1. Mixed programming of C and C++
When a C++ program uses a C language interface, it needs to be declared as an external C interface
extern "C"
{
//添加使用到的C语言接口文件
}
//extern "C" 在这里面的内容都采用gcc编译器进行编译,不使用g++进行编译
Exercise: Use C++ and C interface to complete the function of writing files
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
extern "C"
{
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
}
int main()
{
int fd = open("1.txt", O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0777);
if(fd < 0)
{
cout << "创建文件失败" << endl;
}else{
cout << "创建文件成功" << endl;
}
cout << "请输入数据" << endl;
char buf[1024] = {
0};
cin >> buf;
write(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
close(fd);
}
2. Memory allocation in the computer
1. Memory division in the computer
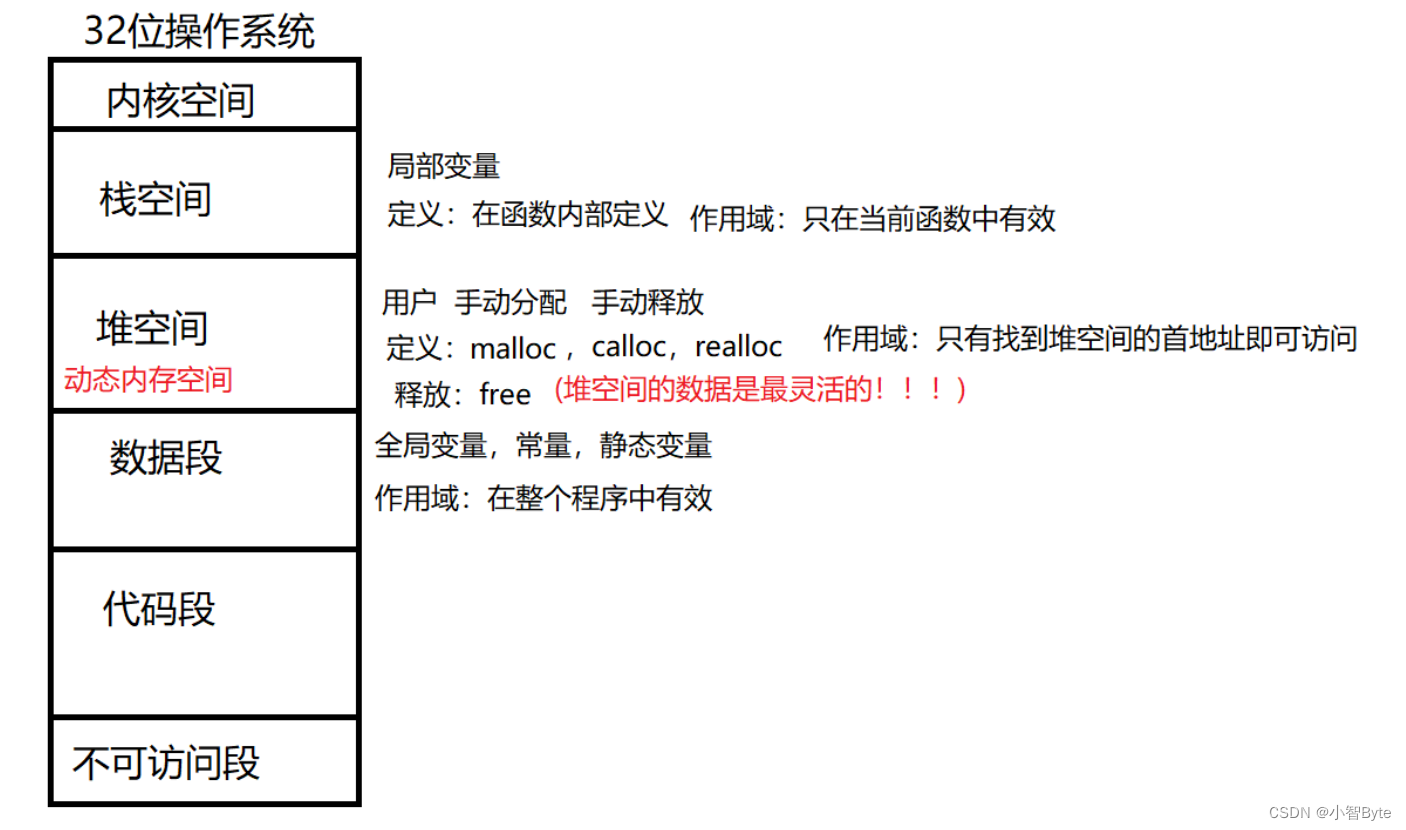
2. The way C language dynamically allocates memory (heap space)
#include <stdlib.h>
void *malloc(size_t size)//分配大小为size大小的空间
void free(void *ptr);//通过堆空间的首地址释放该空间
void *calloc(size_t nmemb, size_t size);//分配 nmemb * size 大小的堆空间
void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size);//把ptr 的堆空间改变大小为size
void *reallocarray(void *ptr, size_t
nmemb, size_t size);//把ptr 的堆空间改变大小为size*nmemb
Exercise: Use the above interface to allocate a heap space of int and a heap space of 100 ints, and assign values to the heap space, output
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
extern "C"
{
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
}
int main()
{
int *a = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*a = 10086;
