6.5 Link Virtualization: the network as the link layer
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
Through a key concept of the network from the VC - fixed-length labels, forwarding speed can be improved lP router. The goal is to use forward lP datagram routing device, but is based on technology and a fixed length virtual circuit label, so that the router forwards the data packet (not a destination IP address) according to the label fixed length, thus speeding up the forwarding speed (Label fixed length, the smaller label space these two features to speed up the rate look-up table).
6.6 Data Center Network
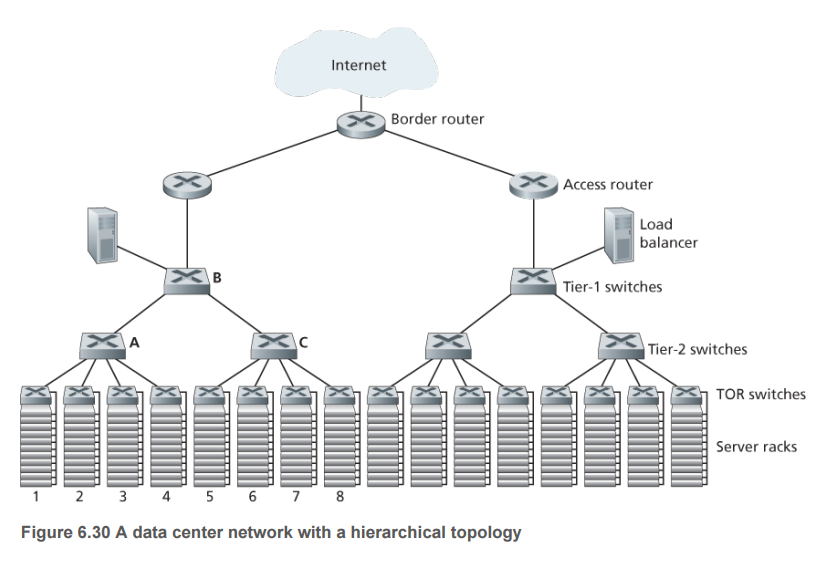
- Internet companies such as FLAG build large data centers, each data center to accommodate hundreds of thousands of hosts too, while supporting different cloud applications. Each data center has its own network of data centers, internal hosts interconnected with each other, and other data center interconnection and Internet
- Huge investment, the monthly cost of a data center hosts more than 10w 1200w knife
- Host data center (called the blade) as the worker bees of the data center: to provide content, store documents, joint implementation of large-scale distributed computing
- A plurality of top of rack switch is connected to multiple border routers
1. Load Balancing
-
- A cloud data center can also provide search application, e-mail, video applications, each application associated with an IP address of a publicly visible, external user sends a request to the address, and receive a response from the address
- The external request is first directed to a load balancer to distribute the request to the host, host-current load as a function of load balancing between the host
- Load balancing based on the packet destination port number (fourth layer) and a destination IP address to make decisions, is referred to as the fourth layer switch
- Client requests - "load balancer -" Host - "Load Balancer -" Customer
- Not only balance workloads between hosts, NAT also provides similar functionality to convert external IP address to internal IP addresses to prevent direct contact with the client hosts
2. Level Architecture
-
- Host to hundreds of thousands of scale, data center applications routers and switches hierarchy
- Border Router - A router access - a first switch layer load balancer + - layer 2 switch - a third layer switch (TOR switch, top of rack, rack switches)
- Host access router under each constitute a single subnet, broadcast traffic is the localization of ARP, VLAN for each subnet into smaller subnets, each composed of hundreds
3. Data center network development trend
-
- Fully connected topology: Each of the first layer are connected to all second switch layer switches
- Modular data center MDC
6.7 Review: History Web page request
6.7.1 Preparation: DHCP, UDP, IP and Ethernet assumed Xiaoming start the computer, connect to the school's Ethernet switch with an Ethernet cable
- Xiaoming computer operating system generates a DHCP packet, encapsulates the packet to the destination port 67 (DHCP server) and UDP segment source port 68 (Brian's DHCP client), the message segments and encapsulates the destination address is a broadcast IP datagram address, source address of 0
- DHCP request packet comprising IP datagrams encapsulated into an Ethernet frame destination MAC address is a broadcast MAC address, the frame is broadcast to all devices connected to the switch (including DHCP server)
- DHCP request broadcast Ethernet frame comprises a first frame is sent Xiaoming computer, so the switch at the output ports of broadcast frames, comprising a port connected to the router, and automatically switch table entry is added to
- Router interface it receives the frame, extracts the IP datagram (because it is broadcast, otherwise, discards the addresses do not match), UDP segment is broken up reaches UDP, DHCP request packets and then extracted from the inside, then DHCP DHCP server received request packet (DHCP service running in the router)
- DHCP server postback DHCP ACK packet, including the IP address, DNS server local IP address, default gateway router IP address, network mask, add UDP segment, then add the IP datagram, and then into an Ethernet frame, the destination MAC address is the MAC address of the computer Xiaoming
- DHCP ACK frame including the transmission by a router to the switch, the switch from forwarding table addressing switch to the output interface
- Bob computer receives the frame, extracts IP datagrams, UDP segment extraction, extraction DHCP ACK messages. Its IP address and DNS server IP address in its IP forwarding table installed at the default gateway address Xiaoming DHCP client records. Xiao Ming computer to send a datagram to the same subnet other than the default gateway.
