Python3 alcançar árvore de vermelho-preto [próximo]
Isto é o que eu olhar para um artigo recente https://www.cnblogs.com/gcheeze/p/11186806.html
Eu li muitos artigos e blog sobre a árvore de vermelho-preto excluir introduzido foi muito, muito complexo, muito Pig levará um bom golpe de um acidente vascular cerebral.
Nós usamos uma maneira simples de lidar, encontramos Para excluir um elemento, nós apontar para ele com o ponteiro d, em seguida, o juiz:
1. Se d é um pontos de nó folha, ao final do ciclo
2. Se o ponto d a uma subárvore direita do nó, em seguida, encontrar o seu sucessor imediato, a troca e seus dados sucessor imediato, d apontando para ele logo após, repetindo os passos 1
3. Se o nó apontado d tem subárvore esquerda, em seguida, encontrar seu antecessor imediato, a troca directa de dados e sua prodrômica, d ponto de seu antecessor imediato, repita o passo 1
Aqui os alunos podem ter perguntas, o que é o sucessor direto, o que é o precursor direto.
FIG mãe borrow disso, como mostrado, um sucessor directo de M é H, F é um precursor de D directa . O recarregamento longe sobrinho e sobrinho perto conceito, como C é muito sobrinho G, C é quase sobrinho H , você vai usar esse conceito!
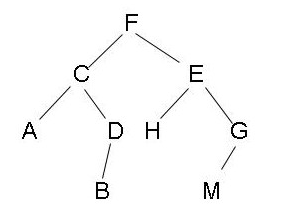
Voltar ao tópico, d ponto final do nó é o nó que deseja excluir. árvore vermelha-preta eliminar o problema é bastante simplificado, este processo é um nó folha apagado!
D é assumido que o nó apontou para D, D é o pai definição nó P, D é o nó irmão S . Comece a juiz:
- D é vermelho , basta apagar (porque: Excluir não afeta a árvore de vermelho-preto de atributos de altura preto)
- D é preto, dividido em dois tipos grande de casos :
- S vermelho
- Se D é o filho esquerdo de P, então S L, restart juiz
- Se D for o filho direito de P, S é retomado dextrose é determinada
- S é preto, 3 tipos de pequeno caso :
- Far sobrinho D é vermelho :
- Se D for o filho esquerdo de P, S L, medida sobrinho preto, suprimido D
- Se D é o filho direito de P, S dextral, longe sobrinho preto, excluídos D
- D muito sobrinho preto, sobrinho vermelho perto :
- Se D é o filho esquerdo de P, perto sobrinho referido como SL, SL destro, SL L, S Black, excluídos D
- Se D é o filho direito de P, perto sobrinho denotado SR, L SR, SR destro, S Black, excluídos D
- D muito sobrinho e sobrinho são quase preto :
- Se P é vermelho, a S vermelho, preto P, D suprimido
- Se P é preto, vermelho S, D. suprimido Mas! Depois dos nós pretas no percurso P 1 será menor, equilibrando assim a operação de continuar para cima, em seguida, ponto P d, retomou é determinado ( mas não o passo subsequente o nó a ser excluído ) foi determinada para cima até o ponto do nó raiz até agora.
