q, len_k)
"""这个函数最核心的一句代码是 seq_k.data.eq(0),
这句的作用是返回一个大小和 seq_k 一样的 tensor,
只不过里面的值只有 True 和 False。
如果 seq_k 某个位置的值等于 0,
那么对应位置就是 True,否则即为 False。
举个例子,输入为 seq_data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 0],
seq_data.data.eq(0) 就会返回
[False, False, False, False, True]
"""
def get_attn_subsequence_mask(seq):
"""建议打印出来看看是什么的输出(一目了然)
seq: [batch_size, tgt_len]
"""
attn_shape = [seq.size(0), seq.size(1), seq.size(1)]
# attn_shape: [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
subsequence_mask = np.triu(np.ones(attn_shape), k=1) # 生成一个上三角矩阵
subsequence_mask = torch.from_numpy(subsequence_mask).byte()
return subsequence_mask # [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
"""
get_attn_subsequence_mask 只有 Decoder 会用到,
主要作用是屏蔽未来时刻单词的信息。
首先通过 np.ones() 生成一个全 1 的方阵,
然后通过 np.triu() 生成一个上三角矩阵
"""
5 ScaledDotProductAtenção
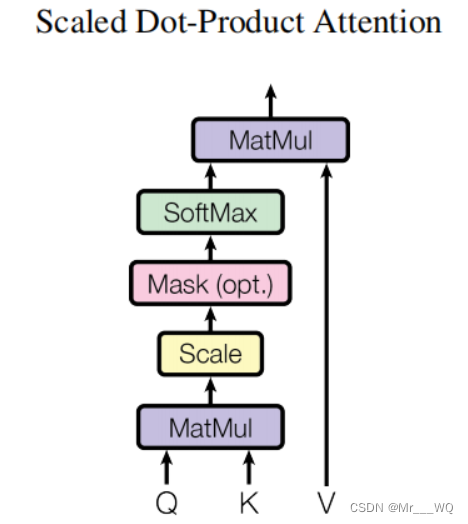
O que é feito aqui é calcular as pontuações por meio de Q e K e, em seguida, multiplicar as pontuações e V para obter o vetor de contexto de cada palavra.
O primeiro passo é multiplicar as transpostas de Q e K. Não há nada a dizer. As pontuações obtidas após a multiplicação não podem ser maximizadas imediatamente. Elas precisam ser adicionadas a attn_mask para filtrar algumas informações que precisam ser filtradas. attn_mask é um parâmetro composto apenas por True e False, e deve garantir que as quatro dimensões de attn_mask e pontuações sejam as mesmas (caso contrário, as posições correspondentes não podem ser adicionadas).Depois que a máscara for concluída, as pontuações podem ser softmaxed. Em seguida, multiplique por V para obter o contexto.
O diagrama de cálculo é o seguinte:
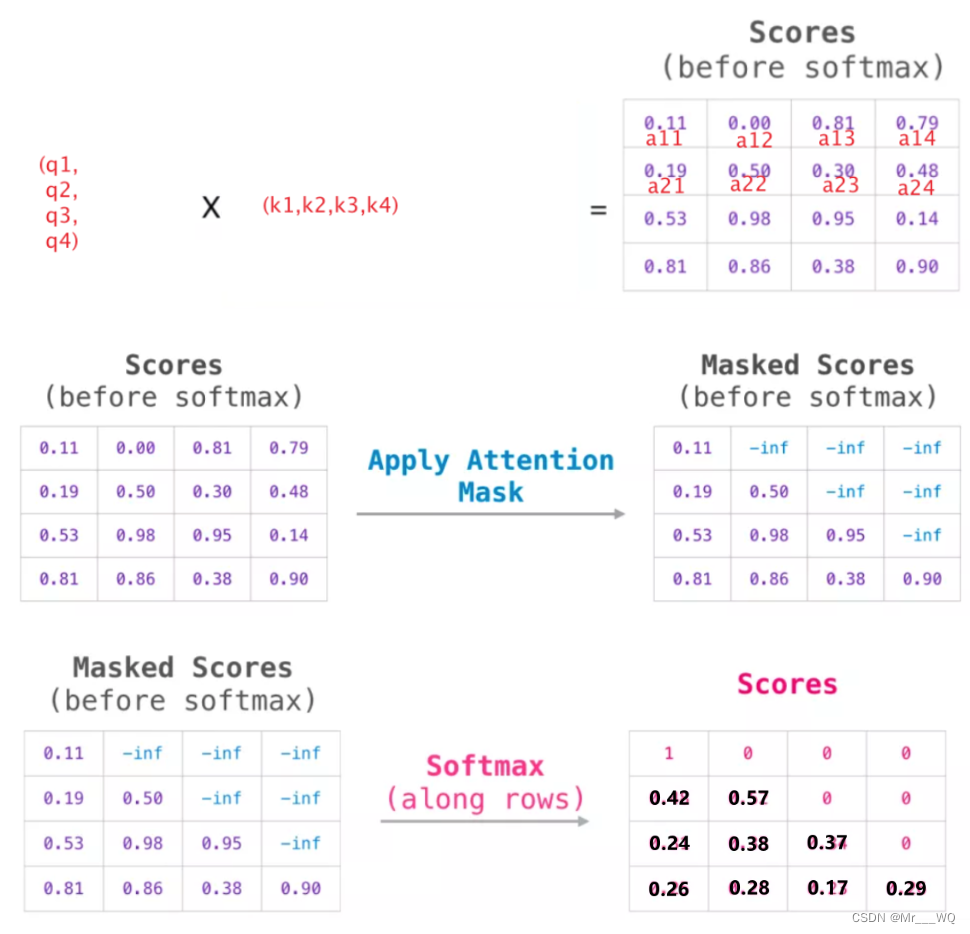
O significado desta tabela de pontuação é o seguinte:
Quando o modelo processa os primeiros dados do conjunto de dados (linha 1), que contém apenas uma palavra (robô), ele concentra 100% de sua atenção nesta palavra.
Quando o modelo processa o segundo dado no conjunto de dados (linha 2), ele contém a palavra (o robô deve). Quando o modelo processa a palavra must, ele concentra 42% de sua atenção no robô e 57% no must.
E assim por diante, continue processando as seguintes palavras.