6.7.2 is still in preparation: DNS and ARP
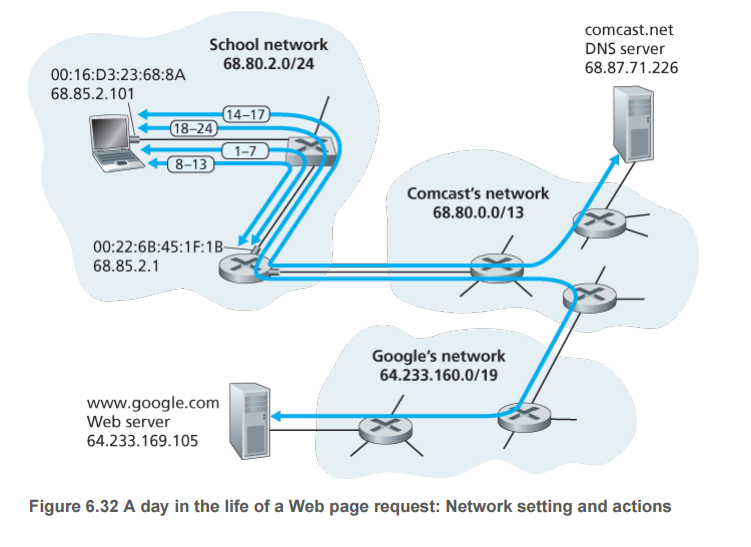
When Xiao Ming will www.baidu.com when the URL input Web browser, open a long list of events that led to the final Baidu home page is displayed on the Web browser.
- 为了生成TCPsocket向baidu.com发送HTTP请求,需要知道其IP地址,小明电脑的操作系统因此生成一个DNS查询报文,将网址放入DNS报文,再将报文放入目的端口号53的UDP报文段,该UDP报文段放入具有IP目的地址为DNS服务器(DHCP服务器返回的)的IP数据报中
- 小明电脑将包含DNS请求报文的数据报放入一个以太网帧中,该帧在链路层需要寻址发送到小明学校网络的网关路由器。为了获得该网关路由器的MAC地址,小明的电脑需要使用ARP协议,将IP地址—》MAC地址
- 小明电脑生成一个目的IP地址为默认网关的ARP查询报文,放在具有目的地址为MAC广播地址的以太网帧中,并向交换机发送该以太网帧,交换机将帧广播给所有连接的设备,包括网关路由器
- 网关路由器在通往学校网络的接口上接收到包含该ARP查询报文的帧,发现在ARP报文中目标IP地址匹配自己的IP地址,网关路由器因此准备一个ARP回答,指示自己的MAC地址。它将ARP回答放在一个以太网帧中,目的地址为小明电脑的MAC地址,并向交换机发送该帧,交换机将该帧交付给小明电脑
- 小明电脑接收包含ARP回答报文的帧,并从ARP回答报文中抽取网关路由器的MAC地址
- 小明电脑终于能使包含DNS查询的以太网帧寻址到网关路由器的MAC地址。该帧中的IP数据报中的目的地址文DNS服务器,而帧具有目的地址网关路由器MAC。小明电脑向交换机发送该帧,交换机将该帧交付给网关路由器
6.7.3 仍在准备:域内路由选择到DNS服务器
- 网关路由器接收该帧并抽取包含DNS查询的IP数据报。路由器查找该数据报的目的地址,根据其转发表决定将数据报发送到comcast网络中最左边路由器
- 最左边路由器收到该帧,抽取IP数据报,检查目的地址,根据转发表为其确定出接口,经过该接口向DNS服务器转发数据报。转发表已根据comcast域内协议(如RIP、OSPF或IS-IS),以及因特网域间协议BGP所填写
- 最终包含DNS查询的IP数据报到达了DNS服务器。DS服务器抽取出DNS查询报文,在其数据库中快速查找www.baidu.com,找到包含该IP地址的DNS源记录(假设缓存在当前DNS服务器,源与权威DNS服务器,否则需要递归、迭代查找)。DNS服务器形成了包含该主机名到IP地址映射的DNS回答报文,放入UDP报文段,通过comcast网络反向转到小明学校路由器,经过以太网交换机到小明电脑
- 小明电脑从DNS报文抽取出www.baidu.com的IP地址
6.7.4 Web客户 - 服务器交互: TCP和HTTP
- 小明电脑有了百度的IP地址,终于能生成TCP套接字,用于向www.baidu.com发送HTTP GET报文。小明生成套接字时,小明电脑中的TCP必须首先与www.baidu.com的TCP执行三次握手。因此小明电脑首先生成具有目的端口80(HTTP)的TCP SYN报文段,将报文段放在目的IP地址为baidu的IP数据报,将数据报放在MAC地址为网关路由器的帧中,向交换机发送该帧
- 在学校网络、comcast网络和百度的路由器朝着www.baidu.com转发包含TCP SYN的数据报,使用每台路由器中的转发表。支配分组经过comcast和百度网络之间域间链路转发的路由器转发表项,是BGP协议决定的
- 包含TCP SYN的数据报到达www.baidu.com,从数据报抽取报文并分解到与80端口向联系的欢迎套接字。对百度HTTP服务器和小明电脑之间的TCP连接生成一个连接套接字。产生一个TCP SYNACK报文段,将其放入向小明电脑寻址的一个数据报中,最后放入链路层帧中,将www.baidu.com连接到其第一条路由器
- 包含TCP SYNACK报文段的数据报通过百度、comcast和学校网络,最终到达小明电脑的以太网卡。数据报在操作系统中分解到TCP套接字,从而进入连接状态
- 借助小明电脑上的套接字,浏览器生成包含要获取URL的HTTP GET报文,报文写入套接字,GET报文成为TCP报文段的数据载荷。交付到百度
- baidu的HTTP服务器从TCPsocket读取HTTP GET报文,生成一个HTTP响应报文,将请求的Web页内容放入HTTP响应体重,将报文发送进TCPsocket
- 小明浏览器从套接字读取HTTP响应,抽取Web网页的html,显示了Web网页