The storage engine mysql
mysql storage engine Overview
What is the storage engine?
MySQL data in a variety of different technologies stored in the file (or memory) in the. Each of these technologies technology uses a different storage mechanism, indexing techniques, lock level and ultimately provide a wide range of different functions and capabilities. By choosing different techniques, you can get extra speed or functionality, thereby improving the overall functionality of your application.
For example, if you are a large number of temporary data in the study, you may need to use memory storage engine. Memory storage engine to store all of the table data in memory. Or, you may need a support transaction processing database (to ensure that the transaction is unsuccessful rollback capability when data).
These different technologies and supporting the associated function is called in MySQL storage engine (also called table type).
MySQL default configuration of many different storage engines, you can pre-set or enabled in the MySQL server. You can choose to apply to servers, databases and tables storage engine in order to choose how to store your information, how to retrieve this information and data when you need to combine what your performance and functionality to provide maximum flexibility for you.
Choose how to store and retrieve your data, this flexibility is the main reason why the MySQL so popular. Other database systems (including most commercial choice) only support one type of data storage .
Unfortunately, other types of database solutions to take the "one size to meet all needs" approach means you are either to sacrifice some performance, either you use a few hours or even days of time detailed adjust your database. Using MySQL, we only need to modify the storage engines we use it
What storage engine mysql support?
mysql5.6 supported storage engines, including InnoDB, MyISAM, MEMORY, CSV, BLACKHOLE, FEDERATED, MRG_MYISAM, ARCHIVE, PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA. Which NDB and InnoDB provides transaction-safe tables, other storage engines are non-transaction-safe tables.
Characteristics of various storage engines
Overview
MySQL servers using multi-layer design and independent modules, plug-in storage engine architecture that allows the engine to the load store operation are new MySQL server, Pluggable Storage Engines portion in the figure. Using MySQL server architecture, providing a consistent and simple application model and API, an application programmer and DBA in the storage level (i.e. Pluggable Storage Engines) may no longer be considered all the underlying implementation details. Thus, although different storage engines have different capabilities, applications are separated therefrom. Storage engine on the secretary to deal with the file system.

Concurrency: some applications has many applications other than the particle size required locking (e.g., row level locking). Transaction support: Not all applications require services, but does require the application of a transaction, it has a well-defined requirements such as ACID compliant and so on. Referential Integrity: foreign key defined by the DDL, the server enforce referential integrity associated database. Physical memory: it includes a wide range of issues, from the total page size tables and indexes, to store data in the required format, to the physical disk. Index support: different applications tend to use different indexing strategies, each storage engine generally has its own indexing method, but some index methods (such as B-tree index) is common to almost all storage engines . Memory cache: Compared with other applications, different applications respond better to some memory caching strategies, therefore, although some high-speed buffer memory is common (such as a user is connected to all storage engines cache, MySQL's high-speed query cache, etc.), other high-speed buffer strategy uniquely defined only when the use of special storage engine. Performance Help: for parallel operations includes multiple I / O, threads concurrency, database checkpointing, bulk insert processing. Other target properties: may include support for geospatial operations, security restrictions for certain data processing operations and so on.
Concurrency: some applications has many applications other than the particle size required locking (e.g., row level locking). Transaction support: Not all applications require services, but does require the application of a transaction, it has a well-defined requirements such as ACID compliant and so on. Referential Integrity: foreign key defined by the DDL, the server enforce referential integrity associated database. Physical memory: it includes a wide range of issues, from the total page size tables and indexes, to store data in the required format, to the physical disk. Index support: different applications tend to use different indexing strategies, each storage engine generally has its own indexing method, but some index methods (such as B-tree index) is common to almost all storage engines . Memory cache: Compared with other applications, different applications respond better to some memory caching strategies, therefore, although some high-speed buffer memory is common (such as a user is connected to all storage engines cache, MySQL's high-speed query cache, etc.), other high-speed buffer strategy uniquely defined only when the use of special storage engine. Performance Help: for parallel operations includes multiple I / O, threads concurrency, database checkpointing, bulk insert processing. Other target properties: may include support for geospatial operations, security restrictions for certain data processing operations and so on.
