1.TestNG common comment
@Test a class marker or as part of the test method
@BeforeMethod annotated method will be run before each test method run
@AfterMethod annotated method will be run after each test method run
@BeforeClass annotated method will be run only once, before calling all methods run in the current class
@AfterClass annotated method will be run only once, after the call to run all the methods in the current class
@BeforeSuite tag method: run before a test suite (suite) begin
@AfterSuite tag method: After running a test suite (suite) all test method execution
@BeforeGroups this method is to ensure that these belong to any group running a test method that is called
After @AfterGroups this method is to ensure that the operation of any of these groups belong to the last test method that is called
@BeforeTest is operated for the xml file test label, a test run before each execution tag in xml
@AfterTest is operated for the xml file test label, the label run after each test performed in xml
Code Example 1.1
. 1 public class BasicAnnotince { 2 // basic annotations, the method used to mark a portion of the test . 3 @Test (Groups = ". 1" ) . 4 public void TestCase1 () { . 5 System.out.println ( "I test use Case. 1 " ); . 6 } . 7 @Test (Groups =" 2 " ) . 8 public void testCase2 () { . 9 System.out.println (" I test 2 " ); 10 } . 11 @BeforeMethod 12 is public void beforeMethod1 ( ) { 13 System.out.println ( "beforeMethod- run before each test case execution" ); 14 } 15 @AfterMethod 16 public void afterMethod2 () { . 17 System.out.println ( "afterMethod- run after each test case execution " ); 18 is } . 19 @BeforeClass 20 is public void beforeClass1 () { 21 is System.out.println (" beforeClass1- called before the current method for operating class " ); 22 is } 23 is @AfterClass 24 public void afterClass1 () { 25 the System .out.println ( "afterClass1- called after running all the methods in the current class."); 26 is } 27 @BeforeSuite 28 public void beforeSuite1 () { 29 System.out.println ( "beforeSuite run" ); 30 } 31 is @AfterSuite 32 public void afterSuite1 () { 33 is System.out.println ( "Run afterSuite a " ); 34 is } 35 @BeforeTest 36 public void beforeTest1 () { 37 [ System.out.println (" beforeTest- run before beginning the test method " ); 38 is } 39 @AfterTest 40 public void afterTest1() { 41 System.out.println("afterTest1-在测试方法结束之后运行"); 42 } 43 @BeforeGroups("1") 44 public void beforeGroups() { 45 System.out.println("beforeGroups-111111"); 46 } 47 @AfterGroups("1") 48 public void afterGroups() { 49 System.out.println("afterGroups-111111"); 50 } 51 }
