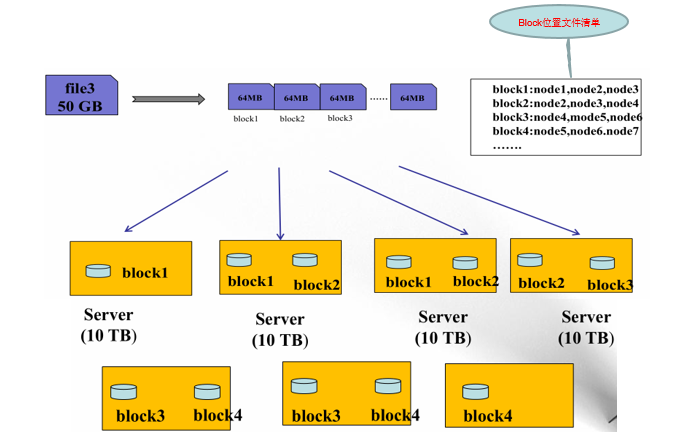
- Stored in byte format
- Linear file into pieces (Block): Offset offset (byte)
- Block dispersed storage nodes in the cluster
- Block consistent single file size, file with the file can be inconsistent
- Block can set the number of copies, copies disorderly dispersed in different nodes
- Do not exceed the number of copies of the number of nodes
- Block file uploads can set the size and number of copies (not enough resources to open up the process)
- Block number of copies of the files uploaded can be adjusted to the same size (2.x 128MB 3 blocks)
- Only support Write Once Read Many, that only one writer
- You can append additional data
HDFS architecture model
- File metadata MetaData, file data
- Metadata
- The data itself
- The NameNode (master) node stores file metadata: single node posix
- DataNode (from) node to save data file Block: Multi-node
- DataNode and NameNode remain heartbeat, submit Block List
- HdfsClient NameNode interact with metadata information
- HdfsClient DataNode interact with data files Block (cs)
- DataNode server using data blocks stored in the local file system
HDFS architecture diagram 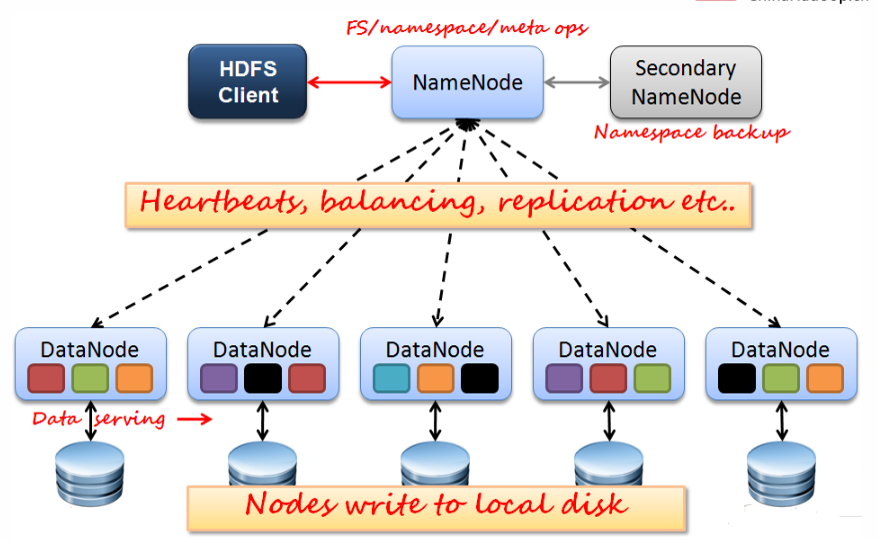
HDFS design
- Uniformly dispersed storage dfs.blocksize = 128M
- Backup redundant memory dfs.replication = 3
NameNode (NN)
- RAM-based storage: disk will not exchange (two-way)
- It exists only in memory
- Persistence (one-way)
- NameNode main functions:
- Reading and writing to accept service clients
- Block list information collected DataNode reporting
- NameNode save metadata information includes
- Owership and file permissions
- File size, time
- (Block List: Block Offset), position information (persistence does not exist)
- Block copy of each position (reported by the DataNode)
NameNode persistence
- NameNode of metadata information after startup will be loaded into memory
- metadata stored in a disk file called "fsimage" (point in time backup)
- Block location information is not saved to fsimage
- edits记录对metadata的操作日志…>Redis
- 二者的产生时间和过程?(format)
SecondaryNameNode(SNN)
- 它不是NN的备份(但可以做备份),它的主要工作是帮助NN合并edits log,减少NN启动时间。
- SNN执行合并时机
- 根据配置文件设置的时间间隔fs.checkpoint.period 默认3600秒
- 根据配置文件设置edits log大小 fs.checkpoint.size 规定edits文件的最大值默认是64MB
SNN合并流程图
DataNode(DN)
- 本地磁盘目录存储数据(Block),文件形式
- 同时存储Block的元数据信息文件
- 启动DN时会向NN汇报block信息
- 通过向NN发送心跳保持与其联系(3秒一次),如果NN 10分钟没有收到DN的心跳,则认为其已经lost,并copy其上的block到其它DN
HDFS优点
- 高容错性
- 数据自动保存多个副本
- 副本丢失后,自动恢复
- 适合批处理
- 移动计算而非数据
- 数据位置暴露给计算框架(Block偏移量)
- 适合大数据处理
- GB 、TB 、甚至PB 级数据
- 百万规模以上的文件数量
- 10K+ 节点
- 可构建在廉价机器上
- 通过多副本提高可靠性
- 提供了容错和恢复 机制
HDFS缺点
- 低延迟数据访问
- 比如毫秒级
- 低延迟与高吞吐率
- 小文件存取
- 占用NameNode 大量内存
- 寻道时间超过读取时间
- 并发写入、文件随机修改
- 一个文件只能有一个写者
- 仅支持append
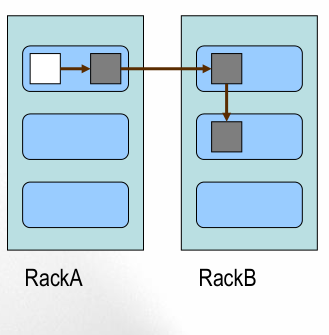
Block的副本放置策略
- 第一个副本:放置在上传文件的DN;如果是集群外提交,则随机挑选一台磁盘不太满,CPU不太忙的节点。
- 第二个副本:放置在于第一个副本不同的 机架的节点上。
- 第三个副本:与第二个副本相同机架的节点。
- 更多副本:随机节点