The above requirements will be reflected in different needs, it is impossible to achieve through a single system, some of the above characteristics is itself contradictory, the problem of fish and bear's paw. To choose to do the above, the storage engine is a form of a plug-in engine, certain requirements may be used. Below, some of the existing storage engine, and the basic characteristics:
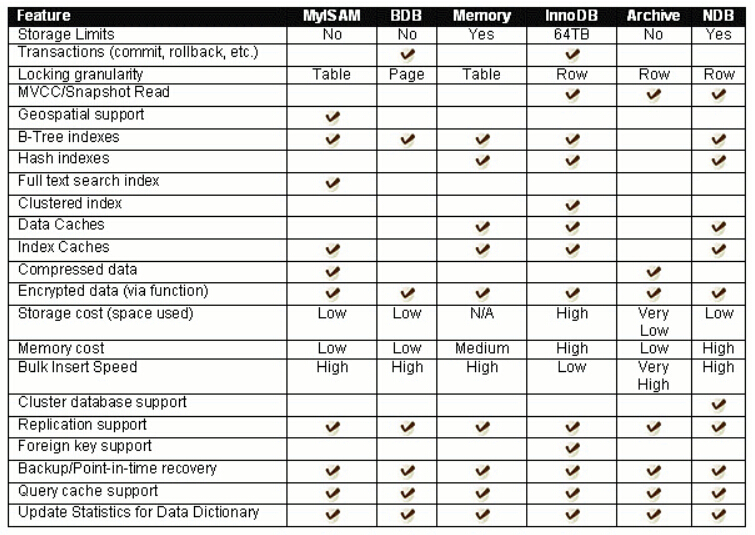

InnoDB MySql version 5.6 the default storage engine. InnoDB is a transaction-safe storage engine that has commit, rollback, and crash recovery features to protect user data. InnoDB row-level locking, and Oracle-style consistent non-locking read to enhance its multi-user concurrency and performance. InnoDB user data stored in the index to reduce aggregation query based on common primary key brings the I / O overhead. To ensure data integrity, InnoDB also supports foreign key constraints. MyISAM MyISAM neither support transactions do not support foreign keys, its advantages are fast access speed, but the table-level locking limits its performance in terms of read and write load, so it is often used in read-only or read-mostly data Scenes. Memory stores all data in memory, applied to the scene to look for non-critical data by fast. Memory type table access data very quickly, because it's data is stored in memory, and use HASH indexes by default, but once the service is shut down, the data table will be lost BLACKHOLE black hole storage engine, similar to the Unix / dev / null, Archive only receives but does not save the data. Query on the table this engine often returns an empty set. Such a table may be applied to the DML statement needs to be sent from the server, but does not retain the primary server and the backup of such data from the master configuration. CSV its table really is a comma-delimited text file. CSV table allows you to import and export data in CSV format, the same format and read and write scripts and applications interact with data. Since CSV table without an index, you'd better put InnoDB table data in general will operate only in the import or export phase uses about CSV table. NDB (Aka NDBCLUSTER) - this engine is particularly suitable for cluster data requires the highest degree of uptime and availability of applications. Note: NDB storage engine is not supported in the standard MySql 5.6 version. Currently supports MySql cluster versions: Based on MySql 5.1 of MySQL Cluster NDB 7.1; based on MySQL Cluster NDB MySql 5.5 of 7.2; based on MySQL Cluster NDB MySql 5.6 7.3. Also based on MySql 5.6 of MySQL Cluster NDB 7.4 is currently under development. Merge allows developers to MySql DBA or series of identical MyISAM tables are grouped and put them as an object reference. For ultra-large-scale data scenarios, such as a data warehouse. Federated provides the ability to create a logical database from a plurality of different physical machines coupled MySql server. Or the market for distributed data scenarios. Example This storage engine to save the example illustrates how to start writing new storage engines MySql source. It is aimed at developers who are interested. This storage engine is a losers do not. "Stub." You can use this engine to create the table, but you can not save any data to which can not retrieve any index from them.
