Directorio de artículos
Uso del grupo de subprocesos ThreadPoolExecutor
Uso del grupo de subprocesos ThreadPoolExecutor
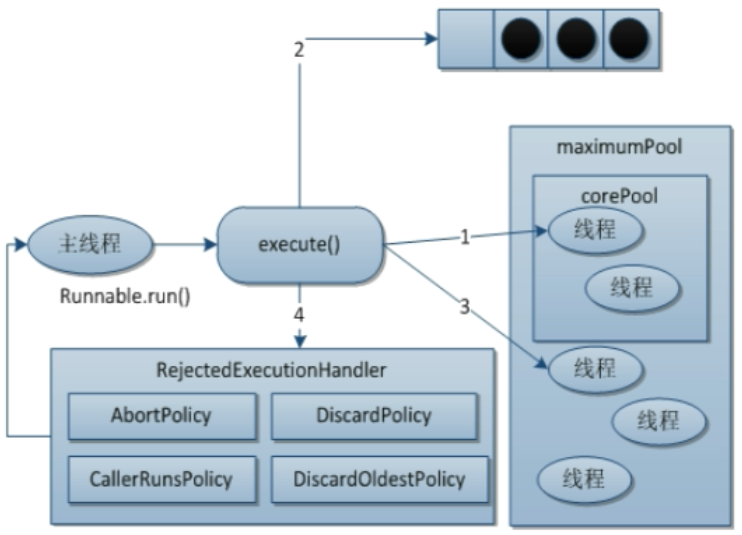
El siguiente código está basado en JDK1.8.
package thread;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* 第四种使用Java多线程的方式,线程池
*/
public class MyThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Fixed Thread Pool");
fixedThreadPool();
System.out.println("Single Thread Pool");
singleThreadPool();
System.out.println("Cached Thread Pool");
cachedThreadPool();
System.out.println("Custom Thread Pool");//自定义的线程池
customThreadPool();
}
private static void customThreadPool() {
ExecutorService threadPool=
new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,
5,
1L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t办理业务");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
private static void cachedThreadPool() {
//不定量线程
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t办理业务");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
private static void singleThreadPool() {
//一池1个线程
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t办理业务");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
private static void fixedThreadPool() {
//一池5个线程
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//一般常用try-catch-finally
//模拟10个用户来办理业务,每个用户就是一个线程
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t办理业务");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
prueba
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Custom Thread Pool");
customThreadPool();
}
private static void customThreadPool() {
ExecutorService threadPool=
new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,
5,
1L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t办理业务");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
correr
Custom Thread Pool
pool-1-thread-2 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-2 办理业务
pool-1-thread-2 办理业务
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务
pool-1-thread-3 办理业务
pool-1-thread-4 办理业务
pool-1-thread-2 办理业务
pool-1-thread-5 办理业务
Al simular 15 usuarios para manejar negocios, cada usuario es un hilo de solicitud externo
//模拟15个用户来办理业务,每个用户就是一个来自外部的请求线程
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t办理业务");
});
}
rejectedExecutionEn este momento se lanzó una excepción.
Si no se lanza ninguna excepción, intente varias veces.
Por que utilizar un grupo de subprocesos personalizado
