OSI network model and the network connection device
OSI model
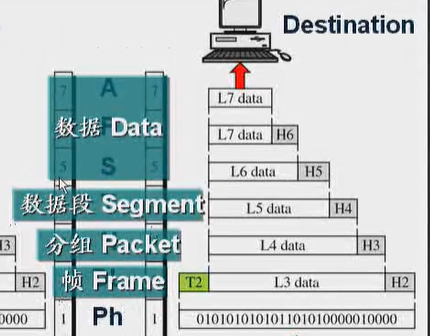
A transmission unit for transmission protocol (PDU) between 7 is called professional layer.
- (Application layer) transport layer 7-5 pdu called: data
- (Transport Layer) Layer 4 transport pdu called: segment (data segment)
- (Network layer) transport layer 3 pdu called: packet (packet)
- (Link layer) transmission is called Layer 2 pdu: frame (frames)
tcp / ip protocol family
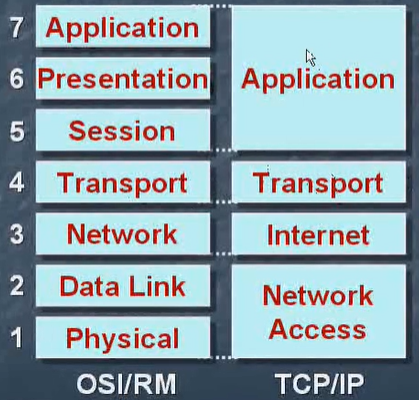
To achieve a total OSI7-layer model of it, and simplifies OSI7-layer model, with only four layers is realized.
- Application Layer: http, ftp and other protocols
- Transport Layer: tcp, udp and other agreements
- Network Layer: ip protocol
- Physical Layer: OSI7 in the physical layer and link layer
Features LAN and WAN data transmission