Instruções adicionais:
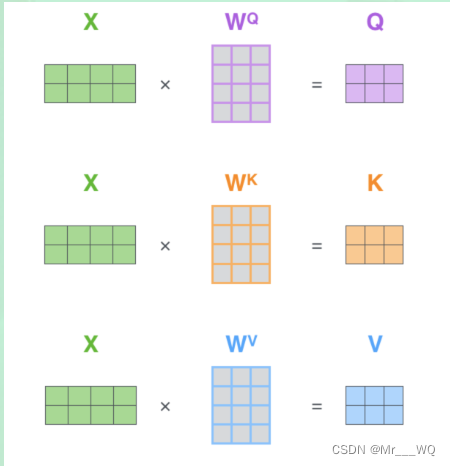
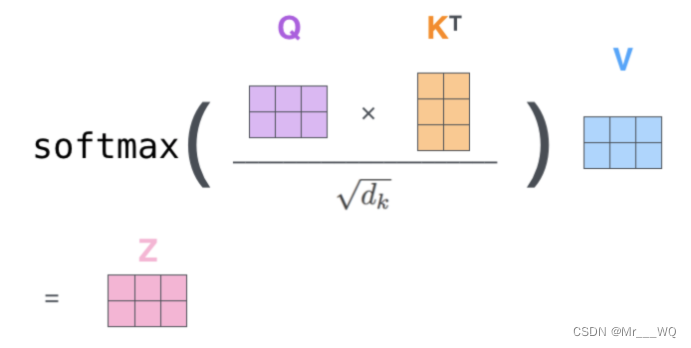
código mostrado abaixo:
class ScaledDotProductAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ScaledDotProductAttention, self).__init__()
def forward(self, Q, K, V, attn_mask):
"""
Q: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_k]
K: [batch_size, n_heads, len_k, d_k]
V: [batch_size, n_heads, len_v(=len_k), d_v]
attn_mask: [batch_size, n_heads, seq_len, seq_len]
说明:在encoder-decoder的Attention层中len_q(q1,..qt)和len_k(k1,...km)可能不同
"""
scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-1, -2)) / np.sqrt(d_k) # scores : [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, len_k]
# mask矩阵填充scores(用-1e9填充scores中与attn_mask中值为1位置相对应的元素)
scores.masked_fill_(attn_mask, -1e9) # Fills elements of self tensor with value where mask is True.
attn = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(scores) # 对最后一个维度(v)做softmax
# scores : [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, len_k] * V: [batch_size, n_heads, len_v(=len_k), d_v]
context = torch.matmul(attn, V) # context: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_v]
# context:[[z1,z2,...],[...]]向量, attn注意力稀疏矩阵(用于可视化的)
return context, attn
6 Feed Forward和Adicionar&Norma
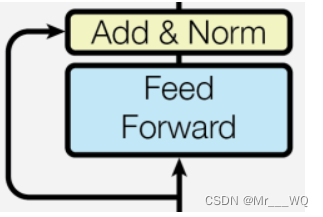
# Pytorch中的Linear只会对最后一维操作,所以正好是我们希望的每个位置用同一个全连接网络
class PoswiseFeedForwardNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(PoswiseFeedForwardNet, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(d_model, d_ff, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(d_ff, d_model, bias=False)
)
def forward(self, inputs):
"""
inputs: [batch_size, seq_len, d_model]
"""
residual = inputs
output = self.fc(inputs)
return nn.LayerNorm(d_model).to(device)(output + residual) # [batch_size, seq_len, d_model]
7 MultiHeadAtenção
Combinação de múltiplas autoatenções:
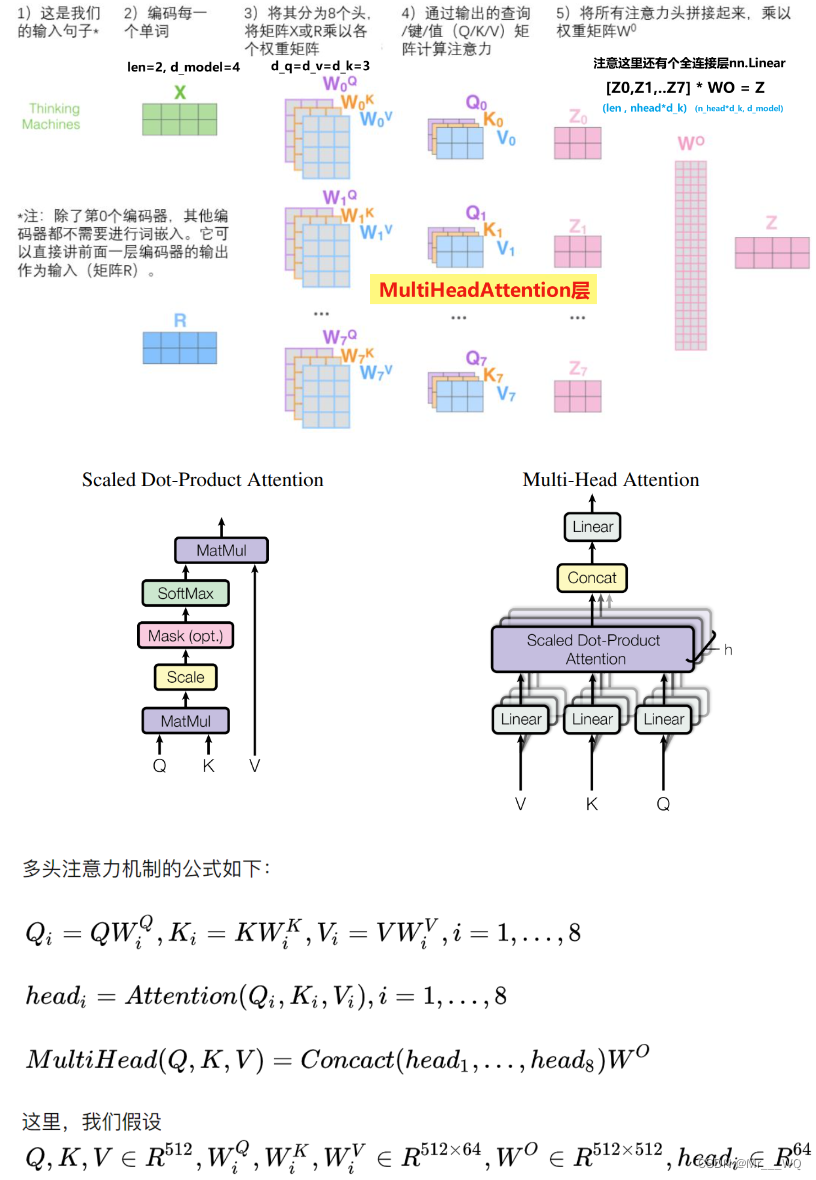
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
"""这个Attention类可以实现:
Encoder的Self-Attention
Decoder的Masked Self-Attention
Encoder-Decoder的Attention
输入:seq_len x d_model
输出:seq_len x d_model
"""
def __init__(self):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__()
self.W_Q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k * n_heads,
bias=False) # q,k必须维度相同,不然无法做点积
self.W_K = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k * n_heads, bias=False)
self.W_V = nn.Linear(d_model, d_v * n_heads, bias=False)
# 这个全连接层可以保证多头attention的输出仍然是seq_len x d_model
self.fc = nn.Linear(n_heads * d_v, d_model, bias=False)
def forward(self, input_Q, input_K, input_V, attn_mask):
"""
input_Q: [batch_size, len_q, d_model]
input_K: [batch_size, len_k, d_model]
input_V: [batch_size, len_v(=len_k), d_model]
attn_mask: [batch_size, seq_len, seq_len]
"""
residual, batch_size = input_Q, input_Q.size(0)
# 下面的多头的参数矩阵是放在一起做线性变换的,然后再拆成多个头,这是工程实现的技巧
# B: batch_size, S:seq_len, D: dim
# (B, S, D) -proj-> (B, S, D_new) -split-> (B, S, Head, W) -trans-> (B, Head, S, W)
# 线性变换 拆成多头
# Q: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_k]
Q = self.W_Q(input_Q).view(batch_size, -1,
n_heads, d_k).transpose(1, 2)
# K: [batch_size, n_heads, len_k, d_k] # K和V的长度一定相同,维度可以不同
K = self.W_K(input_K).view(batch_size, -1,
n_heads, d_k).transpose(1, 2)
# V: [batch_size, n_heads, len_v(=len_k), d_v]
V = self.W_V(input_V).view(batch_size, -1,
n_heads, d_v).transpose(1, 2)
# 因为是多头,所以mask矩阵要扩充成4维的
# attn_mask: [batch_size, seq_len, seq_len] -> [batch_size, n_heads, seq_len, seq_len]
attn_mask = attn_mask.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, n_heads, 1, 1)
# context: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_v], attn: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, len_k]
context, attn = ScaledDotProductAttention()(Q, K, V, attn_mask)
# 下面将不同头的输出向量拼接在一起
# context: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_v] -> [batch_size, len_q, n_heads * d_v]
context = context.transpose(1, 2).reshape(
batch_size, -1, n_heads * d_v)
# 这个全连接层可以保证多头attention的输出仍然是seq_len x d_model
output = self.fc(context) # [batch_size, len_q, d_model]
return nn.LayerNorm(d_model).to(device)(output + residual), attn
