Table of contents
1. Multidimensional array library numpy
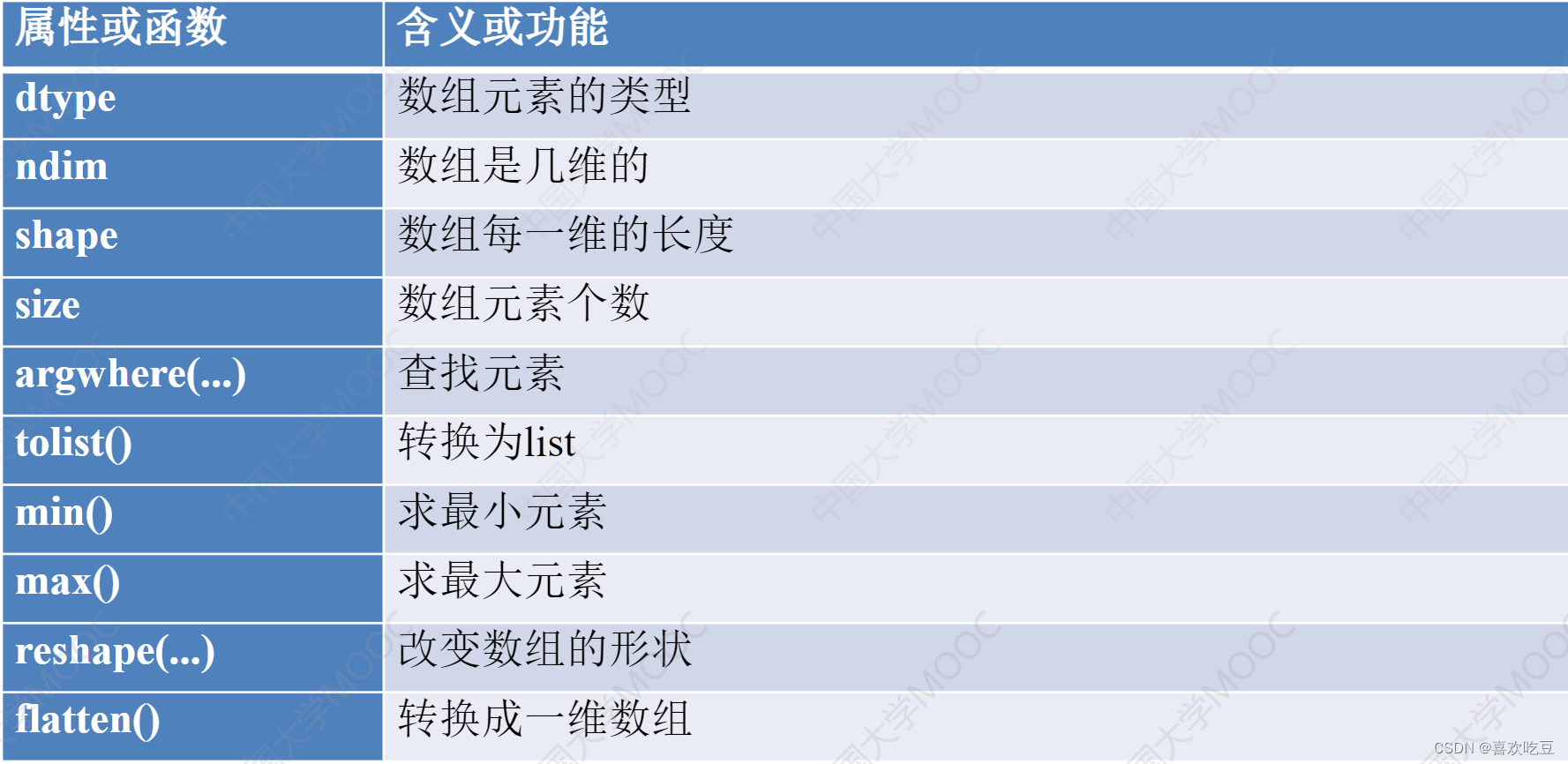
2. Add and delete numpy array elements
2) numpy deletes array elements
3) Find elements in numpy array
4) Mathematical operations on numpy arrays
2. Data analysis library pandas
1. DataFrame construction and access
DataFrame is a two-dimensional table with row and column labels, each column is a Series
2. DataFrame slicing and statistics
3. DataFrame analysis statistics
4. Modification, addition and deletion of DataFrame
5. Read and write excel and csv documents
1) Use pandas to read excel documents
2) Use pandas to read and write csv files
3. Use matplotlib for data display
3. Draw a comparison histogram (with multiple sets of data)
4. Draw scatter points and line charts
8. Draw multi-layer radar charts
1. Multidimensional array library numpy
➢Multidimensional array library, it is very convenient to create multidimensional arrays and can replace multidimensional lists
➢It is faster than multidimensional lists
➢Supports various mathematical operations of vectors and matrices
➢All element types must be the same
1. Operation function:
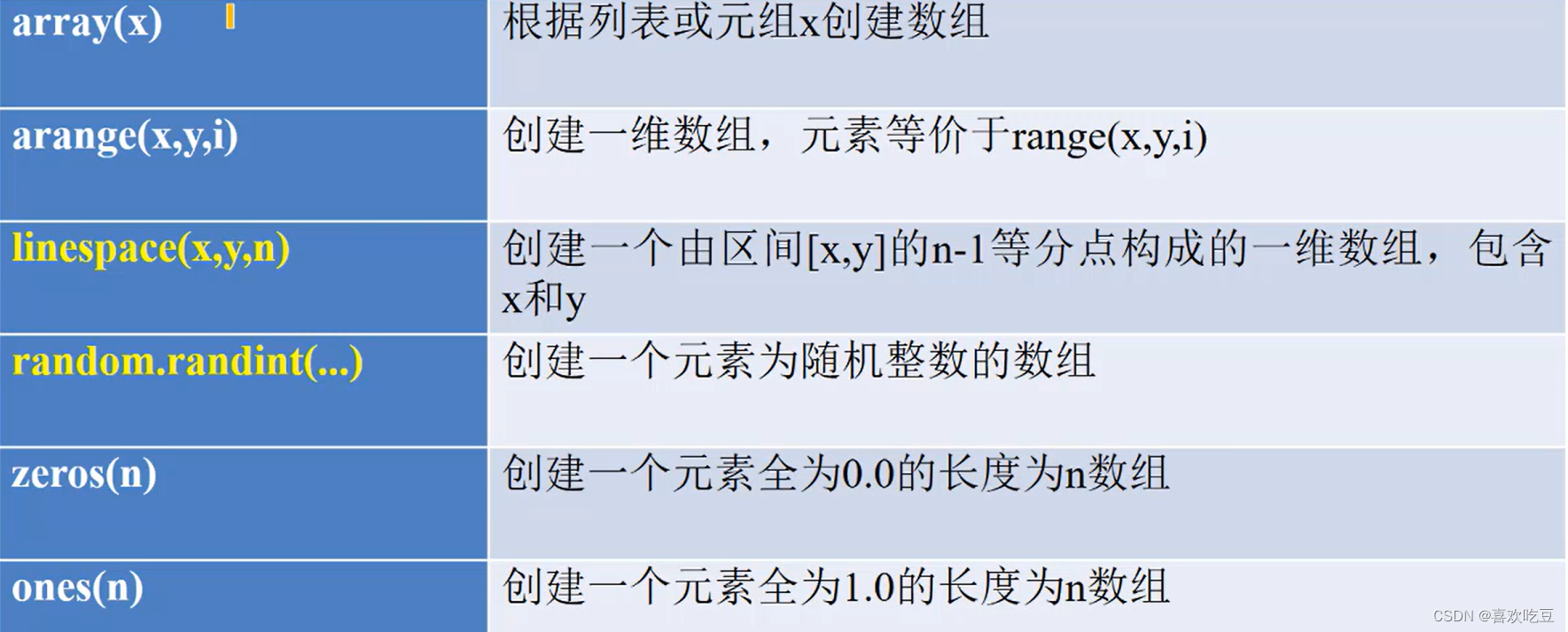
import numpy as np #以后numpy简写为np
print (np.array([1,2,3]) ) #>>[1 2 3]
print (np. arange(1,9,2) ) #>>[13 5 7]
print (np. linspace(1,10,4)) #>>[ 1. 4. 7. 10. ]
print (np . random. randint (10,20, [2,3]) )
#>>[[12 19 12]
#>> [19 13 10 ]]
print (np . random. randint (10,20,5) ) #>> [12 19 19 10 13]
a = np. zeros (3)
print (a)
#>>[ 0. 0. 0.]
print(list(a) )
#>>[0.0,0.0,0.0]
a = np. zeros((2 ,3) ,dtype=int) #创建- t个2行3列的元素都是整数0的数组
import numpy as np
b = np.array([i for i in range (12) ])
#b是[ 0 1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
a = b.reshape( (3,4) )
#转换成3行4列的数组,b不变
print (len(a) )
#>>3 a有3行
print(a. size )
#>>12 a的元素个数是12
print (a. ndim)
#>>2 a是2维的
print (a. shape)
#>>(3, 4) a是3行4列
print (a. dtype)
#>>int32 a的元素类型 是32位的整数
L = a.tolist ()
#转换成列表,a不变
print (L)
#>>[[0,1,2,3],[4,5,6,7],[8,9,10,11]]
b = a. flatten ()
#转换成一维数组
print (b)
#>>[0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
2. Add and delete numpy array elements
Once a numpy array is generated, elements cannot be added or deleted. The above function returns a new array.
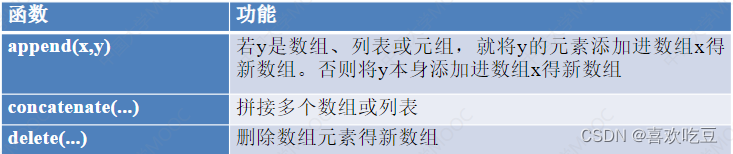
1) Add array elements
import numpy as np
a = np.array((1,2,3) )
