perro guardián
El perro guardián, también llamado temporizador de vigilancia, es un circuito temporizador. Generalmente tiene una entrada llamada alimentar al perro o patear al perro; una salida se envía al terminal RST de la MCU. Cuando la MCU está funcionando normalmente, emite una señal a la alimentación de vez en cuando. La terminal del perro se borra para el WDT. Si el perro no es alimentado durante más del tiempo especificado (normalmente cuando el programa se acaba) y el temporizador WDT excede, se dará una señal de reinicio. a la MCU para restablecer la MCU. Evite que la MCU falle.
toda la idea
- El módulo del kernel inicializa el registro de control de vigilancia y habilita la vigilancia.
- El proceso de vigilancia del usuario patea al perro con regularidad
1. Análisis del código del espacio de usuario.
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
static void
die(const char *msg, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, msg);
fprintf(stderr, "%s: ERROR: ", "watchdog");
vfprintf(stderr, msg, ap);
va_end(ap);
exit(1);
}
static void
watchdog_write_pidfile(void)
{
char pidfile[80];
char pidbuf[16];
int fd;
int ret;
snprintf(pidfile, sizeof(pidfile), "/var/run/%s.pid", "watchdog");
fd = open(pidfile, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
if (errno != ENOENT) {
die("watchdog_write_pidfile: opening pidfile %s for read: %s
",
pidfile, strerror(errno));
}
/* ENOENT is good: the pidfile doesn't exist */
} else {
/* the pidfile exists: read it and check whether the named pid
is still around */
int pid;
char *end;
ret = read(fd, pidbuf, sizeof(pidbuf));
if (ret < 0) {
die("watchdog_write_pidfile: read of pre-existing %s failed: %s
",
pidfile, strerror(errno));
}
pid = strtol(pidbuf, &end, 10);
if (*end != '' && *end != '
') {
die("watchdog_write_pidfile: couldn't parse "%s" as a pid (from file %s); "
"aborting
", pidbuf, pidfile);
}
ret = kill(pid, 0); /* try sending signal 0 to the pid to check it exists */
if (ret == 0) {
die("watchdog_write_pidfile: %s contains pid %d which is still running; aborting
",
pidfile, pid);
}
/* pid doesn't exist, looks like we can proceed */
close(fd);
}
/* re-open pidfile for write, possibly creating it */
fd = open(pidfile, O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (fd < 0)
die("watchdog_write_pidfile: open %s for write/create: %s
", pidfile, strerror(errno));
snprintf(pidbuf, sizeof(pidbuf), "%d
", getpid());
ret = write(fd, pidbuf, strlen(pidbuf));
if (ret < 0) {
die("watchdog_write_pidfile: writing my PID to lockfile %s: %s
",
pidfile, strerror(errno));
}
close(fd);
}
void watchdog_func()
{
FILE *file;
file = fopen("/proc/watchdog_kick","w+");
if(file)
{
fputs("111", file);
fclose(file);
}
}
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t pid;
char tmpBuff[30] = {0};
int res = 0;
int fd;
int interval;
int sec,micro_sec;
sigset_t sigset;
if(argc >= 2)
interval = atoi(argv[1]);
else
interval = 500;
if(interval >= 10000){
printf("watchdog interval too long,should not more than 10s
");
interval = 1000;
}
sec = interval/1000;
micro_sec = (interval % 1000) * 1000;
watchdog_write_pidfile();
/* unblock sigalarm and sigterm signal */
sigaddset(&sigset,SIGALRM);
if(sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK,&sigset,NULL) < 0)
printf("sigprocmask error
");
// Register watchdog_func to SIGALRM
signal(SIGALRM, watchdog_func);
struct itimerval tick;
memset(&tick, 0, sizeof(tick));
//printf("interval:%d.
",interval);
// Timeout to run function first time
tick.it_value.tv_sec = sec; // sec
tick.it_value.tv_usec = micro_sec; // micro sec.