LAN: in the form of a broadcast communication, it is assumed in the LAN with a hub (Hub) connected to the A, B, C three hosts, when A and C communication, because it is a broadcast mode of transmission, it can listen to B but also C and A communication, but we found the target address B is not their own, so I ignored it.
Because it is a broadcast mode of transmission, when A and B are simultaneously communicating, B and C, or B and A is not able to communicate the. Because of the hub, only one channel, only one other end of communication, the next communication can begin.
WAN: point to point way communication. Parallel communications between hosts.
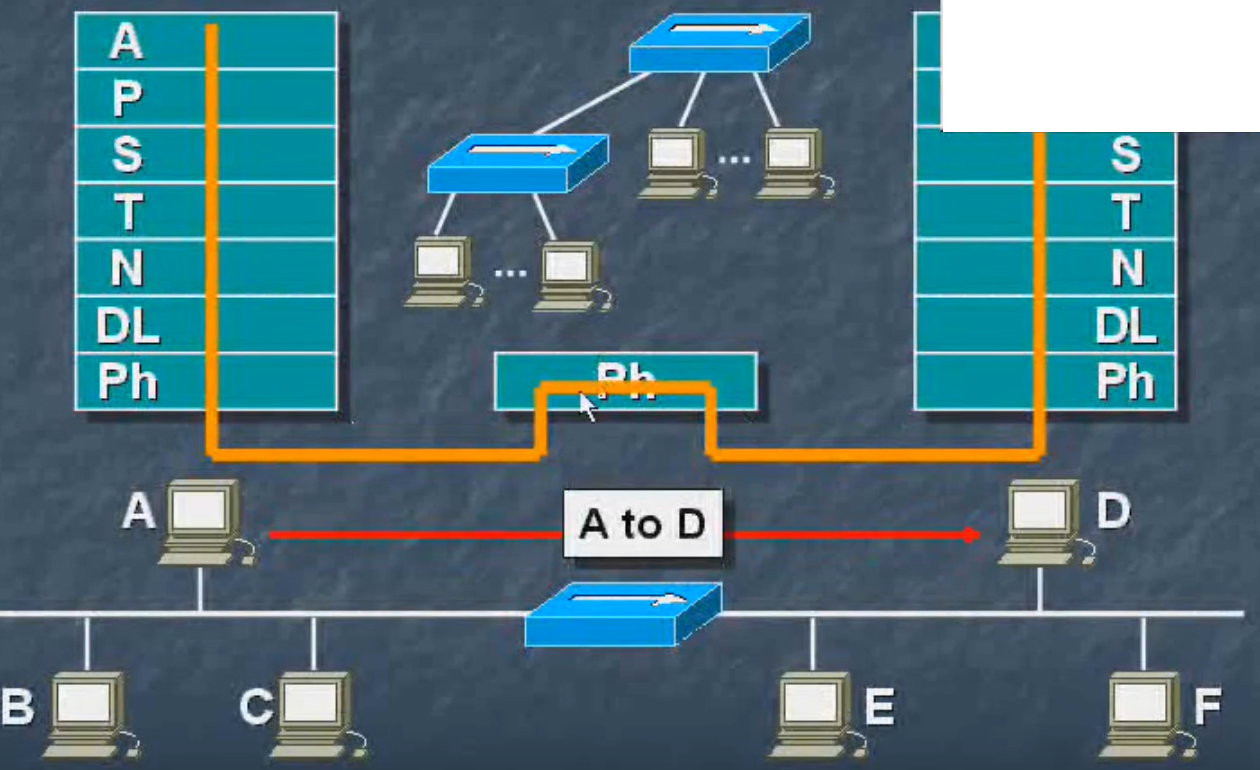
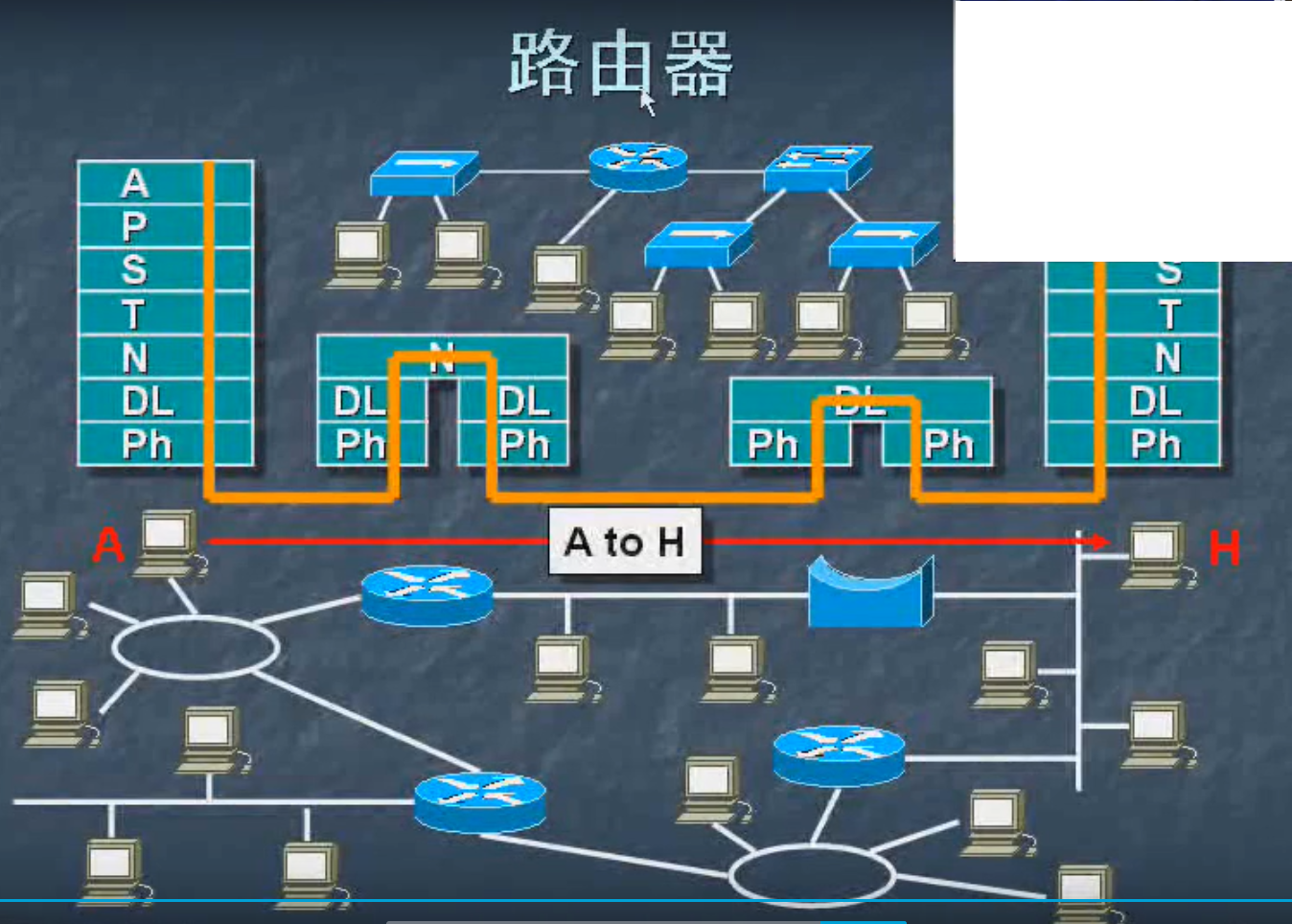
Network-connected devices

A hub (hub) / repeater (repeater): only a physical layer in the OSI communication. Connection to the host.
Hosts hub, since the channel is only one, so only the same time between the two hosts can communicate to the rest of the queue, and the host are the shared bandwidth concentrator.
A hub connected to another hub, there are drawbacks above.
