1. Propósito
Registre información anormal y registros de operaciones específicas en la base de datos a través de aop y anotación.
2. Introducir dependencias
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>3. Anotaciones personalizadas

4. Aspect define el punto de entrada y el proceso de entrada.
@Aspect
@Component
@EnableAsync
public class SystemLogAspect extends EsgBaseController {
private static Log log = LogFactory.getLog(SystemLogAspect.class);
@Autowired
SysLogService sysLogService;
@Autowired
LogQueue logQueue;
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.mixislink.common.OperationAnnotation)")
public void logPointCut() {}
//@AfterRunning: 返回通知 rsult为返回内容
@Before(value="logPointCut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("调用了前置通知");
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
handle(joinPoint,null,request);
}
//@AfterThrowing: 异常通知
@AfterThrowing(pointcut="logPointCut()",throwing="e")
public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e) {
log.info("调用了异常通知");
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
handle(joinPoint,e,request);
}
// @Async("asyncServiceExecutor")
@Async
public void handle(final JoinPoint joinPoint,final Exception e,final HttpServletRequest request){
SysLog sysLog = new SysLog();
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
OperationAnnotation op = method.getAnnotation(OperationAnnotation.class);
if (op != null){
sysLog.setRemark(op.remark());
sysLog.setSystype(op.sysType());
sysLog.setOpType(op.opType());
}
//请求的 类名、方法名
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
String methodName = signature.getName();
String ip = this.getIpAddress(request);
String url = request.getRequestURI();
String param = getParams(joinPoint);
sysLog.setRequestUrl(url + "&"+ param);
sysLog.setMethod(className + "." + methodName + "()");
sysLog.setIpAddress(ip);
try {
if (e != null){
sysLog.setRemark(e.getMessage());
sysLog.setLogType(1);
logQueue.add(sysLog);
}else {
if (!op.onlyErr()){
sysLog.setLogType(0);
logQueue.add(sysLog);
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("handle systemLog 出现异常",ex);
}
}
public String getIpAddress(HttpServletRequest request){
String ipAddress = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for");
if(ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if(ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if(ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getRemoteAddr();
if(ipAddress.equals("127.0.0.1") || ipAddress.equals("0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1")){
//根据网卡取本机配置的IP
InetAddress inet=null;
try {
inet = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ipAddress= inet.getHostAddress();
}
}
//对于通过多个代理的情况,第一个IP为客户端真实IP,多个IP按照','分割
if(ipAddress!=null && ipAddress.length()>15){ //"***.***.***.***".length() = 15
if(ipAddress.indexOf(",")>0){
ipAddress = ipAddress.substring(0,ipAddress.indexOf(","));
}
}
return ipAddress;
}
public String getParams(JoinPoint joinPoint){
ParameterRequestWrapper requestWrapper = (ParameterRequestWrapper) joinPoint.getArgs()[0];
Map map = requestWrapper.getParameterMap();
return map != null ? JSON.toJSONString(map): null;
}Aquí hablamos de que se llamará a Before antes de que se ejecute el método, se llamará a AfterThrowing cuando se lance una excepción. Lo más importante es que si detecta la excepción con try catch en su método, no irá a AfterThrowing, a menos que usar manualmente throw in the catch para reiniciar Lanzando una excepción , este problema me ha molestado durante mucho tiempo.
Luego agregué un campo onlyErr en el comentario. Cuando es verdadero, solo registrará cuando el método tenga una excepción. Cuando es falso, no solo registrará la excepción, sino que también registrará el registro de operaciones personalizado, de modo que yo Solo desea registrar la excepción pero no desea registrarla. Simplemente agregue este campo al registro de operaciones.
5. Inicie el procesamiento de la cola e inserte periódicamente registros en la base de datos por lotes.
@Slf4j
@Component
public class LogTask {
@Autowired
LogQueue logQueue;
@Autowired
SysLogService sysLogService;
private volatile List<SysLog> operLogs = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 500)
public void logFixDelay(){
//获取日志信息
while (true){
SysLog operLog = logQueue.poll();
if(null==operLog){
break;
}
operLogs.add(operLog);
}
if(operLogs.size()>0){
try{
log.info("######################批量添加系统日志"+operLogs.size());
sysLogService.insertAll(operLogs);
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("批量添加系统日志异常:",e);
operLogs.clear();
}
operLogs.clear();
}
}
}6. Herramientas
@Component
public class LogQueue {
//LinkedList实现了Queue接口,可以用LinkedList做一个队列,这里使用阻塞队列BlockingQueue
private volatile Queue<SysLog> dataQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
//添加日志信息
public void add(SysLog logininfor) {
dataQueue.add(logininfor);
}
//获取日志信息,用于插入到数据库中。
public SysLog poll() { return dataQueue.poll(); }
}7. Esto se completa básicamente, el uso es el siguiente:
@RequiresPermissions("sys:sysLog:list")
@OperationAnnotation(remark = "分页查询SysLog信息",sysType = 1,opType = 4)
@RequestMapping(value = "/selectAll",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public HttpEntity selectAll(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
EngineParameter ep = initParameter(request);
try {
return sysLogService.selectAll(ep);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("SysLog",e);
throw e;
}
}Agregue las anotaciones @OperationAnnotation donde desee iniciar sesión, ¡y eso es todo! ! !
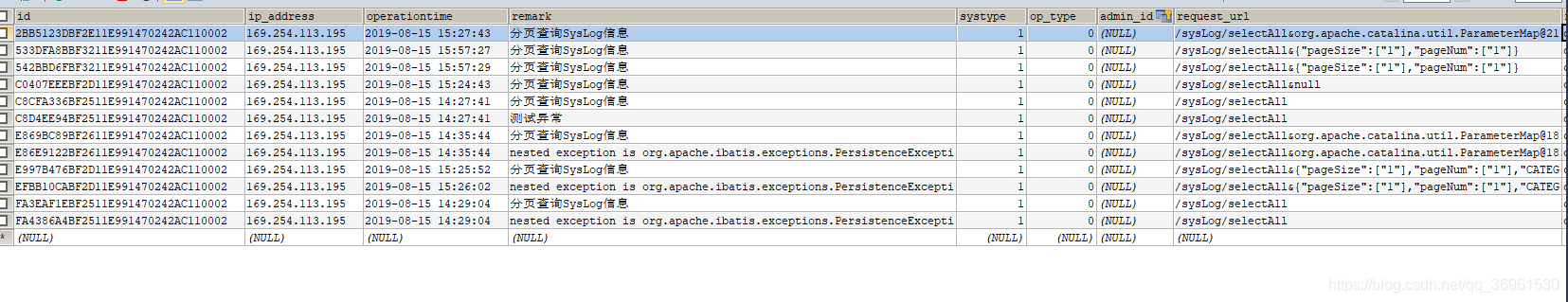
El efecto es el siguiente