contenido
prefacio
Este blog explicará el código fuente de implementación de MMDetection sobre Darknet53, la columna vertebral. De hecho, he aprendido muchas versiones del código yolov3 antes, pero todas están basadas en el código fuente de varios archivos de configuración, y no hay una construcción de red completa. código, así que quiero cambiarlo durante los experimentos. Cuando se usa la red de yolov3, encontrará que no tiene forma de comenzar, cambie el archivo de configuración y no sepa por dónde comenzar. Recientemente aprendí MMDetection, por lo que planeo comenzar con esta red de detección de objetivos de una etapa más simple y clásica para desentrañar el misterio de MMDetection (un poco de escribir una pequeña composición...).
[Estructura de la red Darknet53 (ambas son imágenes robadas, soy demasiado perezoso para dibujarlas yo mismo)]
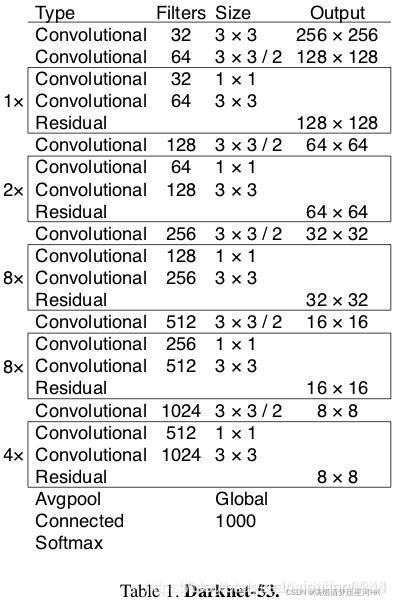
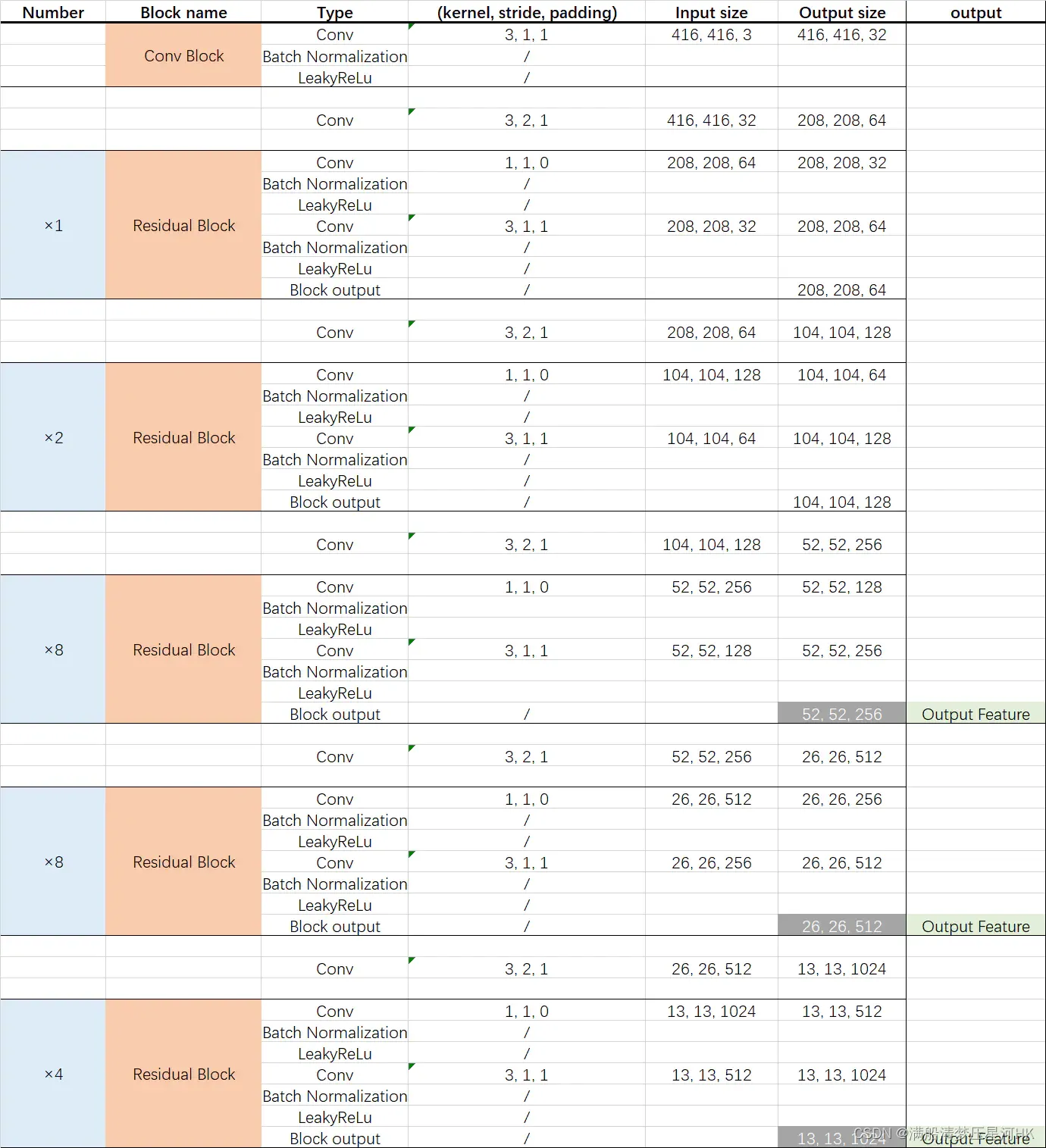
Bueno, lo anterior tiene una comprensión básica de Darkent53, comencemos a construir Backbone.
1. Archivo de configuración
Los archivos de configuración relacionados con la red troncal son los siguientes:
Nombre del modelo_nombre de la red troncal_nombre del conjunto de datos
yolov3_d53_mstrain-608_273e_pest.py
model = dict(
type='YOLOV3',
backbone=dict(
type='Darknet', # backbone类型
depth=53, # 网络层数
out_indices=(3, 4, 5), # 输出的stage的序号
init_cfg=dict(type='Pretrained', checkpoint='open-mmlab://darknet53')), # 预训练模型:open-mmlab://darknet53
二、Darknet
