JAVA implementa el algoritmo MD5, el algoritmo SHA1 y el algoritmo SHA256
MD5, SHA1 y SHA256 son los algoritmos hash más comunes. El hashCode en JAVA es de tipo int y ocupa 64 bits.
MD5 es un algoritmo de cálculo de código hash de 128 bits;
SHA1 es un algoritmo de cálculo de código hash de 160 bits;
SHA256 es un algoritmo de cálculo de código hash de 256 bits.
HashCode de cálculo MD5
package utils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class MD5Utils {
public static String md5Code(String input) {
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
byte[] hash = digest.digest(input.getBytes("UTF-8"));
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < hash.length; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & hash[i]);
if (hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Test
public void test() {
String str = "Welcome";
String res = md5Code(str);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
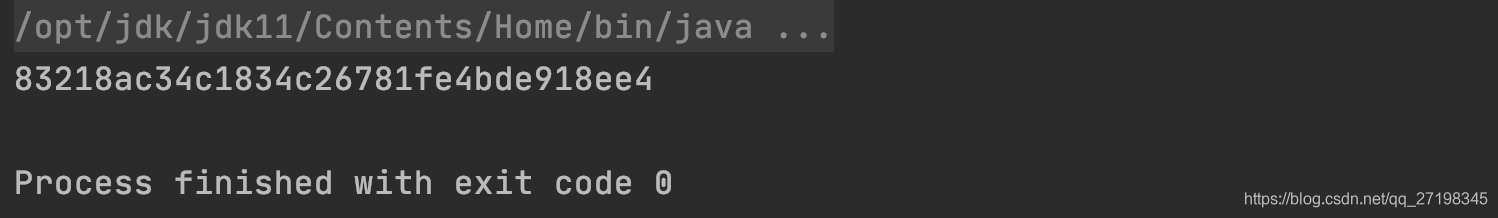
SHA1 calcular hashCode
package utils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class SHA1Utils {
public static String sha1Code(String input) {
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA1");
byte[] hash = digest.digest(input.getBytes("UTF-8"));
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < hash.length; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & hash[i]);
if (hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Test
public void test() {
String str = "Welcome";
String res = sha1Code(str);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
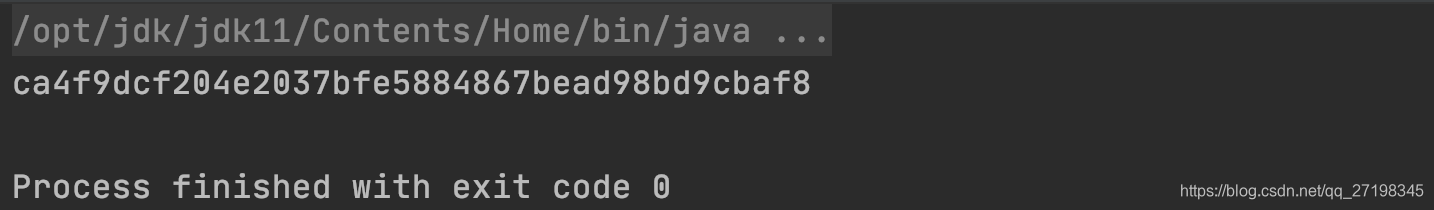
SHA256 calcular hashCode
package utils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class SHA256Utils {
public static String sha256Code(String input) {
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
byte[] hash = digest.digest(input.getBytes("UTF-8"));
StringBuffer hexString = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < hash.length; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & hash[i]);
if (hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Test
public void test() {
String value = "Welcome";
String res = sha256Code(value);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