1.2 operating results

2. Test Kit
Code Example 2.1
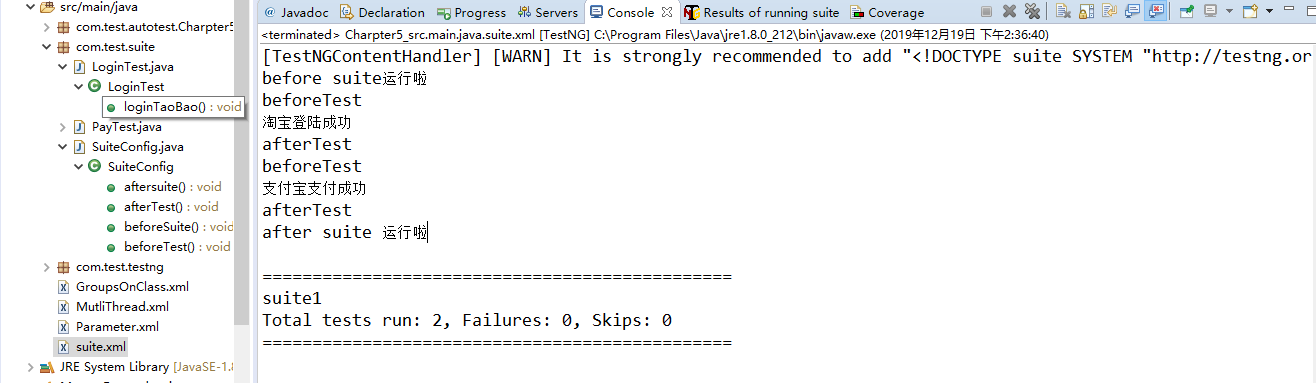
1 public class SuiteConfig { 2 @BeforeSuite 3 public void beforeSuite(){ 4 System.out.println("before suite运行啦"); 5 } 6 7 @AfterSuite 8 public void aftersuite(){ 9 System.out.println("after suite 运行啦"); 10 } 11 12 @BeforeTest 13 public void beforeTest(){ 14 System.out.println("beforeTest"); 15 } 16 17 @AfterTest 18 public void afterTest(){ 19 System.out.println("afterTest"); 20 } 21 }
2.2 operating results
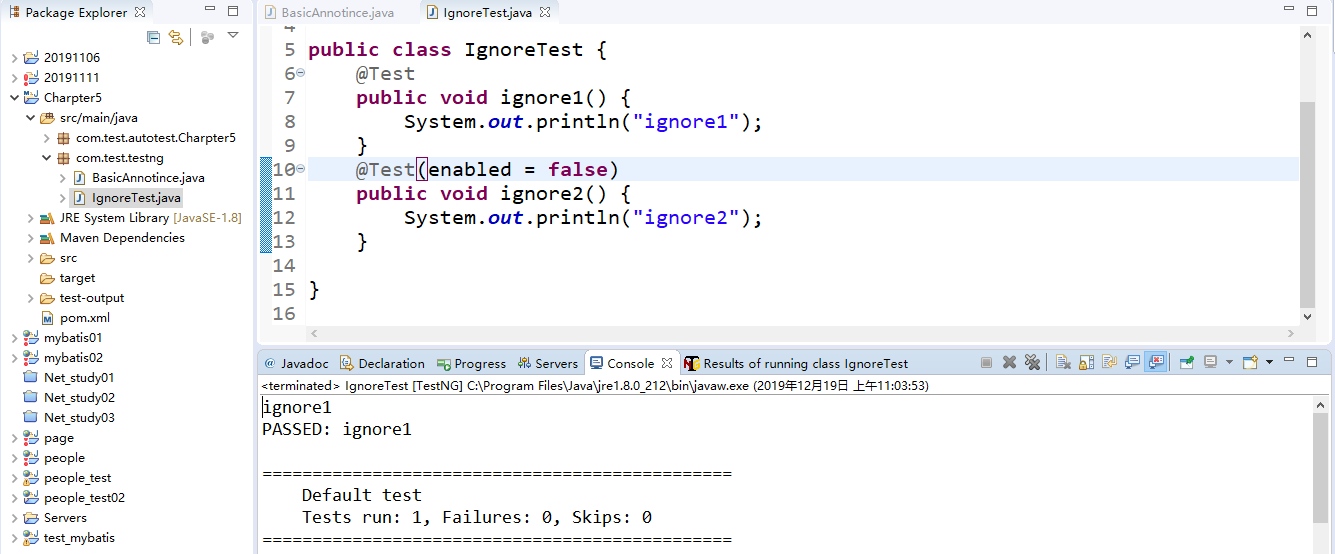
3. Ignoring tests: @Test (enabled = false)
Code Example 3.1
1 public class IgnoreTest { 2 @Test 3 public void ignore1() { 4 System.out.println("ignore1"); 5 } 6 @Test(enabled = false) 7 public void ignore2() { 8 System.out.println("ignore2"); 9 } 10 }
3.2运行结果
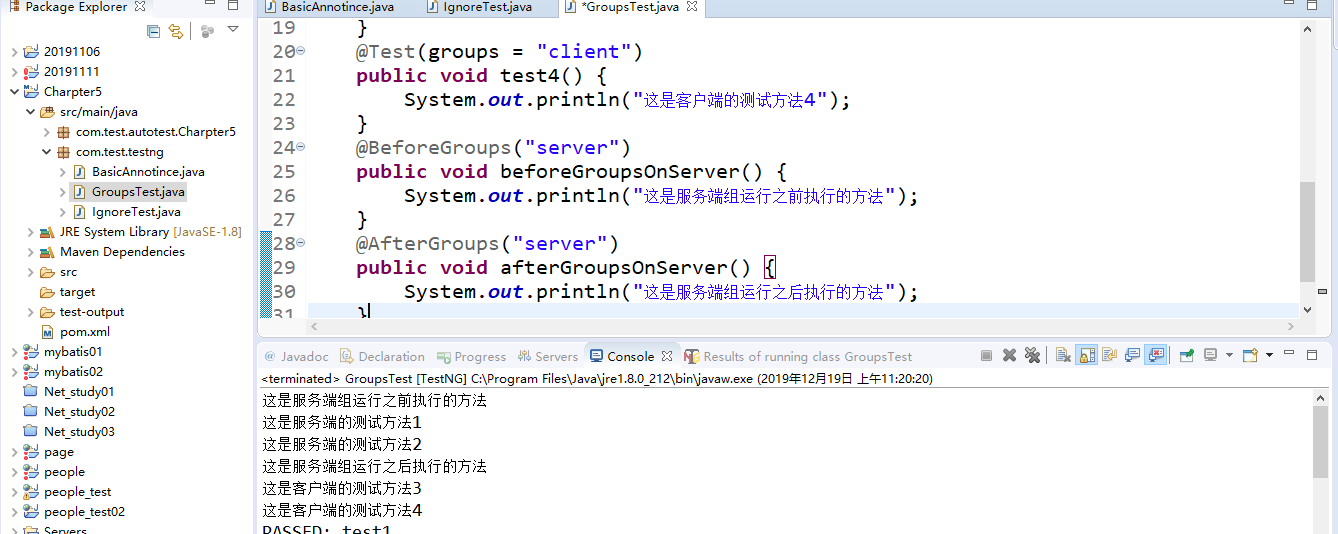
4.组测试@Test(groups = "组名"),@BeforeGroups("组名"),@AfterGroups("组名")
4.1代码示例