InnoDB MySql version 5.6 the default storage engine. InnoDB is a transaction-safe storage engine that has commit, rollback, and crash recovery features to protect user data. InnoDB row-level locking, and Oracle-style consistent non-locking read to enhance its multi-user concurrency and performance. InnoDB user data stored in the index to reduce aggregation query based on common primary key brings the I / O overhead. To ensure data integrity, InnoDB also supports foreign key constraints. MyISAM MyISAM neither support transactions do not support foreign keys, its advantages are fast access speed, but the table-level locking limits its performance in terms of read and write load, so it is often used in read-only or read-mostly data Scenes. Memory stores all data in memory, applied to the scene to look for non-critical data by fast. Memory type table access data very quickly, because it's data is stored in memory, and use HASH indexes by default, but once the service is shut down, the data table will be lost BLACKHOLE black hole storage engine, similar to the Unix / dev / null, Archive only receives but does not save the data. Query on the table this engine often returns an empty set. Such a table may be applied to the DML statement needs to be sent from the server, but does not retain the primary server and the backup of such data from the master configuration. CSV its table really is a comma-delimited text file. CSV table allows you to import and export data in CSV format, the same format and read and write scripts and applications interact with data. Since CSV table without an index, you'd better put InnoDB table data in general will operate only in the import or export phase uses about CSV table. NDB (Aka NDBCLUSTER) - this engine is particularly suitable for cluster data requires the highest degree of uptime and availability of applications. Note: NDB storage engine is not supported in the standard MySql 5.6 version. Currently supports MySql cluster versions: Based on MySql 5.1 of MySQL Cluster NDB 7.1; based on MySQL Cluster NDB MySql 5.5 of 7.2; based on MySQL Cluster NDB MySql 5.6 7.3. Also based on MySql 5.6 of MySQL Cluster NDB 7.4 is currently under development. Merge allows developers to MySql DBA or series of identical MyISAM tables are grouped and put them as an object reference. For ultra-large-scale data scenarios, such as a data warehouse. Federated provides the ability to create a logical database from a plurality of different physical machines coupled MySql server. Or the market for distributed data scenarios. Example This storage engine to save the example illustrates how to start writing new storage engines MySql source. It is aimed at developers who are interested. This storage engine is a losers do not. "Stub." You can use this engine to create the table, but you can not save any data to which can not retrieve any index from them.
Commonly used storage engine and application scenarios
InnoDB
For transaction processing applications, support for foreign keys, and row-level locking. If the application for completeness things have relatively high requirements, data requirements under concurrent conditions consistency, data insertion and query operations in addition, also it includes many updates and deletes, then the InnoDB storage engine is more appropriate. In addition to effectively reduce the InnoDB caused by the lock deletes and updates can also ensure the integrity of the transaction commit and rollback for similar billing system or financial system for data accuracy requirements are relatively high system suitable choice.
MyISAM
If the application is read and insert operations-based, only a few of update and delete operations, and the integrity of the transaction, concurrency do not ask, you can choose the storage engine.
Memory
All data stored in memory, in the need to quickly locate records and other similar data environment, providing fast access. Memory drawback is that there are restrictions on the size of the table, although the database because of an abnormal termination, then data can be restored to normal, but once the database is shut down, the data will be stored in memory loss.