Deve haver três locais onde MultiHeadAttention() é chamado no código completo. A camada do codificador o chama uma vez, e os input_Q, input_K e input_V passados são todos enc_inputs; a camada do decodificador o chama duas vezes e na primeira vez que ele passa in é dec_inputs.Os passados são dec_outputs, enc_outputs e enc_outputs.
8 Camada do Codificador
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.enc_self_attn = MultiHeadAttention()
self.pos_ffn = PoswiseFeedForwardNet()
def forward(self, enc_inputs, enc_self_attn_mask):
"""E
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
enc_self_attn_mask: [batch_size, src_len, src_len] mask矩阵(pad mask or sequence mask)
"""
# enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model], attn: [batch_size, n_heads, src_len, src_len]
# 第一个enc_inputs * W_Q = Q
# 第二个enc_inputs * W_K = K
# 第三个enc_inputs * W_V = V
enc_outputs, attn = self.enc_self_attn(enc_inputs, enc_inputs, enc_inputs,
enc_self_attn_mask) # enc_inputs to same Q,K,V(未线性变换前)
enc_outputs = self.pos_ffn(enc_outputs)
# enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
return enc_outputs, attn
9 Codificador
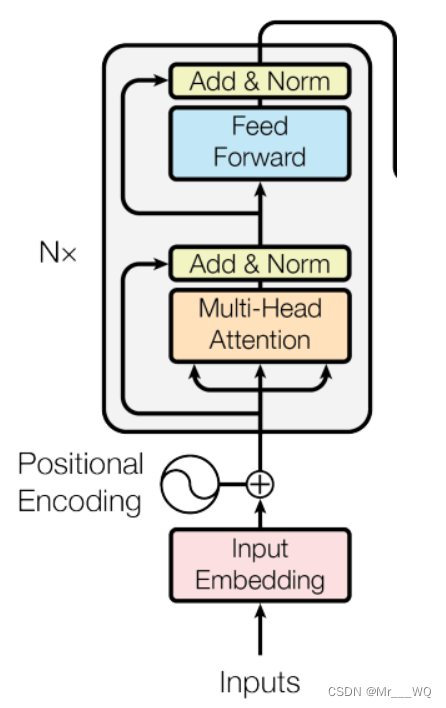
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.src_emb = nn.Embedding(src_vocab_size, d_model) # token Embedding
self.pos_emb = PositionalEncoding(
d_model) # Transformer中位置编码时固定的,不需要学习
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([EncoderLayer() for _ in range(n_layers)])
def forward(self, enc_inputs):
"""
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len]
"""
enc_outputs = self.src_emb(
enc_inputs) # [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
enc_outputs = self.pos_emb(enc_outputs.transpose(0, 1)).transpose(
0, 1) # [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
# Encoder输入序列的pad mask矩阵
enc_self_attn_mask = get_attn_pad_mask(
enc_inputs, enc_inputs) # [batch_size, src_len, src_len]
enc_self_attns = [] # 在计算中不需要用到,它主要用来保存你接下来返回的attention的值(这个主要是为了你画热力图等,用来看各个词之间的关系
for layer in self.layers: # for循环访问nn.ModuleList对象
# 上一个block的输出enc_outputs作为当前block的输入
# enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model], enc_self_attn: [batch_size, n_heads, src_len, src_len]
enc_outputs, enc_self_attn = layer(enc_outputs,
enc_self_attn_mask) # 传入的enc_outputs其实是input,传入mask矩阵是因为你要做self attention
enc_self_attns.append(enc_self_attn) # 这个只是为了可视化
return enc_outputs, enc_self_attns
10 Camada decodificadora
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.dec_self_attn = MultiHeadAttention()
self.dec_enc_attn = MultiHeadAttention()
self.pos_ffn = PoswiseFeedForwardNet()
def forward(self, dec_inputs, enc_outputs, dec_self_attn_mask, dec_enc_attn_mask):
"""
dec_inputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
dec_self_attn_mask: [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
dec_enc_attn_mask: [batch_size, tgt_len, src_len]
"""
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model], dec_self_attn: [batch_size, n_heads, tgt_len, tgt_len]
dec_outputs, dec_self_attn = self.dec_self_attn(dec_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_inputs,
dec_self_attn_mask) # 这里的Q,K,V全是Decoder自己的输入
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model], dec_enc_attn: [batch_size, h_heads, tgt_len, src_len]
dec_outputs, dec_enc_attn = self.dec_enc_attn(dec_outputs, enc_outputs, enc_outputs,
dec_enc_attn_mask) # Attention层的Q(来自decoder) 和 K,V(来自encoder)
# [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
dec_outputs = self.pos_ffn(dec_outputs)
# dec_self_attn, dec_enc_attn这两个是为了可视化的
return dec_outputs, dec_self_attn, dec_enc_attn
11 Decodificador
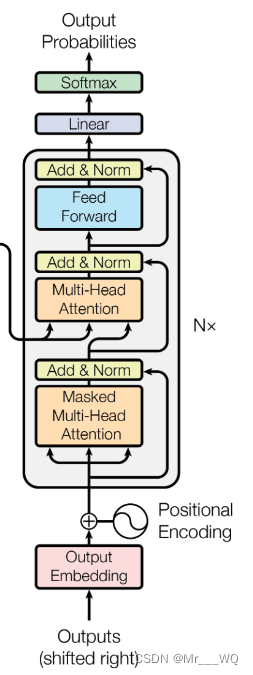
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.tgt_emb = nn.Embedding(
tgt_vocab_size, d_model) # Decoder输入的embed词表
self.pos_emb = PositionalEncoding(d_model)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([DecoderLayer()
for _ in range(n_layers)]) # Decoder的blocks
def forward(self, dec_inputs, enc_inputs, enc_outputs):
"""
dec_inputs: [batch_size, tgt_len]
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len]
enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model] # 用在Encoder-Decoder Attention层
"""
dec_outputs = self.tgt_emb(
dec_inputs) # [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
dec_outputs = self.pos_emb(dec_outputs.transpose(0, 1)).transpose(0, 1).to(
device) # [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
