typora-copy-images-to: images
What is polymorphism?
For example:
This creates a generic object:
Cat cat x = new (); cat creates an object, and by reference to this class of the object x points to the cat;
Polymorphic objects:
Animal x1 = new Cat (); x1 parent class reference point to this cat subclass objects;
This reference x1 form that is have the cat, but also with the shape of animals.
Simply put: that is, an object corresponding to different types, how to reflect it in the code? Parent class or subclass object reference point interface.
Polymorphism of three conditions exist:
- Have inheritance relations
- Subclasses override inherited methods
- References to parent child class object
Polymorphic Examples
Animal superclass
class Animal {
int num = 10;
static int age = 20;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("动物吃饭");
}
public static void sleep(){
System.out.println("动物睡觉");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("动物在奔跑");
}
}Cat subclass
class Cat extends Animal{
int num = 66;
static int age = 40;
String name = "tomCat";
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃饭");
}
public static void sleep(){
System.out.println("猫睡觉");
}
public void catMouse(){
System.out.println("猫在抓老鼠");
}
}Test category
/**
* @ClassName: DuotaiDemo
* @author: benjamin
* @version: 1.0
* @description: 多态举例
*/
public class DuotaiDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 父类引用指向了子类对象
Animal am = new Cat();
am.eat();
am.sleep();
am.run();
System.out.println(am.num);
System.out.println(am.age);
}
}result
Cats eat
animals sleeping
animals on the run
10
20
problem found
Subclasses override a non-static member method eat (): Cat food
Subclasses override a static member method sleep (): animals sleep
Subclass the parent class member method is not overridden run (): Animals in the running
to sum up:
Member variable : Compile look to the left (parent), run to the left to see the (parent)
Member method : Compile look to the left (parent), run to the right to see (subclass)
Static methods : do not involve polymorphisms object. Because static functions as the load and load class. Direct calls can use the class name.
Features Examples
Member variables
Simply put: the compiler and runtime are referenced to the left of the equal sign
Compile time: Reference Is there a class member variable called variable belongs there, compile, not, fail to compile;
Runtime: Reference Is there a class member variable called variable belongs to, and run the member variable belongs to class.
For example:
Performing DuotaiFu f = new DuotaiZi (); case subtype lifting supertype, by looking for parent supertype
public class DuotaiDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DuotaiFu f = new DuotaiZi();
System.out.println(f.num);//3
}
}
class DuotaiFu{
int num = 3;
}
class DuotaiZi extends DuotaiFu{
int num = 4;
}Graphic memory
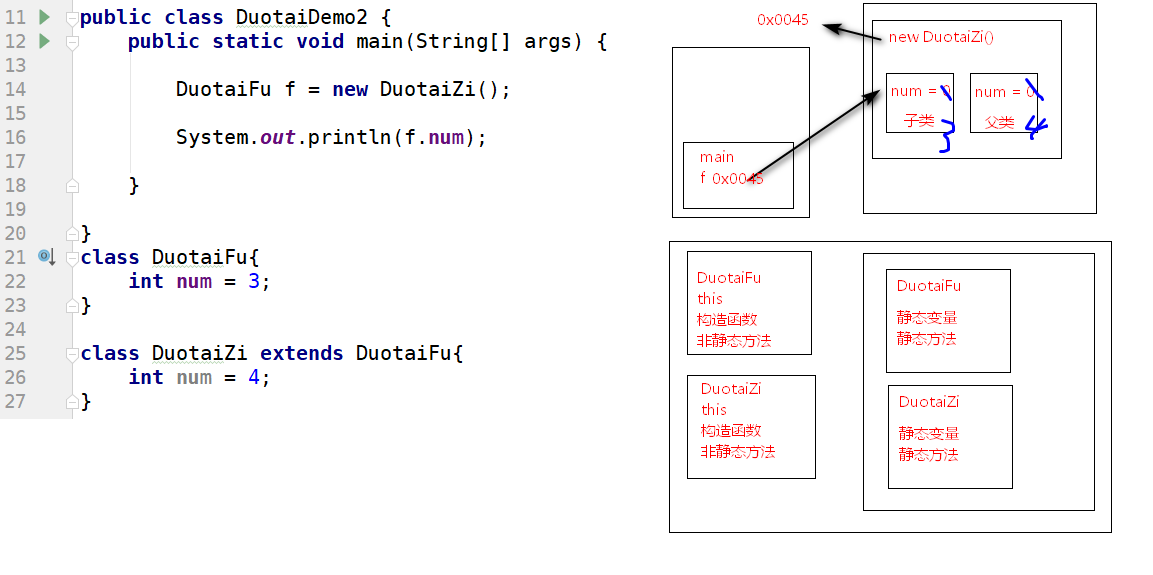
Member function (focus)
Non-static function
Simply put: Look left compile time, runtime look to the right
Compilation: Is there a function call references a class variable belongs there, compile, not, fail to compile;
Runtime: reference is whether there is a function called class object belongs.