Aquí no planeo comenzar desde el archivo de configuración y cómo leer la configuración y luego registrarme para encontrar la clase Darknet (BaseModule). Nuestro centro de aprendizaje aquí se ubicará en la construcción de darknet53. En cuanto a la interpretación y el registro del archivo de configuración operaciones como MMCV, puede ver mi otro blog de interpretación de código fuente: [Aprendizaje del marco de detección de objetivos de MMDetection] .
2.1, Introducción a la clase Darknet y configuración de parámetros globales
@BACKBONES.register_module()
class Darknet(BaseModule):
"""Darknet backbone.
Args:
depth (int): Depth of Darknet. Currently only support 53.
out_indices (Sequence[int]): Output from which stages.
frozen_stages (int): Stages to be frozen (stop grad and set eval mode).
-1 means not freezing any parameters. Default: -1.
conv_cfg (dict): Config dict for convolution layer. Default: None.
norm_cfg (dict): Dictionary to construct and config norm layer.
Default: dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True)
act_cfg (dict): Config dict for activation layer.
Default: dict(type='LeakyReLU', negative_slope=0.1).
norm_eval (bool): Whether to set norm layers to eval mode, namely,
freeze running stats (mean and var). Note: Effect on Batch Norm
and its variants only.
pretrained (str, optional): model pretrained path. Default: None
init_cfg (dict or list[dict], optional): Initialization config dict.
Default: None
Example:
>>> from mmdet.models import Darknet
>>> import torch
>>> self = Darknet(depth=53)
>>> self.eval()
>>> inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 416, 416)
>>> level_outputs = self.forward(inputs)
>>> for level_out in level_outputs:
... print(tuple(level_out.shape))
...