#a是[123]
b = np. append(a,10)<
#a不会发生变化
print (b)
#>>[1 2 3 10]
print (np. append(a, [10,20] ) )
#>>[1 2 3 10 20]
C=np. zeros ( (2,3) , dtype=int)
#c是2行3列的全0数组
print (np. append(a,c) )
#>>[1 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0]
print (np. concatenate( (a, [10,20] ,a)) )
#>>[1 2 3 10 20 1 2 3]
print (np. concatenate( (C, np. array([[10 ,20,30]] ) ) ) )
#c拼接一行[10, 20 ,30]得新数组
print (np. concatenate( (C, np.array([[1,2], [10,20]])) ,axis=1) )
#c的第0行拼接了1,2两个元素、第1行拼接了10 , 20两个新元素后得到新数组
2) numpy deletes array elements
import numpy as np
a = np.array((1,2,3,4) )
b = np.delete(a,1) #删除a中下标为1的元素, a不会改变
print (b)
#>>[1_ 3 4]
b = np.array([[1,2,3,4] ,[5,6, 7,8], [9,10,11,121])
print (np. delete (b,1 ,axis=0) )
#删除b的第1行得新数组
#>>[[1 2 3 4]
#>>[9 10 11 12]]
print (np. delete (b,1 ,axis=1) )
#删除b的第1列得新数组
print (np. delete (b,[1,2] ,axis=0) )
#删除b的第1行和第2行得新数组
print (np. delete (b,[1,3] ,axis=1) )
#删除b的第1列和第3列得新数组
3) Find elements in numpy array
import numpy as np
a = np.array( (1,2,3,5,3,4) )
pos = np. argwhere(a==3)
#pos是[[2] [4] ]
a = np.array([[1,2,3] , [4,5,2]])
print(2 in a)
#>>True
pos = np. argwhere(a==2)
#pos是[[0 1] [1 2]]
b = a[a>2]
#抽取a中大于2的元素形成一个一维数组
print (b)
#>>[3 4 5]
a[a>2]=-1
#a变成[[12-1][-1-12]]
4) Mathematical operations on numpy arrays
import numpy as np
a = np.array( (1,2,3,4) )
b=a+1
print (b)
#>>[2 3 4 5]
print (a*b)
#>>[2 6 12 20] a,b对应元素相乘
print (a+b)
#>>[3579]a,b对应元素相加
c = np.sqrt(a*10) #a*10是[10 20 30 40]
print(c)
#>>[ 3. 16227766 4. 47213595 5. 47722558 6.32455532]
3. Slice of numpy array
A slice of a numpy array is a "view", which is a part of the original array, not a copy of a part.
import numpy as np
a=np.arange(8)
#a是[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
b = a[3:6]
#注意,b是a的一部分
print (b)
#>>[3 4 5]
c = np.copy(a[3:6])
#c是a的一部分的拷贝
b[0] = 100
#会修改a
print(a)
#>>[ 0 1 2 100 4 6 7]
print(c)
#>>[3 4 5] c不受b影响
a = np.array([[1,2,3,4] ,[5,6,7,8] , [9,10,11,12] , [13,14,15,16]])
b = a[1:3,1:4]
#b是>>[[678][101112]]
2. Data analysis library pandas
1. DataFrame construction and access
➢The core function is to perform various operations on two-dimensional tables, such as adding, deleting, modifying, and finding the sum, variance, median, average, etc. of column data. ➢Requires numpy support. ➢If there is openpyxI or xIrd or xIwt
support
, You can also read and write excel documents.
