1. Introduction
Nous avons brièvement analysé le processus de démarrage d'AMS dans le chapitre 5 de [Android Framework Series]AMS的启动流程 du chapitre précédent . Dans ce chapitre, voyons AMScomment cela se fait.Activity的启动
Launcher启动Jetons un coup d'œil ensemble ci-dessousActivity的启动流程
Cet article est basé sur l'analyse du code source d'Android10 (Q)
2 Processus de démarrage du lanceur
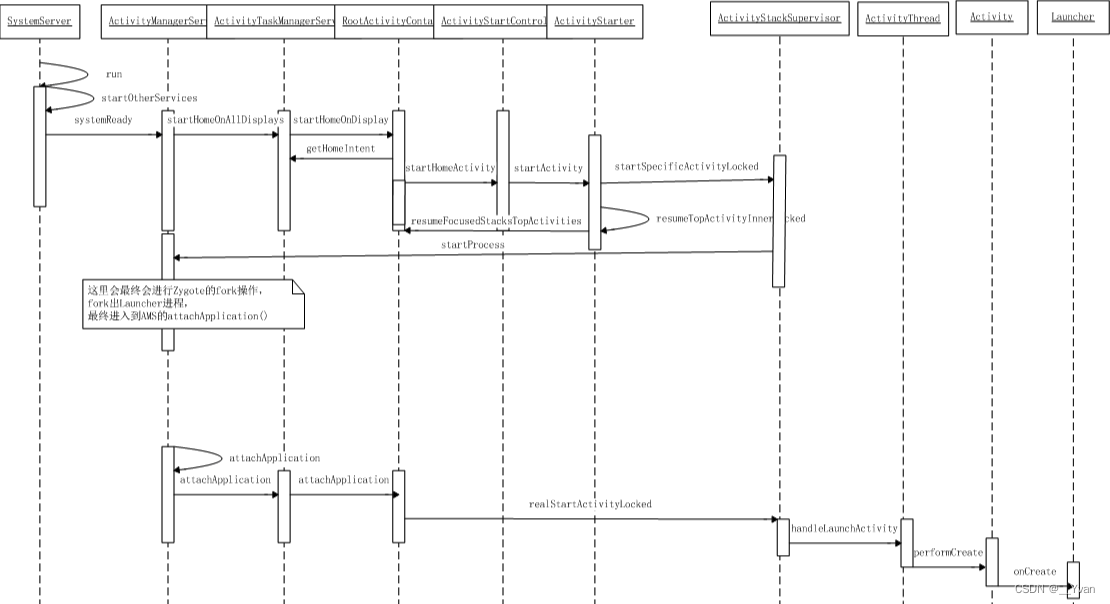
2.1 SystemServer démarre AMS, prêt à démarrer Launcher
À partir du processus de démarrage AMS du chapitre 5 de [Android Framework Series], nous pouvons savoir :
- Une fois le téléphone allumé, il démarrera
system_server进程, puis appelleraSystemServerlamain()méthode, - En
main()méthode enstartBootstrapServices()démarrant AMS. - Après cela , il est appelé
startOtherServices()via la méthode pour informer que le code tiers peut être exécuté.AMSsystemReady()AMS systemReady()méthode, en appelantstartHomeOnAllDisplays()pour démarrer l’activité initiale.
2.2 Démarrage du processus et prélude au démarrage de l'activité
2.2.1 ActivityManagerService avec startHomeOnAllDisplays()
Poursuivons startHomeOnAllDisplays()l'analyse à partir de la méthode :
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
8967
8968 public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback, TimingsTraceLog traceLog) {
......
// 调用ActivityTaskManagerService的startHomeOnAllDisplays方法(就是启动Launcher的Activity)
9084 mAtmInternal.startHomeOnAllDisplays(currentUserId, "systemReady");
......
9144 }
Ici mAtmInternalil s'agit ActivityTaskManagerServiced'un objet, et startHomeOnAllDisplays()la méthode appelle directement RootActivityContainerla méthode du même nom que l'objet.
2.2.2 ActivityTaskManagerService avec startHomeOnAllDisplays()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityTaskManagerService.java
6691 @Override
6692 public boolean startHomeOnAllDisplays(int userId, String reason) {
6693 synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
// 此处会调用mRootWindowContainer对象的startHomeOnAllDisplays函数
// 这边的mRootWindowContainer参数的值是从WindowManagerService中的mRoot参数对应的对象
// mRootWindowContainer参数是通过AMS的setWindowManager函数调用,进而调用ATMS.LocalServices的setWindowManager函数得到的
// 因此,此处需要注意的是RootWindowContainer对象的mWmService参数对应的是WindowManagerService对象
// mService参数对应的是ActivityTaskManagerService对象
6694 return mRootActivityContainer.startHomeOnAllDisplays(userId, reason);
6695 }
6696 }
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RootActivityContainer.java
332 boolean startHomeOnAllDisplays(int userId, String reason) {
333 boolean homeStarted = false;
// getChildCount获取显示设备数目,这个主要从mChildren参数中获取对应的数量
// mChildren是一个WindowList的一个对象,其包含的数据是在setWindowManager函数被调用时,
// 从DisplayManagerService中获取到的Display的数目,
334 for (int i = mActivityDisplays.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 获取到对应新建的DisplayContent的displayId
335 final int displayId = mActivityDisplays.get(i).mDisplayId;
// 调用startHomeOnDisplay函数
336 homeStarted |= startHomeOnDisplay(userId, reason, displayId);
337 }
338 return homeStarted;
339 }
......
366 boolean startHomeOnDisplay(int userId, String reason, int displayId, boolean allowInstrumenting,
367 boolean fromHomeKey) {
368 // Fallback to top focused display if the displayId is invalid.
// 由于DisplayManagerService中获取到的displayId不为INVALID_DISPLAY,因此此处判断条件不满足
// 如果displayId无效,则退回到顶层拥有焦点的显示设备
369 if (displayId == INVALID_DISPLAY) {
370 displayId = getTopDisplayFocusedStack().mDisplayId;
371 }
372
373 Intent homeIntent = null;
374 ActivityInfo aInfo = null;
375 if (displayId == DEFAULT_DISPLAY) {
// 获取Lancher的第一个页面的intent,其category为Intent.CATEGORY_HOME
376 homeIntent = mService.getHomeIntent();
// 通过intent找到Launcher中AndroidManifest对应的activity标签,解析出相应的activityInfo和applicationInfo信息
377 aInfo = resolveHomeActivity(userId, homeIntent);
378 } else if (shouldPlaceSecondaryHomeOnDisplay(displayId)) {
// 多屏显示功能,可以参考官网说明
// https://source.android.google.cn/devices/tech/display/multi_display/system-decorations#launcher
379 Pair<ActivityInfo, Intent> info = resolveSecondaryHomeActivity(userId, displayId);
380 aInfo = info.first;
381 homeIntent = info.second;
382 }
383 if (aInfo == null || homeIntent == null) {
384 return false;
385 }
386
387 if (!canStartHomeOnDisplay(aInfo, displayId, allowInstrumenting)) {
388 return false;
389 }
390
// 在启动前,校验是否满足启动条件,大概校验了displayId的有效性、对应activity的启动模式、是否处于工厂测试模式等等
392 homeIntent.setComponent(new ComponentName(aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
393 homeIntent.setFlags(homeIntent.getFlags() | FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
// 传入的fromHomeKey的值为false
395 if (fromHomeKey) {
396 homeIntent.putExtra(WindowManagerPolicy.EXTRA_FROM_HOME_KEY, true);
397 }
398 // Update the reason for ANR debugging to verify if the user activity is the one that
399 // actually launched.
400 final String myReason = reason + ":" + userId + ":" + UserHandle.getUserId(
401 aInfo.applicationInfo.uid) + ":" + displayId;
// 转到ActivityStartController类中继续调用startHomeActivity方法
402 mService.getActivityStartController().startHomeActivity(homeIntent, aInfo, myReason,
403 displayId);
404 return true;
405 }
......
412 ActivityInfo resolveHomeActivity(int userId, Intent homeIntent) {
413 final int flags = ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS;
414 final ComponentName comp = homeIntent.getComponent();
415 ActivityInfo aInfo = null;
416 try {
417 if (comp != null) {
418 // Factory test.
419 aInfo = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().getActivityInfo(comp, flags, userId);
420 } else {
421 final String resolvedType =
422 homeIntent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(mService.mContext.getContentResolver());
423 final ResolveInfo info = AppGlobals.getPackageManager()
424 .resolveIntent(homeIntent, resolvedType, flags, userId);
425 if (info != null) {
426 aInfo = info.activityInfo;
427 }
428 }
429 } catch (RemoteException e) {
430 // ignore
431 }
432
433 if (aInfo == null) {
434 Slog.wtf(TAG, "No home screen found for " + homeIntent, new Throwable());
435 return null;
436 }
437
438 aInfo = new ActivityInfo(aInfo);
439 aInfo.applicationInfo = mService.getAppInfoForUser(aInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
440 return aInfo;
441 }
Comme vous pouvez le voir dans le code ci-dessus, voici principalement quatre choses effectuées dans l'ordre
RootActivityContainerLauncherDans le cours, plusieurs interfaces principales seront démarrées ici pour le cas de plusieurs périphériques d'affichage . Bien entendu, ici, nous analysons uniquement le cas du périphérique d'affichage par défaut.ATMSLagetHomeIntentfonction passée pour démarrerActivityunIntentobjetresolveHomeActivityLa fonction obtient l'objetPMSde l'interface de démarrageActivityInfo- Grâce à la fonction
ActivityStartControllerde l'objetstartHomeActivitypour démarrer le correspondantActivity
2.2.3 ActivityStartController et startHomeActivity()
Continuons à regarder la méthode ActivityStartControllerdans startHomeActivity():
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStartController.java
......