(1, 256, 52, 52)
(1, 512, 26, 26)
(1, 1024, 13, 13)
"""
# Dict(depth: (layers, channels))
arch_settings = {
# 深度 5个stage的重复个数 5个stage的输入channel和输出channel
53: ((1, 2, 8, 8, 4), ((32, 64), (64, 128), (128, 256), (256, 512),
(512, 1024)))
}
2.2, __init__ inicialización
def __init__(self,
depth=53, # backbone深度
out_indices=(3, 4, 5), # backbone输出的stage的序号(输出向Neck)
frozen_stages=-1, # 哪些层需要冻结权重训练
conv_cfg=None, # 卷积层配置
norm_cfg=dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True), # norm层配置
act_cfg=dict(type='LeakyReLU', negative_slope=0.1), # 激活函数配置
norm_eval=True, # 是否将norm layer设置为eval mode 相应的需要冻结mean and var参数
pretrained=None, # 预训练配置
init_cfg=None): # 初始化配置
super(Darknet, self).__init__(init_cfg)
if depth not in self.arch_settings:
raise KeyError(f'invalid depth {
depth} for darknet')
self.depth = depth # backbone深度
self.out_indices = out_indices # backbone输出的stage的序号(输出向Neck)
self.frozen_stages = frozen_stages # 哪些层需要冻结权重训练
# 5个stage的重复个数 5个stage的输入channel和输出channel
self.layers, self.channels = self.arch_settings[depth]
# 卷积的配置文件 一般conv_cfg=None norm_cfg=BN act_cfg=LeakyReLU
cfg = dict(conv_cfg=conv_cfg, norm_cfg=norm_cfg, act_cfg=act_cfg)
# backbone的第一层
self.conv1 = ConvModule(3, 32, 3, padding=1, **cfg)
# self.cr_blocks:存放所有的卷积名即通过name可以直接用self.name找到
self.cr_blocks = ['conv1']
# 依次遍历搭建其他的5个stage [1,2,8,8,4]
for i, n_layers in enumerate(self.layers):
layer_name = f'conv_res_block{
i + 1}' # 每一个stage的name
in_c, out_c = self.channels[i] # 每一个stage的输入输出channel
self.add_module( # 调用make_conv_res_block函数,搭建当前stage
layer_name,
self.make_conv_res_block(in_c, out_c, n_layers, **cfg))
self.cr_blocks.append(layer_name) # 更新self.cr_blocks
# 是否将norm layer设置为eval mode 相应的需要冻结mean and var参数
# Note: Effect on Batch Norm and its variants only.
self.norm_eval = norm_eval
assert not (init_cfg and pretrained), \
'init_cfg and pretrained cannot be setting at the same time'
# pretrained=str self.init_cfg 导入预训练初始化配置
if isinstance(pretrained, str):
warnings.warn('DeprecationWarning: pretrained is deprecated, '
'please use "init_cfg" instead')
self.init_cfg = dict(type='Pretrained', checkpoint=pretrained)
# pretrained=None and init_cfg=None 设置为Kaiming初始化配置
elif pretrained is None:
