1 Dijkstra algorithm
1.1 algorithm basic information
- Solve the problem / proposed background
- Single-source shortest path (in the weighted directed graph, each vertex find the shortest path remaining from a vertex to)
- ALGORITHM
- how are you
- Ascending order according to path length, the shortest path algorithm for sequentially generating
- The scope of the Dijkstra algorithm applies only to FIG model [] weight is positive in
- how are you
- time complexity
- O (n ^ 3)
- Supplement
- It is also applicable to multi-source shortest path [] (recommended: Floyd algorithm (dynamic programming, O (n ^ 3)))
Dijkstra time complexity: O (n ^ 3)
1.2 Algorithm Description
- It is also applicable to multi-source shortest path [] (recommended: Floyd algorithm (dynamic programming, O (n ^ 3)))
- 1.2.1 solving process (specific ideas)

- 1.2.2 Example
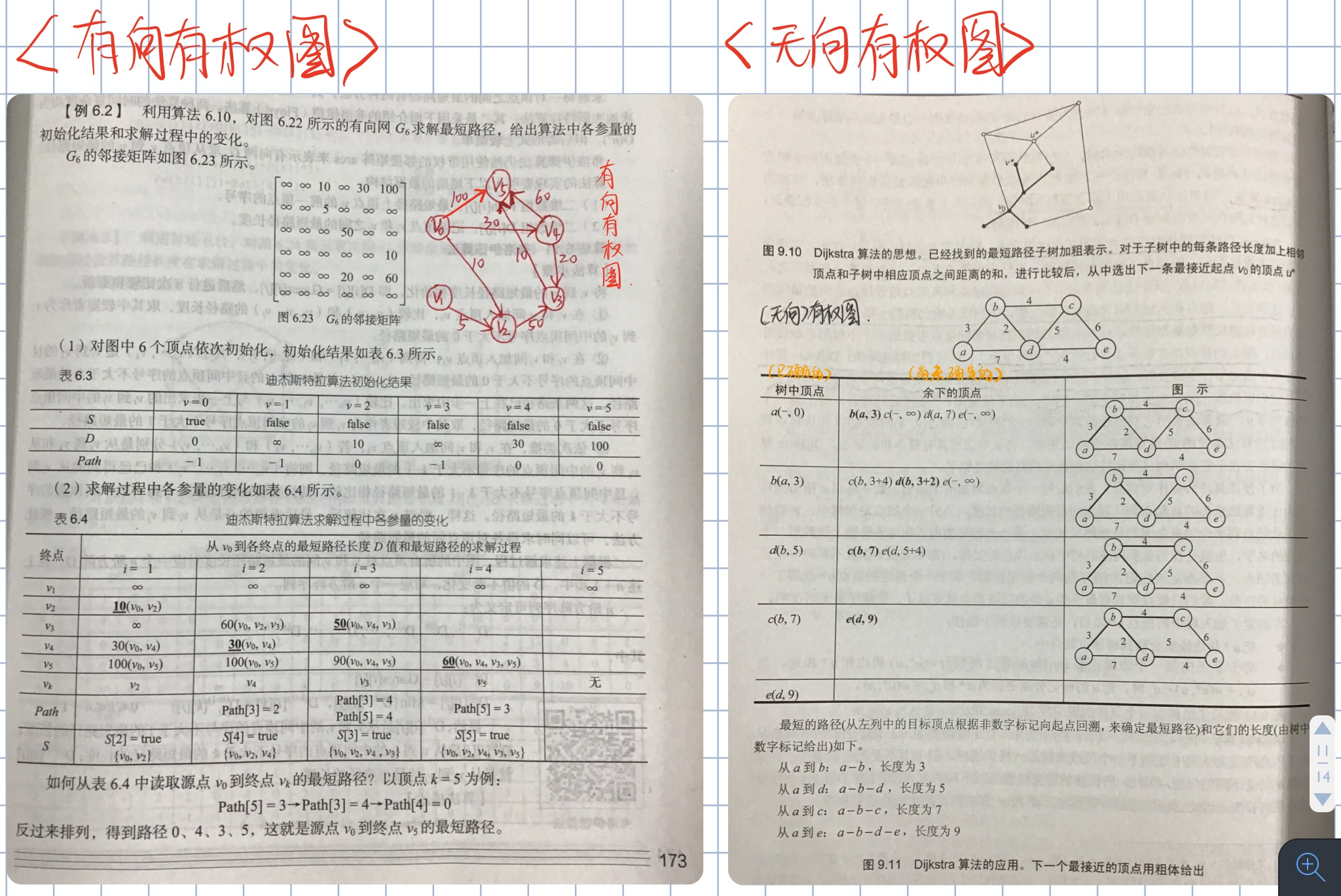
1.2 Programming reproduction
- 1> FIG defined model (the adjacency matrix notation) of the basic memory structure []
# define MaxInt 32767 // 表示极大值 即 ∞ (无穷大)
# define MVNum 100 // 最大顶点数
typedef int VertexType; // 假设顶点的数据类型为整型
typedef int ArcType; // 假设Vi与Vj之边的权值类型为整型
typedef struct {
VertexType vexs[MVNum]; // 顶点表 (存储顶点信息)
ArcType arcs[MVNum][MVNum]; // 邻接矩阵
int vexnum,arcnum; // 图的当前顶点数与边数
}AMGraph; // Adjacent Matrix Graph 邻接矩阵图 - 2> Dijkstra algorithm defined auxiliary data structure []

bool S[MVNum]; // S[i] 记录从源点V0到终点Vi是否已被确定为最短路径长度 【划分确定与未确定: 跟贪心算法的适用范围(不可取消性)有直接联系】
// true:表已确定;false:表尚未确定
ArcType D[MVNum]; // D[i] 记录从源点V0到终点Vi的【当前】最短路径【长度】
int Path[MVNum]; // Path[i] 记录从源点V0到终点Vi的【当前】最短路径上【Vi的[直接前驱]的顶点序号】 - 3> Initialization (the adjacency matrix) with a weighted graph model of the FIG.