Mysql storage engine used in
Storage Engine related sql statement
View the current default storage engine: MySQL> Show the Variables like "default_storage_engine"; to query the current database storage engines support mysql> show engines \ G;
 result
result
Specify the storage engine to build the table
Specify when construction of the table
MySQL> Create Table AI (ID BIGINT (12 is), name VARCHAR (200 is)) ENGINE = MyISAM; MySQL> Create Table Country (ID int (. 4), CNAME VARCHAR (50)) ENGINE = the InnoDB; may be used alter table statement modify an existing table storage engine. mysql> alter table ai engine = innodb ;
Specified in the configuration file
File # my.ini [mysqld] default = INNODB-Storage-Engine
mysql workflow
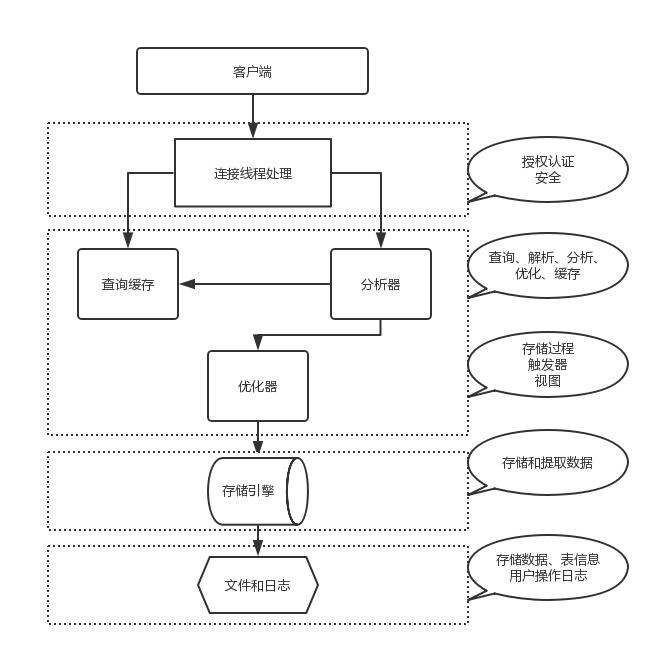
MySQL架构总共四层,在上图中以虚线作为划分。
首先,最上层的服务并不是MySQL独有的,大多数给予网络的客户端/服务器的工具或者服务都有类似的架构。比如:连接处理、授权认证、安全等。
第二层的架构包括大多数的MySQL的核心服务。包括:查询解析、分析、优化、缓存以及所有的内置函数(例如:日期、时间、数学和加密函数)。同时,所有的跨存储引擎的功能都在这一层实现:存储过程、触发器、视图等。
第三层包含了存储引擎。存储引擎负责MySQL中数据的存储和提取。服务器通过API和存储引擎进行通信。这些接口屏蔽了不同存储引擎之间的差异,使得这些差异对上层的查询过程透明化。存储引擎API包含十几个底层函数,用于执行“开始一个事务”等操作。但存储引擎一般不会去解析SQL(InnoDB会解析外键定义,因为其本身没有实现该功能),不同存储引擎之间也不会相互通信,而只是简单的响应上层的服务器请求。
第四层包含了文件系统,所有的表结构和数据以及用户操作的日志最终还是以文件的形式存储在硬盘上。
mysql存储引擎概述
什么是存储引擎?
MySQL中的数据用各种不同的技术存储在文件(或者内存)中。这些技术中的每一种技术都使用不同的存储机制、索引技巧、锁定水平并且最终提供广泛的不同的功能和能力。通过选择不同的技术,你能够获得额外的速度或者功能,从而改善你的应用的整体功能。
例如,如果你在研究大量的临时数据,你也许需要使用内存存储引擎。内存存储引擎能够在内存中存储所有的表格数据。又或者,你也许需要一个支持事务处理的数据库(以确保事务处理不成功时数据的回退能力)。
这些不同的技术以及配套的相关功能在MySQL中被称作存储引擎(也称作表类型)。
MySQL默认配置了许多不同的存储引擎,可以预先设置或者在MySQL服务器中启用。你可以选择适用于服务器、数据库和表格的存储引擎,以便在选择如何存储你的信息、如何检索这些信息以及你需要你的数据结合什么性能和功能的时候为你提供最大的灵活性。
选择如何存储和检索你的数据的这种灵活性是MySQL为什么如此受欢迎的主要原因。其它数据库系统(包括大多数商业选择)仅支持一种类型的数据存储。
遗憾的是,其它类型的数据库解决方案采取的“一个尺码满足一切需求”的方式意味着你要么就牺牲一些性能,要么你就用几个小时甚至几天的时间详细调整你的数据库。使用MySQL,我们仅需要修改我们使用的存储引擎就可以了
mysql支持哪些存储引擎?
