
1 Introduction
SpringbootAutomatic configuration is convenient, reduces the complexity of development on us, then automatically configure what principle is it? Before I also wrote an article analyzes.
Springboot series (three) Spring Boot automatically configured . Since the automatic configuration used in the binding configuration file, if you do not know the use of common configuration file, you can refer to this article. Springboot series (two) Spring Boot configuration file .
At this time, by learning Springbootautomatic configuration mode, writing its own starter, to deepen understanding of the auto-configuration.
Familiar patterns, help to improve the preparation of starternormative, write your own starterfirst before learning Springbootthe official starterand common integration framework starterwritten in a way, you can appreciate the mystery.
2. Springboot official mode
Select an official automatic configuration analysis, here on the choice of common configuration port number configuration.
2.1 The introduction of dependence
Before using the port number we need to introduce web-dependent.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>If you look at startermany things, perhaps you have found a hair model , Springbootofficial starternames are spring-boot-starter-xxxxnamed.
View spring-boot-starter-webwill find, in fact, rely on just an empty box, in addition to rely on other pomthan there is no single line of code.
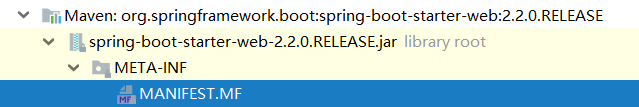
At this time, we found another pattern : starteronly rely on other pom, not code.
So spring-boot-starter-webin the end it depends on what content?
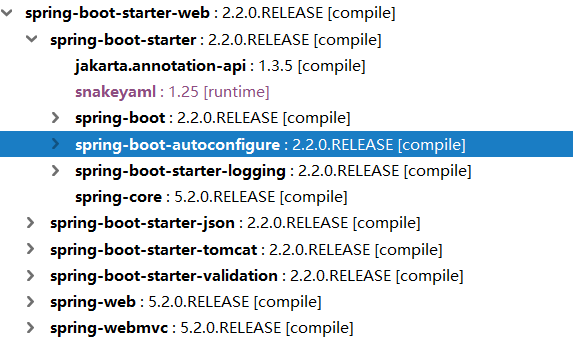
Observe the dependency information, and then the other official reference starter, can find several fixed introduction, may be referred pattern introduced dependence.
- Dependence
spring-boot-starter. - Dependence
spring-boot-autoconfigure.
2.2 Automatic Configuration
Introducing rely only configure the port number, like this.
server.port=8090IDEA in by clicking server.portto find the configuration file class-bound. You can see the configuration will eventually be injected into classes ServerPropertiesclass porton the property.
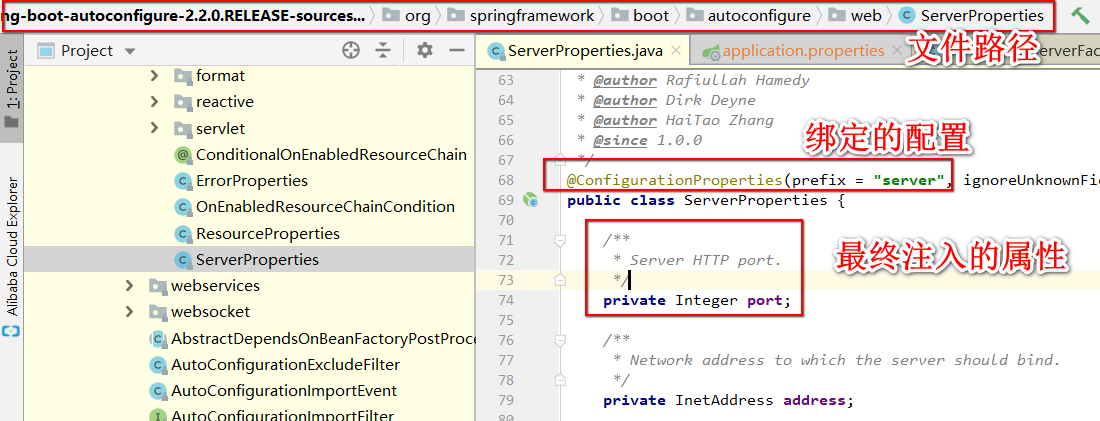
Well, this ServerPropertiesin the end is where to use it? Continue the search, and found a Servletcall-related.