➢The most critical class: DataFrame, representing a two-dimensional table
Important classes of pandas: Series
Series is a one-dimensional table. Each element is labeled and subscripted. It has both list and dictionary access forms.
import pandas as pd
s = pd. Series (data=[80, 90,100] , index=['语文', '数学', '英语'])
for x in s:
#>>80 90 100
print(x,end=" ")
print ("")
print(s['语文'] ,s[1])
#>>80 90 标签和序号都可以作为下标来访问元
print(s[0:2] [ '数学'])
#>>90 s[0:2]是切片
print(s['数学': '英语'] [1])
#>>100
for i in range (len (s. index) ) :
#>>语文 数学 英语
print(s. index[i] ,end = " ")
s['体育'] = 110
#在尾部添加元素,标签为'体育',值为110
s. pop('数学')
#删除标签为'数学’的元素
s2 = s. append (pd . Series (120, index = [' 政治'])) #不改变s
print(s2['语文'] ,s2['政治'])
#>>80 120
print (1ist(s2) )
#>>[80,100, 110, 120]
print(s.sum() ,s.min() ,s .mean() ,s . median() )
#>>290 80 96. 66666666667 100.0输出和、 最小值、平均值、中位数>
print (s . idxmax() ,s. argmax () )
#>>体育 2 输出最大元素的标签和下标
DataFrame is a two-dimensional table with row and column labels, each column is a Series
import pandas as pd
pd.set_ option( 'display . unicode.east asian width' , True)
#输出对齐方面的设置
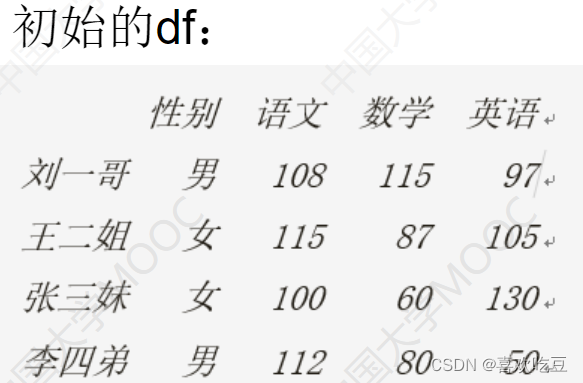
scores = [['男' ,108 ,115,97] ,['女' ,115,87,105] , ['女' ,100, 60 ,130]
['男' ,112,80,50]]
names = ['刘一哥,'王二姐’,'张三妹',李四弟'] .
courses = ['性别', '语文', '数学', '英语']
df = . pd.DataFrame (data=scores ,index = names , columns = courses)
print (df)
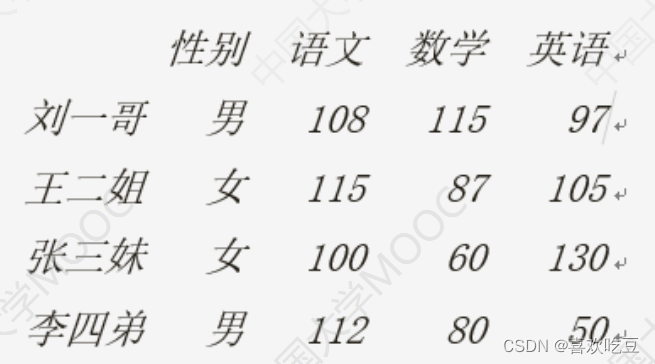
print (df. values[0] [1] , type (df. values) ) #>>108. <class numpy . ndarray '>
print (list (df. index) )
#>>['刘一哥','王二姐','张三妹','李四弟']
print (list (df. columns) )
#>>['性别','语文','数学','英语']
print (df . index[2] ,df . columns[2]) #>>张三妹 数学
s1 = df['语文']
#s1是个Series,代表'语文'那一列
print(s1['刘一哥'] ,s1[0])
#>>108 108 刘一哥语文成绩
print(df['语文']['刘一哥'])
#>>108 列索引先写
s2 = df.1oc['王二姐']
#s2也是个Series,代表“王二姐”那一行
print(s2['性别'] ,s2['语文'] ,s2[2])
#>>女 115 87 二姐的性别、语文和数学分数
2. DataFrame slicing and statistics
#DataFrame的切片:
#1loc[行选择器,.列选择器] 用下标做切片
#Ioc[行选择器,列选择器] 用标签做切片
#DataFrame的切片是视图
df2 = df. iloc[1:3] #行切片,是视图,选1 ,2两行
dt2 = df.1c['王二姐':张三妹'] #和上一行等价
print (df2)

df2 = df. i1oc[: ,0:3] #列切片(是视图),选0、1. 2三列
df2 = df.1oc[:, '性别': '数学'] #和上一行等价
print (df2)

df2 = df.i1oc[:2,[1,3]] #行列切片
df2 = df.1oc[:'王二姐',['语文', '英语']] #和上一行等价
print (df2)

df2 = df.i1oc[[1,3] ,2:4] #取第1、3行,第2、3列<