1 public class GroupsTest { 2 @Test(groups = "server") 3 public void test1() { 4 System.out.println("这是服务端的测试方法1"); 5 } 6 @Test(groups = "server") 7 public void test2() { 8 System.out.println("这是服务端的测试方法2"); 9 } 10 @Test(groups = "client") 11 public void test3() { 12 System.out.println("这是客户端的测试方法3"); 13 } 14 @Test(groups = "client") 15 public void test4() { 16 System.out.println("这是客户端的测试方法4"); 17 } 18 @BeforeGroups("server") 19 public void beforeGroupsOnServer() { 20 System.out.println("这是服务端组运行之前执行的方法"); 21 } 22 @AfterGroups("server") 23 public void afterGroupsOnServer() { 24 System.out.println("这是服务端组运行之后执行的方法"); 25 } 26 }
4.2运行结果
5.类分组测试@Test(groups = "组名"),xml中include标签name属性为组名
5.1代码示例
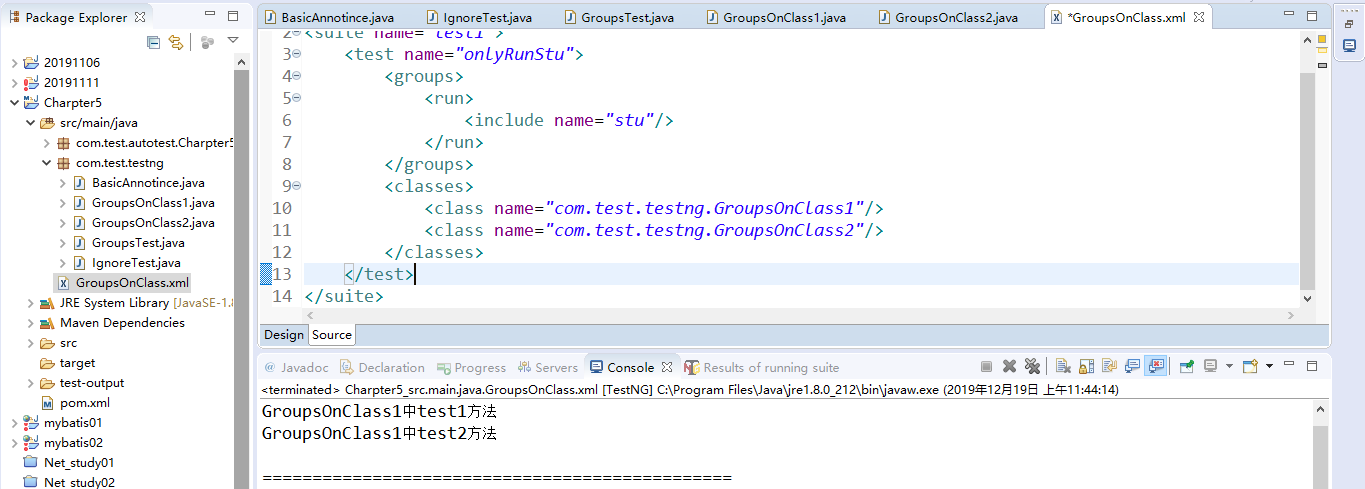
@Test(groups = "stu") public class GroupsOnClass1 { public void test1() { System.out.println("GroupsOnClass1中test1方法"); } public void test2() { System.out.println("GroupsOnClass1中test2方法"); } }
@Test(groups = "tea") public class GroupsOnClass2 { public void test1() { System.out.println("GroupsOnClass2中test1方法"); } public void test2() { System.out.println("GroupsOnClass2中test2方法"); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<suite name="test1">
<test name="onlyRunStu">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="stu"/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.test.testng.GroupsOnClass1"/>