For example:
show function is running, holding this reference, point to the object 0x0034 (new Zi ()), the object is to find the show method of operation;
public class DuotaiDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DuotaiFu f = new DuotaiZi();
f.show();
}
}
class DuotaiFu{
void show(){
System.out.println("fu show...");
}
}
class DuotaiZi extends DuotaiFu{
void show(){
System.out.println("zi show...");
}
}
// zi show...Memory illustration:
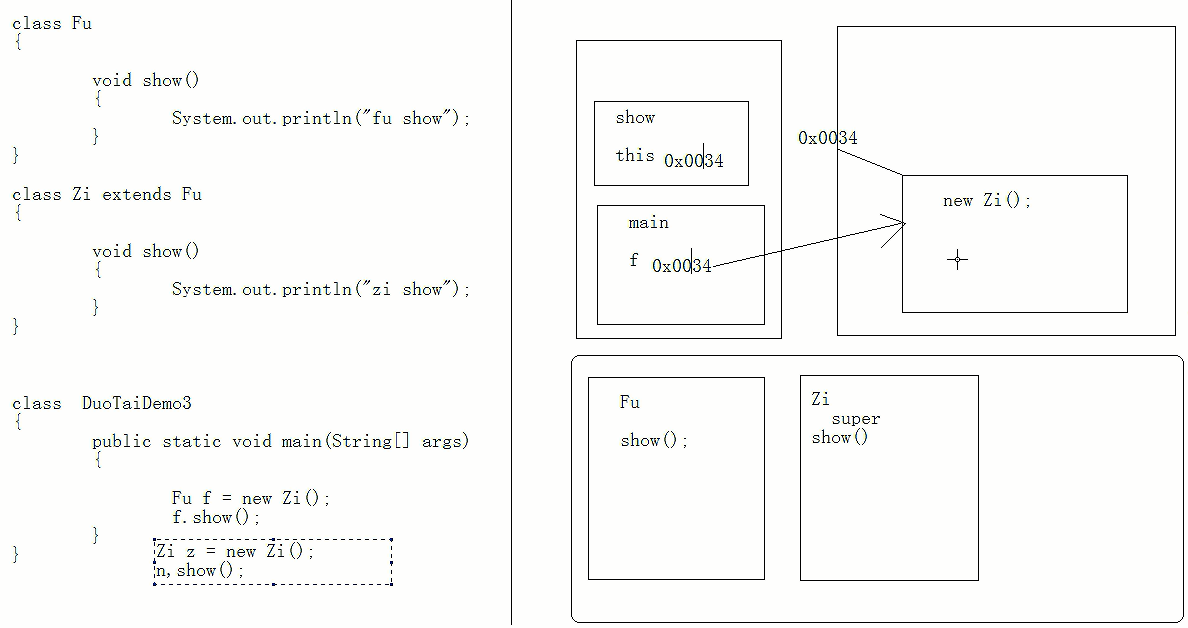
Static function
It does not involve polymorphisms object. Because static functions as the load and load class. Direct calls can use the class name.
Compilation: Are there references a static method call type variable belongs;
Runtime: Are there references a static method call type variable belongs;
For example:
Non-static method must be bound to the specified object, in order to run;
package java_demo_2;
public class DuotaiDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DuotaiFu f = new DuotaiZi();
f.method();
DuotaiFu.method();
DuotaiZi.method();
}
}
class DuotaiFu{
void show(){
System.out.println("fu show...");
}
static void method(){
System.out.println("父类静态方法");
}
}
class DuotaiZi extends DuotaiFu{
void show(){
System.out.println("zi show...");
}
static void method(){
System.out.println("子类静态方法");
}
}result:
Parent class static methods
parent class static method
sub-class static method
Downcast and upcast
Upcast:
- Concept:
Animal a = new Cat();cat ascend into the type of animal, but the cat-specific functions will be inaccessible. - Objective: To restrict access to specific features, professional talk is upward transition.
Downcast:
The concept: If the unique features with specific animals cats want, you can object downcast. Such as:
Cat c = (Cat) am;
c.catchMouse();
Objective: To use a specific method in the subclass.
For example:
// 向上转型
Animal am = new Cat();
am.eat();
// 向下转型
Cat cat = (Cat) am;
cat.catMouse();
System.out.println(cat.name);
输出
猫在抓老鼠
tomCatType conversion exception:
For the transformation, from start to finish we are doing in the class object type of change. Cats - Animals - Cats
Cat c2 = (Cat) d; c2.catchMouse();//ClassCastException // 不能把一个猫——动物——狗;报错
Type judgment:
instanceof : Indicates whether the object is an instance of a particular class, only reference data for determining the type commonly used prior to the transition determination robustness downward run.
For example:
public class DuotaiDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//向上转型
Animal c = new Cat();
Animal d = new Dog();
method(c);
method(d);
public static void method(Animal a){
a.eat();
if(a instanceof Cat){
Cat c = (Cat) a;//向下转型,执行对象的特有方法;
c.catchMouse();
}
else if(a instanceof Dog){
Dog d = (Dog) a;
d.lookHome();
}
}
}Reference links
Polymorphism in a few words can explain the JAVA intuitive about it? - Answer the dog program - know almost
https://www.zhihu.com/question/30082151/answer/120520568