Business technology architecture
Architecture implementation
A gateway layer
Is a processing request for different network protocols on the nature of the gateway layer protocol such as HTTP, TCP protocol, of course, other protocols may be processed. Specifically shown below:
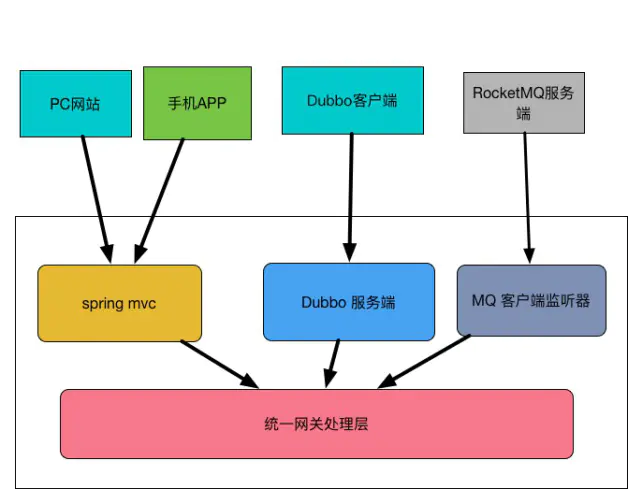
1.HTTP request
General requests from PC end and APP are based on the HTTP protocol for handling HTTP requests program, the industry is already very mature. First, the container itself Tomcat HTTP request processing complexity of the package out,
Secondly, spring mvc request process provides for RESTful encoding greatly reduces the complexity of development. All we do is for the controller in accordance with the division of business areas, such as in accordance with the order, membership to divide large areas, a variety of methods which is operating in this field.
Gateway controller here is uniform treated layer, each controller for only three things a method, first, the request is parsed and assembled into parameter internal parameters, the second call to the underlying business logic of the service execution, returns the result of the third assembly,
For unusual circumstances, need to record and convert the exception stack logs the error code, do not expose the stack information to the caller.
2.TCP request
For TCP request processing program, the industry has also been very mature, such as Netty. However, the underlying TCP requests after all, too, we tend to develop their own protocol based on the TCP protocol. In addition, many distributed framework is based on the TCP protocol,
For example RPC frame Dubbo, message frame RocketMQ like. From standalone systems to distributed systems, multi-layer gateway is nothing more than the logical processing TCP requests, in theory, the underlying business is no need to perceive themselves in the end for a stand-alone environment or a distributed environment,
A gateway to the shield layer is different call details of such an external source. In Dubbo server, we need to implement a remote interface and remote service call forwarding internal forwarding logic is very simple, first of all is to parse the parameters and assembling the internal parameters,
Interface performs service logic then calls the service layer, final assembly returns the result, exception handling is also required to do out here, to prevent abnormal exposure to external applications.
to sum up:
Gateway protocol layer processed essentially simultaneously converge to the business logic layer gateway, not exposed to the outside when the internal business logic reconstructed external caller does not need to perceive these changes,
When an external call source increases, the internal service logic does not need to change this perception, so that the internal and external caller business logic decoupling.
II. Business Layer
Business layer is a system, whether it is a local business systems, business layer single system or distributed systems group are carrying business processes and rules.
Service from outside to inside layer comprising three layers: a service business, the business process is the second layer, the third layer is a business component. FIG follows:
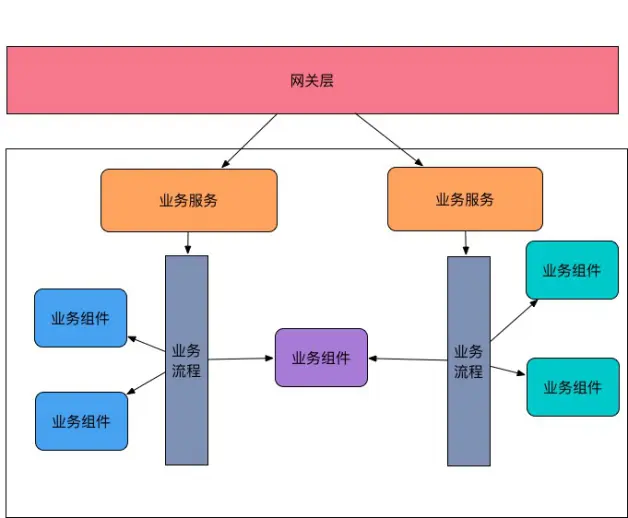
1. Business Services
Business is business services layer of uniform external facade, which consists of three areas: the business interface, the Senate and the parameters.
a) Service Interface
A service interface represents one area of business services, such as order domain of business services, says the interface OrderService, members of the business domain service is represented by the interface MemberService.