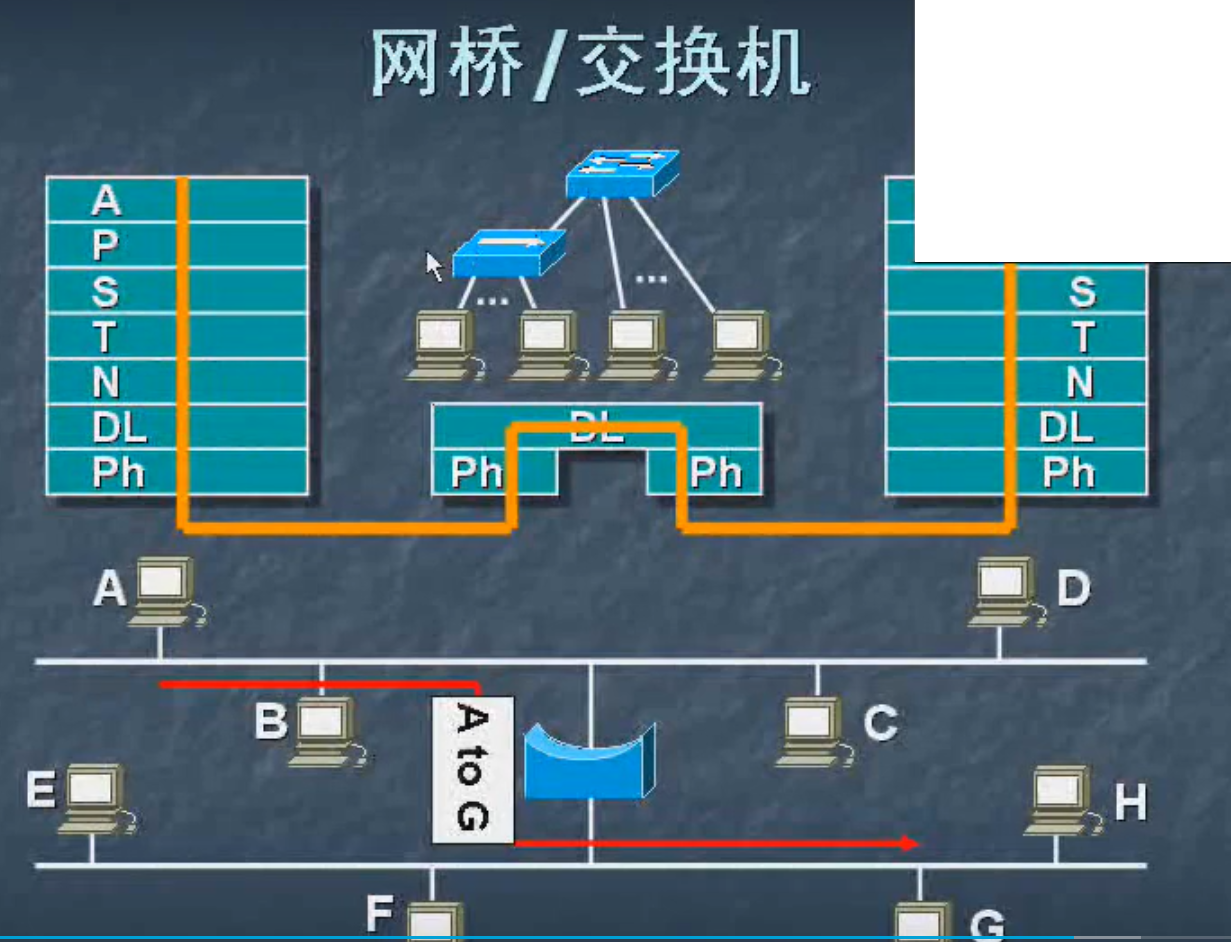
Switch (switch) / bridge (bridge): the link layer in the OSI communication. Can be connected to the host can also be connected hub.
An internal switch address table, the address forwarding table. Words, since the port on the same switch, there is no need to forward the panels A and D communicate. A and G, then the communication, since in a different port, it is necessary to forward the switch.
A plurality of hubs can be connected to the switch, if there are four hosts at the hub 1, the bandwidth is 10M hub 1, then 4 1 hosts share the bandwidth of 10M hub; 8 hosts if the hub 2, to the hub 2 Bandwidth is 100M, then the hosts in the hub 8 2 shared 10M bandwidth. So Hub 1 and Hub 2 will have their bandwidth.
The user is concerned, speed is faster.
Router (router): in the network layer in the OSI. It can be connected to different networks.
Particular can connect different networks, dial-up if the network is 1, 2 Ethernet network, you can only use a router to connect, you can not use the switch. The reason is that the network is a link layer and network layer 2 link is not the same place, it can not be connected. The router is connected at the network layer, the networks 1 and 2 in the network layer is the same, it can be connected with a router.
c / c ++ mutual learning QQ group: 877 684 253