- Far sobrinho D é vermelho :
- S vermelho
implementação de código:
# 红黑树节点
class RBN(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # 数据域
self.color = 0 # 0红 1黑
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.parent = None
# 红黑树
class RBT(object):
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def treePrint(self):
print('红黑树: start')
self.midTraverse(self.root)
print('红黑树: end')
# 中序遍历
def midTraverse(self, x):
if x == None:
return
self.midTraverse(x.left)
colorStr = '黑' if x.color == 1 else '红'
parentStr = '父=' + ('nil' if x.parent == None else str(x.parent.data))
print(x.data, colorStr, parentStr)
self.midTraverse(x.right)
# 添加一个节点
def add(self, x):
# 如果没有根节点 作为根节点
if self.root == None:
self.root = x
x.color = 1 # 根节点为黑色
return
# 寻找合适的插入位置
p = self.root
while p != None:
if x.data < p.data:
if p.left == None:
p.left = x
x.parent = p
self.addFix(x)
break
p = p.left
elif x.data > p.data:
if p.right == None:
p.right = x
x.parent = p
self.addFix(x)
break
p = p.right
else:
return
# 调整红黑树
def addFix(self, x):
while True:
if x == self.root: # 如果处理到根节点了 则着色为黑
x.color = 1
return
p = x.parent # 爸爸
if p.color == 1 or x.color == 1: # 自己和爸爸只要有一个是黑的 就构不成双红 则返回
return
# 接下来分析红爸爸情况
g = p.parent # 爷爷 红爸爸肯定有爸爸,因为红色绝不是根节点
u = g.left if p == g.right else g.right # 叔叔 叔叔可能为空节点
if u != None and u.color == 0: # 红叔叔 则着色 然后从爷爷开始向上继续调整
u.color = p.color = 1 # 叔叔和爸爸都变黑色
g.color = 0 # 爷爷变红色
x = g # x指向爷爷,然后继续循环
continue
# 接下来分析黑叔叔得情况 有四种情况 左左,左右,右左,右右
if p == g.left and x == p.left: # 左左
# 以爸爸为支点右旋爷爷
self.rotateRight(p)
elif p == g.left and x == p.right: # 左右
# 以x为支点左旋爸爸
self.rotateLeft(x)
# 以x为支点右旋爷爷(上面的旋转把爷爷变成了新爸爸)
self.rotateRight(x)
elif p == g.right and x == p.right: # 右右 其实就是 左左的镜像
# 以爸爸为支点左旋爷爷
self.rotateLeft(p)
elif p == g.right and x == p.left: # 右左 其实就是 左右的镜像
# 以x为支点右旋爸爸
self.rotateRight(x)
# 以x为支点左旋爷爷(上面的旋转把爷爷变成了新爸爸)
self.rotateLeft(x)
#
# 关于红黑树的旋转,一直是个难搞的点
# 这里我提供一个口诀:
# 右旋: 支点占旋点原位,支点的右给旋点作为左,旋点作为支点的右
# 左旋: 支点占旋点原位,支点的左给旋点作为右,旋点作为支点的左
#
# 右旋 p支点
def rotateRight(self, p):
g = p.parent # 支点的父节点就是旋点
# 右旋g
if g == self.root: # 若g是根节点 则p升为根节点
self.root = p
p.parent = None
else: # 若g不是根节点 那么必然存在g.parent p占据g的位置
gp = g.parent
p.parent = gp
if g == gp.left:
gp.left = p
else:
gp.right = p
g.left = p.right
if p.right != None:
p.right.parent = g
p.right = g
g.parent = p
# g和p颜色交换
p.color, g.color = g.color, p.color
# 左旋 p 支点
def rotateLeft(self, p):
g = p.parent # 支点的父节点就是旋点
# 左旋g
if g == self.root: # 若g是根节点 则p升为根节点
self.root = p
p.parent = None
else: # 若g不是根节点 那么必然存在g.parent p占据g的位置
gp = g.parent
p.parent = gp
if g == gp.left:
gp.left = p
else:
gp.right = p
g.right = p.left
if p.left != None:
p.left.parent = g
p.left = g
g.parent = p
# g和p颜色交换
p.color, g.color = g.color, p.color
# 删除一个节点
def delete(self, x):
# 查找要删除的节点
d = self.root
while d != None:
if x.data < d.data:
d = d.left
elif x.data > d.data:
d = d.right
else:
break
if d == None:
print('要删除的', x.data, '已经不存在了')
return
# 如果要删除的节点不是叶子节点,我们需要做d的指向转移,直到d指向的是叶子节点就结束循环
while d.left != None or d.right != None:
# 如果存在右子树 则找直接后继(也就是右子树的最左后代),交换数据, d指向这个后继,重复循环
if d.right != None:
nextNode = self.getMostLeft(d.right)
d.data, nextNode.data = nextNode.data, d.data
d = nextNode
continue
# 如果存在左子树 则找到直接前驱(也就是左子树的最右后代),交换数据,d指向这个前驱,重复循环
elif d.left != None:
preNode = self.getMostRight(d.left)