<class name="com.test.testng.GroupsOnClass2"/>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
5.2运行结果
6.异常测试@Test(expectedExceptions = 异常类名)
6.1代码示例
1 public class ExceptionTest { 2 @Test(expectedExceptions = RuntimeException.class) 3 public void runTimeExceptionSuccess() { 4 System.out.println("这是成功的异常测试"); 5 throw new RuntimeException(); 6 } 7 }
6.2运行结果

7.依赖测试:@Test(dependsOnMethods = {"XXX方法名"} ) ,当被依赖的方法执行失败,依赖的方法忽略
7.1代码示例
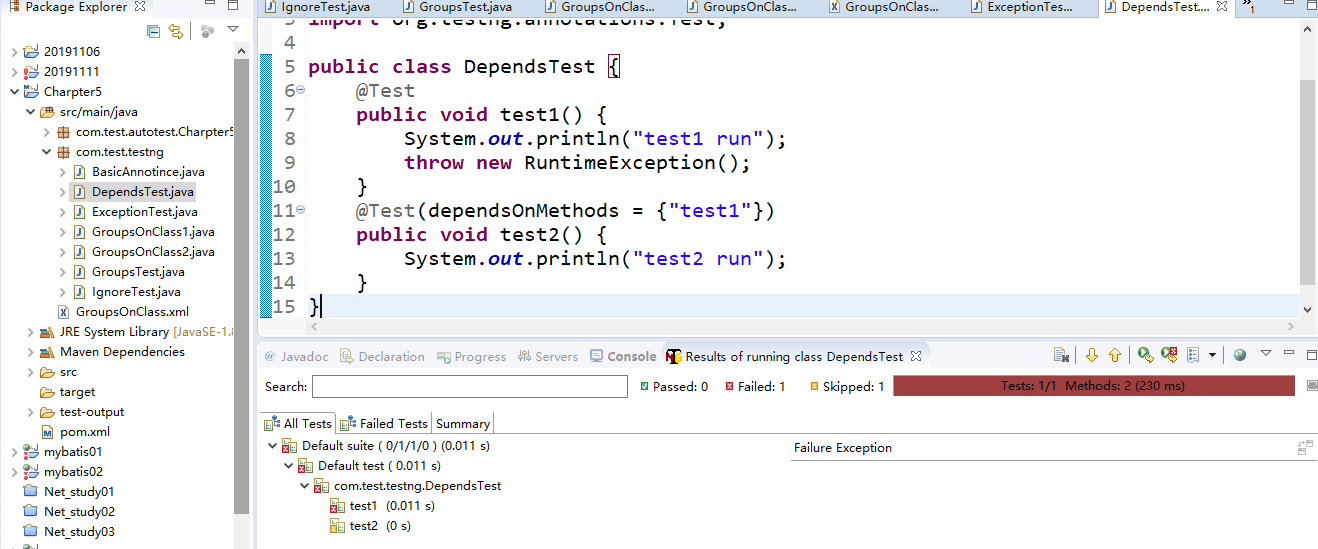
1 public class DependsTest { 2 @Test 3 public void test1() { 4 System.out.println("test1 run"); 5 throw new RuntimeException(); 6 } 7 @Test(dependsOnMethods = {"test1"}) 8 public void test2() { 9 System.out.println("test2 run"); 10 } 11 }
7.2运行结果
8.参数化测试——xml文件参数化
8.1代码示例
1 public class ParameterTest { 2 @Test 3 @Parameters({"name","age"}) 4 public void paraTest(String name,int age) { 5 System.out.println("name="+name+",age="+age); 6 } 7 }
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <suite name="test2"> 3 <test name="para"> 4 <classes> 5 <!--注意 parameter中的name要跟@Parameters中的对应--> 6 <parameter name="name" value="张三"></parameter> 7 <parameter name="age" value="23"></parameter> 8 <class name="com.test.testng.ParameterTest"/> 9 </classes> 10 </test> 11 </suite>