cout << *a << endl;
free(a);
char *b = (char *)calloc(100, sizeof(char));
strcpy(b, "hello world");
cout << b << endl;
free(b);
}
3. Dynamic memory allocation in C++
In C++, use new to allocate heap space, and use delete to release heap space
①, syntax: allocate a heap space
数据类型 *变量名 = new 数据类型//分配一块内存空间
int *p = new int//一条龙服务!!自己计算空间的大小,自己进行类型的转换!!
int *q = new int(10086);//支持在分配空间的时候对堆空间进行初始化
释放堆空间:
delete 变量名
②, Syntax: allocate multiple heap spaces
数据类型 *变量名 = new 数据类型[size];//->size用户需要分配多少块这样的堆空间
例子: 分配100 块int 类型的堆空间
int *p = new int[100];
例子: 分配多块堆空间并初始化
int *q = new int[5]{
1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
释放多块堆空间:
delete []变量名;
Exercise: Allocate 10 blocks of float heap space and 100 blocks of char type heap space, and initialize the output
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
extern "C"
{
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
}
int main()
{
float *p = new float[10]{
1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5};
cout << p[0] << endl;
char *q = new char[100];
strcpy(q, "hello world");
cout << q << endl;
delete []p;
delete []q;
return 0;
}
Example: Using new to allocate a two-dimensional array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
extern "C"
{
#include <stdio.h>
}
int main()
{
//开辟二维数组空间
int (*p)[10] = new int[10][10];
//对二维数组进行赋值
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
(p[i][j]) = j;
cout << p[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
delete[]p; // 释放动态分配的内存
return 0;
}
③. Summarize the difference between new and malloc