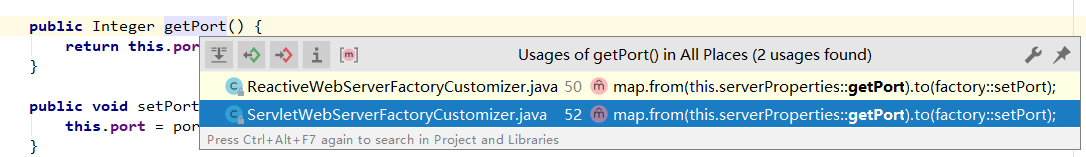
It was found to be ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizerthe class was called, which defines the class
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;Configured to use the property.
Continue to see this type of call, found only one class of this class, this class is ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.
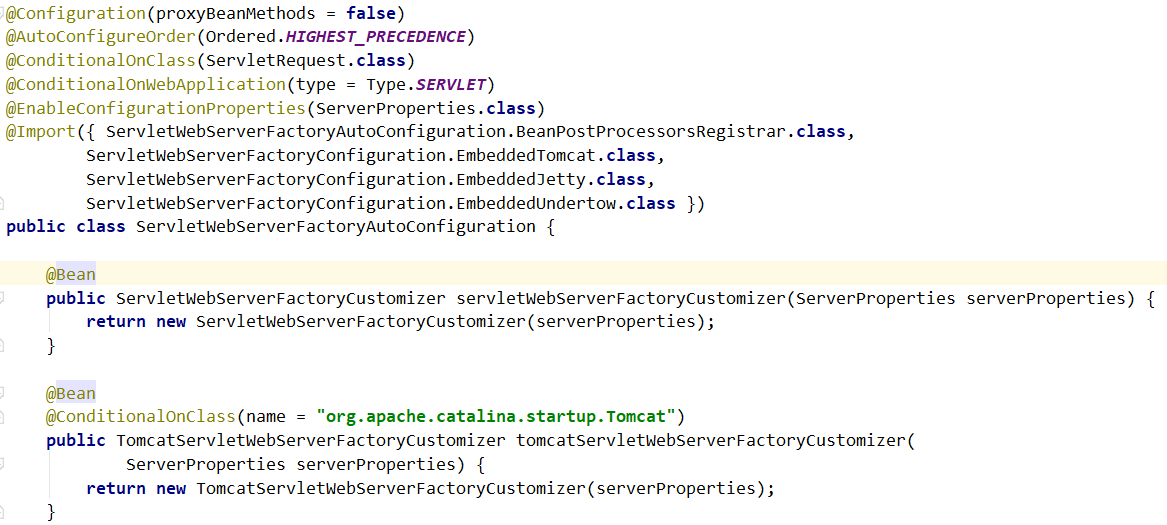
According to our understanding of annotations, this class is the main class of the auto-configuration. While classes are automatically configured to AutoConfigurationend.
Look at a few notes of this class means.
- A higher priority level.
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)- Only in
ServletRequestexistence and it is effective when a Web application class.
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)- It opens the
ServerPropertiesconfiguration bindings.
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)- Introducing several classes.
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })Bean while the injection configuration to the factory for the rest of calls.
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer servletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}Automatic configuration just do these things? According to previous article in the analysis, we know more than the code, there is at least a specified automatic configuration class configuration file to be read. That is spring.factoriesfile.
If you do not know, you can look at this article. Springboot series (three) Spring Boot automatically configured .
Indeed the case, you can spring.factoriesfind the track to the top of the class.
That is ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.
According to the above analysis, we can find Springbootthe official starterseveral modes .
- Use
XXXPropertiesautomatic bindingXXXconfiguration information at the beginning, such as:ServerProperties. - The
XXXPropertiesclass definition to be used, as:ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer. - Preparation of a
XXXAutoConfiguration, openXXXPropertiesthe automatic configuration, define the scene to take effect, create a class needed toBeanplant. SuchServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfigurationas: .
3. Third-party integration mode
SpringbootIf all of the official framework are written to starter, it is unrealistic. So many third-party frameworks need to be integrated into the initiative springboot, so we chose a common framework for analysis of its starterimplementation. As it has been seen springbootofficial starterhow is configured third-party framework is similar, so the process will be observed the following explicitly stated that the same point, do not compare detailed comparison.
Select here mybatis-spring-boot-starterto learn analysis.
3.1 introduces dependence
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>Here mybatisthe frame starterdependent conform to certain rules , i.e., XXX-Spring-Boot-Starter .
This observation starter, found that it did not do any of code to achieve, and this is springbootan official agreement.

