Tabla de contenido:
1. Introducción a la pila
1. La definición de pila
Pila : Mesa lineal especial que solo permite insertar y eliminar elementos en un extremo fijo. Un extremo de las operaciones de inserción y eliminación de datos se denomina parte superior de la pila y el otro extremo se denomina parte inferior de la pila . Los elementos de datos de la pila cumplen con el principio LIFO (último en entrar, primero en salir)
• Empujar : la operación de inserción de la pila se llama empujar / empujar , y los datos se colocan en la parte superior de la pila.
• Pop : la operación de eliminación de la pila se llama pop. Los datos de salida también están en la parte superior de la pila.
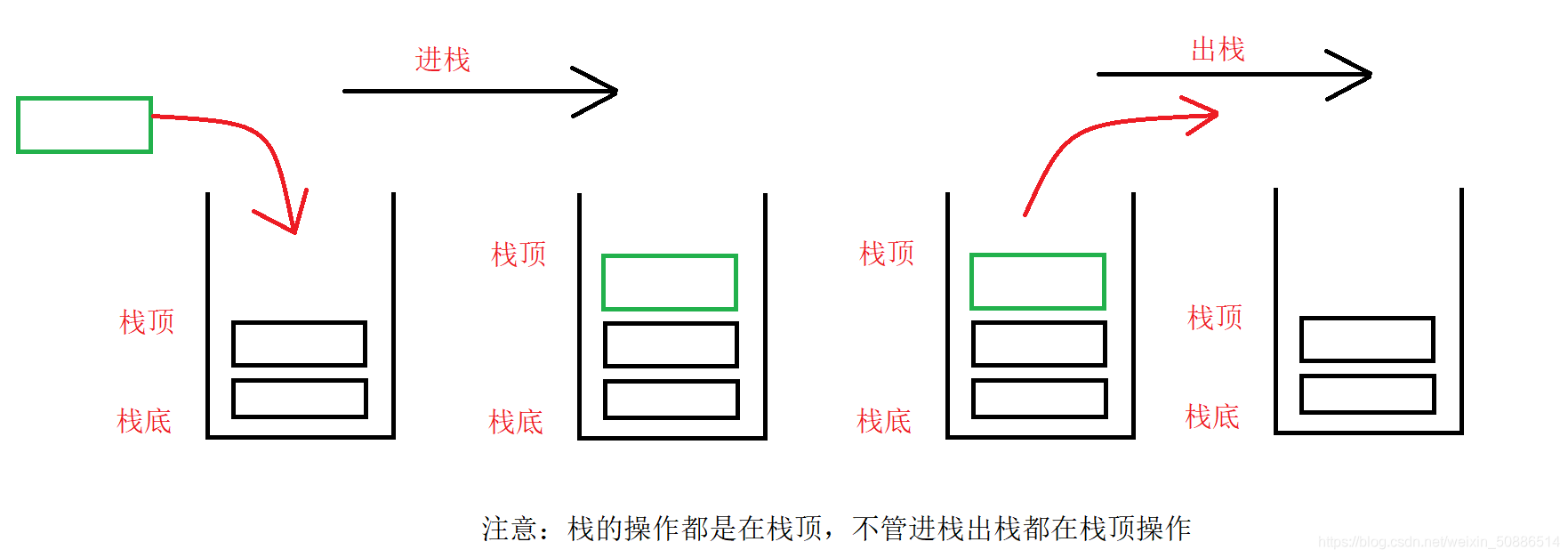
2. Diagrama esquemático de la estructura de la pila y el pop
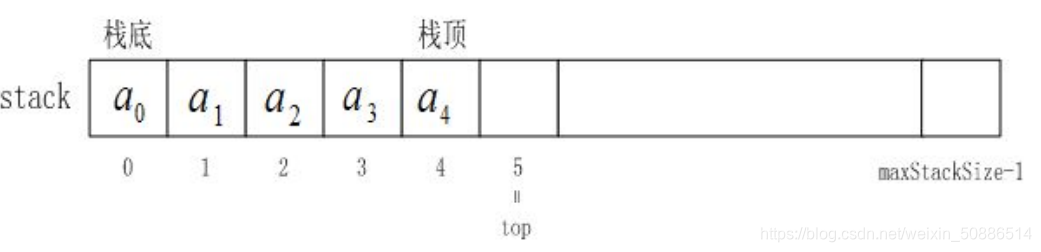
Forma de matriz:
estructura de cadena:
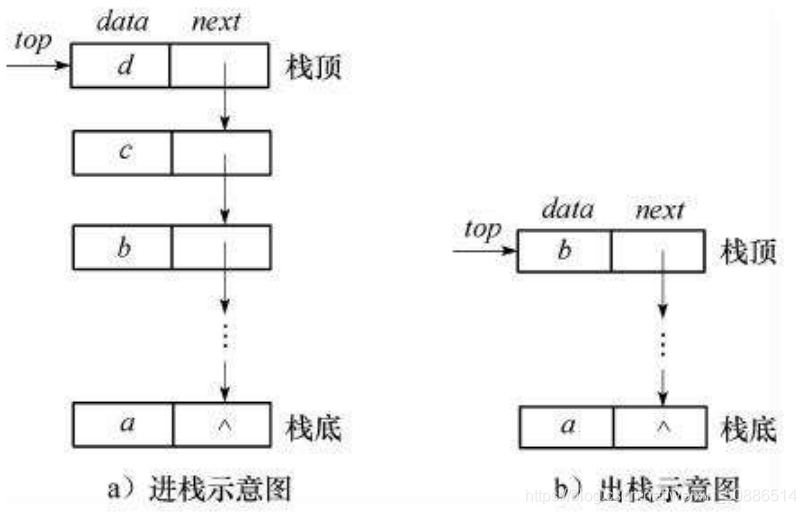
Según la figura, ambas operaciones se realizan en la parte superior
3. Implementación de la pila (se recomienda una matriz)
(1) Gestión e interfaz de pila Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;//动态数组
int top; //栈顶
int capacity; //容量
}Stack;
//初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pst);
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst);
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType data);
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst);
//获取栈中有效元素的个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst);
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
//检测栈是否为空,为空返回1,非空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* pst);
(2) La realización de cada función de interfaz de la pila Stack.c
#include"Stack.h"
//初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType)* 4);
if (pst->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
}
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 4;
}
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType data)
{
assert(pst);
//空间不够需要增容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
//增容为原来的2倍
int* tem = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType)* pst->capacity * 2);
if (tem == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
pst->a = tem;
pst->capacity = pst->capacity * 2;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = data;
pst->top++;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
//判断栈是否为空
//相当于assert(pst->top != 0);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
//获取栈中有效元素的个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
//因为初始化top是0,如果初始化top是-1则返回top+1;
return pst->top;
}
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//检测栈是否为空,为空返回1,非空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
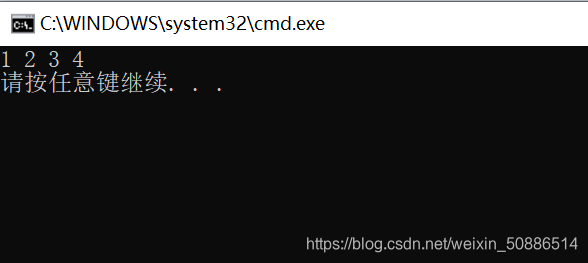
(3) prueba test.c
#include"Stack.h"
void test()
{
//定义一个栈
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
