Forwarding: ip _ forward function
to reach the final destination of the packet non-system needs to be forwarded. Only when ipforwarding zero or when packet
when the source is included in the route, ipintr only call forwarding function to achieve ip _ forward algorithm. When the packet contains
the source routing, ip _ dooptions call ip _ forward, and the second parameter is set to 1 srcrt.
ip _ forward route in the routing table configuration interface is shown by FIG.
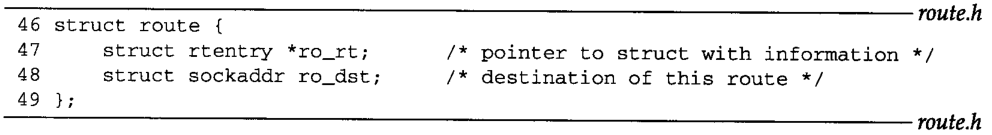
4 6 - 4 9 route structure has two members: ro _ rt, pointer rtentry structure; ro _ dst, a
sockaddr structure, designated _ RO associated with the routing destination item referred to rt. The destination is in the kernel routing table using
to find the key routes of
our two-part discussion ip _ forward. Determining a first part allows the system to forward the packet, to modify the IP header, is divided and
routed groups. The second part of the process ICMP redirect packet, and the packet is transmitted to the ip _ output. As shown below.
1. The packet forwarding it for
8 6 7 - 8 7 1 ip _ froward the first parameter is a pointer to a pointer mbuf chain, which contains mbuf to be forwarded
packet. Srcrt If the second parameter is non-zero, the packet since the source route option (see section 9.6) is being forwarded.
8 7 9 - 8 8 4 if the following statements identify and discard packets.
• link-layer broadcast
any support broadcast network interface driver must receive the broadcast packet M _ BCAST flag. If the packet is
addressed to a broadcast address of the Ethernet, the ether _ input put M _ BCAST set. Extensive link layer does not forward
broadcast packets.
RFC 11 2 2 not allowed to transmit a link-layer broadcast manner unicast packet addressed to the IP address, and
where the packet is discarded.
• loopback packet
addressed to the loopback packet networks, in _ canforward return 0. These packets will be submitted to the ipintr _ IP
F orward, because feedback interface is not configured correctly.
• Network 0 and Class E addresses
for these packets, in _ canforward return 0. The destination address is not valid, and since there is no host receives
these packets, they should not continue to flow in the network.
• Class D address of
a packet addressed to the Class D multicast address should be a multi-function ip _ mforward not by ip _ forward process.
in _ canforward reject class D (multicast) address.
RFC 791 requires all system processing the packets must survival time (TTL) field subtract at least 1, even if the TTL is
in seconds calculated. Because of this requirement, TTL generally considered to be jumping on the number of IP packets can be dropped before passing
boundaries. From a technical point of view, if the router is holding packets over one second, it must take more than one ip _ ttl minus.
