1, DNS Service Overview:
The DNS ( Domain the Name System ) domain name system, has a very important role in the TCP / IP network, can resolve domain names and IP addresses of service.
DNS is a distributed database , hierarchical naming system logical structure, like an inverted tree, the logical tree structure called the domain name space, due to the division of the DNS name space, so that the agencies can use your own domain name space created DNS information.
Note: DNS domain name space, the maximum depth of the tree is not more than 127 layers, each node in the tree can store up to 63 characters.
1.1, domain and domain name
DNS each node of the tree represents a domain, through these nodes, the entire domain name space divided into a hierarchy.
The domain name space for each domain, were represented by the domain name.
Domain: usually consists of a fully qualified domain name ( the FQDN of the logo). FQDN is shown which can accurately position relative to the root DNS domain, i.e. the node to the root of a complete presentation of DNS using reverse to the root node are written, and each node with "." Separated, for DNS google domain, its fully qualified domain name (FQDN)
As google.com.
For example: host name is bigserver, the domain name is mycompany.com, then FQDN is bigserver.mycompany.com.
For example, google subdomain com domain, which represents Google.com method, and the subdomain www google domain, can be used www.google.com FIG.
Note: In general, FQDN strict naming restrictions, the length can not exceed 256 bytes , only allowed to use characters az, 0-9, AZ
And minus (-). Dot (.) Only (e.g. "google.com") or the end of the domain name FQDN used between flag.
Domain names are case-sensitive.
From the top level to the lower layer, it can be divided into: a root domain, top-level domain, two domains, subdomains .
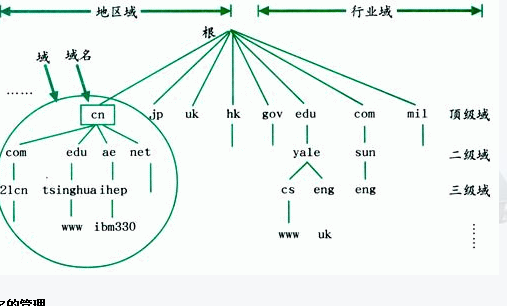
Internet top-level domain name space is the root domain (root) , which records important information on the Internet DNS, Internet domain name registered by the management authority, the agency assigned responsibility for the management of the various parts of the domain name space to connect to the Internet organizations.
Global has 13 root (root) server . A primary server, a secondary server 12 ; 9 in the United States . Two in Europe , one in a Japanese (921)
DNS root domain Here is the top-level domain, but also by the Internet domain name registration authority management.
There are three types of top-level domains:
Organization domain : the use of three-character code, represents the main function of the organization's activities or DNS domain contains. For example, com for commercial institutions and organizations , EDU for educational institutions and organizations , GOV for government institutions and organizations , MIL military institutions and organizations , NET network institutions and organizations , ORG non-profit institutions and organizations , int international institutions and organizations .
Address field : the use of country code of two characters. Such as cn for China , KR Korea , US for the United States .
Reverse Domain : This is a special domain , the name for the in-addr.arpa , is used to map IP addresses to names (reverse lookup).
For lower-level domain top-level domains, Internet domain name registration authority delegated to various organizations to the Internet. Map host names and IP addresses of the domain when an organization has licensed certain part of the domain name space, the organization is responsible for naming domain and its subdomains assigned, including computers and other devices in the domain, and manages the distribution of information.
1.2 , zone (Zone)
Region is part of the DNS name space, which contains a set of resource records stored on the DNS server.
The concept of using zones, DNS servers to answer queries about hosts in their own area, each region has its own authorization server.
1.3 , the primary domain name server and secondary domain name server
When the secondary server zone starts, which is connected to the zone master server and initiate a transfer zone, the secondary server periodically zone master server and the communication area, the viewing area of the data is changed. If you change, it starts to transmit data update.
Each district must have a primary server, while each district must have at least a secondary server, or if the area of the primary server crashes, you can not resolve the name of the area.
Secondary server advantages:
1 ) Fault Tolerance
After you configure the secondary server, in the case of the district primary server crashes, the client can still resolve the name of the area. The main region generally
Secondary server and server area installed in different subnets, so if the connection is interrupted to a subnet, DNS clients can
Direct access to another subnet name server.