df2 = df.1oc[['王二姐' , '李四弟'],'数学': '英语'] #和上一行等价
print (df2)

3. DataFrame analysis statistics
print ("---下面是DataFrame的分析和统计---")
print (df. T)
#df . T是df的转置矩阵,即行列互换的矩阵
print (df . sort_ values ( '语文' , ascending=False)) #按语文成绩降序排列
print (df.sum() [ '语文'] ,df .mean() ['数学'],df .median() ['英语'])
#>>435 85.5 101.0语文分数之和、 数学平均分、英语中位数
print(df .min() ['语文'] ,df .max() ['数学'])
#>>100 115 语文最低分,数学最高分
print (df .max(axis = 1)['王二姐'1) #>>115 二姐的最高分科目的分数
print (df['语文' ] . idxmax() )
#>>王二姐 语文最高分所在行的标签
print(df['数学] . argmin())
#>>2 数学最低分所在行的行号
print (df.1oc[ (df['语文'] > 100) & (df['数学'] >= 85)])


4. Modification, addition and deletion of DataFrame
print ("---下面是DataFrame的增删和修改---")
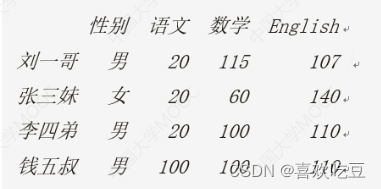
df.1oc['王二姐', '英语'] = df. iloc[0,1] = 150 #修改王二姐英语和刘一哥语文成绩
df['物理'] = [80, 70,90,100]
#为所有人添加物理成绩这-列
df. insert(1, "体育", [89,77, 76,45])
#为所有人插入体育成绩到第1列
df.1oc['李四弟'] = ['男' ,100 ,100 ,100 ,100,100] #修改李四弟全部信息
df.1oc[: , '语文'] = [20,20,20,20]
#修改所有人语文成绩
df.1oc[ '钱五叔'] = [ '男' , 100 , 100 ,100, 100 , 100]
#加一行
df.1oc[: , '英语'] += 10
#>>所有人英语加10分
df. columns = ['性别', '体育', '语文', '数学', 'English', '物理'] #改列标签
print (df)

df.drop( ['体育', '物理'] ,axis=1, inplace=True) #删除体育和物理成绩
df.drop( '王二姐' ,axis = 0,inplace=True)
#删除王二姐那一行
print (df)
df.drop ( [df. index[i] for i in range(1,3) ] ,axis=0 , inplace = True)
#删除第1,2行
df .drop( [df . columns[i] for i in range(3) ] ,axis = y 1 , inplace=
True) #删除第0到2列
5. Read and write excel and csv documents
➢Requires openpyxI (for .xIsx files) or xIrd or xIwt support (old .xls files)
➢Each worksheet read is a DataFrame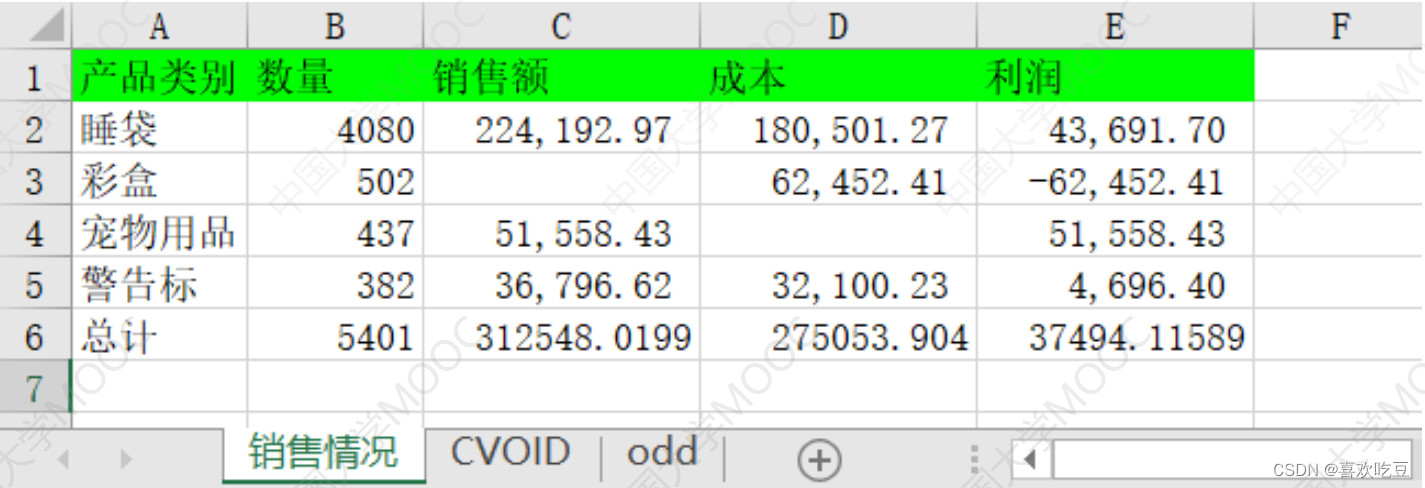
1) Use pandas to read excel documents
import pandas as pd
pd.set option ( ' display . unicode.east asian width' , True)
dt = pd. read excel ("'excel sample.xlsx" , sheet name= [ '销售情况' ,1] ,
index col=0) #读取第0和第1张二工作表
df =
dt [ '销售情况']
#dt是字典,df是DataFrame
print (df. iloc[0,0] ,df.loc[ 'I睡袋' , '数量'])
#>>4080 4080
print (df)
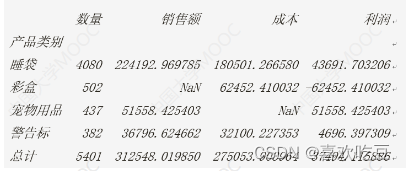
print (pd. isnu1l (df.1oc['彩盒', '销售额']))
#>> True
df . fillna (0 , inplace= =True)
#将所有NaNa用0替换
print(df.loc[ '彩盒' , '销售额'] ,df. iloc[2,2] )
#>>0.0 0.0
df.to excel (filename, sheet_ name="Sheet1", na_ rep='',.. ...)
➢Write the data in the DataFrame object df to the "Sheet1" worksheet in the exce1 document filename, NaN is replaced with ' '.
