9.3 represents the relationship between
General representation of the relationship:
- All relationships are listed;
- To use a {T, F} mapping
Representation of special relationship
- 0-1 matrix (zero-one matrix) is represented;
- There is represented by a directed graph (directed graph)
It shows the relationship with the adjacency matrix
He said 0-1 matrix M R is the adjacency matrix R, defined as follows:
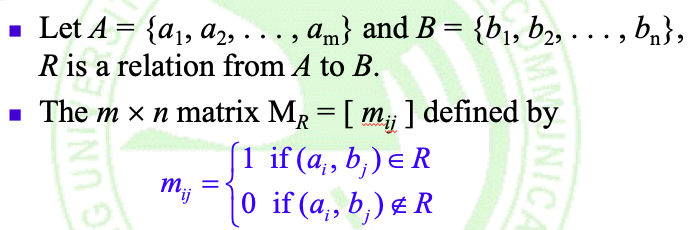
- 0-1 by the observation matrix, it is easy to find the following properties:
- Has a reflexive (reflexive) 0-1 matrix main diagonal are all "1"
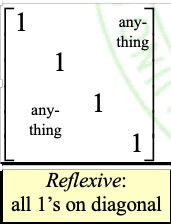
- Have the non-reflexive (irreflexive) 0-1 main diagonal matrix are all "0"
- 0-1 principal diagonal matrix has any of symmetry (Symmetric) and symmetrical about the main diagonal elements are equal

- 0-1 have any major diagonal matrix inversion symmetry (. Associative), the element on the main diagonal symmetry can not be both "1"

- Definition of two adjoining matrices join a boolean OR operation on these two matrices (boolean 'or')
- Definition of two adjoining matrices meet a Boolean AND operation of these two matrices (boolean 'and')
Express complex relationships with the 0-1 matrix:
Order M S◦R = [T ij of ], M R & lt = [R & lt ij of ], M S = [S ij of ]
the M S◦R = M R & lt ⊙ M S
wherein, ⊙ represents two Boolean matrix multiplication (boolean product)
例:
\[ M_R = \left[\begin{matrix} 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{matrix} \right] \]
\[ and \quad M_S = \left[\begin{matrix} 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] \]
The M S◦R for each t ij by the M R & lt i-th row and M S for Boolean j-th column multiplication, the adjacency matrix is obtained S◦R:
\ [S◦R of M_ {} = \ left [ \ begin {matrix} 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \ end {matrix} \ right] \]
Boolean matrix multiplication calculator
Chart shows the relationship with
understanding:
- Vertex (vertex)
- 边(arc or edge)
- Digraph (directed graph or digraph)
Example: a relation expressed there using the FIG:

- And the out-degree of
- A vertex number as a starting point of an arrow: the degree of a vertex
- The degree of a vertex: the vertex number of the end point of the arrow a

Restriction
If R is defined in the relation of A and B is a subset of A, the limit R (the restriction of R to B) of B is:R ∩ (B × B)
- FIG special properties
- FIG reflexive: Each node has a loopback

- Figure has anti-reflexive: no link from point
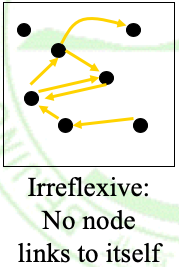
- Figure reflexive: All arrows are bi-directional

FIG reflexive: No double arrow

- Special attention: ① not only not anti-symmetric asymmetric map; ② no neither reflexive nor anti-reflexive Fig...
- Some equivalence relation:
There is a relation R, and its adjacency matrix M R , △ is provided an equivalence relation, i.e. M △ is the identity matrix
①. R自反 <= => △ ⊆ R <= => all 1's on its main diagonal
②. R反自反 <= => △ ∩ R = ∅ <= => all 0's on its main diagonal
③. R对称反对称非对称显然不赘述
④. R传递 <= => MR=[mij]具有这个性质:如果mij = 1,并且mjk = 1,那么mik = 1.
④. R传递 ==> R2 ⊆ R, because if a and c are connected by a path of length 2 in R, then they must be connected by a path of length 1.
- 误区:


The answer is NO!