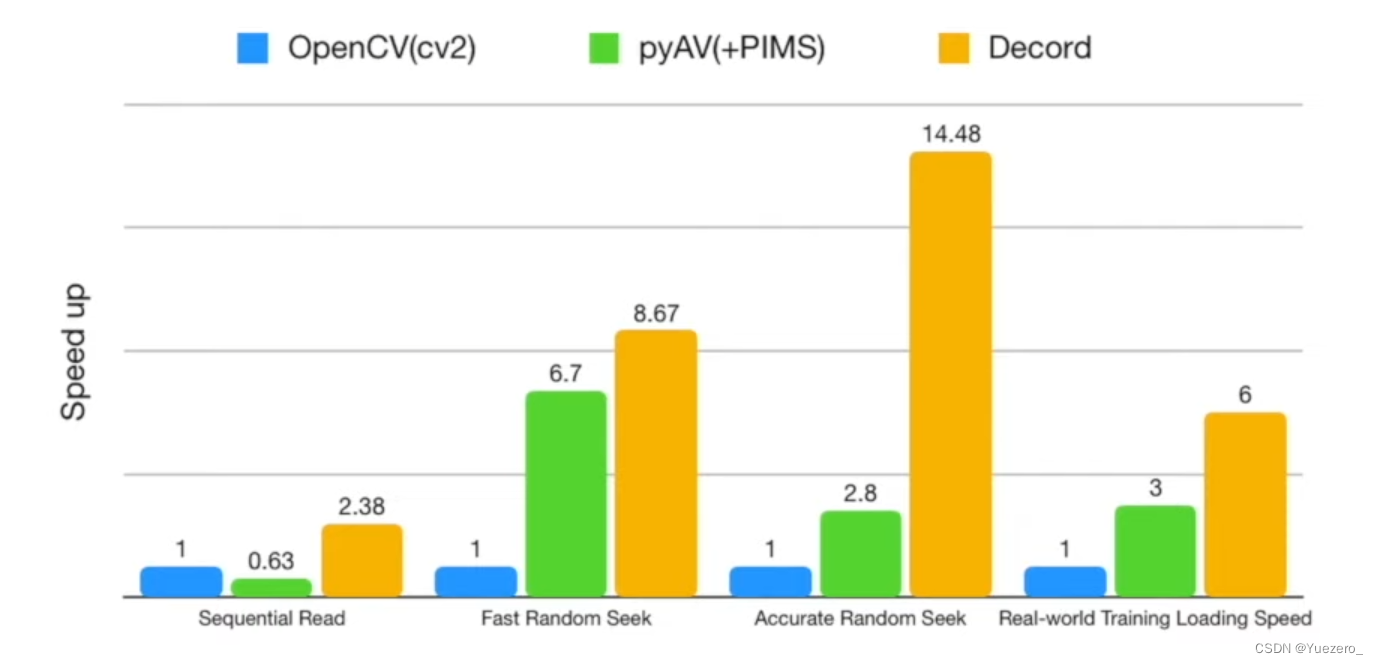
¡Decord bloquea 6 veces más que Opencv! !
1. Tutoriales
leer vídeo
# 1、读取使用
from decord import VideoReader
from decord import cpu, gpu
vr = VideoReader('tiny-Kinetics-400\\abseiling\\_4YTwq0-73Y_000044_000054.mp4', ctx=cpu(0))
print('video frames:', len(vr))
>>> video frames: 300
cargar el marco especificado
# 加载指定帧
frames = vr.get_batch([1, 3, 5, 7, 200])
print(frames.shape)
>>> (5, 256, 454, 3)
guardar marco como imagen
# 2、保存帧为图片
frame1 = vr[5].asnumpy()
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(frame1)
plt.axis('off')
>>> (-0.5, 453.5, 255.5, -0.5)

2. Guión de captura de fotogramas de vídeo
import cv2
import os
from decord import VideoReader
from decord import cpu
from tqdm import tqdm
video_bytes = "tiny-Kinetics-400\\abseiling\\_4YTwq0-73Y_000044_000054.mp4" # 视频路径
pic_folder = "frames" # 抽帧保存文件夹
file_basename = "abseiling" # 文件名前缀
archive_fps = 30 # 间隔帧数
# 压缩大图片的大小
def resize_image(image):
height, width = image.shape[:2]
n_width = int(256 * width / max(width, height))
n_height = int(256 * height / max(width, height))
img_new = cv2.resize(image, (n_width, n_height))
return img_new
# 读取视频
vr = VideoReader(video_bytes, ctx=cpu(0))
fra_num = len(vr) # 所有帧长度
# 获取指定帧并进行resize保存(使用tqdm显示进度)
frames = vr.get_batch(list(range(0, fra_num, archive_fps))).asnumpy()
for count, frame in tqdm(enumerate(frames), total=len(frames)):
frame = resize_image(frame)
image_name = f"{
file_basename}_{
count}.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(pic_folder, image_name), cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))