View mybatis-spring-boot-starterdependency, there are many, and auto-configuration related mainly yes.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>3.2 Automatic Configuration
View mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigurethe content discovery and springbootan official of autoconfigurethe structure is the same.
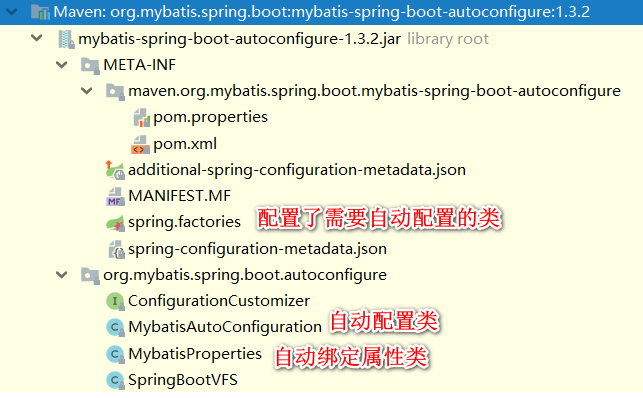
mybatisAlso through the automatic configuration spring.factoriesto indicate auto-configuration, and then by XxxAutoConfigurationbinding XxxPropertiesto auto-configuration.
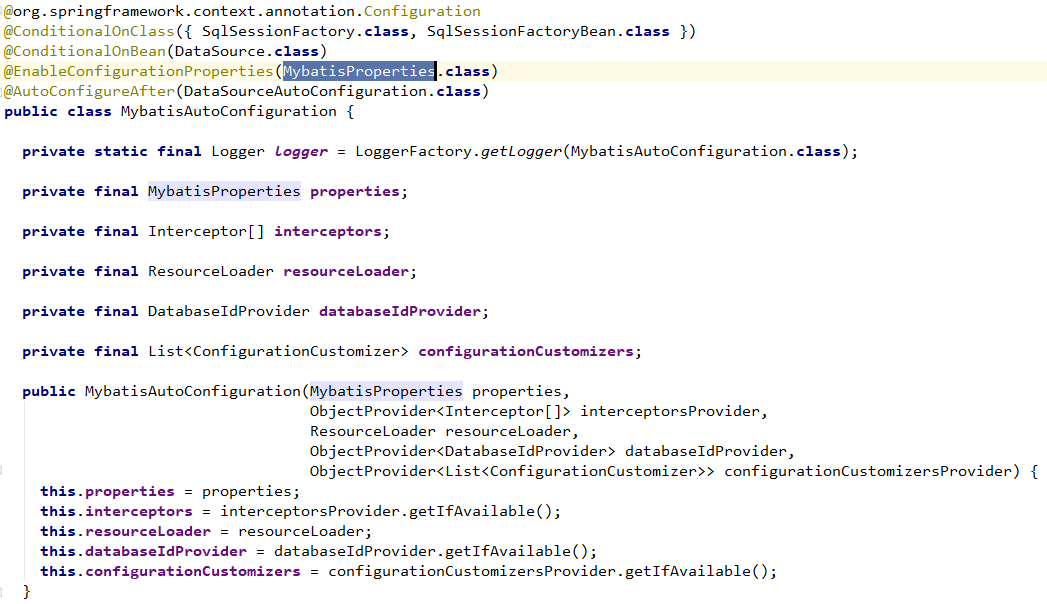
In principle, and the top springbootofficial starteris the same, so do not do too much introduced.
4. Write your own starter
Said so much, and finally to the practical operation of the link, by the above description, we can roughly draw write your own startersteps.
- Create a name for
xxx-spring-boot-starterthe starter project. - Create a name for the
xxx-spring-boot-autoconfigureproject.- Write attribute binding class
xxxProperties. - Write the service class, the introduction
xxxProperties. - Write automated configuration class
XXXAutoConfigurationinjection configuration. - Create a
spring.factoriesfile that specifies the class to be automatically configured.
- Write attribute binding class
- Starter project is empty project for introducing
xxx-spring-boot-autoconfigureother dependencies. - Project introduction
starter, configuration information needs to be configured.
4.1 Creating a starter project
Since the start does not need to implement the code, you only need to rely on other projects, so directly create an empty maven project. But the name must be standardized.
Created here starterShi myapp-spring-boot-starter.

pom file is very simple, only we need to introduce the next to be created myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>net.codingme.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- 启动器 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- 引入自动配置项目 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.codingme.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>4.2 Creating automatic configuration items
Combined with the face of starterthe analysis, create a name for the immediate myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigureproject. Project was introduced only springboota parent project and spring-boot-starter.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.codingme.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
The overall structure of the project Figure.