StackPush(&st, 4);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
//取一个删一个
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
}
StackDestroy(&st);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}

2. Introducción a la cola
1. Definición de cola
Cola : una tabla lineal especial que solo permite insertar datos en un extremo y eliminar datos en el otro extremo . La cola sigue el principio de FIFO (primero en entrar, primero en salir)
• En la cola : el final de la operación de inserción se llama el final
de la cola • Fuera de la cola : el final de la operación de eliminación se denomina cabeza de la cola
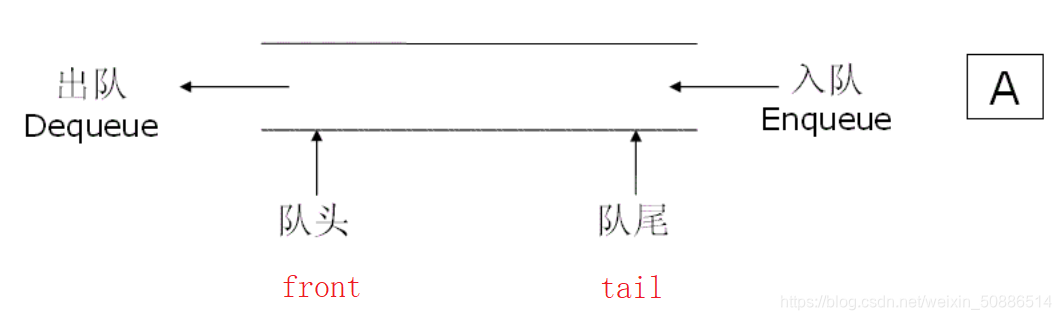
2. Implementación de la cola (se recomienda usar una lista vinculada)
(1) Interfaz y gestión de colas de Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int QDatatype;
//链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDatatype data;
//指向下一个节点的指针
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
//队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* front;//头指针
QueueNode* tail;//尾指针
}Queue;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
//队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x);
//队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//检测队列是否为空,为空返回1,非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//获取队列中有效元素的个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//获取队列头部元素
QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//获取队列队尾元素
QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq);
(2) Implementación de Queue.c de las diversas funciones de interfaz de la cola
#include"Queue.h"
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->front = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->front;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode* Next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = Next;
}
pq->front = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->front = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
//队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//队列不能为空
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//如果只有一个节点,防止tail野指针
if (pq->front == pq->tail)
{
free(pq->front);
pq->front = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//多个节点
else
{
QueueNode* Next = pq->front->next;
free(pq->front);
pq->front = Next;
}
}
//检测队列是否为空,为空返回1,非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->front == NULL ? 1 : 0;
}
//获取队列中有效元素的个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int count = 0;
QueueNode* cur = pq->front;
while (cur)
{
++count;
cur = cur->next;
}
return count;
}
//获取队列头部元素
QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->front->data;
}
//获取队列队尾元素
QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
(3) prueba test.c
#include"Queue.h"
void TestQueue()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
TestQueue();
return 0;
}