171 void startHomeActivity(Intent intent, ActivityInfo aInfo, String reason, int displayId) {
// 创建一个ActivityOptions的对象
172 final ActivityOptions options = ActivityOptions.makeBasic();
// FULLSCREEN模式启动Activity
173 options.setLaunchWindowingMode(WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN);
174 if (!ActivityRecord.isResolverActivity(aInfo.name)) {
// 判断当前是否拥有多个Launcher并处于选择Launcher状态,否的话设置ACTIVITY_TYPE_HOME属性,直接启动Launcher的Activity
178 options.setLaunchActivityType(ACTIVITY_TYPE_HOME);
179 }
180 options.setLaunchDisplayId(displayId);
// 执行启动任务
181 mLastHomeActivityStartResult = obtainStarter(intent, "startHomeActivity: " + reason)
182 .setOutActivity(tmpOutRecord)
183 .setCallingUid(0)
184 .setActivityInfo(aInfo)
185 .setActivityOptions(options.toBundle())
186 .execute();
187 mLastHomeActivityStartRecord = tmpOutRecord[0];
188 final ActivityDisplay display =
189 mService.mRootActivityContainer.getActivityDisplay(displayId);
190 final ActivityStack homeStack = display != null ? display.getHomeStack() : null;
191 if (homeStack != null && homeStack.mInResumeTopActivity) {
192 // If we are in resume section already, home activity will be initialized, but not
193 // resumed (to avoid recursive resume) and will stay that way until something pokes it
194 // again. We need to schedule another resume.
195 mSupervisor.scheduleResumeTopActivities();
196 }
197 }
......
Exécutez la tâche de démarrage, obtainStarter()récupérez l'objet du pool de tampons dans la méthode ActivityStarter(créez-en un s'il n'y en a pas) et execute()démarrez l'activité via la méthode
2.2.4 ActivityStarter-execute()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStarter.java
......
509 int execute() {
510 try {
511 // TODO(b/64750076): Look into passing request directly to these methods to allow
512 // for transactional diffs and preprocessing.
513 if (mRequest.mayWait) {
514 return startActivityMayWait(mRequest.caller, mRequest.callingUid,
515 mRequest.callingPackage, mRequest.realCallingPid, mRequest.realCallingUid,
516 mRequest.intent, mRequest.resolvedType,
517 mRequest.voiceSession, mRequest.voiceInteractor, mRequest.resultTo,
518 mRequest.resultWho, mRequest.requestCode, mRequest.startFlags,
519 mRequest.profilerInfo, mRequest.waitResult, mRequest.globalConfig,
520 mRequest.activityOptions, mRequest.ignoreTargetSecurity, mRequest.userId,
521 mRequest.inTask, mRequest.reason,
522 mRequest.allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
523 mRequest.originatingPendingIntent, mRequest.allowBackgroundActivityStart);
524 } else {
525 return startActivity(mRequest.caller, mRequest.intent, mRequest.ephemeralIntent,
526 mRequest.resolvedType, mRequest.activityInfo, mRequest.resolveInfo,
527 mRequest.voiceSession, mRequest.voiceInteractor, mRequest.resultTo,
528 mRequest.resultWho, mRequest.requestCode, mRequest.callingPid,
529 mRequest.callingUid, mRequest.callingPackage, mRequest.realCallingPid,
530 mRequest.realCallingUid, mRequest.startFlags, mRequest.activityOptions,
531 mRequest.ignoreTargetSecurity, mRequest.componentSpecified,
532 mRequest.outActivity, mRequest.inTask, mRequest.reason,
533 mRequest.allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
534 mRequest.originatingPendingIntent, mRequest.allowBackgroundActivityStart);
535 }
536 } finally {
537 onExecutionComplete();
538 }
539 }
......
mRequest.mayWaitIl n'y a pas d'affectation avant l'exécution execute(), la valeur par défaut est false, continuons à regarder startActivity()la méthode :
2.2.5 ActivityStarter et startActivity()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStarter.java
......
611 private int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, Intent ephemeralIntent,
612 String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo, ResolveInfo rInfo,
613 IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
614 IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int callingPid, int callingUid,
615 String callingPackage, int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags,
616 SafeActivityOptions options,
617 boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, boolean componentSpecified, ActivityRecord[] outActivity,
618 TaskRecord inTask, boolean allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
619 PendingIntentRecord originatingPendingIntent, boolean allowBackgroundActivityStart) {
......
// 创建被启动的Activity对应的ActivityRecord对象
899 ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, callerApp, callingPid, callingUid,
900 callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.getGlobalConfiguration(),
901 resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified, voiceSession != null,
902 mSupervisor, checkedOptions, sourceRecord);
903 if (outActivity != null) {
904 outActivity[0] = r;
905 }
906
907 if (r.appTimeTracker == null && sourceRecord != null) {
908 // If the caller didn't specify an explicit time tracker, we want to continue
909 // tracking under any it has.
910 r.appTimeTracker = sourceRecord.appTimeTracker;
911 }
912
913 final ActivityStack stack = mRootActivityContainer.getTopDisplayFocusedStack();
// 如果我们启动的activity与当前恢复的activity的uid不同,请检查是否允许应用程序切换。
917 if (voiceSession == null && (stack.getResumedActivity() == null
918 || stack.getResumedActivity().info.applicationInfo.uid != realCallingUid)) {
919 if (!mService.checkAppSwitchAllowedLocked(callingPid, callingUid,
920 realCallingPid, realCallingUid, "Activity start")) {
921 if (!(restrictedBgActivity && handleBackgroundActivityAbort(r))) {
922 mController.addPendingActivityLaunch(new PendingActivityLaunch(r,
923 sourceRecord, startFlags, stack, callerApp));
924 }
925 ActivityOptions.abort(checkedOptions);
926 return ActivityManager.START_SWITCHES_CANCELED;
927 }
928 }
929
930 mService.onStartActivitySetDidAppSwitch();
931 mController.doPendingActivityLaunches(false);
932
933 final int res = startActivity(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, startFlags,
934 true /* doResume */, checkedOptions, inTask, outActivity, restrictedBgActivity);
935 mSupervisor.getActivityMetricsLogger().notifyActivityLaunched(res, outActivity[0]);
936 return res;
937 }
......
1386 private int startActivity(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
1387 IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
1388 int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,
1389 ActivityRecord[] outActivity, boolean restrictedBgActivity) {
1390 int result = START_CANCELED;
1391 final ActivityStack startedActivityStack;
1392 try {
1393 mService.mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();
1394 result = startActivityUnchecked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
1395 startFlags, doResume, options, inTask, outActivity, restrictedBgActivity);
1396 } finally {
......
1431 }
1432
1433 postStartActivityProcessing(r, result, startedActivityStack);
1434
1435 return result;
1436 }
......
// Note: This method should only be called from {@link startActivity}.
1464 private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
1465 IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
1466 int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,
1467 ActivityRecord[] outActivity, boolean restrictedBgActivity) {
......
// 如果正在启动的activity与当前在顶部的activity相同,那么我们需要检查它是否应该只启动一次
1625 final ActivityStack topStack = mRootActivityContainer.getTopDisplayFocusedStack();
1626 final ActivityRecord topFocused = topStack.getTopActivity();
1627 final ActivityRecord top = topStack.topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(mNotTop);
1628 final boolean dontStart = top != null && mStartActivity.resultTo == null
1629 && top.mActivityComponent.equals(mStartActivity.mActivityComponent)
1630 && top.mUserId == mStartActivity.mUserId
1631 && top.attachedToProcess()
1632 && ((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0
1633 || isLaunchModeOneOf(LAUNCH_SINGLE_TOP, LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK))
1634 // This allows home activity to automatically launch on secondary display when
1635 // display added, if home was the top activity on default display, instead of
1636 // sending new intent to the home activity on default display.
1637 && (!top.isActivityTypeHome() || top.getDisplayId() == mPreferredDisplayId);
1638 if (dontStart) {
1639 // For paranoia, make sure we have correctly resumed the top activity.
1640 topStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
1641 if (mDoResume) {
1642 mRootActivityContainer.resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities();
1643 }
1644 ActivityOptions.abort(mOptions);
1645 if ((mStartFlags & START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
1646 // We don't need to start a new activity, and the client said not to do
1647 // anything if that is the case, so this is it!
1648 return START_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER;
1649 }
1650
1651 deliverNewIntent(top);
1652
1653 // Don't use mStartActivity.task to show the toast. We're not starting a new activity
1654 // but reusing 'top'. Fields in mStartActivity may not be fully initialized.