mysql5.6支持的存储引擎包括InnoDB、MyISAM、MEMORY、CSV、BLACKHOLE、FEDERATED、MRG_MYISAM、ARCHIVE、PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA。其中NDB和InnoDB提供事务安全表,其他存储引擎都是非事务安全表。
各种存储引擎的特性
概览
MySQL服务器采用了多层设计和独立模块,插件式存储引擎体系结构,允许将存储引擎加载到正在运新的MySQL服务器中,图中的Pluggable Storage Engines部分。采用MySQL服务器体系结构,由于在存储级别上(也就是Pluggable Storage Engines)提供了一致和简单的应用模型和API,应用程序编程人员和DBA可不再考虑所有的底层实施细节。因此,尽管不同的存储引擎具有不同的能力,应用程序是与之分离的。存储引擎就司职与文件系统打交道了。

并发性:某些应用程序比其他应用程序具有很多的颗粒级锁定要求(如行级锁定)。 事务支持:并非所有的应用程序都需要事务,但对的确需要事务的应用程序来说,有着定义良好的需求,如ACID兼容等。 引用完整性:通过DDL定义的外键,服务器需要强制保持关联数据库的引用完整性。 物理存储:它包括各种各样的事项,从表和索引的总的页大小,到存储数据所需的格式,到物理磁盘。 索引支持:不同的应用程序倾向于采用不同的索引策略,每种存储引擎通常有自己的编制索引方法,但某些索引方法(如B-tree索引)对几乎所有的存储引擎来说是共同的。 内存高速缓冲:与其他应用程序相比,不同的应用程序对某些内存高速缓冲策略的响应更好,因此,尽管某些内存高速缓冲对所有存储引擎来说是共同的(如用于用户连接的高速缓冲,MySQL的高速查询高速缓冲等),其他高速缓冲策略仅当使用特殊的存储引擎时才唯一定义。 性能帮助:包括针对并行操作的多I/O线程,线程并发性,数据库检查点,成批插入处理等。 其他目标特性:可能包括对地理空间操作的支持,对特定数据处理操作的安全限制等。
并发性:某些应用程序比其他应用程序具有很多的颗粒级锁定要求(如行级锁定)。 事务支持:并非所有的应用程序都需要事务,但对的确需要事务的应用程序来说,有着定义良好的需求,如ACID兼容等。 引用完整性:通过DDL定义的外键,服务器需要强制保持关联数据库的引用完整性。 物理存储:它包括各种各样的事项,从表和索引的总的页大小,到存储数据所需的格式,到物理磁盘。 索引支持:不同的应用程序倾向于采用不同的索引策略,每种存储引擎通常有自己的编制索引方法,但某些索引方法(如B-tree索引)对几乎所有的存储引擎来说是共同的。 内存高速缓冲:与其他应用程序相比,不同的应用程序对某些内存高速缓冲策略的响应更好,因此,尽管某些内存高速缓冲对所有存储引擎来说是共同的(如用于用户连接的高速缓冲,MySQL的高速查询高速缓冲等),其他高速缓冲策略仅当使用特殊的存储引擎时才唯一定义。 性能帮助:包括针对并行操作的多I/O线程,线程并发性,数据库检查点,成批插入处理等。 其他目标特性:可能包括对地理空间操作的支持,对特定数据处理操作的安全限制等。
以上要求会在不同的需求中予以体现,通过单独一个系统实现是不可能的,以上特点有些本身就是相互矛盾的,鱼和熊掌的问题。对以上内容做些选择,形成的存储引擎就是一个插件引擎了,某些特定的需求可以使用。如下图,部分现有的存储引擎以及基本特点:


InnoDB MySql 5.6 版本默认的存储引擎。InnoDB 是一个事务安全的存储引擎,它具备提交、回滚以及崩溃恢复的功能以保护用户数据。InnoDB 的行级别锁定以及 Oracle 风格的一致性无锁读提升了它的多用户并发数以及性能。InnoDB 将用户数据存储在聚集索引中以减少基于主键的普通查询所带来的 I/O 开销。为了保证数据的完整性,InnoDB 还支持外键约束。 MyISAM MyISAM既不支持事务、也不支持外键、其优势是访问速度快,但是表级别的锁定限制了它在读写负载方面的性能,因此它经常应用于只读或者以读为主的数据场景。 Memory 在内存中存储所有数据,应用于对非关键数据由快速查找的场景。Memory类型的表访问数据非常快,因为它的数据是存放在内存中的,并且默认使用HASH索引,但是一旦服务关闭,表中的数据就会丢失 BLACKHOLE 黑洞存储引擎,类似于 Unix 的 /dev/null,Archive 只接收但却并不保存数据。对这种引擎的表的查询常常返回一个空集。这种表可以应用于 DML 语句需要发送到从服务器,但主服务器并不会保留这种数据的备份的主从配置中。 CSV 它的表真的是以逗号分隔的文本文件。CSV 表允许你以 CSV 格式导入导出数据,以相同的读和写的格式和脚本和应用交互数据。