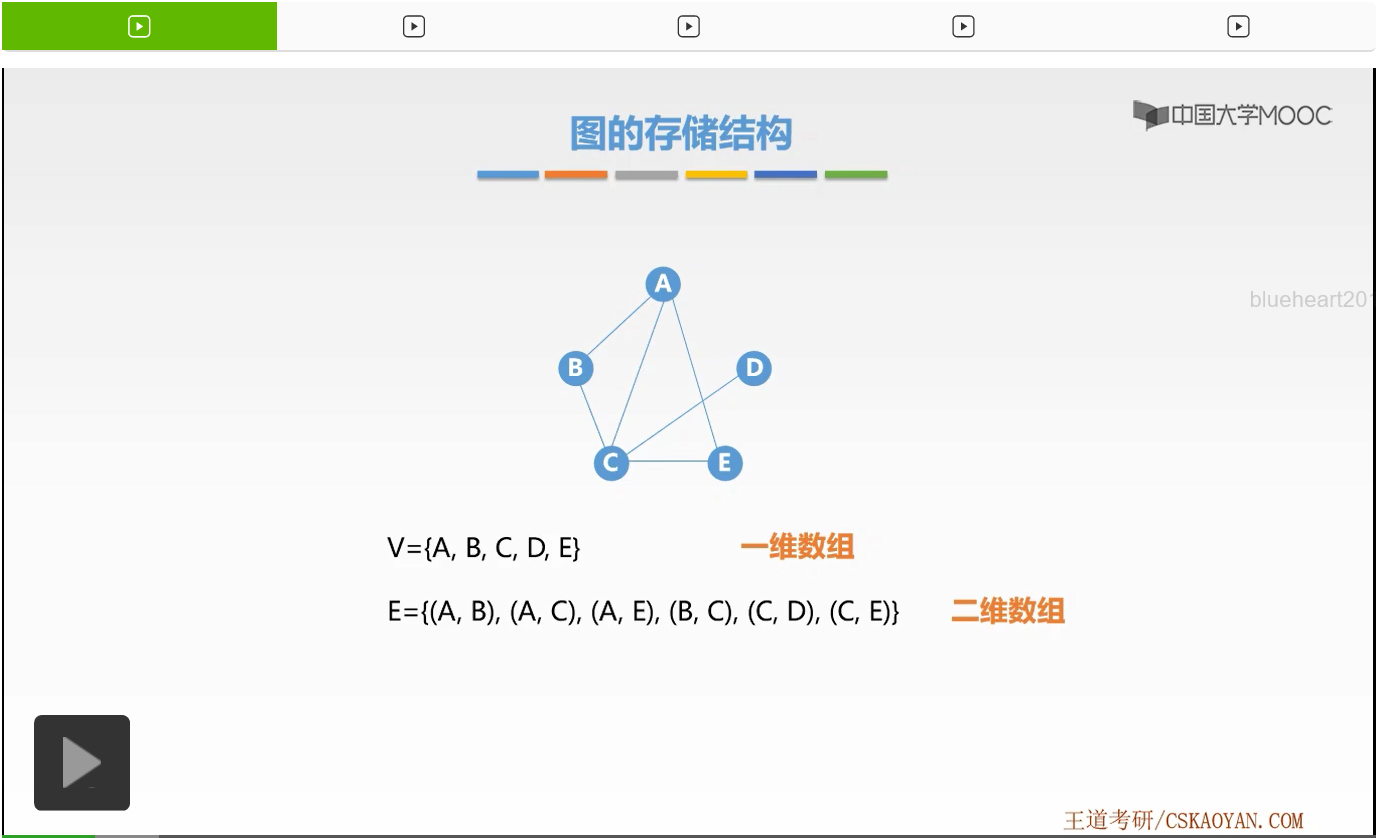
The lesson we learned about the logical structure of the graph, diagram and related definitions important basic concepts. We present to contact the class of the basic structure of FIG. Figure how to store it? Today is the method of learning adjacency matrix.

What is the adjacency matrix, we look at one such example. This is an undirected graph, it tells us a lesson on how to represent this figure had it? If the graph is G, we have two collections. The first is a set of points V, which holds all the nodes. The second is a set of edges E, which holds the relationship between the point of what we call taking sides. So we store this figure is not that store a collection of the set of edges that point ah. How to store it? Among adjacency matrix we used a one-dimensional array to store every node. And with a two-dimensional array to store the each side. How to store it? How to store it? In fact, it is a fact, it is a form of a matrix. So where the row number indicates the starting end side of the column number is represented termination point, the value of which indicates whether or not there is the side of the edge as well as some heavy weight. This is a two-dimensional array representation edges.