if init_cfg is None:
self.init_cfg = [
dict(type='Kaiming', layer='Conv2d'),
dict(
type='Constant',
val=1,
layer=['_BatchNorm', 'GroupNorm'])
]
else:
raise TypeError('pretrained must be a str or None')
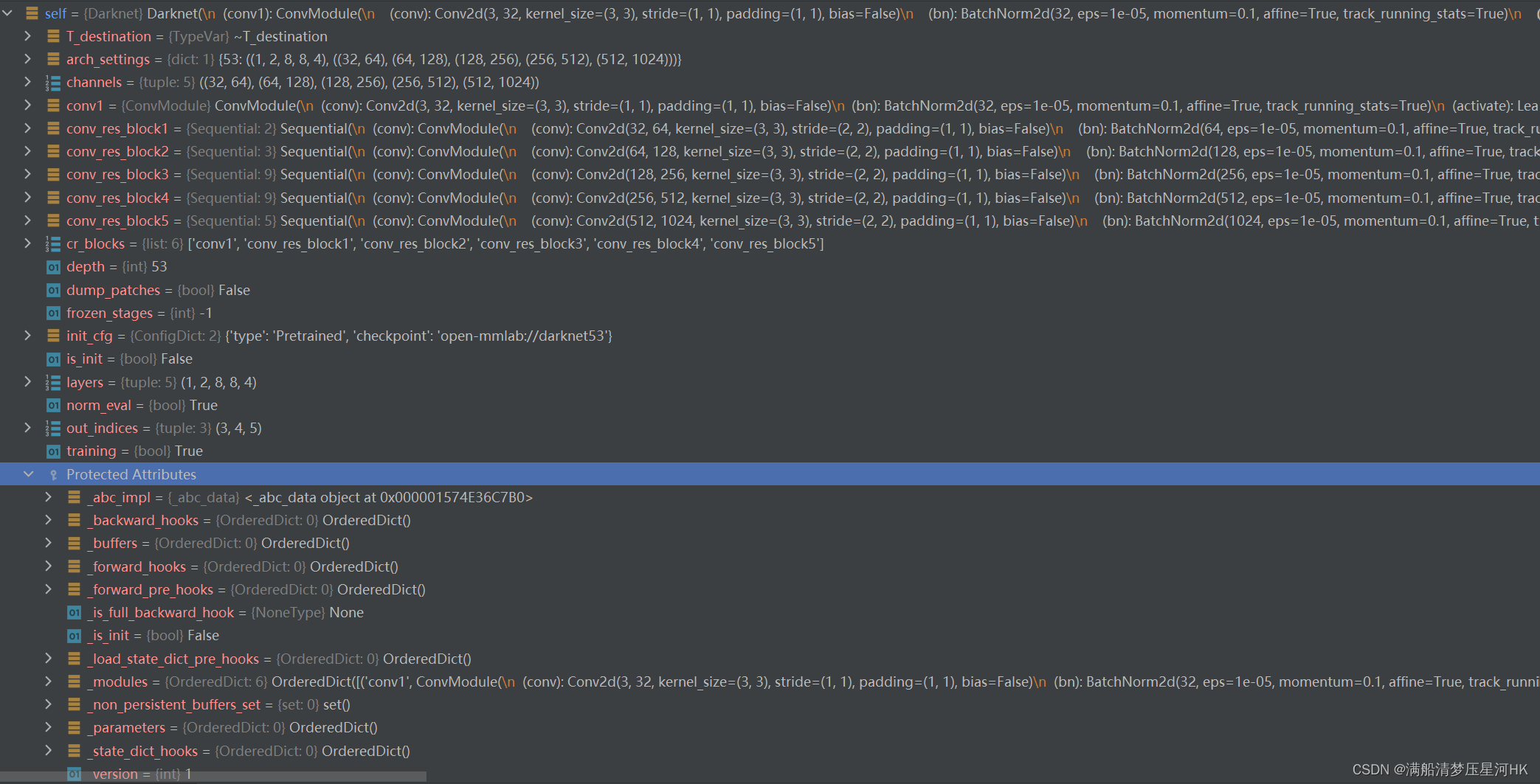
Después de la inicialización, puede ver que existen estas variables en sí mismo (Darknet):
2.3 Razonamiento directo
def forward(self, x):
outs = [] # 存放backbone的3个输出feature map
for i, layer_name in enumerate(self.cr_blocks): # 遍历每一个操作名称
# getattr:返回对象self的一个name=layer_name的属性(就是__init__搭建的一个层结构)
cr_block = getattr(self, layer_name)
x = cr_block(x) # 前向推理
# 如果i in self.out_indices 就将当前层的输出feature map保存到outs
# 值得注意的是i=0就是backbone的第一个卷积层 i=1~5就是后面需要在make_conv_res_block中搭建的5个模块
# 其中第3、4、5三个模块输出到Neck中
if i in self.out_indices:
outs.append(x)
# 返回outs 3个输出feature map会在YOLOV3的forward中传入YOLOv3Neck
return tuple(outs)
2.4, etapa de compilación 1-5
En este punto, combinado con las dos figuras al comienzo del artículo, debe estar muy familiarizado con la estructura de toda la columna vertebral en general. El resto es una pregunta: cómo se construye este stage1-stage5, que involucra dos funciones: make_conv_res_block y ResBlock.
función make_conv_res_block:
@staticmethod
def make_conv_res_block(in_channels, # stage的输入channel
out_channels, # stage的输出channel out_channels=2*in_channels
res_repeat, # 这个stage的ResBlock重复个数
conv_cfg=None, # 卷积配置 一般是None
norm_cfg=dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True), # norm layer配置 一般是BN
act_cfg=dict(type='LeakyReLU', # 激活函数配置 一般是LeakyReLU
negative_slope=0.1)):
"""In Darknet backbone, ConvLayer is usually followed by ResBlock. This
function will make that. The Conv layers always have 3x3 filters with
stride=2. The number of the filters in Conv layer is the same as the
out channels of the ResBlock.
Args:
in_channels (int): The number of input channels.
out_channels (int): The number of output channels.
res_repeat (int): The number of ResBlocks.
conv_cfg (dict): Config dict for convolution layer. Default: None.
norm_cfg (dict): Dictionary to construct and config norm layer.
Default: dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True)
act_cfg (dict): Config dict for activation layer.