d.data, preNode.data = preNode.data, d.data
d = preNode
continue
# print('要删除的是', d.data);
# 接下来处理要删除的节点是叶子节点的情况吧 #
needDelete = True
while True:
# 如果d是根节点,直接删除
if self.root == d:
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
return
# 如果d的是红色,那么直接删除
if self.isRed(d):
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
return
# 如果d是黑色,设s指向兄弟节点(根据红黑树左右子树黑色高度相等的性质,s指向的节点必定存在),分好几种情况
p = d.parent
s = p.right if d == p.left else p.left
# print(d.data, d.color, p.data)
# 1 如果s是红色
if self.isRed(s):
if d == p.left:
self.rotateLeft(s)
else:
self.rotateRight(s)
continue # 旋转后 再重新判断
sl = s.left
sr = s.right
# 2 如果s是黑色,又分好几种情况
if d == p.left: # d是p的左孩子
# 2.1 如果d的远侄为红(有远侄的话必定为红,否则不满足红黑树的黑色高度性质)
if self.isRed(sr):
self.rotateLeft(s)
sr.color = 1
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
return
# 2.2 如果d的远侄为黑,近侄为红(有近侄的话必定为红,否则不满足红黑树的黑色高度性质)
if not self.isRed(sr) and self.isRed(sl):
self.rotateRight(sl)
self.rotateLeft(sl)
s.color = 1
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
return
# 2.3 如果d的远侄和近侄都是黑,也就是d是叶子节点,分2种情况
# 2.3.1 如果p是红色 s变红 p变黑 删除d
if p.color == 0:
s.color = 0
p.color = 1
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
return
# 2.3.1 如果p是黑色 s变红 删除d 然后d指向p重复判断步骤
s.color = 0
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
d = p
continue
else: # d是p的右孩子
# 2.1 如果d的远侄为红(有远侄的话必定为红,否则不满足红黑树的黑色高度性质)
if self.isRed(sl):
self.rotateRight(s)
sl.color = 1
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
return
# 2.2 如果d的远侄为黑,近侄为红(有近侄的话必定为红,否则不满足红黑树的黑色高度性质)
if not self.isRed(sl) and self.isRed(sr):
self.rotateLeft(sr)
self.rotateRight(sr)
s.color = 1
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
return
# 2.3 如果d的远侄和近侄都是黑,也就是d是叶子节点,分2种情况
# 2.3.1 如果p是红色 s变红 p变黑 删除d
if p.color == 0:
s.color = 0
p.color = 1
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
return
# 2.3.1 如果p是黑色 s变红 删除d 然后d指向p重复判断步骤
s.color = 0
if needDelete:
self.deleteDirectly(d)
needDelete = False
d = p
continue
# 是否是红色节点
def isRed(self, x):
return x != None and x.color == 0
# 找到x的最左的后代
def getMostLeft(self, x):
while x.left != None:
x = x.left
return x
# 找到y的最右后代
def getMostRight(self, x):
while x.right != None:
x = x.right
return x
# 直接删除x节点
def deleteDirectly(self, x):
if x == self.root:
self.root = None
else:
p = x.parent
if x == p.left:
p.left = None
else:
p.right = None
if __name__ == '__main__':
rbt = RBT()
# datas = [10, 20, 30, 15]
# datas = [11, 2, 14, 1, 7, 15, 5, 8, 4]
datas = [12, 1, 9, 2, 0, 11, 7, 19, 4, 15,
18, 5, 14, 13, 10, 16, 6, 3, 8, 17]
for x in datas:
rbt.add(RBN(x))
print('=====================================================')
rbt.treePrint()
print('=====================================================')
rbt.delete(RBN(12))
rbt.delete(RBN(1))
rbt.delete(RBN(9))
rbt.delete(RBN(2))
rbt.delete(RBN(0))
rbt.delete(RBN(11))
rbt.delete(RBN(7))
rbt.delete(RBN(19))
rbt.delete(RBN(4))
rbt.delete(RBN(15))
rbt.delete(RBN(18))
# rbt.delete(RBN(5))
# rbt.delete(RBN(14))
# rbt.delete(RBN(13))
# rbt.delete(RBN(10))
# rbt.delete(RBN(16))
# rbt.delete(RBN(6))
# rbt.delete(RBN(3))
# rbt.delete(RBN(8))
# rbt.delete(RBN(17))
rbt.treePrint()
Conclusão é correta.
Além disso, voltou a sublinhar que "esquerda" e "destro" Estes dois artigos mencionados:
右旋: 支点占旋点原位,支点的右给旋点作为左,旋点作为支点的右,交换支点和旋点的颜色
左旋: 支点占旋点原位,支点的左给旋点作为右,旋点作为支点的左,交换支点和旋点的颜色