The interface can be divided into read and write interfaces to perform in accordance with the nature of the interface, such as OrderReadService and OrderWriteService. Separation of the benefits of reading and writing can be read and written to cluster groups to manage traffic, of course, read and write separate stand-alone system is not much significance.
The method embodied in the form of field service interface operation places, such as the single domain has the createOrder orders, cancel orders, etc. cancelOrder operation.
For these operations, try to devise methods have business meaning, rather than CRUD, of course, for some simple business, can only CRUD.
b) the parameters
Next, it is the reference design. For read into the reference method is relatively simple, not discussed. For the write method, we have designed the reference-level data model.
You first need to design a common data model, such as order data model, business data models, data models and other merchandise, and then the character data in the data model and certain business combination, the composition of the Request object,
The service request object in a different operation differ, the corresponding result is returned Response, which is also returned with the different parameters for different services.
for example:
拿下餐饮订单来说,首先,我们应该识别出这些业务流程中一些比较基础的数据模型,比如餐饮领域的菜品、桌位等,这些模型之所以说是基础模型,
是因为,不管下什么餐饮订单,菜品和桌位肯定是逃不了的,它们是可以被复用的!因此,我们分别为这些基础模型设计相对于的DO(Domian Object):DishDO(菜品)、BoardDO(桌位)等等,
接下来,我们为下餐饮订单设计一个请求对象DishOrderCreateRequest其中DishOrderCreateRequest内部包含了DishDO和BoardDO,另外会包含一些特定的属性,比如人数啊,折扣啊等等,
这样一来就能做到通用和灵活兼顾,DishOrderCreateRequest代表的个性化的灵活的业务入参,而DishDO和BoardDO等则代表了不易变化的基础模型。
c) 出参
最后,是出参的设计。对于写方法,一般出参比较简单。对于读方法,出参往往是一个结构与层次比较复杂的组合对象。
比如查询一个订单,这个订单有订单基本信息,还有商品信息,收货人地址信息等。在设计出参的时候,结构上要设计成组合对象,但是真正查询的时候,通过查询选择器,去查询不同的组合对象。
比如查询选择器设置商品查询为true,地址查询为false,那么这次查询出的订单就只包含商品,而不包含地址。
2.业务流程
业务流程其实就是对业务规则的解释,只是这种解释使用代码去实现的,我们要做的其实就是准确翻译这些业务规则,并维护好这些业务规则。