- 1. new can automatically calculate the size of the data type
- 2. New can be initialized when allocating heap space, but malloc cannot
- 3. When allocating heap space, using new will call <<the constructor in the class>>, malloc will not work
In C++ development, new is used to allocate heap space memory
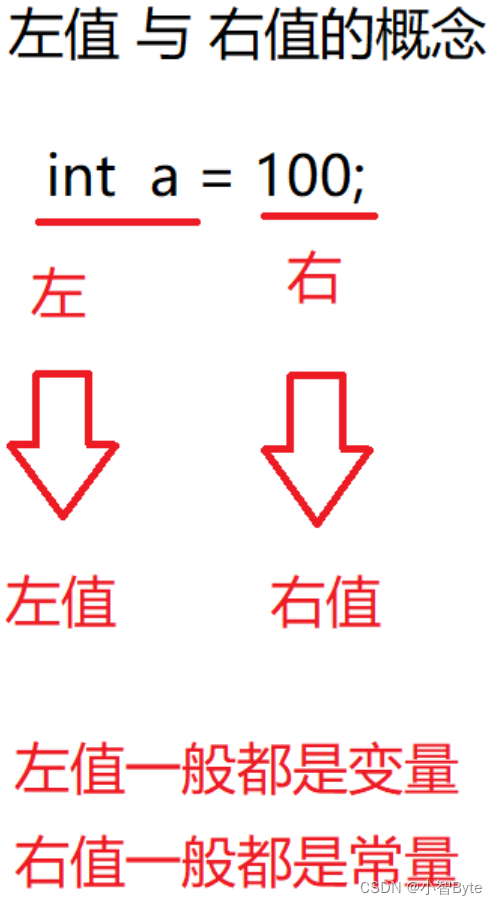
3. References in C++
1. Reference: Alias the known variable, and the memory will not allocate new memory space for the reference (saving memory space)
2. Grammar of references
数据类型 &引用名 = 引用的变量名
int a = 100;
int &q = a;//a与q是完全等价的
- Advantages: In the process of passing parameters, no new variable space will be allocated, saving space
- Occasions of use: generally used to pass as parameters, allowing the function to directly access the data itself, saving the generation of temporary space
Exercise: Write a function that swaps the values of two parameters
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int &a, int &b) // 正确的函数名是 swap,而不是 swep
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
// 交换 a 和 b 的值
swap(a, b); // 正确调用 swap 函数
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
return 0; // 添加返回值,符合 main 函数的返回类型为 int
}
Note: When initializing a reference, the value of the reference is a variable. If the referenced value is a constant, a constant reference is required.
const int &p = 1000;//对常量进行引用
3. Constant reference
effect:
- 1. Prevent the reference name from modifying the original data
- 2. Reference data constants
grammar:
const 数据类型 &引用名 = 引用对象
例子:
int a = 10086;
//定义常量引用
const int &p = a;//别名p无法修改a的值
