The input and while using python
A, Python input () function: obtaining user input string
Python3.x in input () function accepts a standard input data, return type string.
Python2.x in input () is equal to eval(raw_input(prompt)), for acquiring the input console.
the raw_input () will look at all the input as a string, return a string type. The input () having its own characteristics in the treatment of a pure digital input, it returns the type of the input digital (int, float).
Note: input () and the raw_input () function can receive the two strings, but the raw_input () reads the direct input console (any type of input that can be received). As for the input (), it hopes to be able to read a legitimate expression of python, that when you enter the string you must use quotation marks to enclose it up, otherwise it will lead to a SyntaxError.
Unless) there is special need for input (, otherwise we are generally recommended to use raw_input () to interact with the user.
Note: python3 in input () received a default str type.
Function Syntax
input([prompt])Parameter Description:
- prompt: prompt
Solve the problem:
- input data obtained in the end is what type
- Receiving input of a plurality of input parameters, it is how to unpack
- If the number of uncertain input, how to deal with
- To determine whether the input is not a float
- To the input format of the output parameters, the parameters can be predetermined, or a float or int str
1, an example
# 用户输入
# 提示输入内容
pet = input ('请输入您最喜欢的宠物名称:')
print(pet)Output:
请输入您最喜欢的宠物名称:猫咪 猫咪
2, lucky number
In python 3 years, things got everything input, are str type (available type () type of view)
good_luck_num = input('请输入你的吉祥号码:')
print(type(good_luck_num))
print('您输入的是:'+good_luck_num)Output:
请输入你的吉祥号码:9898998 <class 'str'> 您输入的是:9898998
There are input and raw_input in python2 in
- raw_input enjoy are the type str
- automatically generates input type according to the type of input data
We can use Python's built-in function to convert a string into a desired type, such as:
- int (String) String to be converted int type;
- float (String) String to be converted float type;
- bool (String) String to be converted bool type.
3, was selected supermarkets
print('---------超市购物系统---------')
print('1.电子产品 2.化妆品 3.生活用品 4.书籍')
# print('请选择您要购买的产品类型:')
product_type = input('请选择您要购买的产品类型:')
# 判断输入的序号
if product_type == '1':
print('电子产品')
elif product_type =='2':
print('化妆品')
elif product_type =='3':
print('生活用品')
elif product_type =='4':
print('书籍')
else:
print('只能输入1~4的数字')Output:
---------超市购物系统--------- 1.电子产品 2.化妆品 3.生活用品 4.书籍 请选择您要购买的产品类型:4 书籍
4, small practice
(1) Write a program that asks the user's favorite job in the IT industry, and outputs a message such as: "My favorite position is the Python automated operation and maintenance."
gz = input('您最喜欢的IT从业岗位:')
print('我最喜欢的岗位是'+gz)Output:
您最喜欢的IT从业岗位:Python自动化运维 我最喜欢的岗位是Python自动化运维
(2) Write a program that asks students to complete homework today yet? If you enter "y", the output "Today's job done"; if you enter "no", then the output "Today's work will take some time to complete."
zy = input('今天的作业完成了吗?:(y/n)')
if zy == 'y':
print('今天的作业完成了')
elif zy == 'n':
print('今天的作业还需要一段时间才能完成')Output:
今天的作业完成了吗?:(y/n)y 今天的作业完成了
(3) allows the user to enter a three-digit output this number is not a palindrome.
num = input('输入一个三位数')
num2 = num[::-1]
print(num2)
if num == num2:
print('这是个回文数')
elif num != num2:
print('这是个普通数字')Output:
输入一个三位数121 121 这是个回文数
Two, Python While Loops
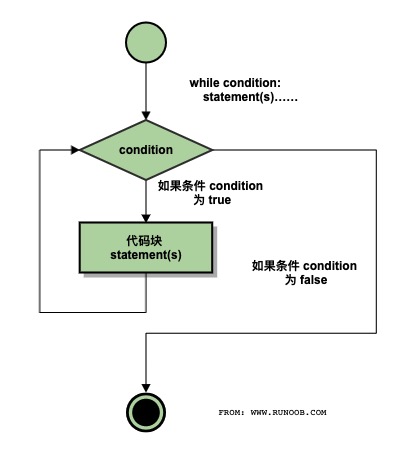
Python programming while statement for executing a program loop, i.e., under certain conditions, implementation of certain program loop, the same processing task needs to repeat the process. The basic form:
while 判断条件(condition):
执行语句(statements)……Execute statement may be a single statement or a block. Determination condition can be any expression, in any non-zero value, or a non-empty (null) are true.