void InitAMGraph(AMGraph &G){
cout<<"Please Input Vertexs Number:";
cin>>G.vexnum;
cout<<"\nPlease Directed Edges Number:";
cin>>G.arcnum;
for(int i=0;i<MVNum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<MVNum;j++){
if(i!=j){ // 【易错】 初始化<Vi, Vj>时: <Vi,Vj> 路径长度无穷大 (i!=j)
G.arcs[i][j] = MaxInt;
} else { // 【易错】 初始化<Vi, Vj>时: <Vi,Vi>【自回环】路径长度为0 (i==i)
G.arcs[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
G.vexs[i] = i;
}
cout<<"\nPlease Input All Directed Edges and their Weight now:";
cout<<"\nDirected Edges(i,j,weight): "<<endl;
int i,j;
int weight;
for(int k=0;k<G.arcnum;k++){
// cout<<"("<<(k+1)<<") ";
cin>>i;cin>>j;cin>>weight;
G.arcs[i][j] = weight;
}
cout<<endl;
}- 4> Dijkstra algorithm: Solving single source shortest path
void ShortestPath_Dijkstra(AMGraph G, int V0){
//step1 n个顶点依次初始化
int n =G.vexnum;
for(int v=0;v<n;v++){
S[v] = false;
D[v] = G.arcs[V0][v];
if(D[v]<MaxInt){
Path[v] = V0;
} else {
Path[v] = -1;
}
}
//step2 将源点V0划入已确定集合S中
S[V0] = true;
D[V0] = 0; // 源点V0到源点V0的最短路径长度必然为0
//step3 贪心算法策略:
// 3.1 循环遍历所有结点:
// 3.2 先确定当前最短路径的终点v;
// 3.3 然后,将v划入已确定集合S中;
// 3.4 最后,以利用结点v更新所有尚未确定的结点的最短路径
int v;
int min;
D[G.vexnum] = MaxInt;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){//3.1循环遍历所有结点 (即 求从源点V0到图中每一顶点(共计n-1个顶点)的最短路径)
//3.2 确定当前最短路径的终点v;
min = MaxInt;
for(int w=0;w<n;w++){
if(S[w]==false && D[w]<min){//比本轮循环中,已知的最短路径还短 【易错/易漏】 S[w]==false : 必须满足当前结点 Vw 属于尚未确定的结点
v = w;
min = D[w];
}
}
//3.3 然后,将v划入已确定集合S中;
S[v] = true;
//3.4 最后,以利用结点v更新所有尚未确定的结点的最短路径
for(int w=0;w<n;w++){
//↓更新Vw结点的最短路径长度为 D[v] + G.arcs[v][w]