//对一个常量进行引用
const int &q = 10086;
4. References as arguments to functions
When the user does not need to modify the value of the parameter, we can pass a constant reference
int add(const int &a, const int &b)
{
return a + b;
}
int main()
{
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
//传递变量
cout << add(a, b) << endl;
//传递常量
cout << add(100, 200) << endl;
}
Special writing:
数据类型 &&引用名 = 常量
int &&aa = 10000;
//这种引用只适用于常量引用,不能引用变量
5. Reference as the return value of the function
Notice:
When the reference is used as the return value of a function, it is necessary to ensure that the space for the return value still exists after the function ends.
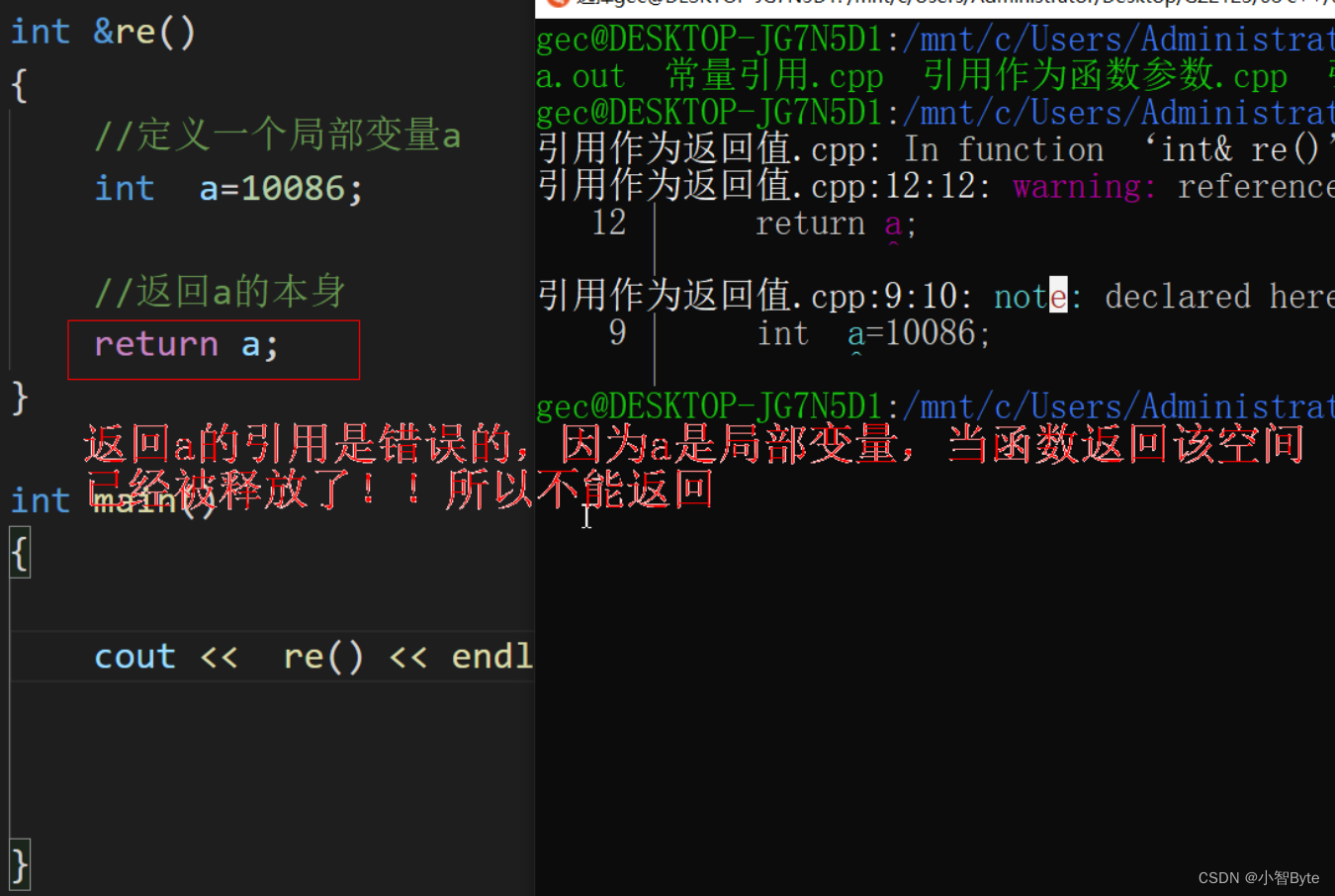
When a reference is used as a return value, it generally returns:
Static variables, global variables, heap space, (passed parameter references)...
space that will not be released
When a reference is returned, the function can be an lvalue
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int &ret()
{
static int a = 100;
static int b = 200;
return a; //需要返回一个值,不能返回表达式 (a + b)
}
int main()
{
int q = ret();//引用作为返回值(q = a)
cout << q << endl;
ret() = 200;//引用作为左值(a = 200)
cout << ret() << endl;
}
6. Precautions for reference
- 1. The reference must be initialized
- 2. When referencing a constant, you need to use const constant reference or && rvalue reference
- 3. The type of reference must match
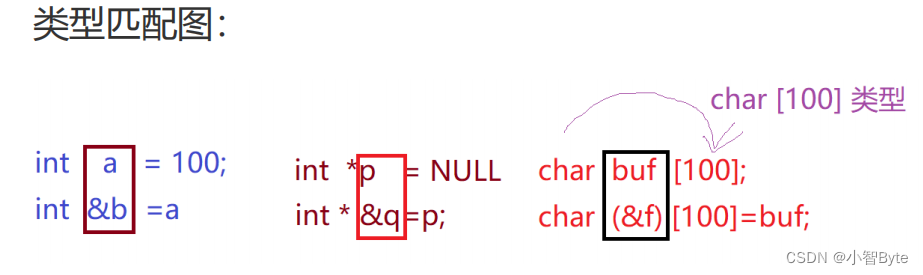
4. When the reference is modified, it cannot be changed (cannot alter the object referenced by the reference-name)