// Interval time to run function
tick.it_interval.tv_sec = sec;
tick.it_interval.tv_usec = micro_sec;
pid = getpid();
snprintf(tmpBuff,30,"renice -19 %d",pid);
system(tmpBuff);
//stop watchdog first
system("echo 1 > /proc/watchdog_kick");
system("echo enable 0 interval 0 > /proc/watchdog_cmd");
// resume watchdog
#ifdef CONFIG_RTL_8197F
system("echo enable 1 interval 32 > /proc/watchdog_cmd");
#else
system("echo enable 1 interval 10 > /proc/watchdog_cmd");
#endif
system("echo 1 > /proc/watchdog_kick");
res = setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &tick, NULL);
if (res) {
printf("Set watchdog timer failed!!/n");
return -1;
}
while(1) {
pause();
}
return 0;
}El proceso de usuario hace principalmente dos cosas:
1. 用户进程设置watchdog intervel
echo enable 1 interval 32 > /proc/watchdog_cmd2. 定时器定时踢狗void watchdog_func()
{
FILE *file;
file = fopen("/proc/watchdog_kick","w+");
if(file)
{
fputs("111", file);
fclose(file);
}
}2. Parte del núcleo
1. Inicialización del registro de control del temporizador de vigilancia
void bsp_enable_watchdog( void )
{
bBspWatchdog = 1;
*(volatile unsigned long *)(0xb800311C)=0x00240000; // 2^24
}
void __init plat_time_init(void) // mips-ori
{
printk(COLOR_RED"[%s:%d] [watchdog] platform timer init
"COLOR_CLEAR, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
{/* 省略部分代码 */}
#ifdef CONFIG_RTL_WTDOG
/* 配置时钟分频寄存器 */
REG32(BSP_CDBR)=(BSP_DIVISOR) << BSP_DIVF_OFFSET;
printk(COLOR_RED"[%s:%d] [watchdog] BSP enable watchdog, BSP_CDBR=0x%x
"COLOR_CLEAR,
__FUNCTION__, __LINE__, ((BSP_DIVISOR) << BSP_DIVF_OFFSET));
/* 使能watchdog */
bsp_enable_watchdog();
wtdog_cdbr = (REG32(BSP_CDBR) >> 16) & 0xffff;
printk(COLOR_RED"[%s:%d] [watchdog] watchdog cdbr=%u
"COLOR_CLEAR, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, wtdog_cdbr);
#endif /* CONFIG_RTL_WTDOG */
{/* 省略部分代码 */}
}
El registro de control de vigilancia se inicializa en: 0x00240000, lo que significa que los dos bits superiores de OVSEL son 10, los dos bits inferiores de OVSEL son 01, OVSEL=1001

2. Cree nodos de proceso (watchdog_cmd y watchdog_kick)
Proporciona dos interfaces para configurar el perro guardián en la capa de aplicación: watchdog_cmd se usa para establecer el intervalo y watchdog_kick se usa para patear al perro.
int __init bsp_watchdog_proc_init(void)
{
proc_create_data("watchdog_reboot", 0, &proc_root,
&watchdog_reboot_proc_fops, NULL);
#ifdef CONFIG_RTL_USERSPACE_WTDOG
proc_create_data("watchdog_cmd", 0, &proc_root,
&watchdog_cmd_proc_fops, NULL);
proc_create_data("watchdog_kick", 0, &proc_root,
&watchdog_kick_proc_fops, NULL);
#endif
return 0;
}2.1 interfaz de escritura de watchdog_cmd
La capa de aplicación escribe la configuración del intervalo de vigilancia en el nodo y la interfaz configura el bit OVSEL del registro de vigilancia.