➢The original filename file will be overwritten
➢If you want to write multiple worksheets in an excel document, you need to use ExcelWrite
# (接.上面程序)
writer = pd. Exce 1Writer ("new.x1sx")
#创建ExcelWri ter对象
df. to exce1 (writer , sheet_ name="S1")
df.T. to exce1 (writer, sheet_ name="S2")
#转置矩阵写入
df.sort_ values( '销售额' , ascending= False) . to exce1 (writer ,
sheet_ name="S3")
#按销售额排序的新DataFrame写入工作表s3
df[ '销售额'] . to excel (writer ,sheet_ name="S4")
#只写入一列
writer . save ()
2) Use pandas to read and write csv files
df. to_ csv (" result. csv" ,sep=" ," ,na rep= 'NA' ,
float_ format="号 .2f" , encoding="gbk")
df = pd. read csv (" result. csv")
3. Use matplotlib for data display
1. Draw a histogram
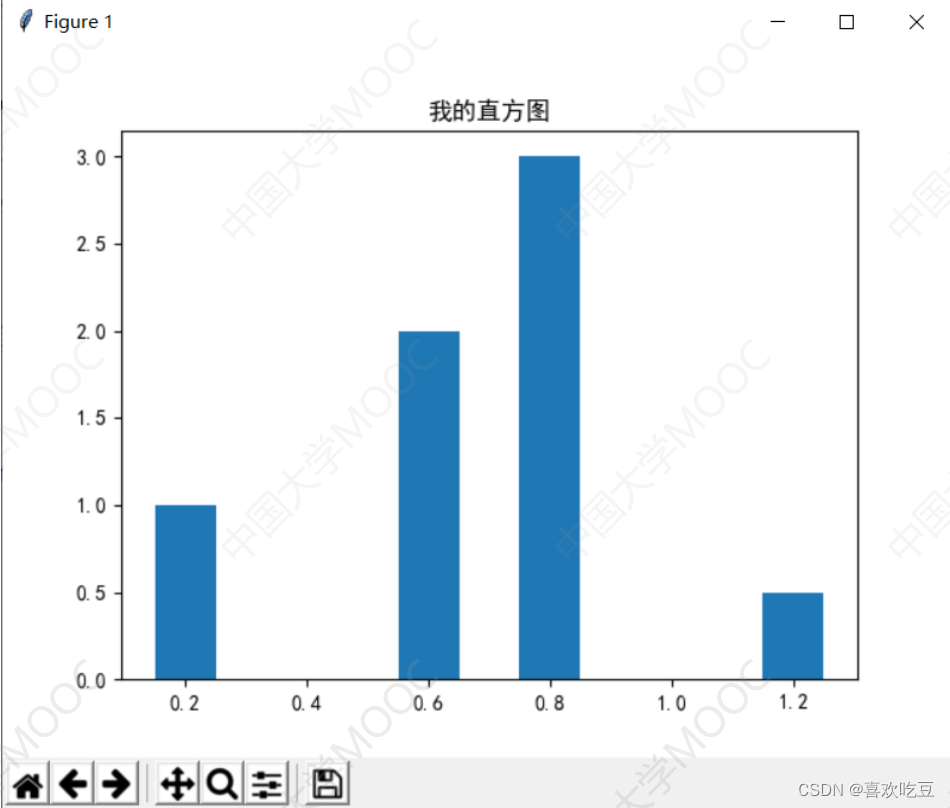
import matp1otlib. pYp1ot as plt #以后plt等价于ma tplotlib . pyplot
from ma tp1ot1ib import rcParams
rcParams[ ' font. family'] = rcParams[ ' font. sans-serif'] = ' SimHei '
#设置中文支持,中文字体为简体黑体
ax = p1t. figure() .add subp1ot ()
#建图,获取子图对象ax
ax.bar(x = (0.2,0.6,0.8,1.2) ,height = (1,2,3,0.5) ,width = 0.1)
#x表示4个柱子中心横坐标分别是0.2,0.6,0.8,1
#height表示4个柱子高度分别是1,2,3,0.5
#width表示柱子宽度0.1
ax.set_ title ('我的直方图)
#设置标题
p1t. show ()
#显示绘图结果
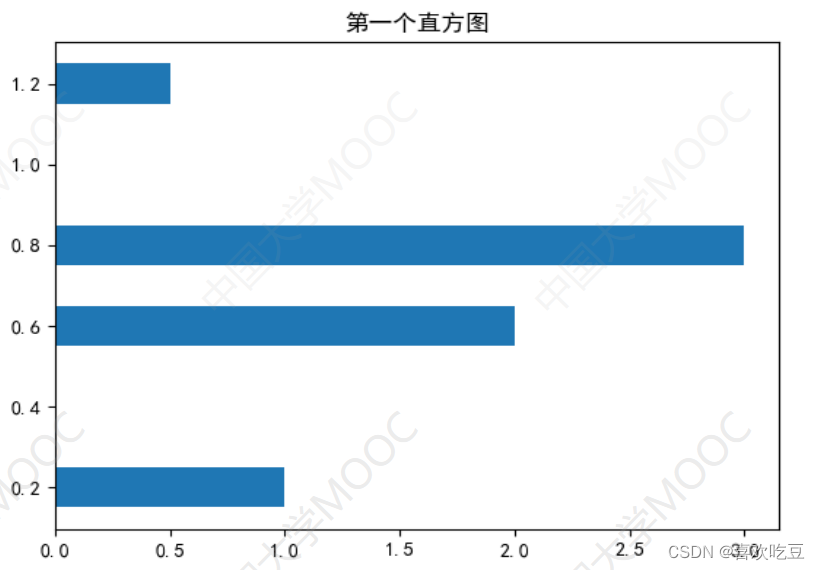
纵向
ax.bar(x = (0.2,0.6,0.8,1.2) ,height = (1,2,3,0.5) ,width = 0.1)
横向
ax.barh(y = (0.2,0.6,0.8,1.2) ,width = (1,2,3,0.5) ,height = 0.1)
2. Draw a stacked histogram

import ma tplotlib. pyp1ot as p1t
ax = plt. figure() . add subp1ot()
labels = ['Jan' ,'Feb' ,'Mar' ,lApr']
num1 = [20, 30, 15, 35]
#Dept1的数据
num2 = [15, 30,40, 20]
#Dept2的数据
cordx = range (len (num1) )
#x轴刻度位置
rects1 = ax.bar(x = cordx,height=num1, width=0.5, color=' red' ,
label="Dept1")
rects2 = ax.bar(x = cordx, height=num2, width=0 .5,color='green' ,
label="Dept2",bottom= =num1 )
ax.set_ y1im(0, 100)
#y轴坐标范围
ax. set_ ylabel ("Profit")