Default: dict(type='LeakyReLU', negative_slope=0.1).
"""
# 注意:
# 1、一个stage = Conv(k=3,s=2,p=1) + ResBlock x n
# 2、整个stage在第一个Conv就将feature map的channel上升为了当前stage输入channel的2倍(即当前stage的输出channel)
# wh下采样为输入feature map的一般半 且之后的所有ResBlock部分的feature map wh不变
# {'conv_cfg': None, 'norm_cfg': {'type': 'BN', 'requires_grad': True}, 'act_cfg': {'type': 'LeakyReLU', 'negative_slope': 0.1}}
cfg = dict(conv_cfg=conv_cfg, norm_cfg=norm_cfg, act_cfg=act_cfg)
model = nn.Sequential()
model.add_module( # 搭建当前stage的第一个3x3Conv 下采样卷积
'conv',
ConvModule( # mmcv内置的卷积搭建模块 类似Pytorch中的Conv2d
in_channels, out_channels, 3, stride=2, padding=1, **cfg))
# 依次搭建res_repeat个ResBlock
# 注意这res_repeat个ResBlock中所有的卷积输出channel都是out_channels
for idx in range(res_repeat):
model.add_module('res{}'.format(idx),
ResBlock(out_channels, **cfg))
return model
Función ResBlock:
class ResBlock(BaseModule):
"""The basic residual block used in Darknet. Each ResBlock consists of two
ConvModules and the input is added to the final output. Each ConvModule is
composed of Conv, BN, and LeakyReLU. In YoloV3 paper, the first convLayer
has half of the number of the filters as much as the second convLayer. The
first convLayer has filter size of 1x1 and the second one has the filter
size of 3x3.
Args:
in_channels (int): The input channels. Must be even.
conv_cfg (dict): Config dict for convolution layer. Default: None.
norm_cfg (dict): Dictionary to construct and config norm layer.
Default: dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True)
act_cfg (dict): Config dict for activation layer.
Default: dict(type='LeakyReLU', negative_slope=0.1).
init_cfg (dict or list[dict], optional): Initialization config dict.
Default: None
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels, # ResBlock的输入channel=输出channel
conv_cfg=None, # conv配置 一般为None
norm_cfg=dict(type='BN', requires_grad=True), # norm layer配置 一般为BN
act_cfg=dict(type='LeakyReLU', negative_slope=0.1), # 激活函数配置 一般为LeakyReLU
init_cfg=None): # 初始化配置 一般为None
super(ResBlock, self).__init__(init_cfg)
# 注意:ResBlock = 1x1Conv+BN+LeakyReLU + 3x3Conv+BN+LeakyReLU
# 第一个卷积将channel下降为输入channel一半 第二个卷积将channel恢复到输入channel大小
# 所以整个ResBlock的输入channel和输出channel相等 且整个ResBlock所有的特征的wh都相等
assert in_channels % 2 == 0 # ensure the in_channels is even
half_in_channels = in_channels // 2 # 第一个卷积的输出channel 要下降为输入的一半
# shortcut
cfg = dict(conv_cfg=conv_cfg, norm_cfg=norm_cfg, act_cfg=act_cfg)
self.conv1 = ConvModule(in_channels, half_in_channels, 1, **cfg) # 1x1conv
self.conv2 = ConvModule( # 3x3conv
half_in_channels, in_channels, 3, padding=1, **cfg)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = out + residual
return out
[Salida de la red troncal]

Devuelve tres mapas de características en formato de tensor con formas: [bs, 256, 64, 64], [bs, 512, 32, 32], [bs, 1024, 16, 16], que se pasarán a la capa Neck (FPN) para la fusión de características.
Resumir
Debido a que he estado aprendiendo el código de la serie yolo durante mucho tiempo, he visto muchas versiones de archivos de configuración de yolov3, yolov4 y yolov5, por lo que esta parte es relativamente simple en su conjunto. Básicamente, miré las dos imágenes en el principio, de acuerdo con el código fuente.Comentarios, y luego la depuración puede entender.
Pero, de hecho, hay algunos códigos sobre MMCV que ignoro selectivamente, como BaseModule y ConvModule. Una es que no hay suficiente tiempo, así que solo puedo echar un vistazo al código principal, y la otra es que soy flojo (jajaja), espero poder compensar este hoyo en el código fuente de MMCV en ¡el futuro!