1. time module
1.1 represents a time of several ways:
- Timestamp (timestamp): Generally speaking, the timestamp indicates that from January 1970 00:00:00 1st offset press in seconds. We run "type (time.time ())", returns a float.
- Formatted time string (Format String)
- Structured time (struct_time): struct_time tuple total of nine elements were nine elements :( year, month, day, hour, minute, second, the first few weeks of the year, day of the year, daylight saving time)
import time
#--------------------------我们先以当前时间为准,让大家快速认识三种形式的时间
print(time.time()) # 时间戳:1487130156.419527
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X")) #格式化的时间字符串:'2017-02-15 11:40:53'
print(time.localtime()) #本地时区的struct_time
print(time.gmtime()) #UTC时区的struct_time1.2 format string time format
%a Locale’s abbreviated weekday name.
%A Locale’s full weekday name.
%b Locale’s abbreviated month name.
%B Locale’s full month name.
%c Locale’s appropriate date and time representation.
%d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31].
%H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23].
%I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12].
%j Day of the year as a decimal number [001,366].
%m Month as a decimal number [01,12].
%M Minute as a decimal number [00,59].
%p Locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM. (1)
%S Second as a decimal number [00,61]. (2)
%U Week number of the year (Sunday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Sunday are considered to be in week 0. (3)
%w Weekday as a decimal number [0(Sunday),6].
%W Week number of the year (Monday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Monday are considered to be in week 0. (3)
%x Locale’s appropriate date representation.
%X Locale’s appropriate time representation.
%y Year without century as a decimal number [00,99].
%Y Year with century as a decimal number.
%z Time zone offset indicating a positive or negative time difference from UTC/GMT of the form +HHMM or -HHMM, where H represents decimal hour digits and M represents decimal minute digits [-23:59, +23:59].
%Z Time zone name (no characters if no time zone exists).
%% A literal '%' character.1.3 times of different formats conversion
Wherein the computer time is recognized only 'timestamp' format, or human programmer can understand the processing time are: 'time formatted string', 'structured time', so with the conversion relationship diagram
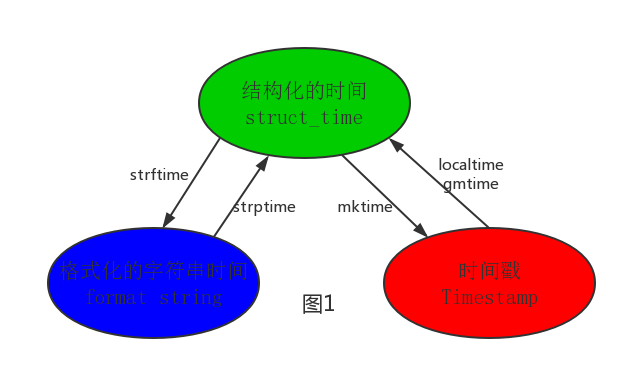
# localtime([secs])
# 将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。
time.localtime()
time.localtime(1473525444.037215)
# gmtime([secs]) 和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()方法是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time。
# mktime(t) : 将一个struct_time转化为时间戳。
print(time.mktime(time.localtime()))#1473525749.0
# strftime(format[, t]) : 把一个代表时间的元组或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和
# time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t未指定,将传入time.localtime()。如果元组中任何一个
# 元素越界,ValueError的错误将会被抛出。
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime()))#2016-09-11 00:49:56
# time.strptime(string[, format])
# 把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作。
print(time.strptime('2011-05-05 16:37:06', '%Y-%m-%d %X'))
#time.struct_time(tm_year=2011, tm_mon=5, tm_mday=5, tm_hour=16, tm_min=37, tm_sec=6,
# tm_wday=3, tm_yday=125, tm_isdst=-1)
#在这个函数中,format默认为:"%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y"。
# asctime([t]) : 把一个表示时间的元组或者struct_time表示为这种形式:'Sun Jun 20 23:21:05 1993'。
# 如果没有参数,将会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。
print(time.asctime())#Sun Sep 11 00:43:43 2016
# ctime([secs]) : 把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转化为time.asctime()的形式。如果参数未给或者为
# None的时候,将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))。
print(time.ctime()) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016
print(time.ctime(time.time())) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016# sleep(secs)
# 线程推迟指定的时间运行,单位为秒。2.datetim module
#时间加减
import datetime
print(datetime.datetime.now()) #返回 2016-08-19 12:47:03.941925
print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()) ) # 时间戳直接转成日期格式 2016-08-19
print(datetime.datetime.now() )
print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(3)) #当前时间+3天
print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(-3)) #当前时间-3天
print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=3)) #当前时间+3小时
print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=30)) #当前时间+30分
# c_time = datetime.datetime.now()
# print(c_time.replace(minute=3,hour=2)) #时间替换3.random module
import random
print(random.random())#(0,1)----float 大于0且小于1之间的小数
print(random.randint(1,3)) #[1,3] 大于等于1且小于等于3之间的整数
print(random.randrange(1,3)) #[1,3) 大于等于1且小于3之间的整数
print(random.choice([1,'23',[4,5]]))#1或者23或者[4,5]
print(random.sample([1,'23',[4,5]],2))#列表元素任意2个组合
print(random.uniform(1,3))#大于1小于3的小数,如1.927109612082716
item=[1,3,5,7,9]
random.shuffle(item) #打乱item的顺序,相当于"洗牌"
print(item)