#y轴含义(标签)
ax. set xticks (cordx )
#设置x轴刻度位置
ax. set_ xlabel ("In year 2020")
#x轴含义(标签)
ax.set_ title ("My Company")
ax. legend()
#在右上角显示图例说明
p1t. show ()
3. Draw a comparison histogram (with multiple sets of data)
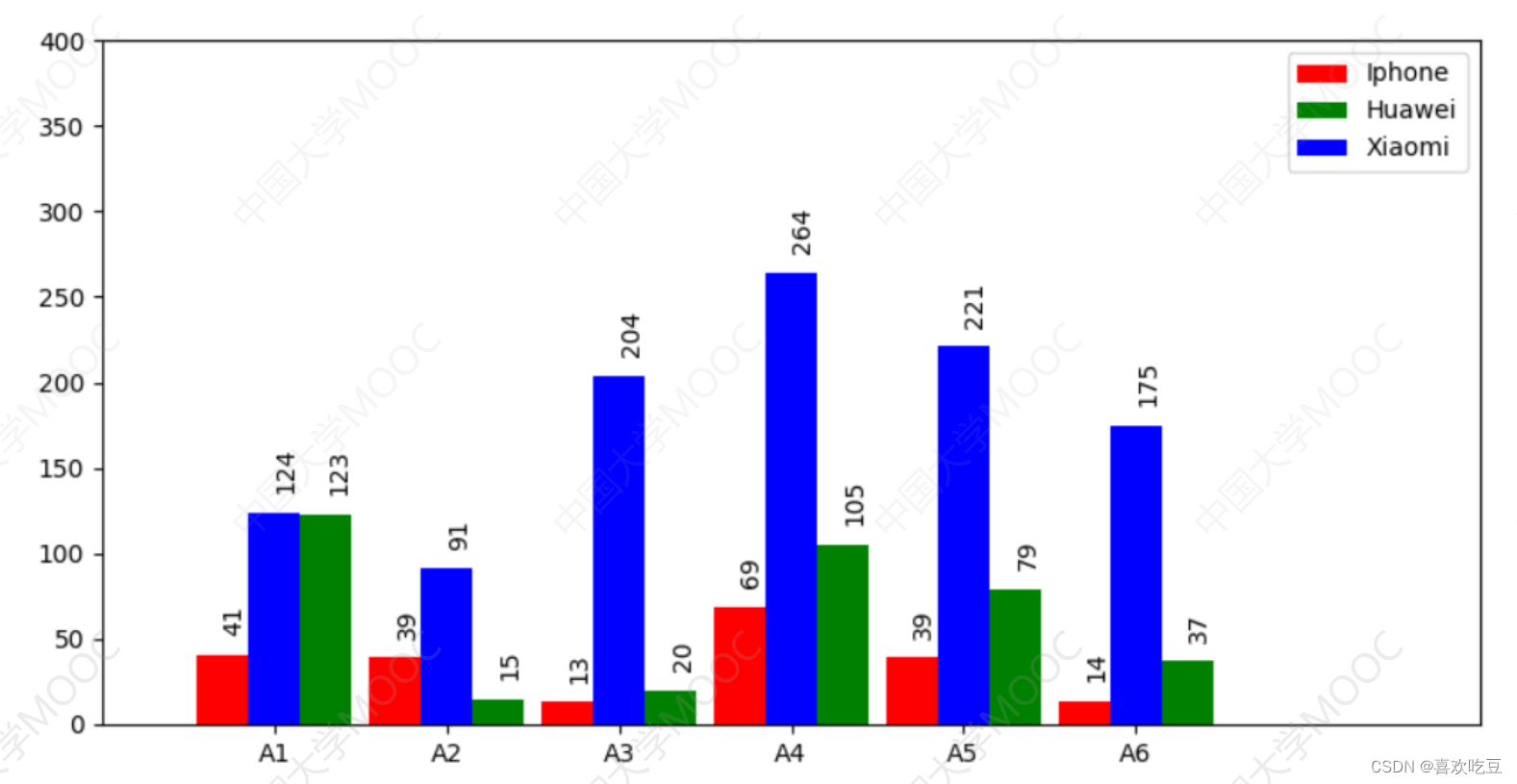
import matplotlib. pyp1ot as plt
ax =. plt. figure (figsize= (10,5)) . add_ subplot () #建图,获取子图对象ax
ax.set ylim(0, 400)
#指定y轴坐标范围
ax.set xlim(0, 80)
#指定x轴坐标范围
#以下是3组直方图的数据
x1=[7,17,27,37,47,57]
#第一-组直方图每个柱子中心点的横坐标
x2 = [13, 23,33,43, 53,63] #第二组直方图每个柱子中心点的横坐标
x3 = [10, 20,30,40, 50, 60]
y1 = [41, 39,13,69,39, 14]
#第一组直方图每个柱子的高度
y2 = [123,15, 20,105,79,37] #第二组直方图每个柱子的高度
y3 = [124,91, 204, 264,221, 175]
rects1 = ax.bar(x1, y1,facecolor='red' ,width=3, label =_ ' Iphone' )
rects2 = ax.bar (x2,y2,facecolor='green' ,width=3, label = ' Huawei ' )
rects3 = ax.bar(x3, y3,facecolor= ='blue',width=3,label = ' Xiaomi )
ax.set_ xticks (x3)
#x轴在x3中的各坐标点下面加刻度
ax. set_ xticklabels( ('A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4' , 'A5', 'A6') )
#指定x轴上每- -刻度下方的文字
ax. legend ()
#显示右.上角三组图的说明
def 1abe1 (ax , rects) : #在rects的每个柱子顶端标注数值
for rect in rects :
height = rect.get_ height()
ax. text (rect.get_ x() + rect.get_ width() /2,
height+14, str (height) , rotation=90) #文字旋转90度
1abe1 (ax, rects1)
label (ax , rects2)
labe1 (ax, rects3)
p1t. show ()
4. Draw scatter points and line charts
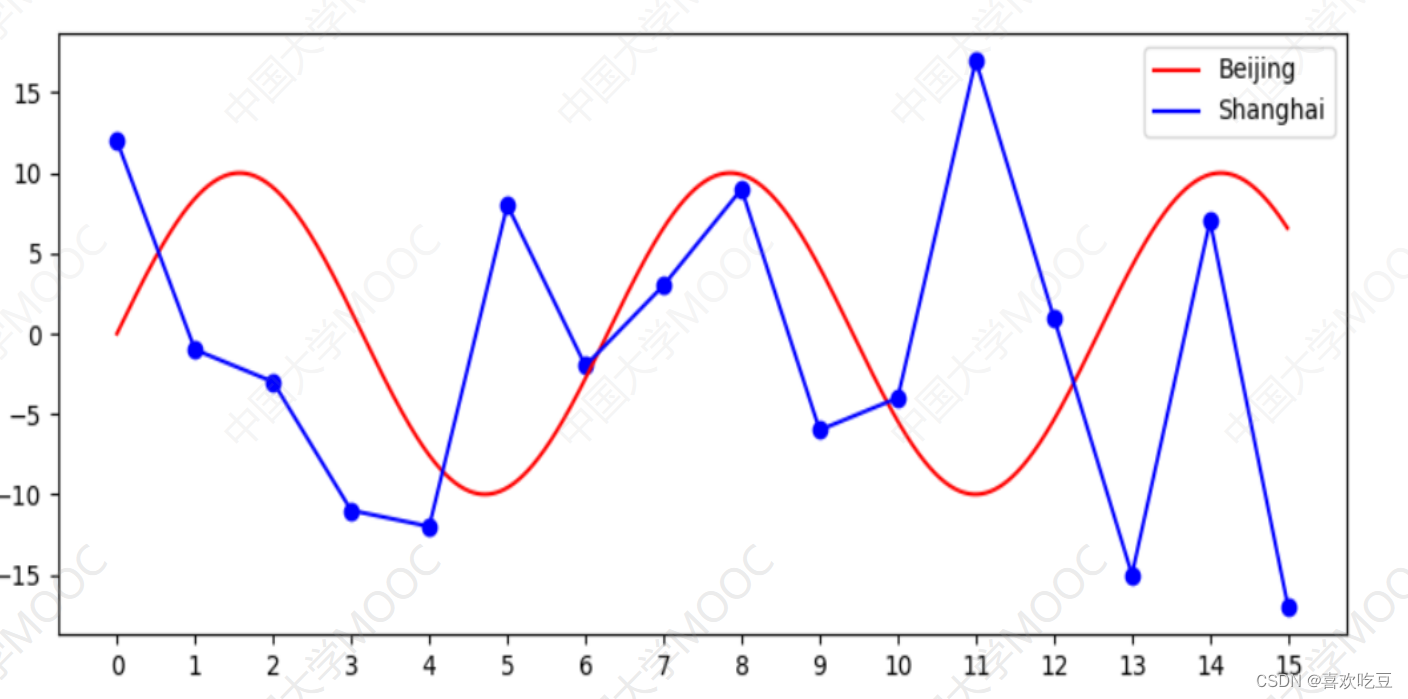
import math , random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def drawPlot(ax) :
xs = [i / 100 for i in range (1500)] #1500个 点的横坐标,间隔0 .01
ys = [10*math.sin(x) for X in xs]
#对应曲线y=10*sin (x).上的1 500个点的y坐标
ax.plot (xs,ys, "red" ,label = "Beijing") #画曲线y= =10*sin (x)
ys = list (range(-18,18) )
random. shuffle (ys)
ax. scatter (range(16),ys[:16] ,c = "blue") #画散点
ax.plot (range(16),ys[:16] ,"blue", label=" Shanghai") #画折线