2 ) reduce the traffic of the wide area link
If a remote area in a large number of clients, users can add a secondary server in a remote area, and the remote client
Configured to query these servers, so that we can prevent a remote client to a DNS query by slow communications link.
3 ) relieving the load on the main server
Secondary server can answer queries of the area, thus reducing the number of queries the district master server must be answered.
1.4 , the DNS concepts
(1) DNS server
The computer running the DNS server program, the DNS database to store information. DNS server will attempt to resolve client queries.
When answering inquiries, if the DNS server can provide the requested information, it is a direct response to the analysis result, if the DNS server
No corresponding domain name information, for the client to provide another server can help address resolution query, if the above two methods
Fails, the client does not respond to information requests or information requested does not exist.
(2) DNS cache
DNS server when parsing client requests, if not the local DNS information, you can ask other DNS servers will be, when
Other domain name server returns the query result, the DNS server will result recorded in the local cache, DNS cache becomes .
The next time the client submits the same request, DNS servers can directly use the information in the cache of DNS resolution.
1.5, see a DNS query process:
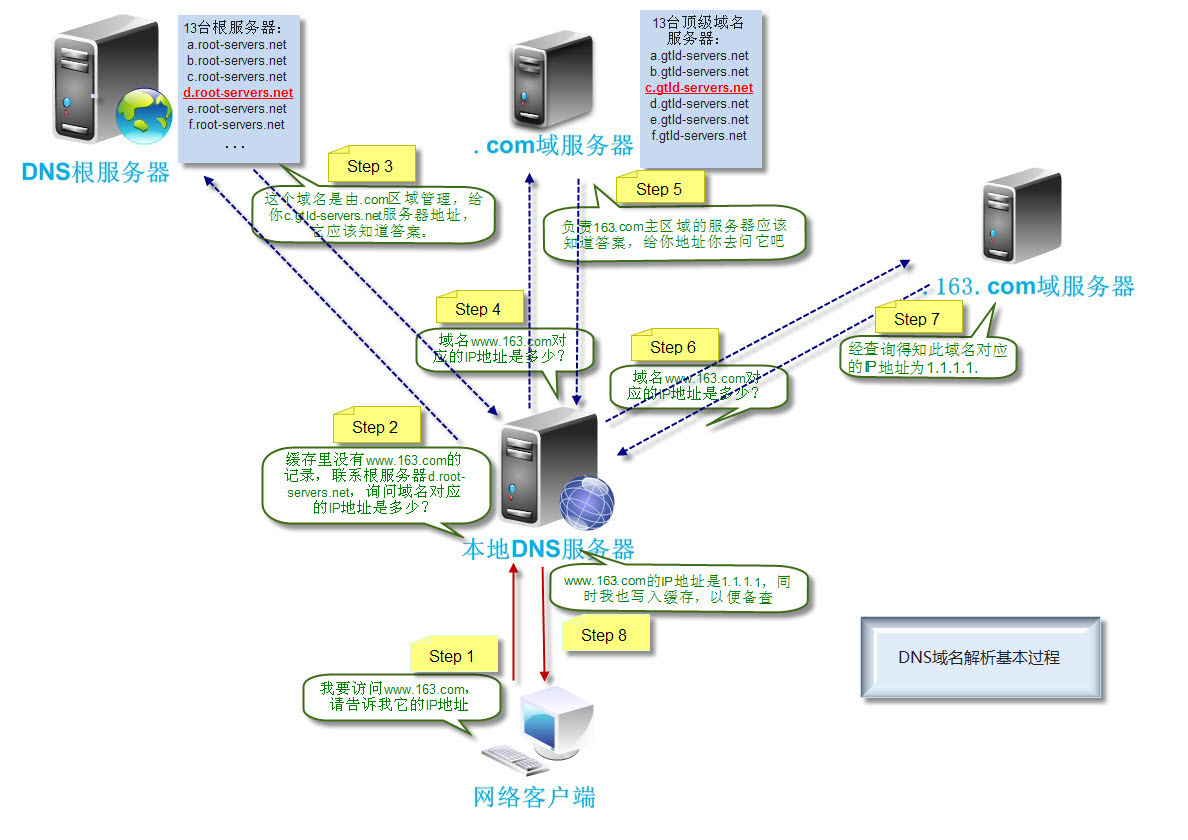
Roughly it works:
The client initiates a request, first check the local cache, there will return, not for the issue of the root domain
Root domain name servers and then returned to the local domain name server is one of the query field of top-level domain name server address
Then, the local server in the domain server sent return addresses ,
The request to query the domain name server queries its cache and record , if there is information about the client query result is returned
Fruit, otherwise notify the client subordinate domain name server address
Local domain name server sends the query to the DNS server returns.
