Chinese remainder theorem, also known as the Chinese remainder theorem (What is the name ah) is a method congruence group (see congruence) to solve the ancient Chinese. Number Theory is an important theorem. First, let a little! example! question! Now!
Notes: Three number abc, the remainder were m1 m2 m3,% calculated for the remainder of this year, && is the "and" operator.
1 , respectively, to find two numbers can be divisible, and meet the minimum number is divisible by more than a third.
K1 % B% C K1 == == 0 &&% A == K1 . 1 ;
K2 % A% K2 == C == 0 &&% B == K2 . 1 ;
K3 % A% B K3 == == 0 && % C == K3 . 1 ;
2 , the three unknowns corresponding to the digital multiplier I plus up, subtract the number of three i.e. an integral multiple of the least common multiple of the results obtained.
Answer = K1 × M1 + K2 × M2 + K3 × M3 - P × (A × B × C);
P to satisfy answer > largest integer 0;
or answer = (K1 × M1 + K2 × M2 + K3 × M3) % (a × b × c) ;
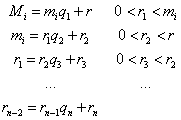
Let's prove little wave
M2 = M1 * set * M * ...... Mn
Mi = M / mi The
set of inverse element Mi Mi ^ (- . 1 ) (mi The MOD)
has Mi * Mi ^ (- . 1 ) ≡ . 1 (mi The MOD )
AI * Mi * Mi ^ (- . 1 ) ≡ai (mi the MOD)
for all j not equal to I
AI * Mi * Mi ^ (- . 1 ) ≡ 0 (MJ MOD)
so the answer is that all AI * Mi * Mi ^ (- . 1 ) (P MOD) value
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 long long x,y; 4 long long a[15],b[15]; 5 long long n; 6 void exgcd(long long A,long long B) 7 { 8 if(B==0) 9 { 10 x=1; 11 y=0; 12 return; 13 } 14 exgcd(B,A%B); 15 long long z=x; 16 x=y; 17 y=z-(A/B)*y; 18 } 19 long long fast(long long a1,long long b1,long long mod) 20 { 21 long long ans=0; 22 a1%=mod; 23 b1%=mod; 24 while(b1) 25 { 26 if(b1&1) 27 { 28 ans=(ans+a1)%mod; 29 } 30 b1>>=1; 31 a1=(a1+a1)%mod; 32 } 33 return ans; 34 } 35 long long china() 36 { 37 long long ans=0; 38 long long M=1; 39 for(long long i=1;i<=n;i++) 40 M*=b[i]; 41 for(long long i=1;i<=n;i++) 42 { 43 long long m=M/b[i]; 44 exgcd(m,b[i]); 45 while(x<0) 46 x+=b[i]; 47 x%=b[i]; 48 ans=(ans+fast(x,fast(m,(a[i]+M)%M,M),M)+M)%M; 49 } 50 return ans; 51 } 52 int main() 53 { 54 cin>>n; 55 for(long long i=1;i<=n;i++) 56 { 57 scanf("%lld",&a[i]); 58 } 59 for(long long i=1;i<=n;i++) 60 { 61 scanf("%lld",&b[i]); 62 } 63 cout<<china(); 64 return 0; 65 }