ax . legend ()
#显示右.上角的各条折线说明
ax.set xticks (range (16) )
#x轴在坐标0,1.. .15处加刻度
ax. set_ xticklabels (range (16)) #指定x轴每个刻度 下方显示的文字
ax = plt. figure (figsize=(10,4) ,dpi=100) .add_ subp1ot() #图像长宽和清晰度
drawP1ot (ax)
p1t. show ()
5. Draw a pie chart
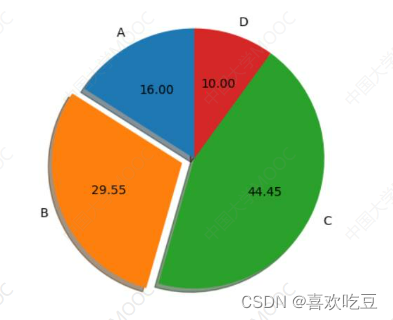
import matplotlib.pyplot as p1t .
def drawPie (ax) :
1bs = ( 'A','B', 'C',
'D' )
#四个扇区的标签
sectors = [16, 29.55, 44.45, 10]
#四个扇区的份额(百分比)
exp1 = [0, 0.1, 0,0]
#四个扇区的突出程度
ax.pie (x=sectors,labels=lbs, exp1ode=exp1,
autopct=18.2f' , shadow=True, labeldistance=1 .1,
pctdistance = 0 .6, startangle = 90)
ax.set_ title ("pie sample")
#饼图标题
ax = p1t. figure() .add subp1ot()
drawPie (ax)
p1t. show()
6. Draw a heat map

import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyp1ot as plt
data = np. random. randint(0,100, 30) .reshape (5,6)
#生成一一个5行六列,元素[0, 100]内的随机矩阵
xlabels = [ 'Beijing', ' Shanghai','Chengdu' ,
' Guangzhou',' Hangzhou',
' Wuhan' ]
ylabels=['2016','2017','2018','2019','20201]
ax = plt. figure (figsize=(10,8)) .add_ subp1ot()
ax.set yticks (range (len (ylabels))) #y轴在坐标 [0 , len (ylabels))处加刻度
ax.set_ yticklabels (ylabels) #设置y轴刻度文字
ax. set_ xticks (range (len (xlabels) ) )
ax.set xticklabels (xlabels)
heatMp = ax. imshow (data,cmap=plt. cm.hot, aspect=' auto' ,
vmin =0,vmax=100)
for i in range (1en (x1abe1s) ) :
for j in range (1en (y1abe1s) ) :
ax. text(i,j ,data[j] [i] ,ha = "center" ,va = "center"
color =
"blue" ,size=26)
p1t. colorbar (heatMp)
#绘制右边的颜色-数值对照柱
plt . xticks (rotation=45 , ha=" right") #将x轴刻度文字进行旋转, 且水平方向右对齐
p1t. title ("Sales Volume (ton) ")
p1t. show ()
7. Draw a radar chart
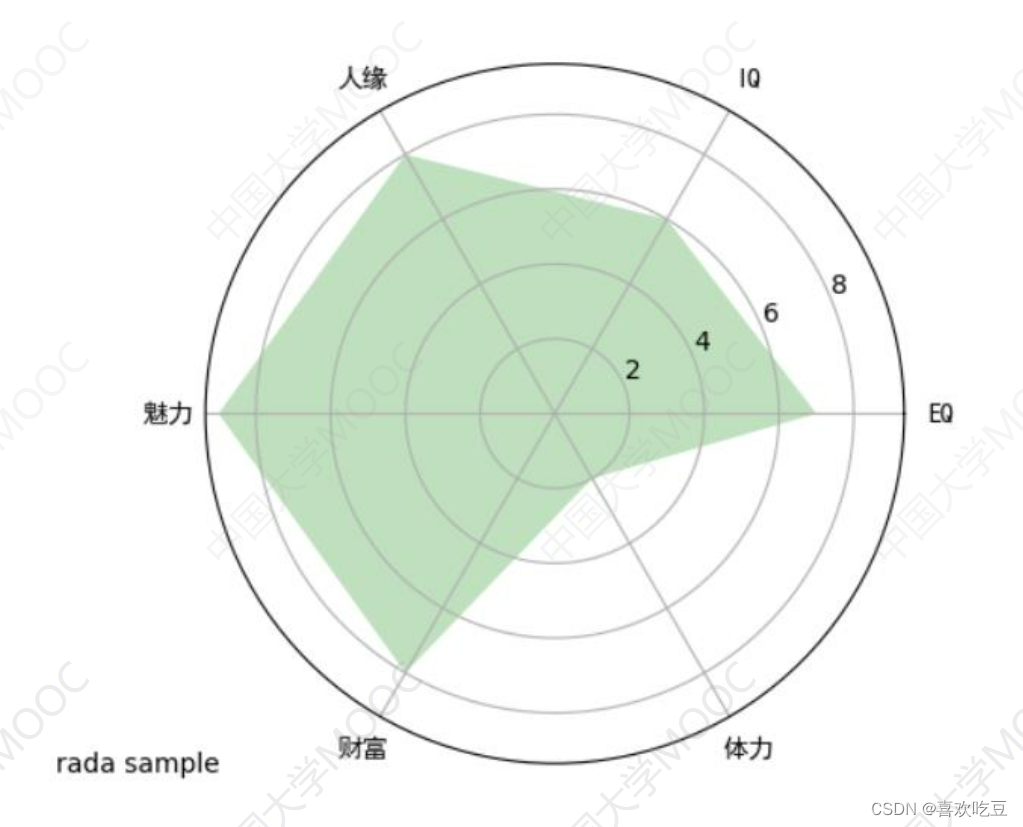
import matplotlib. pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import rcParams
#处理汉字用
def drawRadar (ax) :
pi = 3.1415926