When the determination condition false false, the cycle ends.
Performing the following flow chart:
Gif demonstration Python while statement is executed

A bit more complex:

1, examples: (while loop: If this thing is repetitive to do)
num = 1
while num<10:
print(num,end=" ")
num = num+1Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2, while loop, calculates the sum of the even-numbered 1-100.
#创建一个变量x初始化为2
x = 2
#创建一个变量sum初始化为0
sum = 0
#使用while循环求出0-100所有偶数的和
while x <= 100 :
sum += x
x += 2
#打印输出求和结果
print(sum)Output:
2550
3. Write a program to simulate user login, authentication username and password, maximum input for 3 times, otherwise lock the user.
count = 3
users= 'xgp'
password= '123.com'
i = 3
while i > 0 and i < 4:
# 输入提示
user = input('请输入您的用户名:')
passwd = input('请输入您的密码:')
# 判断用户名和密码
if user == users and passwd == password:
print('登陆成功')
break
else:
# 登陆统计次数
i = i - 1
if i == 0:
print('账号锁定')相比较上面的简单一点 count = 3 while count>0: name = input('请输入用户名:') password = input('请输入密码:') if name == 'xgp' and password == '123.com': print('通过验证,即将登陆......') break else: count = count - 1 print('还剩'+str(count)+"次机会")
Output (1):
请输入您的用户名:1 请输入您的密码:1 请输入您的用户名:1 请输入您的密码:1 请输入您的用户名:1 请输入您的密码:1 账号锁定
Output (2):
请输入您的用户名:xgp 请输入您的密码:123.com 登陆成功
Three, while the loop processing lists and dictionaries
The for loop is an effective way through the list, but in a for loop should not modify the list, otherwise it will lead to Python difficult to track its elements. To modify while traversing the list, you can use a while loop.
By the while loop combined with the use of lists and dictionaries, can collect, store and organize a lot of output, and display for later viewing.
1, similar to the copy list
users = ['alpha','byta','gima']
users_shadow = []
while users:
current_user = users.pop()
users_shadow.append(current_user)
print(users_shadow)Output:
['gima', 'byta', 'alpha']
for replication cycle
for i in users:
users_shdow.append(i)
print(users_shadow)Output:
['gima', 'byta', 'alpha']
2, delete the specified list of elements among the
users = ['alpha','byta','gima']
print(users)
while 'byta' in users:
users.remove('byta')
print(users)Output:
['alpha', 'byta', 'gima'] ['alpha', 'gima']
3. Create a survey program, each cycle when prompted to enter the name and answer the survey, the collected data will be stored in a dictionary
# 创建一个空字典
responses = {}
# 设置标志:表示调查是否继续
flag = True
# 循环操作
while flag:
#提示输入接受调查的名字和回答
name = input('请输入您的名字:')
response = input('清输入您的答案:')
# 将答案存储到字典中
responses[name] = response
# 是否还有人需要参加调查
repeat = input('是否还有人需要参加调查:(yes/no)')
if repeat == 'no':
flag = False
# 显示调查结果
print('\n-------------------调查结果-------------------')
for name,response in responses.items():
print(name + ">>>" + response)Output:
请输入您的名字:wsd 清输入您的答案:123 是否还有人需要参加调查:(yes/no)yes 请输入您的名字:wushaox 清输入您的答案:x 是否还有人需要参加调查:(yes/no)no -------------------调查结果------------------- wsd>>>123 wushaox>>>x