9.参数化测试——DataProvider参数化
9.1代码示例
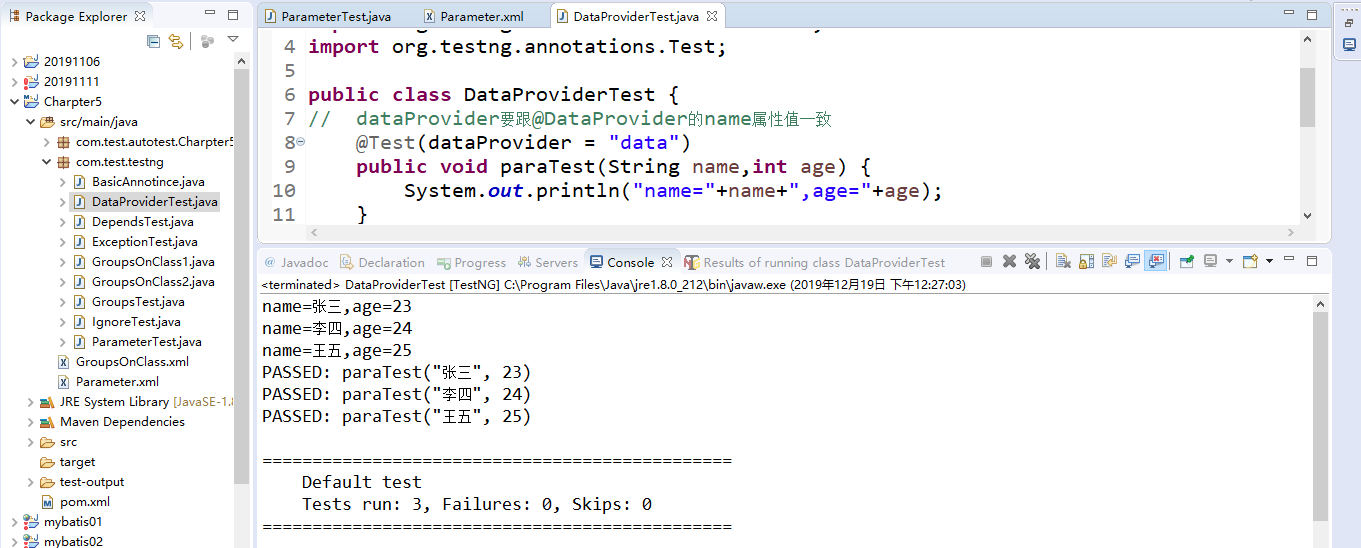
1 public class DataProviderTest { 2 // dataProvider要跟@DataProvider的name属性值一致 3 @Test(dataProvider = "data") 4 public void paraTest(String name,int age) { 5 System.out.println("name="+name+",age="+age); 6 } 7 @DataProvider(name = "data") 8 public Object[][] dataProvider(){ 9 Object[][] o = new Object[][] { 10 {"张三",23}, 11 {"李四",24}, 12 {"王五",25} 13 }; 14 return o; 15 } 16 }
9.2运行结果
9.3根据方法名传值
9.3.1代码示例
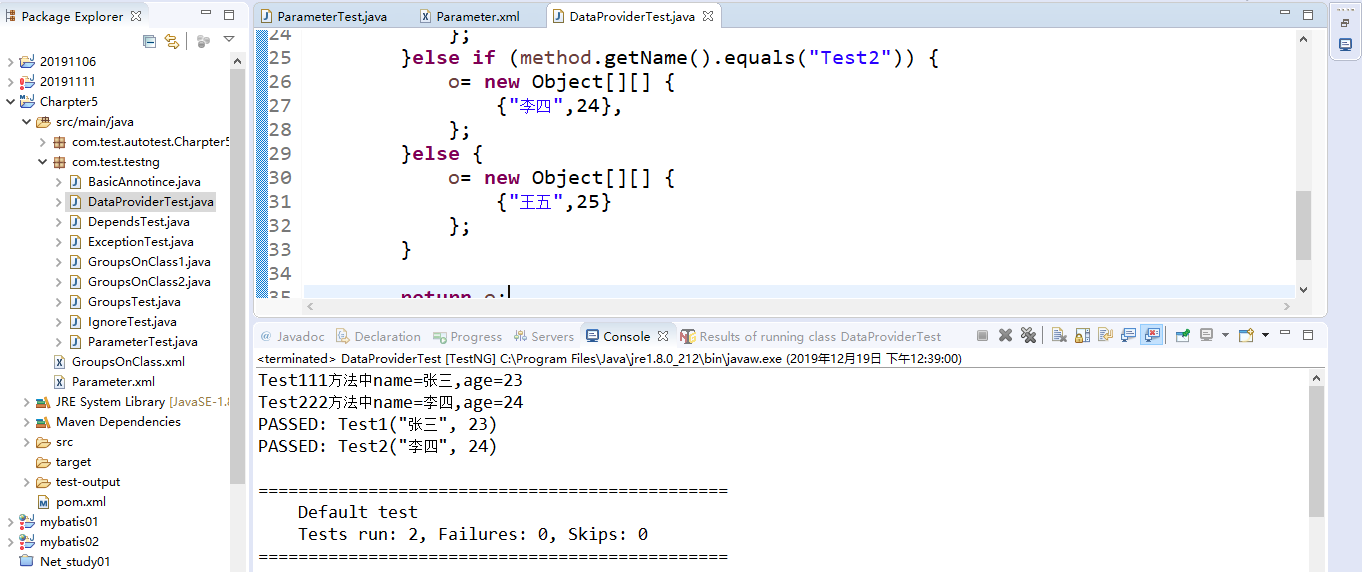
1 public class DataProviderTest { 2 // dataProvider要跟@DataProvider的name属性值一致 3 @Test(dataProvider = "methodData") 4 public void Test1(String name,int age) { 5 System.out.println("Test111方法中name="+name+",age="+age); 6 } 7 @Test(dataProvider = "methodData") 8 public void Test2(String name,int age) { 9 System.out.println("Test222方法中name="+name+",age="+age); 10 } 11 @DataProvider(name = "methodData") 12 public Object[][] dataProvider(Method method){ 13 Object[][] o = null; 14 if (method.getName().equals("Test1")) { 15 o= new Object[][] { 16 {"张三",23}, 17 }; 18 }else if (method.getName().equals("Test2")) { 19 o= new Object[][] { 20 {"李四",24}, 21 }; 22 }else { 23 o= new Object[][] { 24 {"王五",25} 25 }; 26 } 27 28 return o; 29 } 30 }