Local server domain name server returns the query result (if the DNS server does not contain the domain name information query, the query process
Repeat until you return to parse the information to respond to or resolve failed).
Local domain name server to save the results returned to the cache, and returns the result to the client .
1.6, the DNS query: recursive queries, and iterative queries
(1) recursive queries
Recursive query is a type of DNS query mode server, the DNS server receives a client request in this mode, you must be a
More accurate results reply client. If the DNS server queries DNS information is not stored locally, then the server inquiry
Asked another server, and submit query results returned to the client . (In short, one-stop service, to find results that are returned to the client)
(2) iterative query
DNS server queries another way iterative queries, when a client sends a query request, the DNS server does not respond directly to query results, but to tell the client to another DNS server address, the client submits a request again this DNS server , followed by cycle until you return query results so far. ( I do not want trouble, do not know, let you ask others may know of )
1.7 , forward and reverse DNS resolve
1 ) analytical positive
Forward resolution refers to the domain name to IP resolution process addresses.
2 ) reverse lookup
Reverse resolution from IP address to the domain resolution process name. Reverse analysis of the role of verifying the identity of the server.
http://dns.aizhan.com/
1.8 , the DNS resource records
1 ) SOA resource record
At the beginning of each zone area contains an initial authorization record (Start of Authority Record), referred to as SOA record.
SOA defines global parameters domain, set up to manage the entire domain. A zone file only allows the existence and uniqueness of the SOA record .
2 ) NS resource record
NS (the Name Server) record is a domain name server records for the specified domain name to the DNS server which resolved . Each region comprises at least one NS records at the root area.
3 ) A resource record
Address (A) resource records for the FQDN mapped to IP addresses . Because of this record, the DNS server can resolve the FQDN domain names corresponding IP addresses.
4 ) PTR resource record
A relative resource record, pointer (PTR) records the IP address mapped to the FQDN . Used for reverse lookup by IP address, find the domain name.
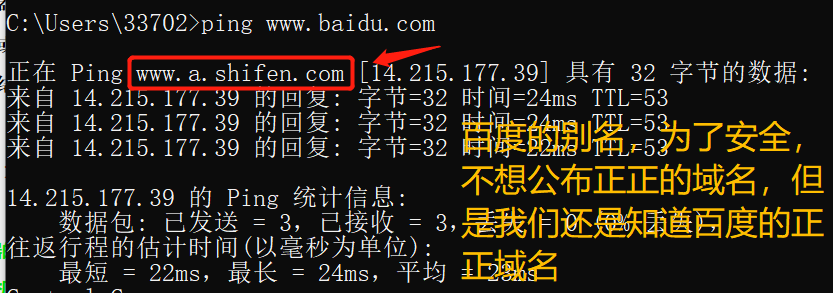
5 ) CNAME resource record
Alias record (CNAME) resource records create aliases of specific FQDN. Users can use CNAME records to hide the implementation details of the users of the network, the client connection can not know the real name.
Example: ping when Baidu, Baidu to resolve the alias server. Baidu has a = CNAME www.a.shifen.com . Alias
6 ) MX resource record
Mail Exchange (MX) resource record for the DNS domain name specified e-mail exchange server.
Mail exchange server is a host processing or forwarding a message for the DNS domain name. It refers to message processing mail to a destination or a different type of message transmitted to the sender. It refers to message forwarding messages sent to the final destination server, the transfer protocol SMTP Simple Mail message transmission to the final destination from the recent mail exchange server, or to the message queue after a certain time.
These are related concepts.
Mode: C / S Mode