# Decoder输入序列的pad mask矩阵(这个例子中decoder是没有加pad的,实际应用中都是有pad填充的)
dec_self_attn_pad_mask = get_attn_pad_mask(dec_inputs, dec_inputs).to(
device) # [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
# Masked Self_Attention:当前时刻是看不到未来的信息的
dec_self_attn_subsequence_mask = get_attn_subsequence_mask(dec_inputs).to(
device) # [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
# Decoder中把两种mask矩阵相加(既屏蔽了pad的信息,也屏蔽了未来时刻的信息)
dec_self_attn_mask = torch.gt((dec_self_attn_pad_mask + dec_self_attn_subsequence_mask),
0).to(device) # [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]; torch.gt比较两个矩阵的元素,大于则返回1,否则返回0
# 这个mask主要用于encoder-decoder attention层
# get_attn_pad_mask主要是enc_inputs的pad mask矩阵(因为enc是处理K,V的,求Attention时是用v1,v2,..vm去加权的,要把pad对应的v_i的相关系数设为0,这样注意力就不会关注pad向量)
# dec_inputs只是提供expand的size的
dec_enc_attn_mask = get_attn_pad_mask(
dec_inputs, enc_inputs) # [batc_size, tgt_len, src_len]
dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns = [], []
for layer in self.layers:
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model], dec_self_attn: [batch_size, n_heads, tgt_len, tgt_len], dec_enc_attn: [batch_size, h_heads, tgt_len, src_len]
# Decoder的Block是上一个Block的输出dec_outputs(变化)和Encoder网络的输出enc_outputs(固定)
dec_outputs, dec_self_attn, dec_enc_attn = layer(dec_outputs, enc_outputs, dec_self_attn_mask,
dec_enc_attn_mask)
dec_self_attns.append(dec_self_attn)
dec_enc_attns.append(dec_enc_attn)
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
return dec_outputs, dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns
12 Transformador

class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Transformer, self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder().to(device)
self.decoder = Decoder().to(device)
self.projection = nn.Linear(
d_model, tgt_vocab_size, bias=False).to(device)
def forward(self, enc_inputs, dec_inputs):
"""Transformers的输入:两个序列
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len]
dec_inputs: [batch_size, tgt_len]
"""
# tensor to store decoder outputs
# outputs = torch.zeros(batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_vocab_size).to(self.device)
# enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model], enc_self_attns: [n_layers, batch_size, n_heads, src_len, src_len]
# 经过Encoder网络后,得到的输出还是[batch_size, src_len, d_model]
enc_outputs, enc_self_attns = self.encoder(enc_inputs)
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model], dec_self_attns: [n_layers, batch_size, n_heads, tgt_len, tgt_len], dec_enc_attn: [n_layers, batch_size, tgt_len, src_len]
dec_outputs, dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns = self.decoder(
dec_inputs, enc_inputs, enc_outputs)
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model] -> dec_logits: [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_vocab_size]
dec_logits = self.projection(dec_outputs)
return dec_logits.view(-1, dec_logits.size(-1)), enc_self_attns, dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns
trem
model = Transformer().to(device)
# 这里的损失函数里面设置了一个参数 ignore_index=0,因为 "pad" 这个单词的索引为 0,这样设置以后,就不会计算 "pad" 的损失(因为本来 "pad" 也没有意义,不需要计算)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=0)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3,
momentum=0.99) # 用adam的话效果不好
for epoch in range(epochs):
for enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs in loader:
"""
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len]
dec_inputs: [batch_size, tgt_len]
dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len]
"""
enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs = enc_inputs.to(
device), dec_inputs.to(device), dec_outputs.to(device)
# outputs: [batch_size * tgt_len, tgt_vocab_size]
outputs, enc_self_attns, dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns = model(
enc_inputs, dec_inputs)
# dec_outputs.view(-1):[batch_size * tgt_len * tgt_vocab_size]
loss = criterion(outputs, dec_outputs.view(-1))
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'loss =', '{:.6f}'.format(loss))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
saída:
def greedy_decoder(model, enc_input, start_symbol):
"""贪心编码
For simplicity, a Greedy Decoder is Beam search when K=1. This is necessary for inference as we don't know the
target sequence input. Therefore we try to generate the target input word by word, then feed it into the transformer.