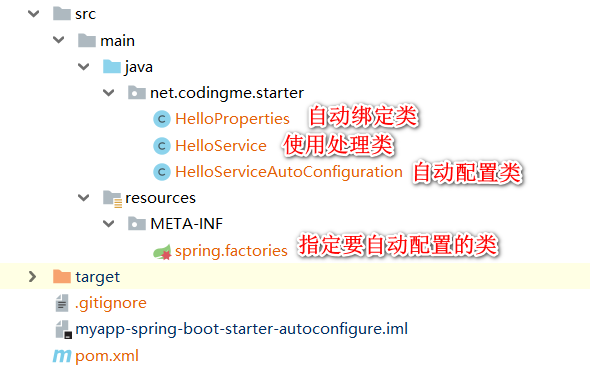
In HelloPropertiesthe annotation by @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "myapp.hello")make class attributes and myapp.helloconfiguration at the beginning of the bind.
/**
* <p>
*
* @Author niujinpeng
* @Date 2019/10/29 23:51
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "myapp.hello")
public class HelloProperties {
private String suffix;
public String getSuffix() {
return suffix;
}
public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
this.suffix = suffix;
}
}Then HelloServicethe sayHellomethod using HelloPropertiesan automatic binding value.
public class HelloService {
HelloProperties helloProperties;
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "Hello " + name + "," + helloProperties.getSuffix();
}
public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() {
return helloProperties;
}
public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) {
this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
}
}In order to HelloServicebe automatically injected and can be used normally HelloProperties, so we
HelloServiceAutoConfigurationput the class in HelloProperties.classthe introduction, and then HelloServiceinjected into Bean.
/**
* web应用才生效
*/
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
/**
* 让属性文件生效
*/
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
/***
* 声明是一个配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean
public HelloService helloService() {
HelloService helloService = new HelloService();
helloService.setHelloProperties(helloProperties);
return helloService;
}
}Finally, spring.factoriesonly you need to specify the class can be automatically configured.
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
net.codingme.starter.HelloServiceAutoConfigurationHere, automatically configure the project is complete. You can myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigureproject execution mvn installto automatically configure the project package to a local warehouse, and then use the same command to myapp-spring-boot-starterinstall to the warehouse. Because the latter depends on the former project, so here the former requires advanced mvn install.
4.3 using a custom launcher
Create a springbootproject myapp-spring-boot-starter-test.
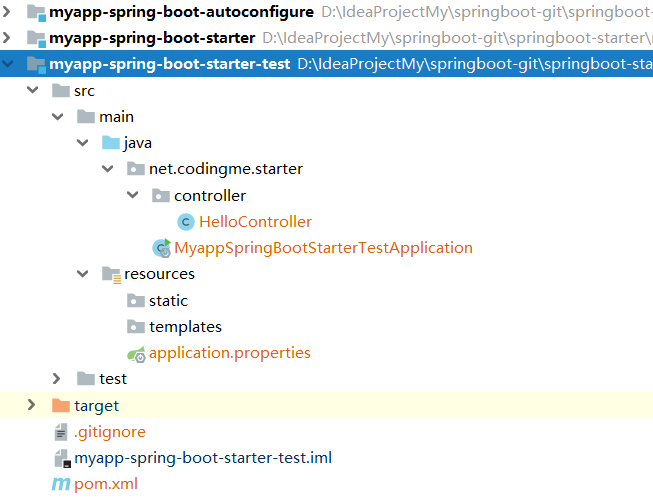
The introduction of webdependency, they have written the introduction myapp-spring-boot-starter.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入自己的 starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.codingme.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>Write a HelloControllerinjection in the auto-configuration HelloServicefor testing.
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(String name) {
return helloService.sayHello(name);
}
}Since the autoConfigureproject is defined in the sayHellomethod will output "Hello" + name + incoming configuration hello.suffix, so we springbootconfigure this property in the configuration file.
myapp.hello.suffix=早上好Run the test project, visit / hello path to pass a name to see automatic configuration has no effect.

From the test results can be automatically configured to see good morning have taken effect. I have written here starterhas also been completed.
The project has spread to Github .
Https://github.com/niumoo/springboot/tree/master/springboot-starter
<End>
my micro letter: wn8398
profile: www.codingme.net
This article is a blogger original article, welcome to reprint, indicate the original link in the apparent position reprint.
No reply to public attention resources can acquire knowledge of core Java interview & finishing materials.