9.3.2运行结果
10.多线程测试——注解方式实现
10.1代码示例
1 public class MultiThreadOnAnnotice { 2 /* 3 * nvocationCount----表示执行的次数 4 threadPoolSize-----表示线程池的内线程的个数 5 * */ 6 @Test(invocationCount = 10,threadPoolSize = 3) 7 public void test1() { 8 System.out.println("MultiThreadOnAnnotice_test1_Thread Id :"+Thread.currentThread().getId()); 9 } 10 }
10.2运行结果
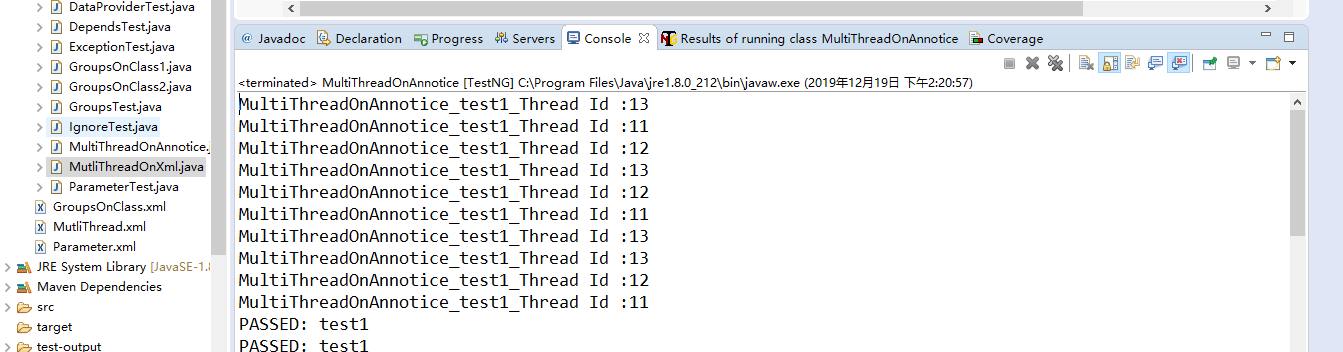
11.多线程测试——xml文件实现
11.1parallel:methods级别
11.1.1代码示例
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <suite name="multi" parallel="methods" thread-count="3"> 3 <!-- 4 tests级别:不同的test tag下的用例可以在不同的线程下执行 5 相同的test tag下的用例只能在同一个线程中去执行 6 classs级别:相同的class tag 下的用例在同一个线程中执行 7 不同的class tag 下的用例可以在不同的线程中执行 8 methods级别:所有用例都可以在不同的线程下去执行 9 10 thread-count:代表了最大并发线程数 11 12 xml文件配置这种方式不能指定线程池,只有方法上才可以指定线程池 13 --> 14 <test name="test1"> 15 <classes> 16 <class name="com.test.testng.MutliThreadOnXml"/> 17 </classes> 18 </test> 19 </suite>
11.1.2运行结果
 11.2parallel:tests级别-不同test tag时
11.2parallel:tests级别-不同test tag时
11.2.1代码示例
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <suite name="multi" parallel="tests" thread-count="3"> 3 <test name="test1"> 4 <classes> 5 <class name="com.test.testng.MutliThreadOnXml"/> 6 </classes> 7 </test> 8 <test name="test2"> 9 <classes> 10 <class name="com.test.testng.MutliThreadOnXml"/> 11 </classes> 12 </test> 13 </suite>