Starting Reference: http://nlp.seas.harvard.edu/2018/04/03/attention.html#greedy-decoding
:param model: Transformer Model
:param enc_input: The encoder input
:param start_symbol: The start symbol. In this example it is 'S' which corresponds to index 4
:return: The target input
"""
enc_outputs, enc_self_attns = model.encoder(enc_input)
# 初始化一个空的tensor: tensor([], size=(1, 0), dtype=torch.int64)
dec_input = torch.zeros(1, 0).type_as(enc_input.data)
terminal = False
next_symbol = start_symbol
while not terminal:
# 预测阶段:dec_input序列会一点点变长(每次添加一个新预测出来的单词)
dec_input = torch.cat([dec_input.to(device), torch.tensor([[next_symbol]], dtype=enc_input.dtype).to(device)],
-1)
dec_outputs, _, _ = model.decoder(dec_input, enc_input, enc_outputs)
projected = model.projection(dec_outputs)
prob = projected.squeeze(0).max(dim=-1, keepdim=False)[1]
# 增量更新(我们希望重复单词预测结果是一样的)
# 我们在预测是会选择性忽略重复的预测的词,只摘取最新预测的单词拼接到输入序列中
# 拿出当前预测的单词(数字)。我们用x'_t对应的输出z_t去预测下一个单词的概率,不用z_1,z_2..z_{t-1}
next_word = prob.data[-1]
next_symbol = next_word
if next_symbol == tgt_vocab["E"]:
terminal = True
# print(next_word)
# greedy_dec_predict = torch.cat(
# [dec_input.to(device), torch.tensor([[next_symbol]], dtype=enc_input.dtype).to(device)],
# -1)
greedy_dec_predict = dec_input[:, 1:]
return greedy_dec_predict
# ==========================================================================================
# 预测阶段
# 测试集
sentences = [
# enc_input dec_input dec_output
['我 有 零 个 女 朋 友 P', '', '']
]
enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs = make_data(sentences)
test_loader = Data.DataLoader(
MyDataSet(enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs), 2, True)
enc_inputs, _, _ = next(iter(test_loader))
print()
print("="*30)
print("利用训练好的Transformer模型将中文句子'我 有 零 个 女 朋 友' 翻译成英文句子: ")
for i in range(len(enc_inputs)):
greedy_dec_predict = greedy_decoder(model, enc_inputs[i].view(
1, -1).to(device), start_symbol=tgt_vocab["S"])
print(enc_inputs[i], '->', greedy_dec_predict.squeeze())
print([src_idx2word[t.item()] for t in enc_inputs[i]], '->',
[idx2word[n.item()] for n in greedy_dec_predict.squeeze()])
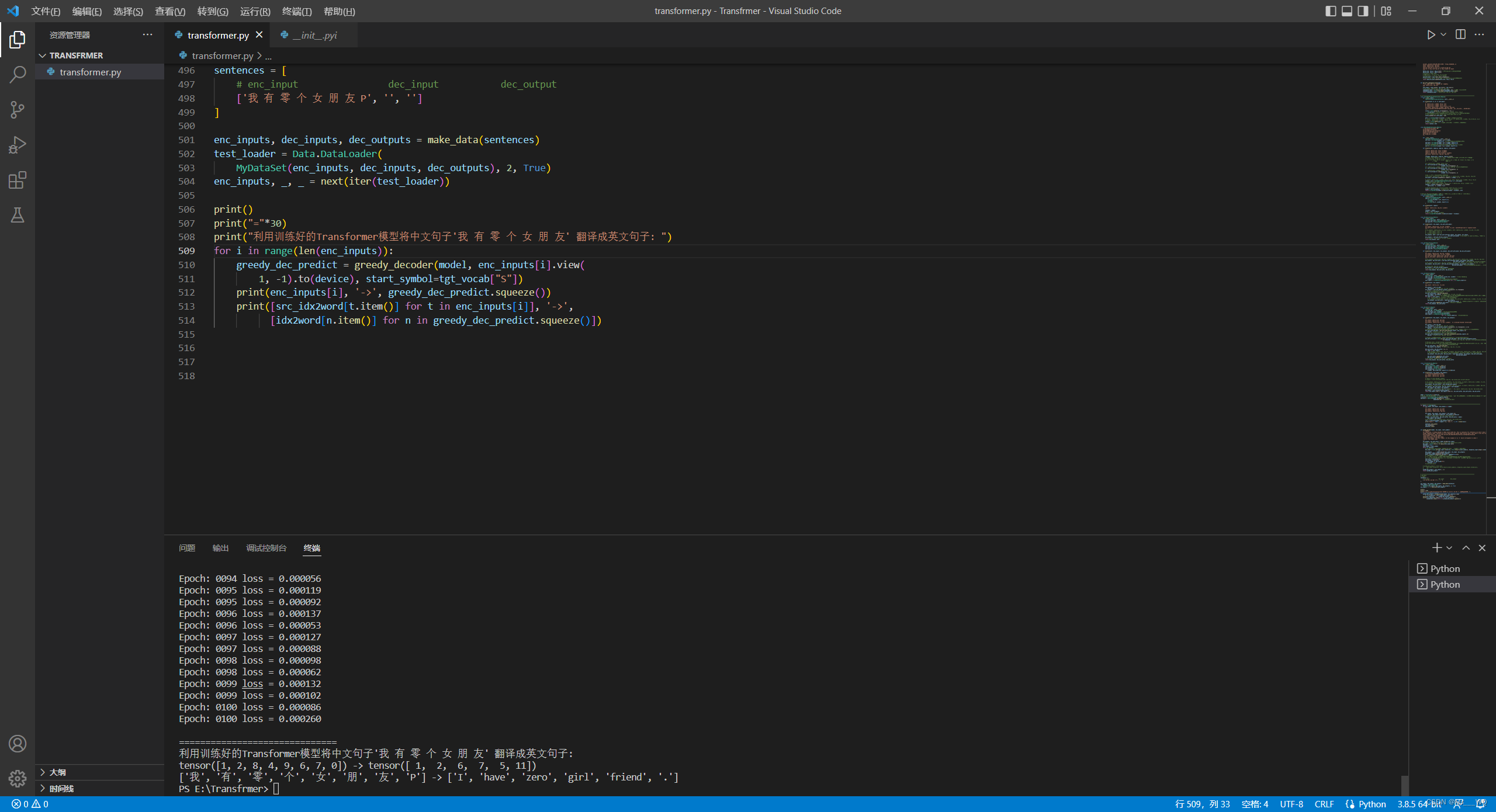
Código completo
Referência do código-fonte:
# ======================================
# === Pytorch手写Transformer完整代码
# ======================================
"""
code by Tae Hwan Jung(Jeff Jung) @graykode, Derek Miller @dmmiller612, modify by shwei
Reference: https://github.com/jadore801120/attention-is-all-you-need-pytorch
https://github.com/JayParks/transformer
"""
# ====================================================================================================
# 数据构建
import math
import torch
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.utils.data as Data
device = 'cpu'
#device = 'cuda'
# transformer epochs
epochs = 100
# epochs = 1000
# 这里我没有用什么大型的数据集,而是手动输入了两对中文→英语的句子
# 还有每个字的索引也是我手动硬编码上去的,主要是为了降低代码阅读难度
# S: Symbol that shows starting of decoding input
# E: Symbol that shows starting of decoding output
# P: Symbol that will fill in blank sequence if current batch data size is short than time steps
# 训练集
sentences = [
# 中文和英语的单词个数不要求相同
# enc_input dec_input dec_output
['我 有 一 个 好 朋 友 P', 'S I have a good friend .', 'I have a good friend . E'],
['我 有 零 个 女 朋 友 P', 'S I have zero girl friend .', 'I have zero girl friend . E'],
['我 有 一 个 男 朋 友 P', 'S I have a boy friend .', 'I have a boy friend . E']
]
# 测试集(希望transformer能达到的效果)
# 输入:"我 有 一 个 女 朋 友"
# 输出:"i have a girlfriend"
# 中文和英语的单词要分开建立词库
# Padding Should be Zero
src_vocab = {'P': 0, '我': 1, '有': 2, '一': 3,
'个': 4, '好': 5, '朋': 6, '友': 7, '零': 8, '女': 9, '男': 10}
src_idx2word = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(src_vocab)}
src_vocab_size = len(src_vocab)
tgt_vocab = {'P': 0, 'I': 1, 'have': 2, 'a': 3, 'good': 4,
'friend': 5, 'zero': 6, 'girl': 7, 'boy': 8, 'S': 9, 'E': 10, '.': 11}
idx2word = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(tgt_vocab)}
tgt_vocab_size = len(tgt_vocab)
src_len = 8 # (源句子的长度)enc_input max sequence length
tgt_len = 7 # dec_input(=dec_output) max sequence length
# Transformer Parameters
d_model = 512 # Embedding Size(token embedding和position编码的维度)
# FeedForward dimension (两次线性层中的隐藏层 512->2048->512,线性层是用来做特征提取的),当然最后会再接一个projection层
d_ff = 2048
d_k = d_v = 64 # dimension of K(=Q), V(Q和K的维度需要相同,这里为了方便让K=V)