Ejemplo: echo enable 1 intervalo 32 > /proc/watchdog_cmd
static ssize_t watchdog_cmd_single_write(struct file * file, const char __user * userbuf,
size_t count, loff_t * off)
{
char flag[64];
int enable,interval;
extern void bsp_enable_watchdog(void);
extern void bsp_disable_watchdog(void);
if (count < 2)
return -EFAULT;
if (userbuf && !copy_from_user(&flag, userbuf, 63)) {
int i;
unsigned int wtdog_intervel,wtdog_intervel0 = 0,wtdog_cdbr,wtdog_maxtime;
sscanf(flag,"enable %d interval %d",&enable,&interval);
if (enable == 0) {
/* disable watchdog */
bsp_disable_watchdog();
} else if (enable == 1) {
if (watchdog_default_flag == 0) {
watchdog_default_flag = 1;
watchdog_default_val = interval;
} else {
if(interval < watchdog_default_val){
printk("
watchdog timeout time should not less than default val,default=%d
",watchdog_default_val);
return -1;
}
}
wtdog_cdbr = (REG32(BSP_CDBR) >> 16) & 0xffff;
i = sizeof(wtdog_tbl)/sizeof(WTDOG_REGTBL_T) - 1;
/* interval计算方法 */
wtdog_maxtime = wtdog_tbl[i].wtdog_val/(LXBUS_CLOCK/wtdog_cdbr);
if (interval > wtdog_maxtime) {
printk("
watchdog max intervale time is %d,please check the set value
", wtdog_maxtime);
return -1;
}
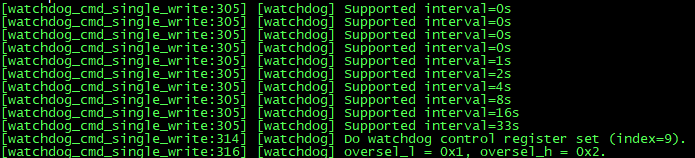
for(i = 0; i < sizeof(wtdog_tbl)/sizeof(WTDOG_REGTBL_T); i++) {
wtdog_intervel = wtdog_tbl[i].wtdog_val/(LXBUS_CLOCK/wtdog_cdbr);
printk(COLOR_GREEN"[%s:%d] [watchdog] Supported interval=%ds
"COLOR_CLEAR,
__FUNCTION__, __LINE__, wtdog_intervel);
if (interval >= wtdog_intervel0
&& interval <= wtdog_intervel) {
goto END;
}
wtdog_intervel0 = wtdog_intervel;
}
END:
printk(COLOR_GREEN"[%s:%d] [watchdog] Do watchdog control register set (index=%d).
"COLOR_CLEAR,
__FUNCTION__, __LINE__, i);
printk(COLOR_GREEN"[%s:%d] [watchdog] oversel_l = 0x%x, oversel_h = 0x%x.
"COLOR_CLEAR,
__FUNCTION__, __LINE__, wtdog_tbl[i].oversel_l, wtdog_tbl[i].oversel_h);
/* 设置wathdog寄存器 */
REG32(BSP_WDTCNR) = ( wtdog_tbl[i].oversel_l << 21) | ( wtdog_tbl[i].oversel_h << 17);
}
return count;
}
return -EFAULT;
}
2.2 interfaz de escritura de watchdog_kick
static ssize_t watchdog_kick_single_write(struct file * file, const char __user * userbuf,
size_t count, loff_t * off)
{
char flag[20];
if (count < 2)
return -EFAULT;
#ifdef CONFIG_RTL_WTDOG
{
/*If kernel fault. reboot whole system so softwatch dog can not kick even*/
extern int is_fault;
if(is_fault)
return count;
}
#endif
if (userbuf && !copy_from_user(&flag, userbuf, 1)) {
if(flag[0] == '1'){
watchdog_kick_state = RTL_WATCHDOG_KICK;
/* kick watchdog here */
*(volatile unsigned long *)(0xB800311c) |= 1 << 23;
}else {
watchdog_kick_state = 0;
}
return count;
}
return -EFAULT;
}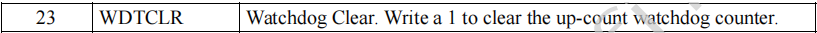
original:
Análisis de vigilancia de Realtek rtl819x-SDK-v3.4.14b: eche un vistazo (zoukankan.com)