由于 CSV 表没有索引,你最好是在普通操作中将数据放在 InnoDB 表里,只有在导入或导出阶段使用一下 CSV 表。 NDB (又名 NDBCLUSTER)——这种集群数据引擎尤其适合于需要最高程度的正常运行时间和可用性的应用。注意:NDB 存储引擎在标准 MySql 5.6 版本里并不被支持。目前能够支持 MySql 集群的版本有:基于 MySql 5.1 的 MySQL Cluster NDB 7.1;基于 MySql 5.5 的 MySQL Cluster NDB 7.2;基于 MySql 5.6 的 MySQL Cluster NDB 7.3。同样基于 MySql 5.6 的 MySQL Cluster NDB 7.4 目前正处于研发阶段。 Merge 允许 MySql DBA 或开发者将一系列相同的 MyISAM 表进行分组,并把它们作为一个对象进行引用。适用于超大规模数据场景,如数据仓库。 Federated 提供了从多个物理机上联接不同的 MySql 服务器来创建一个逻辑数据库的能力。适用于分布式或者数据市场的场景。 Example 这种存储引擎用以保存阐明如何开始写新的存储引擎的 MySql 源码的例子。它主要针对于有兴趣的开发人员。这种存储引擎就是一个啥事也不做的 "存根"。你可以使用这种引擎创建表,但是你无法向其保存任何数据,也无法从它们检索任何索引。
InnoDB MySql 5.6 版本默认的存储引擎。InnoDB 是一个事务安全的存储引擎,它具备提交、回滚以及崩溃恢复的功能以保护用户数据。InnoDB 的行级别锁定以及 Oracle 风格的一致性无锁读提升了它的多用户并发数以及性能。InnoDB 将用户数据存储在聚集索引中以减少基于主键的普通查询所带来的 I/O 开销。为了保证数据的完整性,InnoDB 还支持外键约束。 MyISAM MyISAM既不支持事务、也不支持外键、其优势是访问速度快,但是表级别的锁定限制了它在读写负载方面的性能,因此它经常应用于只读或者以读为主的数据场景。 Memory 在内存中存储所有数据,应用于对非关键数据由快速查找的场景。Memory类型的表访问数据非常快,因为它的数据是存放在内存中的,并且默认使用HASH索引,但是一旦服务关闭,表中的数据就会丢失 BLACKHOLE 黑洞存储引擎,类似于 Unix 的 /dev/null,Archive 只接收但却并不保存数据。对这种引擎的表的查询常常返回一个空集。这种表可以应用于 DML 语句需要发送到从服务器,但主服务器并不会保留这种数据的备份的主从配置中。 CSV 它的表真的是以逗号分隔的文本文件。CSV 表允许你以 CSV 格式导入导出数据,以相同的读和写的格式和脚本和应用交互数据。由于 CSV 表没有索引,你最好是在普通操作中将数据放在 InnoDB 表里,只有在导入或导出阶段使用一下 CSV 表。 NDB (又名 NDBCLUSTER)——这种集群数据引擎尤其适合于需要最高程度的正常运行时间和可用性的应用。注意:NDB 存储引擎在标准 MySql 5.6 版本里并不被支持。目前能够支持 MySql 集群的版本有:基于 MySql 5.1 的 MySQL Cluster NDB 7.1;基于 MySql 5.5 的 MySQL Cluster NDB 7.2;基于 MySql 5.6 的 MySQL Cluster NDB 7.3。同样基于 MySql 5.6 的 MySQL Cluster NDB 7.4 目前正处于研发阶段。 Merge 允许 MySql DBA 或开发者将一系列相同的 MyISAM 表进行分组,并把它们作为一个对象进行引用。适用于超大规模数据场景,如数据仓库。 Federated 提供了从多个物理机上联接不同的 MySql 服务器来创建一个逻辑数据库的能力。适用于分布式或者数据市场的场景。 Example 这种存储引擎用以保存阐明如何开始写新的存储引擎的 MySql 源码的例子。它主要针对于有兴趣的开发人员。这种存储引擎就是一个啥事也不做的 "存根"。你可以使用这种引擎创建表,但是你无法向其保存任何数据,也无法从它们检索任何索引。
常用存储引擎及适用场景
InnoDB
用于事务处理应用程序,支持外键和行级锁。如果应用对事物的完整性有比较高的要求,在并发条件下要求数据的一致性,数据操作除了插入和查询之外,还包括很多更新和删除操作,那么InnoDB存储引擎是比较合适的。InnoDB除了有效的降低由删除和更新导致的锁定,还可以确保事务的完整提交和回滚,对于类似计费系统或者财务系统等对数据准确要求性比较高的系统都是合适的选择。
MyISAM
如果应用是以读操作和插入操作为主,只有很少的更新和删除操作,并且对事务的完整性、并发性要求不高,那么可以选择这个存储引擎。
Memory