//cout<<"S["<<w<<"]:"<<S[w]<<"D["<<v<<"]"<<D[v]<<"G.arcs["<<v<<"]["<<w<<"]"<<"D["<<w<<"]"<<D[w]<<endl;
if(S[w]==false && (D[v] + G.arcs[v][w] < D[w])){//【易错/易漏】 S[w]==false : 必须满足当前结点 Vw 属于尚未确定的结点
D[w] = D[v] + G.arcs[v][w];
Path[w] = v; // 更新 结点Vw的前驱为 v
}
}
v = G.vexnum;
}
}- 5> output D [i], Path [j]
void OutputD(AMGraph G, int V0){
cout<<"Shortest Distance Weight of the Pair of Directed Vertices("<<V0<<", j):"<<endl;
for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){
cout<<D[j]<<"\t";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void OutputPath(AMGraph G,int V0){
cout<<"Shortest Distance Path("<<V0<<",j) of the Pair of Directed Vertices:"<<endl;
for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){
cout<<Path[j]<<"\t";
}
cout<<endl;
}- 6> execute: Main function
int main(){
int V0; //源点V0的下标
AMGraph G;
InitAMGraph(G);
cout<<"Please Input the Index of Source Node 'V0':";
cin>>V0;
ShortestPath_Dijkstra(G, V0);
OutputD(G, V0);
OutputPath(G, V0);
return 0;
}- 7> Test: Output of Main
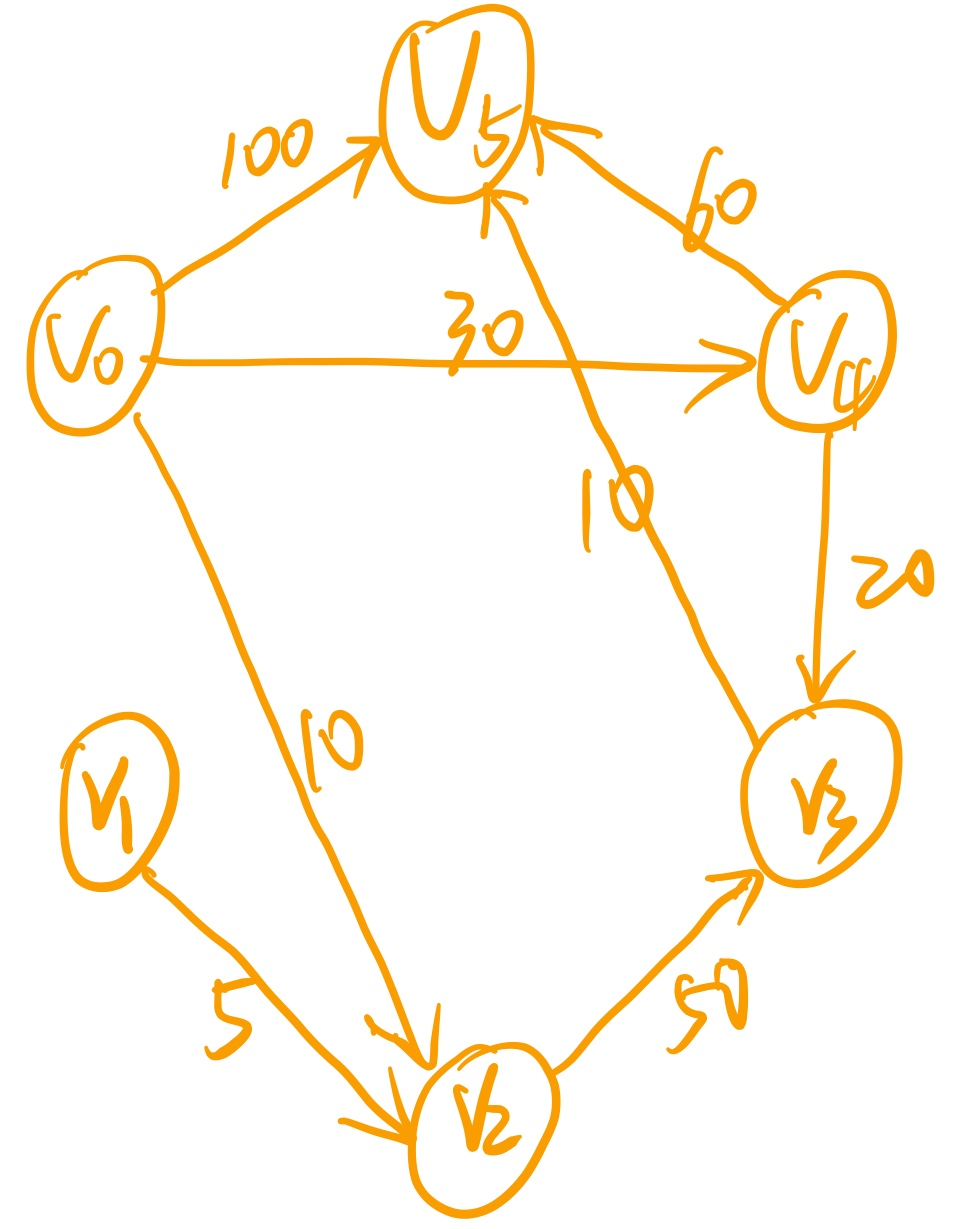
Please Input Vertexs Number:6
Please Directed Edges Number:8
Please Input All Directed Edges and their Weight now:
Directed Edges(i,j,weight):
1 2 5
0 2 10
3 5 10
4 3 20
0 4 30
2 3 50
4 5 60
0 5 100
Please Input the Index of Source Node 'V0':0
Shortest Distance Weight of the Pair of Directed Vertices(0, j):
0 32767 10 50 30 60
Shortest Distance Path(0,j) of the Pair of Directed Vertices:
0 -1 0 4 0 3Reference 2
- "Data Structure (C language / Dongmei Yan Wei Min Wu Weimin eds)"