n_layers = 6 # number of Encoder of Decoder Layer(Block的个数)
n_heads = 8 # number of heads in Multi-Head Attention(有几套头)
# ==============================================================================================
# 数据构建
def make_data(sentences):
"""把单词序列转换为数字序列"""
enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs = [], [], []
for i in range(len(sentences)):
enc_input = [[src_vocab[n] for n in sentences[i][0].split()]]
dec_input = [[tgt_vocab[n] for n in sentences[i][1].split()]]
dec_output = [[tgt_vocab[n] for n in sentences[i][2].split()]]
#[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0], [1, 2, 8, 4, 9, 6, 7, 0], [1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 6, 7, 0]]
enc_inputs.extend(enc_input)
#[[9, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 11], [9, 1, 2, 6, 7, 5, 11], [9, 1, 2, 3, 8, 5, 11]]
dec_inputs.extend(dec_input)
#[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 11, 10], [1, 2, 6, 7, 5, 11, 10], [1, 2, 3, 8, 5, 11, 10]]
dec_outputs.extend(dec_output)
return torch.LongTensor(enc_inputs), torch.LongTensor(dec_inputs), torch.LongTensor(dec_outputs)
enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs = make_data(sentences)
class MyDataSet(Data.Dataset):
"""自定义DataLoader"""
def __init__(self, enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs):
super(MyDataSet, self).__init__()
self.enc_inputs = enc_inputs
self.dec_inputs = dec_inputs
self.dec_outputs = dec_outputs
def __len__(self):
return self.enc_inputs.shape[0]
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.enc_inputs[idx], self.dec_inputs[idx], self.dec_outputs[idx]
loader = Data.DataLoader(
MyDataSet(enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs), 2, True)
# ====================================================================================================
# Transformer模型
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, dropout=0.1, max_len=5000):
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
pe = torch.zeros(max_len, d_model)
position = torch.arange(0, max_len, dtype=torch.float).unsqueeze(1)
div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(
0, d_model, 2).float() * (-math.log(10000.0) / d_model))
pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term)
pe = pe.unsqueeze(0).transpose(0, 1)
self.register_buffer('pe', pe)
def forward(self, x):
"""
x: [seq_len, batch_size, d_model]
"""
x = x + self.pe[:x.size(0), :]
return self.dropout(x)
def get_attn_pad_mask(seq_q, seq_k):
# pad mask的作用:在对value向量加权平均的时候,可以让pad对应的alpha_ij=0,这样注意力就不会考虑到pad向量
"""这里的q,k表示的是两个序列(跟注意力机制的q,k没有关系),例如encoder_inputs (x1,x2,..xm)和encoder_inputs (x1,x2..xm)
encoder和decoder都可能调用这个函数,所以seq_len视情况而定
seq_q: [batch_size, seq_len]
seq_k: [batch_size, seq_len]
seq_len could be src_len or it could be tgt_len
seq_len in seq_q and seq_len in seq_k maybe not equal
"""
batch_size, len_q = seq_q.size() # 这个seq_q只是用来expand维度的
batch_size, len_k = seq_k.size()
# eq(zero) is PAD token
# 例如:seq_k = [[1,2,3,4,0], [1,2,3,5,0]]
# [batch_size, 1, len_k], True is masked
pad_attn_mask = seq_k.data.eq(0).unsqueeze(1)
# [batch_size, len_q, len_k] 构成一个立方体(batch_size个这样的矩阵)
return pad_attn_mask.expand(batch_size, len_q, len_k)
def get_attn_subsequence_mask(seq):
"""建议打印出来看看是什么的输出(一目了然)
seq: [batch_size, tgt_len]
"""
attn_shape = [seq.size(0), seq.size(1), seq.size(1)]
# attn_shape: [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
subsequence_mask = np.triu(np.ones(attn_shape), k=1) # 生成一个上三角矩阵
subsequence_mask = torch.from_numpy(subsequence_mask).byte()
return subsequence_mask # [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
# ==========================================================================================
class ScaledDotProductAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ScaledDotProductAttention, self).__init__()
def forward(self, Q, K, V, attn_mask):
"""
Q: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_k]
K: [batch_size, n_heads, len_k, d_k]
V: [batch_size, n_heads, len_v(=len_k), d_v]
attn_mask: [batch_size, n_heads, seq_len, seq_len]
说明:在encoder-decoder的Attention层中len_q(q1,..qt)和len_k(k1,...km)可能不同
"""
scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-1, -2)) / \
np.sqrt(d_k) # scores : [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, len_k]