11.2.2运行结果
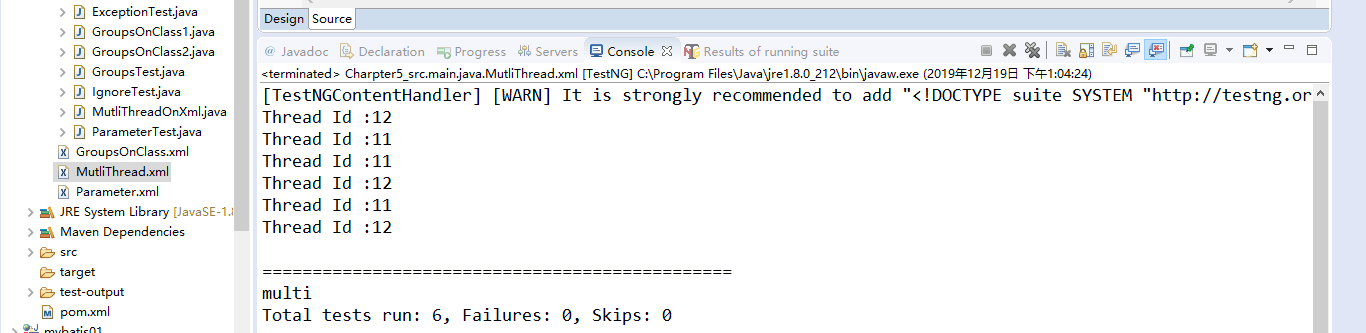
11.3parallel:tests级别-相同test tag时
11.3.1代码示例
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <suite name="multi" parallel="tests" thread-count="3"> 3 <test name="test1"> 4 <classes> 5 <class name="com.test.testng.MutliThreadOnXml"/> 6 </classes> 7 </test> 8 </suite>
11.3.2运行结果
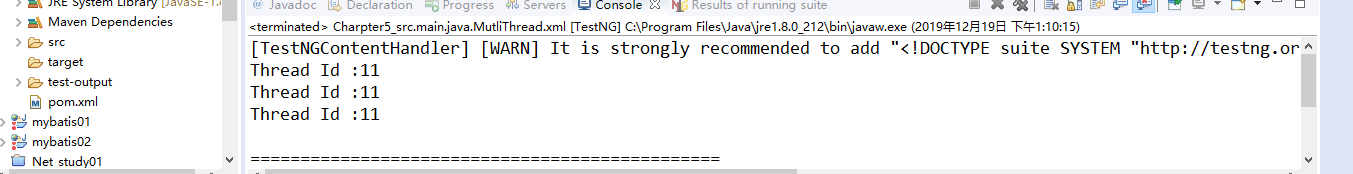
11.4parallel:classes级别
11.4.1代码示例
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <suite name="multi" parallel="classes" thread-count="3"> 3 <test name="test1"> 4 <classes > 5 <class name="com.test.testng.MutliThreadOnXml"/> 6 <class name="com.test.testng.ExceptionTest"/> 7 </classes> 8 </test> 9 <test name="test2"> 10 <classes > 11 <class name="com.test.testng.MutliThreadOnXml"/> 12 </classes> 13 </test> 14 </suite>
11.4.2运行结果
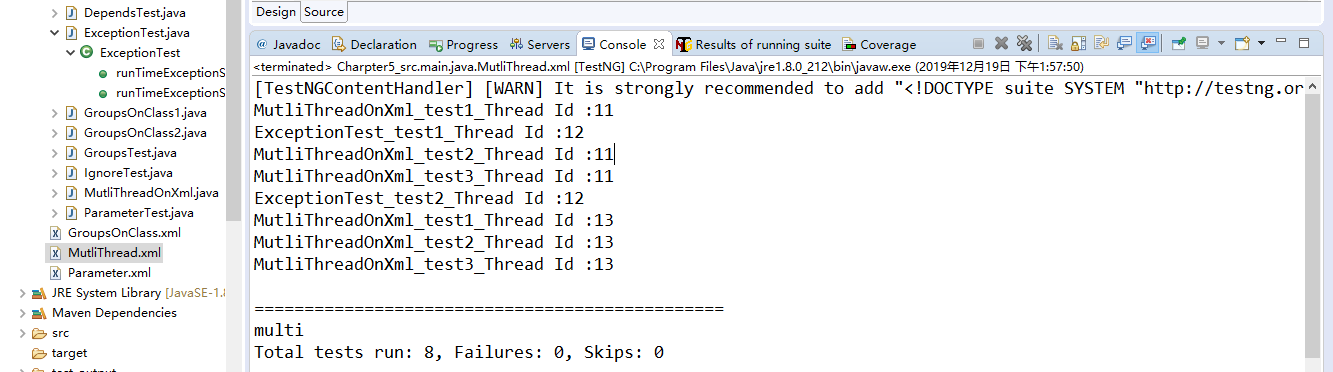
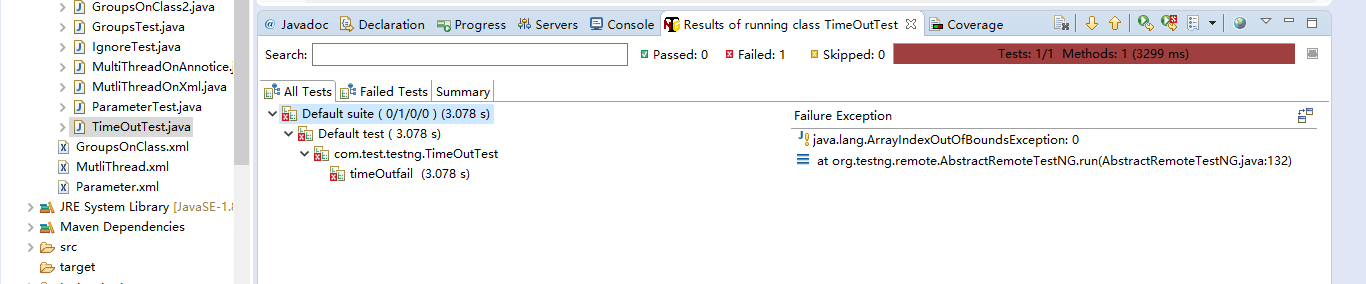
12超时测试——@Test(timeOut = 毫秒值)
12.1代码示例
1 public class TimeOutTest { 2 @Test(timeOut = 3000) 3 public void timeOutfail() throws InterruptedException { 4 Thread.sleep(4000); 5 } 6 7 }
12.2运行结果