1655 mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(top.getTaskRecord(), preferredWindowingMode,
1656 mPreferredDisplayId, topStack);
1657
1658 return START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
1659 }
......
// 往ActivityStack中写入启动的activity记录,同时更新TaskRecord信息
1700 mTargetStack.startActivityLocked(mStartActivity, topFocused, newTask, mKeepCurTransition,
1701 mOptions);
1702 if (mDoResume) {
1703 final ActivityRecord topTaskActivity =
1704 mStartActivity.getTaskRecord().topRunningActivityLocked();
1705 if (!mTargetStack.isFocusable()
1706 || (topTaskActivity != null && topTaskActivity.mTaskOverlay
1707 && mStartActivity != topTaskActivity)) {
// 如果activity无焦点的,我们不能恢复它,但仍然希望确保它在启动时时变得可见(这也将触发入场动画)。
// 此外,我们不希望在当前有覆盖层的Task中恢复activity,
// 因为正在启动的activity只需要处于可见的暂停状态,直到覆盖层被移除。
1714 mTargetStack.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(mStartActivity, 0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
1715 // Go ahead and tell window manager to execute app transition for this activity
1716 // since the app transition will not be triggered through the resume channel.
1717 mTargetStack.getDisplay().mDisplayContent.executeAppTransition();
1718 } else {
1719 // If the target stack was not previously focusable (previous top running activity
1720 // on that stack was not visible) then any prior calls to move the stack to the
1721 // will not update the focused stack. If starting the new activity now allows the
1722 // task stack to be focusable, then ensure that we now update the focused stack
1723 // accordingly.
1724 if (mTargetStack.isFocusable()
1725 && !mRootActivityContainer.isTopDisplayFocusedStack(mTargetStack)) {
1726 mTargetStack.moveToFront("startActivityUnchecked");
1727 }
1728 mRootActivityContainer.resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities(
1729 mTargetStack, mStartActivity, mOptions);
1730 }
1731 } else if (mStartActivity != null) {
1732 mSupervisor.mRecentTasks.add(mStartActivity.getTaskRecord());
1733 }
1734 mRootActivityContainer.updateUserStack(mStartActivity.mUserId, mTargetStack);
1735
1736 mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(mStartActivity.getTaskRecord(),
1737 preferredWindowingMode, mPreferredDisplayId, mTargetStack);
1738
1739 return START_SUCCESS;
1740 }
1741
......
Il appelle la RootActivityContainerméthode resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities()qui démarre ActivityStackle niveau le plus élevé de la cible activity. Continuons à regarder la classe RootActivityContainer resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities():
2.2.6 RootActivityContainerresumeFocusedStacksTopActivities()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RootActivityContainer.java
1148 boolean resumeFocusedStacksTopActivities(
1149 ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target, ActivityOptions targetOptions) {
......
1156 if (targetStack != null && (targetStack.isTopStackOnDisplay()
1157 || getTopDisplayFocusedStack() == targetStack)) {
1158 result = targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
1159 }
1160
1161 for (int displayNdx = mActivityDisplays.size() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
......
1185 if (!resumedOnDisplay) {
1186 // In cases when there are no valid activities (e.g. device just booted or launcher
1187 // crashed) it's possible that nothing was resumed on a display. Requesting resume
1188 // of top activity in focused stack explicitly will make sure that at least home
1189 // activity is started and resumed, and no recursion occurs.
1190 final ActivityStack focusedStack = display.getFocusedStack();
1191 if (focusedStack != null) {
1192 focusedStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
1193 }
1194 }
1195 }
1196
1197 return result;
1198 }
Nous avons ensuite retracé la méthode ActivityStackappelée resumeTopActivityInnerLocked().
2.2.7 ActivityStackresumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStack.java
2565 boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
......
2572 try {
2573 // Protect against recursion.
2574 mInResumeTopActivity = true;
2575 result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
......
2588 } finally {
2589 mInResumeTopActivity = false;
2590 }
2591
2592 return result;
2593 }
......
2613 @GuardedBy("mService")
2614 private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
......
// 暂停上一个activity
2744 boolean pausing = getDisplay().pauseBackStacks(userLeaving, next, false);
2745 if (mResumedActivity != null) {
2746 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
2747 "resumeTopActivityLocked: Pausing " + mResumedActivity);
2748 pausing |= startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, next, false);
2749 }
// 如果最近的activity没有历史记录,但由于设备进入睡眠状态而被停止,而不是停止+销毁,我们需要确保销毁它,因为我们正在使一个新的activity处于最顶层。
2781 if (shouldSleepActivities() && mLastNoHistoryActivity != null &&
2782 !mLastNoHistoryActivity.finishing) {
2783 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
2784 "no-history finish of " + mLastNoHistoryActivity + " on new resume");
2785 requestFinishActivityLocked(mLastNoHistoryActivity.appToken, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED,
2786 null, "resume-no-history", false);
2787 mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
2788 }
2789
2790 if (prev != null && prev != next && next.nowVisible) {
// 下一个activity已经可见,所以现在隐藏前一个activity的窗口,以便我们可以尽快显示新的activity。
// 我们只有在前一个结束时才这样做,这意味着它在resume的那个之上,所以快速隐藏它是有好处的。
// 否则,我们希望按照正常的方式显示resume的activity,
// 这样我们就可以根据新activity是否全屏来决定是否应该隐藏以前的activity
2800 if (prev.finishing) {
2801 prev.setVisibility(false);
2802 if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
2803 "Not waiting for visible to hide: " + prev
2804 + ", nowVisible=" + next.nowVisible);
2805 } else {
2806 if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
2807 "Previous already visible but still waiting to hide: " + prev
2808 + ", nowVisible=" + next.nowVisible);
2809 }
2810
2811 }
2812
2813 // Launching this app's activity, make sure the app is no longer
2814 // considered stopped.
2815 try {
2816 AppGlobals.getPackageManager().setPackageStoppedState(
2817 next.packageName, false, next.mUserId); /* TODO: Verify if correct userid */
2818 } catch (RemoteException e1) {
2819 } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
2820 Slog.w(TAG, "Failed trying to unstop package "
2821 + next.packageName + ": " + e);
2822 }
// 我们正在启动下一个activity,所以告诉window manager,
// 上一个activity很快就会被隐藏。这样,它可以知道在计算所需的屏幕方向时忽略它。
2827 boolean anim = true;
2828 final DisplayContent dc = getDisplay().mDisplayContent;
2829 if (prev != null) {
2830 if (prev.finishing) {
2831 if (DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
2832 "Prepare close transition: prev=" + prev);
2833 if (mStackSupervisor.mNoAnimActivities.contains(prev)) {
2834 anim = false;
2835 dc.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_NONE, false);
2836 } else {
2837 dc.prepareAppTransition(
2838 prev.getTaskRecord() == next.getTaskRecord() ? TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_CLOSE
2839 : TRANSIT_TASK_CLOSE, false);
2840 }
2841 prev.setVisibility(false);
2842 } else {
2843 if (DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
2844 "Prepare open transition: prev=" + prev);
2845 if (mStackSupervisor.mNoAnimActivities.contains(next)) {
2846 anim = false;
2847 dc.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_NONE, false);
2848 } else {
2849 dc.prepareAppTransition(
2850 prev.getTaskRecord() == next.getTaskRecord() ? TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN
2851 : next.mLaunchTaskBehind ? TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN_BEHIND
2852 : TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN, false);
2853 }
2854 }
2855 } else {
2856 if (DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION, "Prepare open transition: no previous");
2857 if (mStackSupervisor.mNoAnimActivities.contains(next)) {
2858 anim = false;
2859 dc.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_NONE, false);
2860 } else {
2861 dc.prepareAppTransition(TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN, false);
2862 }
2863 }
2864
2865 if (anim) {
2866 next.applyOptionsLocked();
2867 } else {
2868 next.clearOptionsLocked();
2869 }
2870
2871 mStackSupervisor.mNoAnimActivities.clear();
2872
2873 if (next.attachedToProcess()) {
// 只有启动过的activity才会进入此分支
......
3025 } else {
3026 // Whoops, need to restart this activity!
3027 if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
3028 next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
3029 } else {
3030 if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW) {
// 冷启动的过渡页,在这里会载入manifest配置的主题背景,
// 如果没有的话,默认白屏或黑屏
3031 next.showStartingWindow(null /* prev */, false /* newTask */,
3032 false /* taskSwich */);
3033 }
3034 if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH, "Restarting: " + next);
3035 }
3036 if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES, "resumeTopActivityLocked: Restarting " + next);
3037 mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
3038 }
3039
3040 return true;
3041 }
Grâce au code source, nous pouvons connaître :
ActivityExécuter d'abordpausel'opération sur la précédente- Redémarrez la cible
activity, - Enfin entré dans
ActivityStackSupervior.startSpecificActivityLocked()la méthode. - Avant de démarrer l'activité,
next.showStartingWindow()la méthode est appelée pour en afficher unwindow,
c'est pourquoi il y a un écran blanc au démarrage à froid .
2.3 Démarrage du processus et nœud de démarrage de l'activité
2.3.1 ActivityStackSupervisorstartSpecificActivityLocked()
La façon dont nous continuons à ActivityStackSupervisortraquerstartSpecificActivityLocked() :
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
......
956 void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
957 // Is this activity's application already running?
// 根据进程名和进程id判断目标进程是否已经创建,如果没有则代表进程未创建
958 final WindowProcessController wpc =
959 mService.getProcessController(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
960
961 boolean knownToBeDead = false;
// 如果进程已经创建,这里直接调用realStartActivityLocked去启动Activity
962 if (wpc != null && wpc.hasThread()) {
963 try {
964 realStartActivityLocked(r, wpc, andResume, checkConfig);
965 return;
966 } catch (RemoteException e) {
967 Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
968 + r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
969 }
......
973 knownToBeDead = true;
974 }
......
979 if (getKeyguardController().isKeyguardLocked()) {
980 r.notifyUnknownVisibilityLaunched();
981 }
982
983 try {
......
// 走到这里说明目标进程未创建,这里使用handler发送消息给ActivityManagerService类,让AMS创建一个新的进程
// 通过发送消息的方式,可避免在ATMS锁被持有的情况下,调用AMS时可能出现的死锁
990 final Message msg = PooledLambda.obtainMessage(
991 ActivityManagerInternal::startProcess, mService.mAmInternal, r.processName,
992 r.info.applicationInfo, knownToBeDead, "activity", r.intent.getComponent());
993 mService.mH.sendMessage(msg);
994 } finally {
995 Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
996 }
997 }
......
Il y a un jugement très important dans la méthode ci-dessus : if(wpc != null && wpc.hasThread()). WindowProcessControllerVérifiez l'objet obtenu par le nom du processus et l'uid de l'application pour déterminer si le processus d'activité à démarrer a été démarré et effectuez respectivement deux logiques clés :
1. Lorsque le processus n'est pas démarré, démarrez le processus
2. Lorsque le processus est démarré , démarrez l'activité
Évidemment, lorsque l'application démarre pour la première fois, le processus n'existe pas encore, premier arrivé, premier servi 进程启动.
2.4 Démarrage du processus
Comme le montre le code ci-dessus, PooledLambda.obtainMessage()via Handler, un message est envoyé Messagepour éviter un blocage qui peut survenir lorsque ATMSl'appel est mis en attente alors que le verrou est maintenu. AMSCet Messageappel est la ActivityManagerServiceméthode startProcess(), l'appel réel est startProcessLocked()la méthode, nous regardons directement à partir d'elle :
2.4.1 startProcessLocked()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
3022 final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,
3023 ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,
3024 HostingRecord hostingRecord, boolean allowWhileBooting,
3025 boolean isolated, boolean keepIfLarge) {
3026 return mProcessList.startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, intentFlags,
3027 hostingRecord, allowWhileBooting, isolated, 0 /* isolatedUid */, keepIfLarge,
3028 null /* ABI override */, null /* entryPoint */, null /* entryPointArgs */,
3029 null /* crashHandler */);
3030 }
ProcessListLa méthode de la classe est appelée ici startProcessLocked(), continuons à regarder en bas.
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ProcessList.java
......
1848 @GuardedBy("mService")
1849 final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,
1850 boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags, HostingRecord hostingRecord,
1851 boolean allowWhileBooting, boolean isolated, int isolatedUid, boolean keepIfLarge,
1852 String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs, Runnable crashHandler) {
1853 long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
1854 ProcessRecord app;
......
// 以下三种情况,我们不需要做任何额外的处理
// (1) 存在一个application 记录
// (2) 调用者认为它仍然存活,或者没有线程对象连接到它,所以我们知道它没有crash
// (3) 有一个pid分配给它,所以它要么正在启动,要么已经运行
1900 if (app != null && app.pid > 0) {
1901 if ((!knownToBeDead && !app.killed) || app.thread == null) {
// 我们已经有应用程序在运行,或者正在等待它出现(我们有一个pid,但还没有它的线程),所以保持它
1904 if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG_PROCESSES, "App already running: " + app);
1905 // If this is a new package in the process, add the package to the list
1906 app.addPackage(info.packageName, info.longVersionCode, mService.mProcessStats);
1907 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: done, added package to proc");
1908 return app;
1909 }
1910
1911 // An application record is attached to a previous process,
1912 // clean it up now.
1913 if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG_PROCESSES, "App died: " + app);
1914 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: bad proc running, killing");
1915 ProcessList.killProcessGroup(app.uid, app.pid);
1916 mService.handleAppDiedLocked(app, true, true);
1917 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: done killing old proc");
1918 }
1919
1920 if (app == null) {
1921 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: creating new process record");
// 创建一条ProcessRecord
1922 app = newProcessRecordLocked(info, processName, isolated, isolatedUid, hostingRecord);
1923 if (app == null) {
1924 Slog.w(TAG, "Failed making new process record for "
1925 + processName + "/" + info.uid + " isolated=" + isolated);
1926 return null;
1927 }
1928 app.crashHandler = crashHandler;
1929 app.isolatedEntryPoint = entryPoint;
1930 app.isolatedEntryPointArgs = entryPointArgs;
1931 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: done creating new process record");
1932 } else {
1933 // If this is a new package in the process, add the package to the list
1934 app.addPackage(info.packageName, info.longVersionCode, mService.mProcessStats);
1935 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: added package to existing proc");
1936 }
1937
1938 // If the system is not ready yet, then hold off on starting this
1939 // process until it is.
1940 if (!mService.mProcessesReady
1941 && !mService.isAllowedWhileBooting(info)
1942 && !allowWhileBooting) {
1943 if (!mService.mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) {
1944 mService.mProcessesOnHold.add(app);
1945 }
1946 if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG_PROCESSES,
1947 "System not ready, putting on hold: " + app);
1948 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: returning with proc on hold");
1949 return app;
1950 }
1951
1952 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: stepping in to startProcess");
// 创建一个进程。
1953 final boolean success = startProcessLocked(app, hostingRecord, abiOverride);
1954 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: done starting proc!");
1955 return success ? app : null;
1956 }
......
Comme vous pouvez le constater, il y a deux étapes importantes lors du démarrage d’un nouveau processus :
new ProcessRecordLocked()Créez d'abord un enregistrement de processus par méthode- Utilisez ensuite
startProcessLocked()la méthode pour créer un processus.
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ProcessList.java
......
1427 @GuardedBy("mService")
1428 boolean startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, HostingRecord hostingRecord,
1429 boolean disableHiddenApiChecks, boolean mountExtStorageFull,
1430 String abiOverride) {
......
//
1619 final String entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
1620
1621 return startProcessLocked(hostingRecord, entryPoint, app, uid, gids,
1622 runtimeFlags, mountExternal, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet, invokeWith,
1623 startTime);
1624 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
1625 Slog.e(ActivityManagerService.TAG, "Failure starting process " + app.processName, e);
......
1633 mService.forceStopPackageLocked(app.info.packageName, UserHandle.getAppId(app.uid),
1634 false, false, true, false, false, app.userId, "start failure");
1635 return false;
1636 }
1637 }
Ici, faites attention à entryPointla valeur de cette variable——— android.app.ActivityThread, elle passera par une longue chaîne d'appels, et RuntimeInitjouera enfin son rôle dans cette classe.
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ProcessList.java
@GuardedBy("mService")
1640 boolean startProcessLocked(HostingRecord hostingRecord,
1641 String entryPoint,
1642 ProcessRecord app, int uid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
1643 String seInfo, String requiredAbi, String instructionSet, String invokeWith,
1644 long startTime) {
1645 app.pendingStart = true;
1646 app.killedByAm = false;
1647 app.removed = false;
1648 app.killed = false;
......
1657 final long startSeq = app.startSeq = ++mProcStartSeqCounter;
1658 app.setStartParams(uid, hostingRecord, seInfo, startTime);
1659 app.setUsingWrapper(invokeWith != null
1660 || SystemProperties.get("wrap." + app.processName) != null);
1661 mPendingStarts.put(startSeq, app);
1662
1663 if (mService.mConstants.FLAG_PROCESS_START_ASYNC) {
// 默认以异步方式启动
1666 mService.mProcStartHandler.post(() -> {
1667 try {
1668 final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = startProcess(app.hostingRecord,
1669 entryPoint, app, app.startUid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
1670 app.seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet, invokeWith, app.startTime);
1671 synchronized (mService) {
1672 handleProcessStartedLocked(app, startResult, startSeq);
1673 }
1674 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
1675 synchronized (mService) {
1676 Slog.e(ActivityManagerService.TAG, "Failure starting process "
1677 + app.processName, e);
1678 mPendingStarts.remove(startSeq);
1679 app.pendingStart = false;
1680 mService.forceStopPackageLocked(app.info.packageName,
1681 UserHandle.getAppId(app.uid),
1682 false, false, true, false, false, app.userId, "start failure");
1683 }
1684 }
1685 });
1686 return true;
1687 } else {
1688 try {
1689 final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = startProcess(hostingRecord,
1690 entryPoint, app,
1691 uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
1692 invokeWith, startTime);
1693 handleProcessStartedLocked(app, startResult.pid, startResult.usingWrapper,
1694 startSeq, false);
1695 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
1696 Slog.e(ActivityManagerService.TAG, "Failure starting process "
1697 + app.processName, e);
1698 app.pendingStart = false;
1699 mService.forceStopPackageLocked(app.info.packageName, UserHandle.getAppId(app.uid),
1700 false, false, true, false, false, app.userId, "start failure");
1701 }
1702 return app.pid > 0;
1703 }
......
1798 private Process.ProcessStartResult startProcess(HostingRecord hostingRecord, String entryPoint,
1799 ProcessRecord app, int uid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
1800 String seInfo, String requiredAbi, String instructionSet, String invokeWith,
1801 long startTime) {
1802 try {
1803 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Start proc: " +
1804 app.processName);
1805 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: asking zygote to start proc");
1806 final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult;
// hostingRecord初始化参数为null,
// 并未指定mHostingZygote属性,因此会进入最后一个分支
1807 if (hostingRecord.usesWebviewZygote()) {
1808 startResult = startWebView(entryPoint,
1809 app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
1810 app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
1811 app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName,
1812 new String[] {
PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
1813 } else if (hostingRecord.usesAppZygote()) {
1814 final AppZygote appZygote = createAppZygoteForProcessIfNeeded(app);
1815
1816 startResult = appZygote.getProcess().start(entryPoint,
1817 app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
1818 app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
1819 app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName,
1820 /*useUsapPool=*/ false,
1821 new String[] {
PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
1822 } else {
1823 startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
1824 app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
1825 app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
1826 app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, app.info.packageName,
1827 new String[] {
PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
1828 }
1829 checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: returned from zygote!");
1830 return startResult;
1831 } finally {
1832 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
1833 }
1834 }
hostingRecordLe paramètre d'initialisation est nul et aucun mHostingZygoteattribut n'est spécifié, il entrera donc dans la dernière branche et appellera la méthodeProcess.start()
2.4.2 Méthode start() du processus
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java
521 public static ProcessStartResult start(@NonNull final String processClass,
522 @Nullable final String niceName,
523 int uid, int gid, @Nullable int[] gids,
524 int runtimeFlags,
525 int mountExternal,
526 int targetSdkVersion,
527 @Nullable String seInfo,
528 @NonNull String abi,
529 @Nullable String instructionSet,
530 @Nullable String appDataDir,
531 @Nullable String invokeWith,
532 @Nullable String packageName,
533 @Nullable String[] zygoteArgs) {
534 return ZYGOTE_PROCESS.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
535 runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
536 abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, packageName,
537 /*useUsapPool=*/ true, zygoteArgs);
538 }
Parmi eux ZYGOTE_PROCESSse trouve un ZygoteProcessobjet qui appelle en fait la méthode ZygoteProcessqu'il contient start().
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
314 public final Process.ProcessStartResult start(@NonNull final String processClass,
315 final String niceName,
316 int uid, int gid, @Nullable int[] gids,
317 int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
318 int targetSdkVersion,
319 @Nullable String seInfo,
320 @NonNull String abi,
321 @Nullable String instructionSet,
322 @Nullable String appDataDir,
323 @Nullable String invokeWith,
324 @Nullable String packageName,
325 boolean useUsapPool,
326 @Nullable String[] zygoteArgs) {
327 // TODO (chriswailes): Is there a better place to check this value?
328 if (fetchUsapPoolEnabledPropWithMinInterval()) {
329 informZygotesOfUsapPoolStatus();
330 }
331
332 try {
333 return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
334 runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
335 abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, /*startChildZygote=*/ false,
336 packageName, useUsapPool, zygoteArgs);
337 } catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
338 Log.e(LOG_TAG,
339 "Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
340 throw new RuntimeException(
341 "Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
342 }
343 }
......
541 private Process.ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(@NonNull final String processClass,
542 @Nullable final String niceName,
543 final int uid, final int gid,
544 @Nullable final int[] gids,
545 int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
546 int targetSdkVersion,
547 @Nullable String seInfo,
548 @NonNull String abi,
549 @Nullable String instructionSet,
550 @Nullable String appDataDir,
551 @Nullable String invokeWith,
552 boolean startChildZygote,
553 @Nullable String packageName,
554 boolean useUsapPool,
555 @Nullable String[] extraArgs)
556 throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
557 ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<>();
558
559 // --runtime-args, --setuid=, --setgid=,
560 // and --setgroups= must go first
561 argsForZygote.add("--runtime-args");
562 argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
563 argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
564 argsForZygote.add("--runtime-flags=" + runtimeFlags);
565 if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT) {
566 argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-default");
567 } else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_READ) {
568 argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-read");
569 } else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_WRITE) {
570 argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-write");
571 } else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_FULL) {
572 argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-full");
573 } else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_INSTALLER) {
574 argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-installer");
575 } else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_LEGACY) {
576 argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-legacy");
577 }
578
579 argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);
580
581 // --setgroups is a comma-separated list
582 if (gids != null && gids.length > 0) {
583 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
584 sb.append("--setgroups=");
585
586 int sz = gids.length;
587 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
588 if (i != 0) {
589 sb.append(',');
590 }
591 sb.append(gids[i]);
592 }
593
594 argsForZygote.add(sb.toString());
595 }
596
597 if (niceName != null) {
598 argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName);
599 }
600
601 if (seInfo != null) {
602 argsForZygote.add("--seinfo=" + seInfo);
603 }
604
605 if (instructionSet != null) {
606 argsForZygote.add("--instruction-set=" + instructionSet);
607 }
608
609 if (appDataDir != null) {
610 argsForZygote.add("--app-data-dir=" + appDataDir);
611 }
612
613 if (invokeWith != null) {
614 argsForZygote.add("--invoke-with");
615 argsForZygote.add(invokeWith);
616 }
617
618 if (startChildZygote) {
619 argsForZygote.add("--start-child-zygote");
620 }
621
622 if (packageName != null) {
623 argsForZygote.add("--package-name=" + packageName);
624 }
625
626 argsForZygote.add(processClass);
627
628 if (extraArgs != null) {
629 Collections.addAll(argsForZygote, extraArgs);
630 }
631
632 synchronized(mLock) {
633 // The USAP pool can not be used if the application will not use the systems graphics
634 // driver. If that driver is requested use the Zygote application start path.
635 return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi),
636 useUsapPool,
637 argsForZygote);
638 }
639 }
Il convient de noter que openZygoteSocketIfNeeded()cette méthode du code ci-dessus, qui utilise socket通信方式, tente de se connecter au serveur avec le chemin /dev/socket/et le nom . La méthode est en fait appelée dans la méthode, le contenu est le suivant :zygote
zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult()attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
422 private Process.ProcessStartResult attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
423 ZygoteState zygoteState, String msgStr) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
424 try {
425 final BufferedWriter zygoteWriter = zygoteState.mZygoteOutputWriter;
426 final DataInputStream zygoteInputStream = zygoteState.mZygoteInputStream;
427
428 zygoteWriter.write(msgStr);
429 zygoteWriter.flush();
430
431 // Always read the entire result from the input stream to avoid leaving
432 // bytes in the stream for future process starts to accidentally stumble
433 // upon.
434 Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
435 result.pid = zygoteInputStream.readInt();
436 result.usingWrapper = zygoteInputStream.readBoolean();
437
438 if (result.pid < 0) {
439 throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
440 }
441
442 return result;
443 } catch (IOException ex) {
444 zygoteState.close();
445 Log.e(LOG_TAG, "IO Exception while communicating with Zygote - "
446 + ex.toString());
447 throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
448 }
449 }
Veuillez faire attention à cette variable de la méthode ci-dessus zygoteWriter, qui est responsable de l'envoi des paramètres de démarrage du processus au serveur, et le serveur incubera le processus. Alors, de quelle classe est ce serveur ?
la réponse estZygoteServer.java
ZygoteServerAu démarrage du système, un Socketserveur est créé pour recevoir la forkdemande du client. ZygoteServerAprès initialisation, runSelectLoop()la méthode sera appelée pour traiter le message du client. Lorsqu'un client demande forkun processus, runSelectLoop()la méthode est transmise à une méthode ZygoteConnectionde la classe processOneCommand()pour traitement.
ZygotePour des informations connexes, veuillez vous référer au chapitre 3 de [Android Framework Series] relatif au processus Zygote.
Continuons à regarder
2.4.3 Méthode processOneCommand() de ZygoteConnection
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
129 Runnable processOneCommand(ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
130 String args[];
131 ZygoteArguments parsedArgs = null;
132 FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
......
267 pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid, parsedArgs.mGids,
268 parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mMountExternal, parsedArgs.mSeInfo,
269 parsedArgs.mNiceName, fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote,
270 parsedArgs.mInstructionSet, parsedArgs.mAppDataDir, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion);
271
272 try {
273 if (pid == 0) {
274 // in child
275 zygoteServer.setForkChild();
276
277 zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
278 IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
279 serverPipeFd = null;
280
281 return handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd,
282 parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote);
283 } else {
284 // In the parent. A pid < 0 indicates a failure and will be handled in
285 // handleParentProc.
286 IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
287 childPipeFd = null;
288 handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd);
289 return null;
290 }
291 } finally {
292 IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
293 IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
294 }
295 }
Zygote.forkAndSpecialize()Programme fork via la méthode statique
2.4.4 Méthode forkAndSpecialize() de Zygote
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote.java
234 public static int forkAndSpecialize(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
235 int[][] rlimits, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String niceName, int[] fdsToClose,
236 int[] fdsToIgnore, boolean startChildZygote, String instructionSet, String appDataDir,
237 int targetSdkVersion) {
238 ZygoteHooks.preFork();
239 // Resets nice priority for zygote process.
240 resetNicePriority();
241 int pid = nativeForkAndSpecialize(
242 uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits, mountExternal, seInfo, niceName, fdsToClose,
243 fdsToIgnore, startChildZygote, instructionSet, appDataDir);
244 // Enable tracing as soon as possible for the child process.
245 if (pid == 0) {
246 Zygote.disableExecuteOnly(targetSdkVersion);
247 Trace.setTracingEnabled(true, runtimeFlags);
248
249 // Note that this event ends at the end of handleChildProc,
250 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "PostFork");
251 }
252 ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
253 return pid;
254 }
255
256 private static native int nativeForkAndSpecialize(int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
257 int runtimeFlags, int[][] rlimits, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String niceName,
258 int[] fdsToClose, int[] fdsToIgnore, boolean startChildZygote, String instructionSet,
259 String appDataDir);
La Zygoteclasse ci-dessus effectue principalement le travail suivant dans ce processus :
- Le prétraitement
dalvikdansZygoteHooksl' appel consiste principalement à arrêter : , , , , attendre la fin de tous les sous-threads, et enfin terminer l'initialisation du tas gc.preFrok4个Daemon子线程HeapTaskDaemonReferenceQueueDaemonFinalizerDaemonFinalizerWatchdogDaemon com_android_internal_os_zygote.cppLa méthode dans l'appelnativeForkAndSpecialize, le travail principal passe parlinux机制forkun processus enfant, et une partie du processus资源处理,selinux权限处理,JAVA堆线程的一些处理.ZygoteHooksLa méthode appeléepostForkCommon, startZygote的4个Daemon线程.
Une fois la méthode exécutée forkAndSpecialize(), le code continuera à s'exécuter ZygoteConnectiondans handleChildProc()cette méthode.
2.4.5 Méthode handleChildProc() de ZygoteConnection
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
560 private Runnable handleChildProc(ZygoteArguments parsedArgs, FileDescriptor[] descriptors,
561 FileDescriptor pipeFd, boolean isZygote) {
......
589 if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null) {
590 WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.mInvokeWith,
591 parsedArgs.mNiceName, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
592 VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(),
593 pipeFd, parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs);
594
595 // Should not get here.
596 throw new IllegalStateException("WrapperInit.execApplication unexpectedly returned");
597 } else {
598 if (!isZygote) {
// 进入此分支
599 return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
600 parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
601 } else {
602 return ZygoteInit.childZygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
603 parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
604 }
605 }
606 }
Continuons à regarder ZygoteInit.zygoteInit()la méthode
2.4.6 Méthode ZygoteInit() de ZygoteInit
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
972 public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
973 ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 初始化运行环境
981 RuntimeInit.commonInit();
// 启动binder线程池
982 ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
// 程序入口函数
983 return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
984 }
2.4.7 Méthode RuntimeInit.applicationInit()
Continuez à regarder la fonction de saisie du programmeRuntimeInit.applicationInit() :
284 protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
285 ClassLoader classLoader) {
286 Class<?> cl;
287
288 try {
289 cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
290 } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
291 throw new RuntimeException(
292 "Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
293 ex);
294 }
295
296 Method m;
297 try {
298 m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] {
String[].class });
299 } catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
300 throw new RuntimeException(
301 "Missing static main on " + className, ex);
302 } catch (SecurityException ex) {
303 throw new RuntimeException(
304 "Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
305 }
306
307 int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
308 if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
309 throw new RuntimeException(
310 "Main method is not public and static on " + className);
311 }
......
319 return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
320 }
......
343 protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
344 ClassLoader classLoader) {
......
350 nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
......
354 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
355 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
356
357 final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);
358
359 // The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
360 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
361
362 // Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
363 return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
364 }
Ici, la méthode dans la variable 反射est obtenue et transmise pour être utilisée pour en construire une . Dès que ceci est exécuté , la méthode dans la variable commencera à s'exécuter .classNamemain()MethodAndArgsCallerRunnableRunnableclassNamemain()
classNameQuelle est exactement la valeur de la variable ?
Vous vous souvenez de cette variable que nous avons soulignée plus tôtentryPoint ? Lecteurs qui ne s’en souviennent pas, veuillez revenir en arrière et vérifier à nouveau. android.app.ActivityThreadC'est la classe cible que nous voulons exécuter.
ActivityThreadL'appel de la méthode de classe mainindique que l'application a terminé le processus de création et d'initialisation du processus, et ce qui suit entrera dans le processus de création et de démarrage de Applicationet Activity.
2.5 Démarrage de l'application
À partir de la version 2.4, la méthode que nous connaissons ActivityThreadest main()appelée et le programme est créé et démarré avec succès.
2.5.1 ActivityThreadmain()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
7310 public static void main(String[] args) {
7311 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
7312
7313 // Install selective syscall interception
7314 AndroidOs.install();
7315
7316 // CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
7317 // disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
7318 // StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
7319 CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
// 初始化应用中需要使用的系统路径
7321 Environment.initForCurrentUser();
7322
7323 // Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
// 为应用设置当前用户的CA证书保存的位置
7324 final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
7325 TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
7326
// 设置进程的名称
7327 Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
// 主线程Looper准备
7329 Looper.prepareMainLooper();
......
// 创建ActivityThread 对象
7342 ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
7343 thread.attach(false, startSeq);
7344
7345 if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
7346 sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
7347 }
......
// 主线程Looper,开启消息循环
7356 Looper.loop();
7357
7358 throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
7359 }
......
2.5.2 ActivityThread的attache()
main()attach()La méthode
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java est appelée dans la méthode
7071 private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq) {
7072 sCurrentActivityThread = this;
7073 mSystemThread = system;
7074 if (!system) {
7075 android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("<pre-initialized>",
7076 UserHandle.myUserId());
// 把对象mAppThread(Binder)放到了RuntimeInit类中的静态变量mApplicationObject中
7077 RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
7078 final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
7079 try {
// 关键:通过Binder调用AMS的attachApplication()方法
7080 mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread, startSeq);
7081 } catch (RemoteException ex) {
7082 throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
7083 }
......
7106 } else {
7107 // Don't set application object here -- if the system crashes,
7108 // we can't display an alert, we just want to die die die.
7109 android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("system_process",
7110 UserHandle.myUserId());
7111 try {
7112 mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
7113 mInstrumentation.basicInit(this);
7114 ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(
7115 this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);
7116 mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null);
7117 mInitialApplication.onCreate();
7118 } catch (Exception e) {
7119 throw new RuntimeException(
7120 "Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);
7121 }
7122 }
......
7144 }
7145
ActivityThreadattachAu sein d'une méthode d'une classe , initialisation par une méthode binderappelée . Nous allons jeter un coup d'oeil:AMSattachApplicationApplication
2.5.3 ActivityManagerService et attachApplication()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
5179 @Override
5180 public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) {
5181 if (thread == null) {
5182 throw new SecurityException("Invalid application interface");
5183 }
5184 synchronized (this) {
5185 int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
5186 final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
5187 final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
5188 attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq);
5189 Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
5190 }
5191 }
2.5.4 ActivityManagerService et attachApplicationLocked()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
4767 private boolean attachApplicationLocked(@NonNull IApplicationThread thread,
4768 int pid, int callingUid, long startSeq) {
......
5046 if (app.isolatedEntryPoint != null) {
5047 // This is an isolated process which should just call an entry point instead of
5048 // being bound to an application.
5049 thread.runIsolatedEntryPoint(app.isolatedEntryPoint, app.isolatedEntryPointArgs);
5050 } else if (instr2 != null) {
// 1.调用ApplicationThread的bindApplication去初始化Application
5051 thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
5052 instr2.mClass,
5053 profilerInfo, instr2.mArguments,
5054 instr2.mWatcher,
5055 instr2.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
5056 mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
5057 isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.isPersistent(),
5058 new Configuration(app.getWindowProcessController().getConfiguration()),
5059 app.compat, getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
5060 mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
5061 buildSerial, autofillOptions, contentCaptureOptions);
5062 } else {
5063 thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, null, profilerInfo,
5064 null, null, null, testMode,
5065 mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
5066 isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.isPersistent(),
5067 new Configuration(app.getWindowProcessController().getConfiguration()),
5068 app.compat, getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
5069 mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
5070 buildSerial, autofillOptions, contentCaptureOptions);
5071 }
5072 if (profilerInfo != null) {
5073 profilerInfo.closeFd();
5074 profilerInfo = null;
5075 }
5076
5077 // Make app active after binding application or client may be running requests (e.g
5078 // starting activities) before it is ready.
5079 app.makeActive(thread, mProcessStats);
5080 checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: immediately after bindApplication");
5081 mProcessList.updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
5082 checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after updateLruProcessLocked");
5083 app.lastRequestedGc = app.lastLowMemory = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
5084 } catch (Exception e) {
......
5093 return false;
5094 }
5095
5096 // Remove this record from the list of starting applications.
5097 mPersistentStartingProcesses.remove(app);
5098 if (DEBUG_PROCESSES && mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) Slog.v(TAG_PROCESSES,
5099 "Attach application locked removing on hold: " + app);
5100 mProcessesOnHold.remove(app);
5101
5102 boolean badApp = false;
5103 boolean didSomething = false;
5104
5105 // See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
5106 if (normalMode) {
5107 try {
// 2.去启动Activity
5108 didSomething = mAtmInternal.attachApplication(app.getWindowProcessController());
5109 } catch (Exception e) {
5110 Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
5111 badApp = true;
5112 }
5113 }
......
5176 return true;
5177 }
Le code ci-dessus fait principalement deux choses :
ApplicationThreadLabindApplication()méthode appelée pour initialiserApplicationest un autre appel inter-processus.ATMSCommencez la cible en allantActivity.
première méthodeApplicationThreadd'analysebindApplication()
2.5.5 ActivityThread et bindApplication()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
996 public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
997 List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
998 ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
999 IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
1000 IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
1001 boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
1002 boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
1003 CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings,
1004 String buildSerial, AutofillOptions autofillOptions,
1005 ContentCaptureOptions contentCaptureOptions) {
......
// 通过handler发消息,启动Application
1053 sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
1054 }
......
1855 switch (msg.what) {
1856 case BIND_APPLICATION:
1857 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication");
1858 AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
1859 handleBindApplication(data);
1860 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
1861 break;
}
......
@UnsupportedAppUsage
6122 private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
......
6379 final LoadedApk pi = getPackageInfo(instrApp, data.compatInfo,
6380 appContext.getClassLoader(), false, true, false);
......
6385 final ContextImpl instrContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, pi,
6386 appContext.getOpPackageName());
6387
6388 try {
6389 final ClassLoader cl = instrContext.getClassLoader();
// 创建仪表
6390 mInstrumentation = (Instrumentation)
6391 cl.loadClass(data.instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance();
6392 } catch (Exception e) {
......
6396 }
6397
6398 final ComponentName component = new ComponentName(ii.packageName, ii.name);
// 初始化仪表盘
6399 mInstrumentation.init(this, instrContext, appContext, component,
6400 data.instrumentationWatcher, data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection);
......
6412 }
......
6425 Application app;
......
6428 try {
6429 // If the app is being launched for full backup or restore, bring it up in
6430 // a restricted environment with the base application class.
// 创建Application
6431 app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
......
6451 try {
6452 mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs);
6453 }
6454 catch (Exception e) {
......
6458 }
6459 try {
// 调用Application的onCreate方法
6460 mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
6461 } catch (Exception e) {
...
6467 }
6468 } finally {
....
6475 }
6497 }
......
J'ai principalement fait trois choses :
- Créez des tableaux de bord.
- Utilisez pour
LoadedApken créer unApplication, mais utilisez finalement laApplicationclasse de tableau de bord créée à l'aide de la réflexion. - Utilisez le tableau de bord pour initialiser
Application, cliquez pour affichermInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate()la méthode.
2.5.6 Instrumentation – callApplicationOnCreate()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java
1181 public void callApplicationOnCreate(Application app) {
1182 app.onCreate();
1183 }
À ce stade, Applicationl'initialisation est terminée.
2.5.7 Une fois l'application démarrée, continuez à démarrer la première activité
AMSLe attachApplicationLocked()fait deux choses :
- La création de l'application est terminée.
- La première Activité à travers le programme de démarrage ATMS
nous amène à continuer à regarder le démarrage de l'Activité :
Ici, mAtmInternal.attachApplication(app.getWindowProcessController())l' objet de classe mAtmInternalest LocalServiceune sous-classe d'ATMS, héritée de ActivityTaskManagerInternal.
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityTaskManagerService.java
6078 final class LocalService extends ActivityTaskManagerInternal {
......
6866 @Override
6867 public boolean attachApplication(WindowProcessController wpc) throws RemoteException {
6868 synchronized (mGlobalLockWithoutBoost) {
6869 return mRootActivityContainer.attachApplication(wpc);
6870 }
6871 }
}
Cette méthode ne fait qu'une seule chose, la RootActivityContainerméthode appelante attachApplication(), continuons à regarder :
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RootActivityContainer.java
768 boolean attachApplication(WindowProcessController app) throws RemoteException {
769 final String processName = app.mName;
770 boolean didSomething = false;
771 for (int displayNdx = mActivityDisplays.size() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
772 final ActivityDisplay display = mActivityDisplays.get(displayNdx);
773 final ActivityStack stack = display.getFocusedStack();
774 if (stack != null) {
775 stack.getAllRunningVisibleActivitiesLocked(mTmpActivityList);
776 final ActivityRecord top = stack.topRunningActivityLocked();
777 final int size = mTmpActivityList.size();
778 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
779 final ActivityRecord activity = mTmpActivityList.get(i);
780 if (activity.app == null && app.mUid == activity.info.applicationInfo.uid
781 && processName.equals(activity.processName)) {
782 try {
783 if (mStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked(activity, app,
784 top == activity /* andResume */, true /* checkConfig */)) {
785 didSomething = true;
786 }
787 } catch (RemoteException e) {
788 Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting activity "
789 + top.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
790 throw e;
791 }
792 }
793 }
794 }
795 }
796 if (!didSomething) {
797 ensureActivitiesVisible(null, 0, false /* preserve_windows */);
798 }
799 return didSomething;
800 }
ActivityStackSupervisorVous pouvez voir que realStartActivityLocked()la méthode appelée ici est cohérente avec la deuxième branche de
notre méthode en 2.3 ActivityStackSupervisor. Il existe deux branches :startSpecificActivityLocked()
- Si le processus n'est pas démarré, utilisez le gestionnaire pour envoyer un message à AMS pour notifier le processus de création ; (analysé en 2.4)
- Le processus a démarré, puis démarrez l'activité.
Regardons le démarrage de l'activité :
2.6 Début de l'activité
2.6.1 ActivityStackSupervisor et realStartActivityLocked()
startSpecificActivityLocked()Appelée dans la méthode realStartActivityLocked(), jetons un coup d'œil à cette méthode :
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
705 boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, WindowProcessController proc,
706 boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {
......
// 创建一个Activity启动事务,同时传入proc.getThread(),
// 该对象实际为ApplicationThread
828 final ClientTransaction clientTransaction = ClientTransaction.obtain(
829 proc.getThread(), r.appToken);
830
831 final DisplayContent dc = r.getDisplay().mDisplayContent;
// 把LaunchActivityItem加入事务中,
// 后面会调用到该类的handleLaunchActivity()方法
832 clientTransaction.addCallback(LaunchActivityItem.obtain(new Intent(r.intent),
833 System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,
834 // TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global
835 // and override configs.
836 mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),
837 mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,
838 r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, proc.getReportedProcState(),
839 r.icicle, r.persistentState, results, newIntents,
840 dc.isNextTransitionForward(), proc.createProfilerInfoIfNeeded(),
841 r.assistToken));
842
843 // Set desired final state.
844 final ActivityLifecycleItem lifecycleItem;
845 if (andResume) {
846 lifecycleItem = ResumeActivityItem.obtain(dc.isNextTransitionForward());
847 } else {
848 lifecycleItem = PauseActivityItem.obtain();
849 }
850 clientTransaction.setLifecycleStateRequest(lifecycleItem);
851
// 在这里启动事务
853 mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction);
......
929 return true;
930 }
Le code clé est commenté, et vous pouvez voir que dans ce code, il est principalement 创建事务transmis en même temps ApplicationThreadet ApplicationThreadhérité de Binder, le but de la transmission ici est principalement utilisé pour communiquer ultérieurement avec le processus APP cible. Démarrez ensuite la transaction, mService.getLifecycleManager()la méthode renvoie ClientLifecycleManagerl'objet, puis continuez à analyser ClientLifecycleManagerla scheduleTransaction()méthode
2.6.2 planningTransaction()
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ClientLifecycleManager.java
45 void scheduleTransaction(ClientTransaction transaction) throws RemoteException {
46 final IApplicationThread client = transaction.getClient();
47 transaction.schedule();
48 if (!(client instanceof Binder)) {
49 // If client is not an instance of Binder - it's a remote call and at this point it is
50 // safe to recycle the object. All objects used for local calls will be recycled after
51 // the transaction is executed on client in ActivityThread.