We call this a two-dimensional matrix array represented as an adjacency matrix.
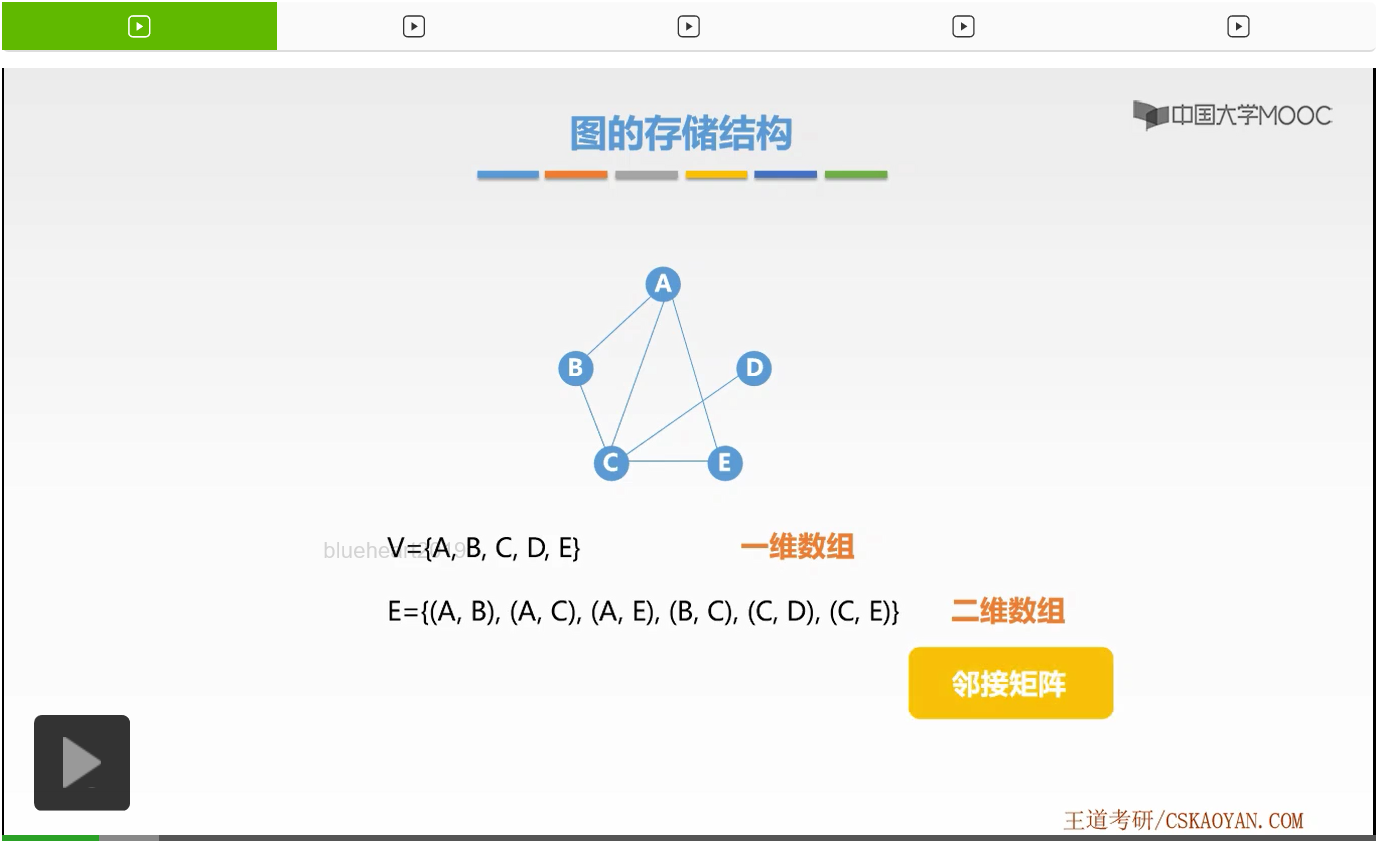
Well, then we have to learn how specific adjacency matrix of diagrams stored. First of all, we require