Routing (routing) defined refers to a packet from source to destination, the decision process of network-wide end path. In the OSI model, primarily in the third routing network layer: to establish a connection between two nodes by addressing, the transport layer is sent source packet, select the appropriate routing and switching node, correct transmitted to the destination address according to the transport layer. Routers forward routing information based on the guidance of the IP packet path, the path routing information provided by forwarding packets.
classification
1. Static routing: The administrator manually define a route to a destination network or several networks.
2. Dynamic Routing: The router according to the rules defined by the routing protocol to exchange routing information, and independently choose the best path.
3. Default Route: A default route is selected when the routing table entry between the packet's destination address of the router and no match can be made.
Generally, the route search order router static routing, dynamic routing, if not more suitable route in the routing table, a default route through out the transport packets, may be integrated using three routes.
1. Static Routes
You can specify a static route in the routing table, you configure the router as static routing. By configuring static routes, the user can arbitrarily specify a path to go through the access network, static routes in the network structure is relatively simple, and generally reaches a certain path through the network only case. Static routing does not require the use of a routing protocol, but the need to manually update the routing table by the router administrator. Static routing, usually can not respond to changes in line routing unreasonable and so on. Thus, usually only a relatively simple route in the network, only the case of using static routing path between the network and routing network.
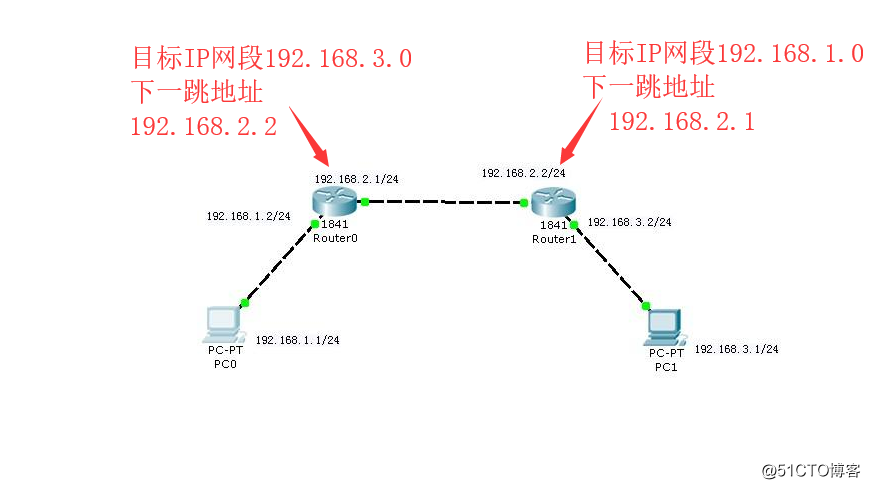
As shown below:
IP packet is 192.168.1.1 wants to transfer to the host IP 192.168.3.1, dried must pass on the same segment as the router is not on. Below, as long as the two network routers to reach the target address with the configuration (IP address that is next to be transmitted) the next hop, the PC0 PC1 with a data transmission can be carried out.
2. Dynamic Routing
由路由器按指定的协议格式在网上广播和接收路由信息,通过路由器之间不断交换的路由信息动态地更新和确定路由表,并随时向附近的路由器广播,这种方式称为动态路由。动态路由器通过检查其他路由器的信息,并根据开销、链接等情况自动决定每个包的路由途径。动态路由方式仅需要手工配置第一条或最初的极少量路由线路,其他的路由途径则由路由器自动配置。动态路由由于较具灵活性,使用配置简单,成为目前主要的路由类型。
动态路由机制的运作依赖路由器的两个基本功能:路由器之间适时的路由信息交换,对路由表的维护:
路由器之间适时地交换路由信息。
动态路由之所以能根据网络的情况自动计算路由、选择转发路径,是由于当网络发生变化时,路由器之间彼此交换的路由信息会告知对方网络的这种变化,通过信息扩散使所有路由器都能得知网络变化。
路由器根据某种路由算法(不同的动态路由协议算法不同)把收集到的路由信息加工成路由表,供路由器在转发IP报文时查阅。
在网络发生变化时,收集到最新的路由信息后,路由算法重新计算,从而可以得到最新的路由表。
路由器之间的路由信息交换在不同的路由协议中的过程和原则是不同的。交换路由信息的最终目的在于通过路由表找到一条转发IP报文的“最佳”路径。每一种路由算法都有其衡量“最佳”的一套原则,大多是在综合多个特性的基础上进行计算,这些特性有:路径所包含的路由器结点数(hop count)、网络传输费用(cost)、带宽(bandwidth)、延迟(delay)、负载(load)、可靠性(reliability)和最大传输单元MTU(maximum transmission unit)。
常见的动态路由协议有:RIP、OSPF、IS-IS、BGP、IGRP/EIGRP。每种路由协议的工作方式、选路原则等都有所不同。
3.缺省路由
要想使每台路由器对到每个可能目的地的路由都进行维护是不可行的,所以路由器可以保存一条缺省路由,或者叫最后的可用路由。当路由器不能用路由表中的一个更具体条目来匹配一个目的网络时,它就将使用缺省路由,即“最后的可用路由”。实际上,路由器用缺省路由来将数据包转发给另一台路由器,这台新的路由器必须要么有一条到目的地的路由,要么有它自己的到另一台路由器的缺省路由,这台新的路由器依次也必须要么有具体路由,要么有另一条缺省路由。依此类推。最后数据包应该被转发到真正有一条到目的地网络的路由器上。没有缺省路由,目的地址在路由表中无匹配表项的包将被丢弃。
缺省路由可以尽可能地将路由表的大小保持的很小,它们使路由器能够转发目的地为任何Internet主机的数据包而不必为每个Internet网络都维护一个路由表条目。