将所有的数据保存在内存中,在需要快速定位记录和其他类似数据的环境下,可以提供极快的访问。Memory的缺陷是对表的大小有限制,虽然数据库因为异常终止的话数据可以正常恢复,但是一旦数据库关闭,存储在内存中的数据都会丢失。
存储引擎在mysql中的使用
存储引擎相关sql语句
查看当前的默认存储引擎: mysql> show variables like "default_storage_engine"; 查询当前数据库支持的存储引擎 mysql> show engines \G;
 结果
结果
指定存储引擎建表
在建表时指定
mysql> create table ai(id bigint(12),name varchar(200)) ENGINE=MyISAM; mysql> create table country(id int(4),cname varchar(50)) ENGINE=InnoDB; 也可以使用alter table语句,修改一个已经存在的表的存储引擎。 mysql> alter table ai engine = innodb;
在配置文件中指定
#my.ini文件 [mysqld] default-storage-engine=INNODB
mysql的工作流程

A total of four MySQL architecture, as the division in the above figure in dashed lines.
First, the top of MySQL service is not unique, giving most of the network client / server tools or services have a similar architecture. For example: connection handling, authorization and authentication, and security.
The second layer architecture includes most of MySQL's core services. Including: query parsing, analysis, optimization, caching, and all built-in functions (for example: date, time, math and encryption function). At the same time, all across storage engine functions are implemented in this layer: stored procedures, triggers, views, and so on.
The third layer contains a storage engine. The storage engines in MySQL storage and retrieval of data. Server communicates through the API, and the storage engine. These interfaces shielding differences between storage engine, such that the differences of the upper transparent inquiry procedure. Storage Engine API may contain a dozen underlying function, for performing a "start transaction" and other operations. But generally not storage engine to parse SQL (InnoDB resolves foreign key definition, since it does not itself implement the function), not between different storage engines communicate with each other, but simply in response to the upper layer request to the server.
The fourth layer includes the file system, all of the tables and data structures, and ultimately logs user operation in the form of files stored on the hard disk.
