A copy of the array
The arraycopy function (), parameters: the source array start index, the start index of the source array, the target array, the target array, the copy length
package com.bjpowernode.java_learning; public class D68_1_CopyOfArrays { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a1 = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; int[] a2 = {10,11,12,13,14,15,16}; System.arraycopy(a1,2,a2,3,3); for(int i=0;i<a2.length;i++) { System.out.println(a2[i]); } } }

Second, the two-dimensional array initialization and traverse
Features 1. The two-dimensional array
(1) two-dimensional array is a special one-dimensional array
(2) a special one-dimensional array, in particular the one-dimensional array each element is a one-dimensional array
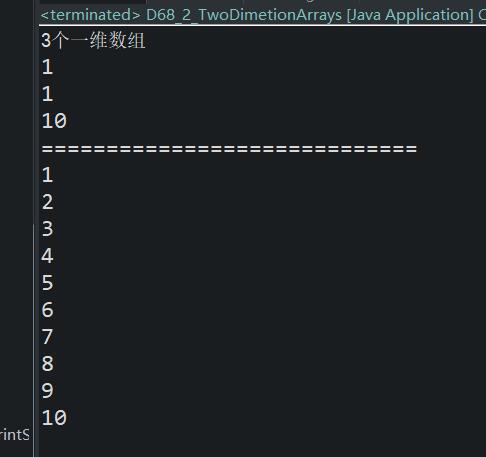
Package com.bjpowernode.java_learning; public class D68_2_TwoDimetionArrays { public static void main (String [] args) { int [] [] A = {{l, 2,3}, {4,5,6}, {. 7, 8,9,10 }}; // above the array the number of one-dimensional array System.out.println (a.length + "one-dimensional array" ); // get the first one-dimensional array of a first element int [] A0 = a [0 ]; int A00 A0 = [0 ]; System.out.println (A00); System.out.println (a [ 0] [0 ]); // get the last one-dimensional the last element of the array System.out.println (a [a.length -1] [a [-a.length. 1]. 1-.length]); //遍历二维数组 System.out.println("============================="); for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { for(int j=0;j<a[i].length;j++) { System.out.println(a[i][j]); } } } }
Third, the dynamic two-dimensional array initialization
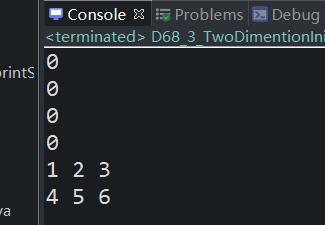
package com.bjpowernode.java_learning; public class D68_3_TwoDimentionInitial { public static void main(String[] args) { //3个一维数组 //每个一维数组中有4个元素 int[][] a = new int[2][2]; //遍历 for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { for(int j=0;j<a[i].length;j++) { System.out.println(a[i][j]); } } m1(new int[][] {{1,2,3},{4,5,6}}); } public static void m1(int[][] a) { for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { for(int j=0;j<a[i].length;j++) { System.out.print(a[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } } }
四、源码:
D68_1_CopyOfArrays.java
D68_2_TwoDimetionArrays.java
D68_3_TwoDimentionInitial.java
https://github.com/ruigege66/Java/blob/master/D68_1_CopyOfArrays.java
https://github.com/ruigege66/Java/blob/master/D68_2_TwoDimetionArrays.java
https://github.com/ruigege66/Java/blob/master/D68_3_TwoDimentionInitial.java
2.CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44630050
3.博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/ruigege0000/
4.欢迎关注微信公众号:傅里叶变换,个人公众号,仅用于学习交流,后台回复”礼包“,获取大数据学习资料
