収集は分散の反対です:
スキャッターは、マップに従ってスキャッターポイントの出力位置を決定するための順次入力です。
#include <thrust/scatter.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/execution_policy.h>
...
// mark even indices with a 1; odd indices with a 0
int values[10] = {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0};
thrust::device_vector<int> d_values(values, values + 10);
// scatter all even indices into the first half of the
// range, and odd indices vice versa
int map[10] = {0, 5, 1, 6, 2, 7, 3, 8, 4, 9};
thrust::device_vector<int> d_map(map, map + 10);
thrust::device_vector<int> d_output(10);
thrust::scatter(thrust::device,
d_values.begin(), d_values.end(),
d_map.begin(), d_output.begin());
// d_output is now {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
Gatherは、マップに従って入力要素の位置を決定し、出力は順番に行われます。
#include <thrust/gather.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/execution_policy.h>
...
// mark even indices with a 1; odd indices with a 0
int values[10] = {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0};
thrust::device_vector<int> d_values(values, values + 10);
// gather all even indices into the first half of the range
// and odd indices to the last half of the range
int map[10] = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
thrust::device_vector<int> d_map(map, map + 10);
thrust::device_vector<int> d_output(10);
thrust::gather(thrust::device,
d_map.begin(), d_map.end(),
d_values.begin(),
d_output.begin());
// d_output is now {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
図に示すように:
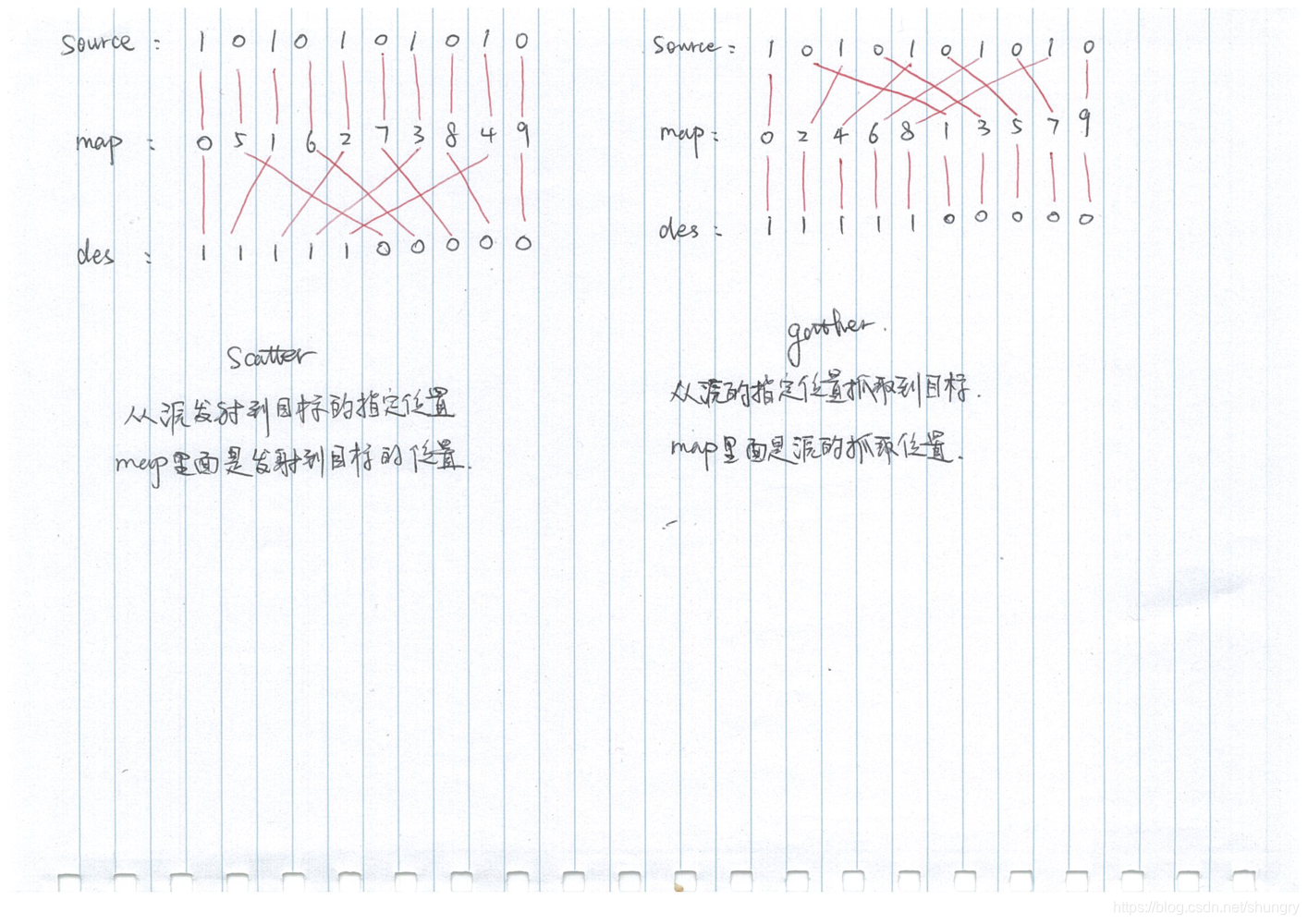
collectは、マップ内のインデックスからd_valuesに値を取得し、それをd_outputの現在の位置に配置します。
詳細については、https://blog.csdn.net/seamanj/article/details/82976687を確認してください
—————————————————
著作権ステートメント:この記事はのオリジナル作品ですCSDNブロガー「Scottf」この記事はCC4.0BY-SAの著作権契約に準拠しています。転載のために、元のソースとこのステートメントへのリンクを添付してください。
元のリンク:https://blog.csdn.net/shungry/article/details/103079320