# mask矩阵填充scores(用-1e9填充scores中与attn_mask中值为1位置相对应的元素)
# Fills elements of self tensor with value where mask is True.
scores.masked_fill_(attn_mask, -1e9)
attn = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(scores) # 对最后一个维度(v)做softmax
# scores : [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, len_k] * V: [batch_size, n_heads, len_v(=len_k), d_v]
# context: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_v]
context = torch.matmul(attn, V)
# context:[[z1,z2,...],[...]]向量, attn注意力稀疏矩阵(用于可视化的)
return context, attn
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
"""这个Attention类可以实现:
Encoder的Self-Attention
Decoder的Masked Self-Attention
Encoder-Decoder的Attention
输入:seq_len x d_model
输出:seq_len x d_model
"""
def __init__(self):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__()
self.W_Q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k * n_heads,
bias=False) # q,k必须维度相同,不然无法做点积
self.W_K = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k * n_heads, bias=False)
self.W_V = nn.Linear(d_model, d_v * n_heads, bias=False)
# 这个全连接层可以保证多头attention的输出仍然是seq_len x d_model
self.fc = nn.Linear(n_heads * d_v, d_model, bias=False)
def forward(self, input_Q, input_K, input_V, attn_mask):
"""
input_Q: [batch_size, len_q, d_model]
input_K: [batch_size, len_k, d_model]
input_V: [batch_size, len_v(=len_k), d_model]
attn_mask: [batch_size, seq_len, seq_len]
"""
residual, batch_size = input_Q, input_Q.size(0)
# 下面的多头的参数矩阵是放在一起做线性变换的,然后再拆成多个头,这是工程实现的技巧
# B: batch_size, S:seq_len, D: dim
# (B, S, D) -proj-> (B, S, D_new) -split-> (B, S, Head, W) -trans-> (B, Head, S, W)
# 线性变换 拆成多头
# Q: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_k]
Q = self.W_Q(input_Q).view(batch_size, -1,
n_heads, d_k).transpose(1, 2)
# K: [batch_size, n_heads, len_k, d_k] # K和V的长度一定相同,维度可以不同
K = self.W_K(input_K).view(batch_size, -1,
n_heads, d_k).transpose(1, 2)
# V: [batch_size, n_heads, len_v(=len_k), d_v]
V = self.W_V(input_V).view(batch_size, -1,
n_heads, d_v).transpose(1, 2)
# 因为是多头,所以mask矩阵要扩充成4维的
# attn_mask: [batch_size, seq_len, seq_len] -> [batch_size, n_heads, seq_len, seq_len]
attn_mask = attn_mask.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, n_heads, 1, 1)
# context: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_v], attn: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, len_k]
context, attn = ScaledDotProductAttention()(Q, K, V, attn_mask)
# 下面将不同头的输出向量拼接在一起
# context: [batch_size, n_heads, len_q, d_v] -> [batch_size, len_q, n_heads * d_v]
context = context.transpose(1, 2).reshape(
batch_size, -1, n_heads * d_v)
# 这个全连接层可以保证多头attention的输出仍然是seq_len x d_model
output = self.fc(context) # [batch_size, len_q, d_model]
return nn.LayerNorm(d_model).to(device)(output + residual), attn
# Pytorch中的Linear只会对最后一维操作,所以正好是我们希望的每个位置用同一个全连接网络
class PoswiseFeedForwardNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(PoswiseFeedForwardNet, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(d_model, d_ff, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(d_ff, d_model, bias=False)
)
def forward(self, inputs):
"""
inputs: [batch_size, seq_len, d_model]
"""
residual = inputs
output = self.fc(inputs)
# [batch_size, seq_len, d_model]
return nn.LayerNorm(d_model).to(device)(output + residual)
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.enc_self_attn = MultiHeadAttention()
self.pos_ffn = PoswiseFeedForwardNet()
def forward(self, enc_inputs, enc_self_attn_mask):
"""E
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
enc_self_attn_mask: [batch_size, src_len, src_len] mask矩阵(pad mask or sequence mask)
"""
# enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model], attn: [batch_size, n_heads, src_len, src_len]
# 第一个enc_inputs * W_Q = Q
# 第二个enc_inputs * W_K = K
# 第三个enc_inputs * W_V = V
enc_outputs, attn = self.enc_self_attn(enc_inputs, enc_inputs, enc_inputs,
enc_self_attn_mask) # enc_inputs to same Q,K,V(未线性变换前)
enc_outputs = self.pos_ffn(enc_outputs)
# enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
return enc_outputs, attn
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.dec_self_attn = MultiHeadAttention()
self.dec_enc_attn = MultiHeadAttention()
self.pos_ffn = PoswiseFeedForwardNet()
def forward(self, dec_inputs, enc_outputs, dec_self_attn_mask, dec_enc_attn_mask):
"""
dec_inputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
dec_self_attn_mask: [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
dec_enc_attn_mask: [batch_size, tgt_len, src_len]
"""
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model], dec_self_attn: [batch_size, n_heads, tgt_len, tgt_len]
dec_outputs, dec_self_attn = self.dec_self_attn(dec_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_inputs,
dec_self_attn_mask) # 这里的Q,K,V全是Decoder自己的输入
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model], dec_enc_attn: [batch_size, h_heads, tgt_len, src_len]
dec_outputs, dec_enc_attn = self.dec_enc_attn(dec_outputs, enc_outputs, enc_outputs,
dec_enc_attn_mask) # Attention层的Q(来自decoder) 和 K,V(来自encoder)
# [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
dec_outputs = self.pos_ffn(dec_outputs)
# dec_self_attn, dec_enc_attn这两个是为了可视化的
return dec_outputs, dec_self_attn, dec_enc_attn
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.src_emb = nn.Embedding(src_vocab_size, d_model) # token Embedding
self.pos_emb = PositionalEncoding(
d_model) # Transformer中位置编码时固定的,不需要学习
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([EncoderLayer() for _ in range(n_layers)])
def forward(self, enc_inputs):
"""
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len]
"""
enc_outputs = self.src_emb(
enc_inputs) # [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
enc_outputs = self.pos_emb(enc_outputs.transpose(0, 1)).transpose(
0, 1) # [batch_size, src_len, d_model]
# Encoder输入序列的pad mask矩阵
enc_self_attn_mask = get_attn_pad_mask(
enc_inputs, enc_inputs) # [batch_size, src_len, src_len]
enc_self_attns = [] # 在计算中不需要用到,它主要用来保存你接下来返回的attention的值(这个主要是为了你画热力图等,用来看各个词之间的关系
for layer in self.layers: # for循环访问nn.ModuleList对象
# 上一个block的输出enc_outputs作为当前block的输入
# enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model], enc_self_attn: [batch_size, n_heads, src_len, src_len]
enc_outputs, enc_self_attn = layer(enc_outputs,
enc_self_attn_mask) # 传入的enc_outputs其实是input,传入mask矩阵是因为你要做self attention
enc_self_attns.append(enc_self_attn) # 这个只是为了可视化
return enc_outputs, enc_self_attns
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.tgt_emb = nn.Embedding(
tgt_vocab_size, d_model) # Decoder输入的embed词表
self.pos_emb = PositionalEncoding(d_model)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([DecoderLayer()
for _ in range(n_layers)]) # Decoder的blocks
def forward(self, dec_inputs, enc_inputs, enc_outputs):
"""
dec_inputs: [batch_size, tgt_len]