业务流程中可以大致分为三种动作节点,1、组装参数节点;2、规则判断节点;3、执行动作节点;其中每个动作节点都是一些业务代码的片段。
举个例子:
下餐饮订单,我们第一步就是将上层传入的参数组装出一个基础的DishOrderDO(组装参数节点),然后按照特定的规则去填充这个DishOrderDO(规则判断节点),然后就是调用DAO去创建DishOrderDO(执行动作节点)。
业务流程是最容易变化的地方,要想维护好业务流程并不容易,总的思想是将大的业务流程拆分成小的业务流程,抽出每个业务流程中共有的代码片段,变成可维护的业务组件。
3.业务组件
a) 基础组件
业务组件其实是将一些内聚的可复用的代码片段进行封装。和业务流程中的三种业务节点相对应,业务组件也分为三种:组装参数组件 、规则判断组件 、动作执行业务组件。
业务组件的抽象往往是对业务有了深刻理解之后才进行的,盲目地进行业务组件的抽象,往往到头来白忙活。
b) 能力
对业务组件进行进一步抽象,可以得到能力。业务能力是具有一定复用性的组件的组合,比如发短信能力=组装短信参数组件+发短信组件。对于发短信能力,可以被不同的业务流程复用,
比如订单下单成功发短信,支付成功发短信,逻辑都是相似的,只有内容不同。
能力是一种粒度比较大的组件,粒度越大,往往复用性就越小,对能力的抽取,也是基于对特定业务深刻的理解,没有一劳永逸的银弹。
c)更高纬度的抽象
对于互联网这样的需求变化极快的场景,更高纬度的组件抽象往往性价比很低,不建议大家去做。
三.基础层
基础层包含两个部分,第一是接口定义,第二是技术组件。
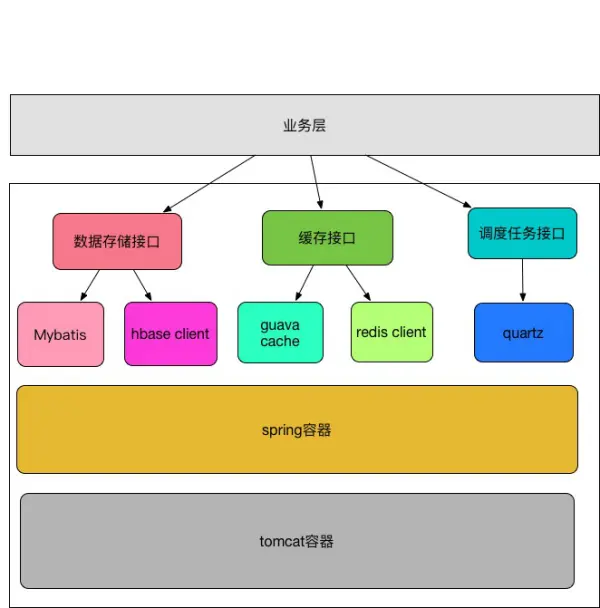
1.接口定义
接口定义是按照不同的技术框架,同时结合业务需要,设计出合理的接口,对于业务组件来说,它们只会感知技术接口,而不会去感知技术实现,我们也不应该将具体的技术细节向上暴露,
这也就是所谓的面向接口编程。技术接口往往是业务与技术之间的桥梁,接口本身是含有业务含义的,最常见的就是DAO接口,我们设计DAO接口的时候,
不会设计成insert、update、query这样业务无关的接口,而是设计成insertUser,updateUserById等等和业务相关的接口,
同样的道理,设计缓存接口的时候,也不能设计成put、get这样的接口,而应该设计成cacheUser,deprecateUser这样的接口。
2.技术组件
单机系统的技术组件一般来说分两种,一种是通用的技术组件,比如:数据存储、缓存、消息和调度任务、事务、锁。一种是基础设施,比如spring容器,tomcat容器。
下面稍微谈谈通用技术组件。
数据存储:数据存储包括关系型数据库、非关系型数据库以及文件存储系统。关系型数据库,比如MySQL,适合存放绝大部分业务数据。非关系型数据库,
比如hbase,可以存放历史日志,也可以对历史的MySQL数据进行归档。文件存储系统,一般都是基于Linux文件系统,比如图片、html文件等等,也有基于HDFS的,用于大数据分析。
缓存:缓存按响应时间分,可以分为纳秒级缓存,毫秒级缓存和百毫秒级缓存。纳秒级缓存就是一般的基于本地内存的缓存,
比如encache,毫秒级缓存一般是集中式的内存缓存,比如memcache,由于访问时远程调用,因此响应时间会延长到几毫秒,百毫秒级缓存一般是集中式可持久化的缓存,
比如redis,由于存在远程访问以及缓存击穿导致的读取持久化记录,它的响应时间会更长些,到几十甚至上百毫秒。单机系统一般用本地内存缓存就够了,当缓存被击穿的时候,直接访问数据库。
消息和调度任务:消息和调度任务本质都是一种异步化的手段,区别在于消息无法控制异步的时间,而调度任务可以。一般,消息发送出去后,监听消息的系统会立即收到消息,
从而立即触发业务逻辑的执行,而调度任务则会按照调度规则,一次或者多次的执行业务逻辑。单机系统中消息和调度任务用到的比较少,在做日志监控的时候可能会用到消息,在进行数据报表统计的时候可能会用到调度任务。
事务:事务本质都是基于数据库去实现的,单机系统的事务就是依赖数据库的事务,我们可以使用spring-tx的事务模板进行事务操作,
在业务逻辑开发中,一定要把握事务的大小,建议把业务比较紧密的一堆数据库操作放在一个事务里,不要随意的为每个方法都开启事务。
锁:单机系统中主要用到两种锁:乐观锁和悲观锁。乐观锁依靠在数据库的业务表加版本字段来实现,每次更新都会去判断版本是否变化,
如果变化则需要重试,这种锁的粒度比较小。悲观锁是基于JDK的Lock接口的,对一个业务流程进行加锁和释放锁的操作,锁的粒度比较粗。