labels = ['EQ', 'IQ','人缘' , '魅力', '财富' , '体力'] #6个属性的名称
attrNum = len (labels)
#attrNum是属性种类数,处等于6
data = [7 ,6,8,9,8,2]
#六个属性的值
angles = [2*pi *i/ attrNum for i in range (attrNum) ]
#angles是以弧度为单位的6个属性对应的6条半径线的角度
angles2 = [x * 180/pi for x in angles]
#angles2是以角度为单位的6个属性对应的半径线的角度
ax.set ylim(0,10)
#限定半径线上的坐标范围
ax. set_ thetagrids (angles2,labels , fontproperties="SimHei" )
#绘制6个属性对应的6条半径
ax. fi1l (angles,data, facecolor= ; : 6 'g' ,alpha= =0.25)
#填充,alpha :透明度
rcParams[' font. family'] = rcParams[' font. sans-serif'] = ' SimHei '
#处理汉字
ax = p1t. figure() . add_ subplot (projection = "polar")
#生成极坐标形式子图
drawRadar (ax)
p1t. show ()
8. Draw multi-layer radar charts
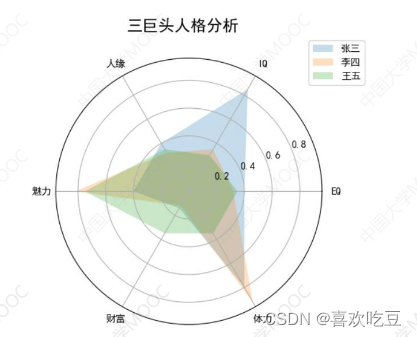
import matplotlib.pyplot as p1t
from ma tplot1ib import rcPar ams
rcParams[ ' font. family'] = rcParams[ ' font. sans-serif'] = ' SimHei !
pi = 3.1415926
labels = ['EQ', 'IQ','人缘', '魅力',财富', '体力] #6个属性的名称
attrNum = len (labels)
names = (张三',李四'王五
data = [[0.40,0.32,0.35] ,
[0.85,0.35,0.30] ,
[0.40,0.32,0.35],[0.40,0.82,0.75] ,
[0.14,0.12,0.35] ,
[0.80,0.92,0.35]]
#三个人的数据
angles = [2*pi*i/attrNum for i in range (attrNum) ]
angles2 = [x * 180/pi for x in ang1es]
ax = p1t. figure() .add_ subp1ot (projection = "polar")
ax. set_ the tagrids (angles2 , labels)
ax.set_ title('三巨头人格分析',y = 1.05) #y指明标题垂直位置
ax. legend (names , 1oc=(0.95,0.9)) #画出右上角不同人的颜色说明
plt. show ()
9. Draw multiple subgraphs
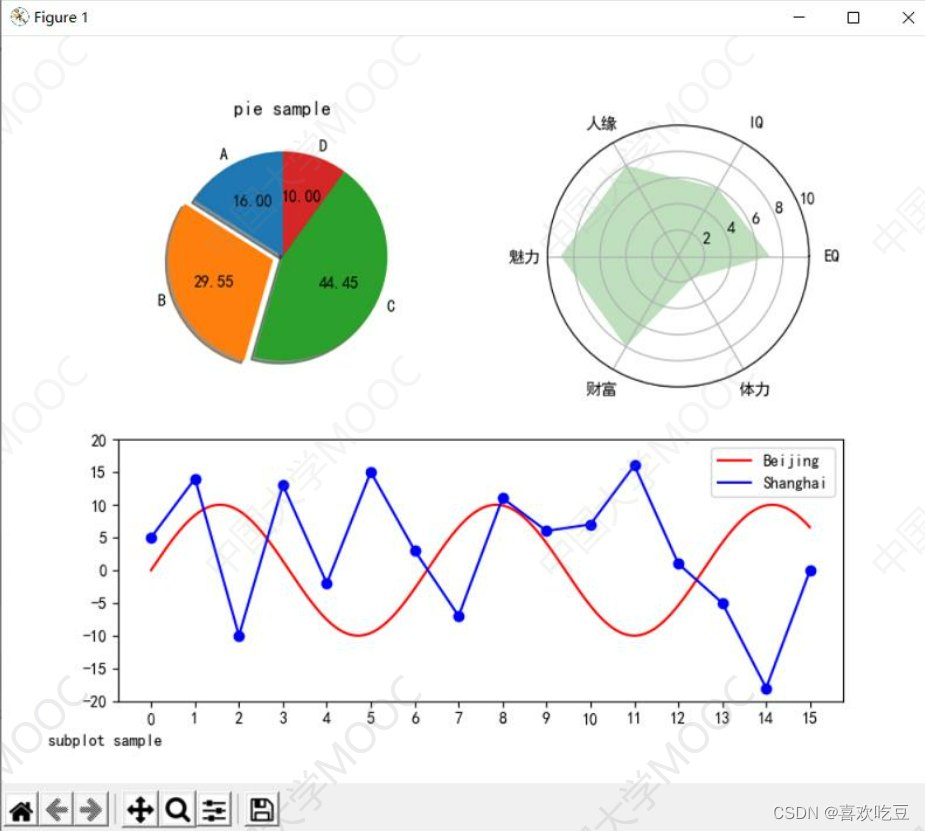
#程序中的import、汉字处理及drawRadar、 drawPie、 drawPlot函数略, 见前面程序
fig = plt. figure (figsize=(8,8) )
ax = fig.add subplot(2,2,1) #窗口分割成2*2,取位于第1个方格的子图
drawPie (ax)
ax = fig.add subplot(2 ,2 ,2 ,projection = "polar" )
drawRadar (ax)
ax = p1t. subp1ot2grid( (2, 2),(1, 0),colspan=2)
#或写成: ax = fig.add subplot(2,1,2)
drawPlot (ax)
plt. figtext(0.05,0.05, ' subplot sample' )
#显示左下角的图像标题
plt. show ()