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len]
enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model] # 用在Encoder-Decoder Attention层
"""
dec_outputs = self.tgt_emb(
dec_inputs) # [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
dec_outputs = self.pos_emb(dec_outputs.transpose(0, 1)).transpose(0, 1).to(
device) # [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
# Decoder输入序列的pad mask矩阵(这个例子中decoder是没有加pad的,实际应用中都是有pad填充的)
dec_self_attn_pad_mask = get_attn_pad_mask(dec_inputs, dec_inputs).to(
device) # [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
# Masked Self_Attention:当前时刻是看不到未来的信息的
dec_self_attn_subsequence_mask = get_attn_subsequence_mask(dec_inputs).to(
device) # [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]
# Decoder中把两种mask矩阵相加(既屏蔽了pad的信息,也屏蔽了未来时刻的信息)
dec_self_attn_mask = torch.gt((dec_self_attn_pad_mask + dec_self_attn_subsequence_mask),
0).to(device) # [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_len]; torch.gt比较两个矩阵的元素,大于则返回1,否则返回0
# 这个mask主要用于encoder-decoder attention层
# get_attn_pad_mask主要是enc_inputs的pad mask矩阵(因为enc是处理K,V的,求Attention时是用v1,v2,..vm去加权的,要把pad对应的v_i的相关系数设为0,这样注意力就不会关注pad向量)
# dec_inputs只是提供expand的size的
dec_enc_attn_mask = get_attn_pad_mask(
dec_inputs, enc_inputs) # [batc_size, tgt_len, src_len]
dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns = [], []
for layer in self.layers:
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model], dec_self_attn: [batch_size, n_heads, tgt_len, tgt_len], dec_enc_attn: [batch_size, h_heads, tgt_len, src_len]
# Decoder的Block是上一个Block的输出dec_outputs(变化)和Encoder网络的输出enc_outputs(固定)
dec_outputs, dec_self_attn, dec_enc_attn = layer(dec_outputs, enc_outputs, dec_self_attn_mask,
dec_enc_attn_mask)
dec_self_attns.append(dec_self_attn)
dec_enc_attns.append(dec_enc_attn)
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model]
return dec_outputs, dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Transformer, self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder().to(device)
self.decoder = Decoder().to(device)
self.projection = nn.Linear(
d_model, tgt_vocab_size, bias=False).to(device)
def forward(self, enc_inputs, dec_inputs):
"""Transformers的输入:两个序列
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len]
dec_inputs: [batch_size, tgt_len]
"""
# tensor to store decoder outputs
# outputs = torch.zeros(batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_vocab_size).to(self.device)
# enc_outputs: [batch_size, src_len, d_model], enc_self_attns: [n_layers, batch_size, n_heads, src_len, src_len]
# 经过Encoder网络后,得到的输出还是[batch_size, src_len, d_model]
enc_outputs, enc_self_attns = self.encoder(enc_inputs)
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model], dec_self_attns: [n_layers, batch_size, n_heads, tgt_len, tgt_len], dec_enc_attn: [n_layers, batch_size, tgt_len, src_len]
dec_outputs, dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns = self.decoder(
dec_inputs, enc_inputs, enc_outputs)
# dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len, d_model] -> dec_logits: [batch_size, tgt_len, tgt_vocab_size]
dec_logits = self.projection(dec_outputs)
return dec_logits.view(-1, dec_logits.size(-1)), enc_self_attns, dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns
model = Transformer().to(device)
# 这里的损失函数里面设置了一个参数 ignore_index=0,因为 "pad" 这个单词的索引为 0,这样设置以后,就不会计算 "pad" 的损失(因为本来 "pad" 也没有意义,不需要计算)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=0)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3,
momentum=0.99) # 用adam的话效果不好
# ====================================================================================================
for epoch in range(epochs):
for enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs in loader:
"""
enc_inputs: [batch_size, src_len]
dec_inputs: [batch_size, tgt_len]
dec_outputs: [batch_size, tgt_len]
"""
enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs = enc_inputs.to(
device), dec_inputs.to(device), dec_outputs.to(device)
# outputs: [batch_size * tgt_len, tgt_vocab_size]
outputs, enc_self_attns, dec_self_attns, dec_enc_attns = model(
enc_inputs, dec_inputs)
# dec_outputs.view(-1):[batch_size * tgt_len * tgt_vocab_size]
loss = criterion(outputs, dec_outputs.view(-1))
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'loss =', '{:.6f}'.format(loss))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
def greedy_decoder(model, enc_input, start_symbol):
"""贪心编码
For simplicity, a Greedy Decoder is Beam search when K=1. This is necessary for inference as we don't know the
target sequence input. Therefore we try to generate the target input word by word, then feed it into the transformer.
Starting Reference: http://nlp.seas.harvard.edu/2018/04/03/attention.html#greedy-decoding
:param model: Transformer Model
:param enc_input: The encoder input
:param start_symbol: The start symbol. In this example it is 'S' which corresponds to index 4
:return: The target input
"""
enc_outputs, enc_self_attns = model.encoder(enc_input)
# 初始化一个空的tensor: tensor([], size=(1, 0), dtype=torch.int64)
dec_input = torch.zeros(1, 0).type_as(enc_input.data)
terminal = False
next_symbol = start_symbol
while not terminal:
# 预测阶段:dec_input序列会一点点变长(每次添加一个新预测出来的单词)
dec_input = torch.cat([dec_input.to(device), torch.tensor([[next_symbol]], dtype=enc_input.dtype).to(device)],
-1)
dec_outputs, _, _ = model.decoder(dec_input, enc_input, enc_outputs)
projected = model.projection(dec_outputs)
prob = projected.squeeze(0).max(dim=-1, keepdim=False)[1]
# 增量更新(我们希望重复单词预测结果是一样的)
# 我们在预测是会选择性忽略重复的预测的词,只摘取最新预测的单词拼接到输入序列中
# 拿出当前预测的单词(数字)。我们用x'_t对应的输出z_t去预测下一个单词的概率,不用z_1,z_2..z_{t-1}
next_word = prob.data[-1]
next_symbol = next_word
if next_symbol == tgt_vocab["E"]:
terminal = True
# print(next_word)
# greedy_dec_predict = torch.cat(
# [dec_input.to(device), torch.tensor([[next_symbol]], dtype=enc_input.dtype).to(device)],
# -1)
greedy_dec_predict = dec_input[:, 1:]
return greedy_dec_predict
# ==========================================================================================
# 预测阶段
# 测试集
sentences = [
# enc_input dec_input dec_output
['我 有 零 个 女 朋 友 P', '', '']
]
enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs = make_data(sentences)
test_loader = Data.DataLoader(
MyDataSet(enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs), 2, True)
enc_inputs, _, _ = next(iter(test_loader))
print()
print("="*30)
print("利用训练好的Transformer模型将中文句子'我 有 零 个 女 朋 友' 翻译成英文句子: ")
for i in range(len(enc_inputs)):
greedy_dec_predict = greedy_decoder(model, enc_inputs[i].view(
1, -1).to(device), start_symbol=tgt_vocab["S"])
print(enc_inputs[i], '->', greedy_dec_predict.squeeze())
print([src_idx2word[t.item()] for t in enc_inputs[i]], '->',
[idx2word[n.item()] for n in greedy_dec_predict.squeeze()])
resultado: