definition
DNS cache poisoning, also known as DNS spoofing, is an attack method that finds and exploits vulnerabilities in the DNS system to direct traffic from legitimate servers to fake servers. Unlike general phishing attacks using illegal URLs, this attack uses legal URL addresses.
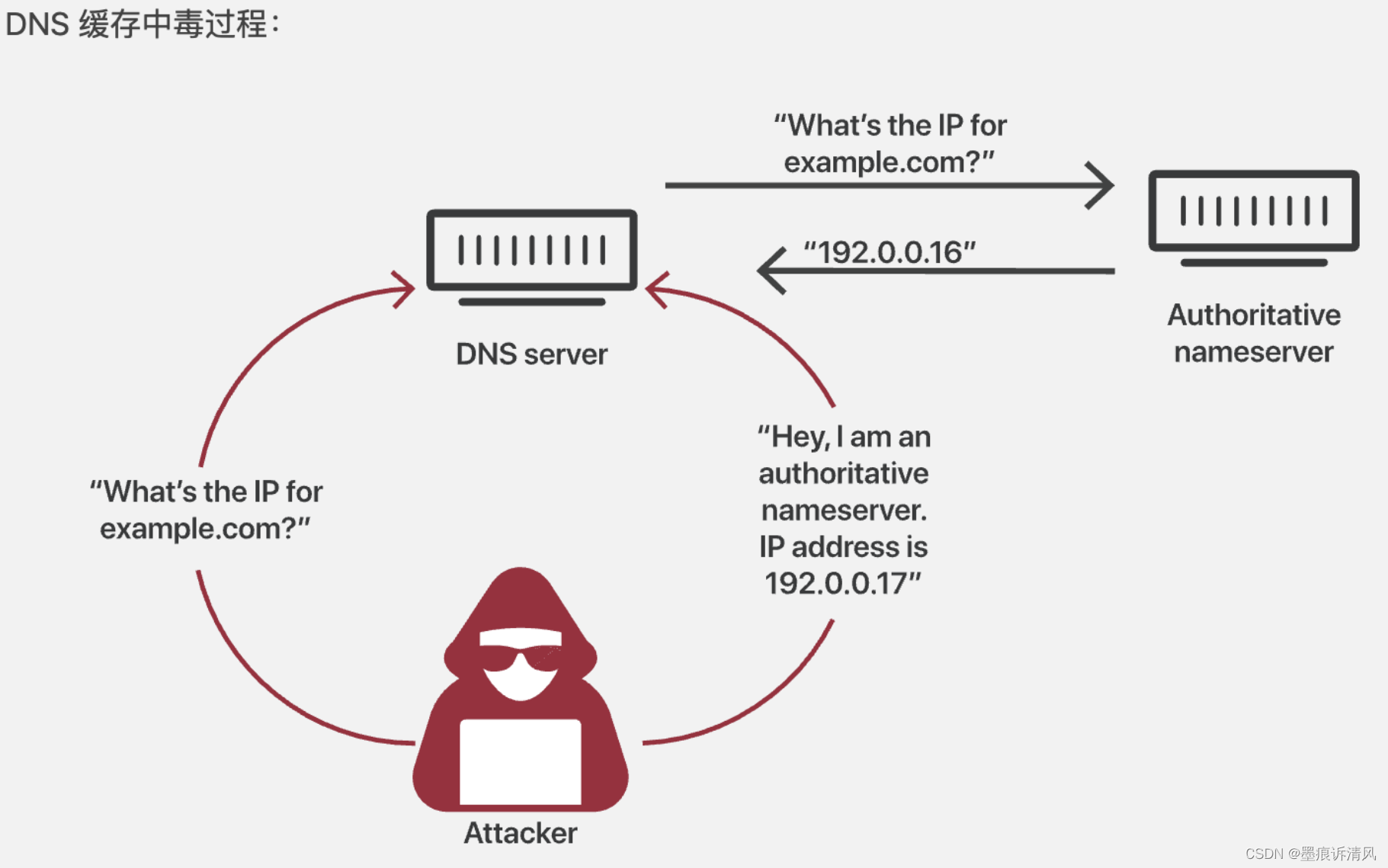
How DNS Cache Poisoning Works
In the actual DNS resolution process, when a user requests a certain website, the browser will first search the DNS cache in the machine. If the mapping relationship between the website and the IP is recorded in the DNS cache, it will directly return the result to the user. Initiate access to the obtained IP address. If there is no relevant record in the cache, the recursive server will be entrusted to initiate a recursive query.
This query mechanism shortens the global query time and allows users to obtain a faster access experience, but there are also certain security risks.
If an attacker controls the user's host or uses malicious software to attack the user's DNS cache, he can tamper with the domain name mapping relationship in the DNS cache and point the domain name resolution result to a false IP.
In this case, when the user initiates a request to the website again, the resolution of the DNS system will directly return the false mapping relationship to the user, leading the user to the false site, thereby causing information leakage and affecting property security.
How to Prevent DNS Cache Poisoning
DNS cache poisoning may seem scary, but there are still ways to deal with it. The following practices can effectively deal with the harm caused by DNS poisoning.
1. Keep your antivirus software active and updated
Usually&#x