52 transaction.recycle();
53 }
54 }
On voit clairement dans la méthode ClientLifecycleManagerde la classe que la méthode de l'objet scheduleTransaction()est en fait appelée ici et la méthode saisie continue d'être analysée.ClientTransactionschedule()ClientTransactionschedule()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/servertransaction/ClientTransaction.java
134 public void schedule() throws RemoteException {
135 mClient.scheduleTransaction(this);
136 }
Dans la méthode ClientTransactionde la classe , la méthode est schedule()à nouveau appelée , et ce mClient est en fait l'objet passé lors de la création de l'Activity pour démarrer la transaction , c'est-à-dire voici la méthode appelée depuis le cross-process ** (le deuxième traitement croisé) * *, puis saisissez l'analyse dans la méthode .mClientscheduleTransaction()ApplicationThreadAMS进程ApplicationThreadscheduleTransaction()ApplicationThreadscheduleTransaction()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
904 private class ApplicationThread extends IApplicationThread.Stub {
1665 public void scheduleTransaction(ClientTransaction transaction) throws RemoteException {
1666 ActivityThread.this.scheduleTransaction(transaction);
1667 }
}
ApplicationThreadC'est ActivityThreadune classe interne, héritée de IApplicationThread.Stub, IApplicationThread.Stubet héritée de Binder, donc l'essence est toujours une Binder, utilisée pour communiquer entre ActivityThreadet AMS. Continuez à analyser la méthode, la méthode scheduleTransaction()appelée ici ActivityThreadest en fait la méthode de la classe parent , cliquez pour analyser.scheduleTransaction()ActivityThreadClientTransactionHandler
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ClientTransactionHandler.java
45 void scheduleTransaction(ClientTransaction transaction) {
46 transaction.preExecute(this);
47 sendMessage(ActivityThread.H.EXECUTE_TRANSACTION, transaction);
48 }
handlerEnvoyez un message dans cette méthode H.EXECUTE_TRANSACTION, et Messageil objcontient l'objet de transaction démarré Activity. Et Handlerl'implémentation spécifique de ceci est l'objet ActivityThreaddans H, puis recherchez handlel'endroit où le message est reçu pour continuer l'analyse.
2.6.3 Traitement des messages du gestionnaire dans ActivityThread
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1853 public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
1854 if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
1855 switch (msg.what) {
......
2014 case EXECUTE_TRANSACTION:
2015 final ClientTransaction transaction = (ClientTransaction) msg.obj;
2016 mTransactionExecutor.execute(transaction);
2017 if (isSystem()) {
2018 // Client transactions inside system process are recycled on the client side
2019 // instead of ClientLifecycleManager to avoid being cleared before this
2020 // message is handled.
2021 transaction.recycle();
2022 }
2023 // TODO(lifecycler): Recycle locally scheduled transactions.
2024 break;
......
2031 }
L'endroit où le message du gestionnaire est reçu est défini dans ActivityThreadla classe. Ici, la méthode est à nouveau appelée TransactionExecutor. execute()Cliquez pour continuer l'analyse
2.6.4 Exécution de TransactionExecutor
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/servertransaction/TransactionExecutor.java
69 public void execute(ClientTransaction transaction) {
......
95 executeCallbacks(transaction);
96
97 executeLifecycleState(transaction);
98 mPendingActions.clear();
99 if (DEBUG_RESOLVER) Slog.d(TAG, tId(transaction) + "End resolving transaction");
100 }
......
104 public void executeCallbacks(ClientTransaction transaction) {
......
124 final int size = callbacks.size();
125 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
126 final ClientTransactionItem item = callbacks.get(i);
127 if (DEBUG_RESOLVER) Slog.d(TAG, tId(transaction) + "Resolving callback: " + item);
128 final int postExecutionState = item.getPostExecutionState();
129 final int closestPreExecutionState = mHelper.getClosestPreExecutionState(r,
130 item.getPostExecutionState());
131 if (closestPreExecutionState != UNDEFINED) {
132 cycleToPath(r, closestPreExecutionState, transaction);
133 }
// item的类型其实就是LaunchActivityItem
135 item.execute(mTransactionHandler, token, mPendingActions);
136 item.postExecute(mTransactionHandler, token, mPendingActions);
......
148 }
149 }
Dans la méthode, les méthodes executeCallback()de la transaction seront parcourues callbacket exécutées.Ceux -ci ont été ajoutés lors de la création précédente , et les objets ajoutés sont en fait des objets de sous - classes de la classe . Par conséquent, il faut appeler la méthode de la classe et saisir la méthode de la classe pour continuer l'analyse.executecallbacksActivity启动事务callbackClientTransactionItemLaunchActivityItemitem.execute(mTransactionHandler, token, mPendingActions)LaunchActivityItemexecute()LaunchActivityItemexecute()
2.6.5 LaunchActivityItem et Execute()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/servertransaction/LaunchActivityItem.java
76 public void execute(ClientTransactionHandler client, IBinder token,
77 PendingTransactionActions pendingActions) {
78 Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
79 ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord(token, mIntent, mIdent, mInfo,
80 mOverrideConfig, mCompatInfo, mReferrer, mVoiceInteractor, mState, mPersistentState,
81 mPendingResults, mPendingNewIntents, mIsForward,
82 mProfilerInfo, client, mAssistToken);
// 注意这里:启动Activity
83 client.handleLaunchActivity(r, pendingActions, null /* customIntent */);
84 Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
85 }
Dans la méthode LaunchActivityItemde la classe execute(), la méthode est appelée client.handleLaunchActivity(), voici clientle ClientTransactionHandlertype et ClientTransactionHandlerla classe d'implémentation est ActivityThread, donc ici elle revient à la classe, et la méthode ActivityThreadest appelée , et l'analyse continue.handleLaunchActivity()
2.6.6 ActivityThread et handleLaunchActivity()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
3380 @Override
3381 public Activity handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r,
3382 PendingTransactionActions pendingActions, Intent customIntent) {
......
// 初始化 Activity 的 WindowManager,每一个 Activity 都会对应一个“窗口”
3404 WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
// 这里是重点
3409 final Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
......
3430 return a;
3431 }
2.6.7 ActivityThread – performLaunchActivity()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
3158 /** Core implementation of activity launch. */
3159 private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
......
3178 ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);
3179 Activity activity = null;
3180 try {
// 1.通过反射创建目标 Activity 对象
3181 java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
3182 activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
3183 cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
3184 StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
3185 r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
3186 r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
3187 if (r.state != null) {
3188 r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
3189 }
3190 } catch (Exception e) {
......
3196 }
3197
3198 try {
3199 Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
.......
3209 if (activity != null) {
......
// 2.创建window
3217 Window window = null;
3218 if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
3219 window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
3220 r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
3221 r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
3222 }
3223 appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
// 3.调用 attach 方法建立 Activity 与 Context 之间的联系,
// 创建 PhoneWindow 对象,并与 Activity 进行关联操作
3224 activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
3225 r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
3226 r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
3227 r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback,
3228 r.assistToken);
.......
3236 int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
3237 if (theme != 0) {
// 设置主题
3238 activity.setTheme(theme);
3239 }
3240
3241 activity.mCalled = false;
// 4.通过 Instrumentation 最终调用 Activity 的 onCreate 方法
3242 if (r.isPersistable()) {
3243 mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
3244 } else {
3245 mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
3246 }
3247 if (!activity.mCalled) {
3248 throw new SuperNotCalledException(
3249 "Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
3250 " did not call through to super.onCreate()");
3251 }
3252 r.activity = activity;
3253 }
......
3266 } catch (Exception e) {
......
3272 }
3273
3274 return activity;
3275 }
Le code principal a été commenté, faisant principalement les choses suivantes,
- Créez l'objet cible
Activityen utilisant la réflexion ; - créer
PhoneWindowdes objets, attachliaison de méthode d'appelActivity;- méthode appelée
Activity_onCreate
A l'étape 4, c'est la méthode Instrumentationappelée par Activity, onCreate()cliquez pour voir callActivityOnCreate()la méthode.
2.6.8 Instrumentation – callActivityOnCreate()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java
1297 public void callActivityOnCreate(Activity activity, Bundle icicle) {
1298 prePerformCreate(activity);
1299 activity.performCreate(icicle);
1300 postPerformCreate(activity);
1301 }
......
1310 public void callActivityOnCreate(Activity activity, Bundle icicle,
1311 PersistableBundle persistentState) {
1312 prePerformCreate(activity);
1313 activity.performCreate(icicle, persistentState);
1314 postPerformCreate(activity);
1315 }
Vous pouvez voir la méthode appelée Activity, performCreate()entrez performCreate()la méthode à afficher :
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java
7795 final void performCreate(Bundle icicle, PersistableBundle persistentState) {
......
// 在这里调用了Activity的生命周期onCreate方法
7799 if (persistentState != null) {
7800 onCreate(icicle, persistentState);
7801 } else {
7802 onCreate(icicle);
7803 }
......
7812 }
À ce stade, la méthode Activitya été créée et appelée onCreate(), et le rappel du cycle de vie a commencé
3 Résumé
Comme il y a trop de classes et de méthodes impliquées, je vais résumer brièvement le processus global de démarrage de Launcher :
SystemServerAprès leAMSdémarrage,AMScommencez à démarrerLauncher.AMSDéterminez si le processus auquelActivityappartient la cible existe et informezZygotele processus de créer un nouveau processus s'il n'existe pas.- Le nouveau processus entre dans
ActivityThreadl'main()entrée, initialiseLooperet informeAMSle processus d'initialiserApplication. - En même temps ,
AMSil est exécuté à nouveauActivity启动, puisApplicationThreadla cible de départ est notifiéeActivity. ActivityThreadAprès avoir reçu la notification, exécutezActivityles opérations de création et d'initialisation.