View the current system supports inotify
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /proc/sys/fs/inotify
总用量 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 6月 11 09:44 max_queued_events
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 6月 11 09:44 max_user_instances
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 6月 11 09:44 max_user_watches
If the output above appears, the system supports
inofity-tools Download: http://github.com/downloads/rvoicilas/inotify-tools/inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
upload their own virtual machine-related directory
[root@localhost hbk]# ll -h |grep inotify
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 351K 6月 11 09:58 inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
[root@localhost hbk]# pwd
/root/hbk
Decompression
[root@localhost hbk]# tar -zxvf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
Compile installation
[root@localhost hbk]# cd inotify-tools-3.14
[root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# ./configure
[root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# make && make install
Installed by default in / usr / local / bin directory, a total of two programs
inotifywait and inotifywatch
So even if the installation was successful.
Simple to use inotiry introduction, this tool generally used to monitor changes in the file directory, delete the new modifications, changes and other property, inotify able to receive relevant information, and log output, you can do with rsync server file real-time synchronization.
[root@localhost bin]# /usr/local/bin/inotifywait --help
inotifywait 3.14
Wait for a particular event on a file or set of files.
Usage: inotifywait [ options ] file1 [ file2 ] [ file3 ] [ ... ]
Options:
-h|--help Show this help text.
@<file> Exclude the specified file from being watched.
--exclude <pattern>
Exclude all events on files matching the
extended regular expression <pattern>.
--excludei <pattern>
Like --exclude but case insensitive.
-m|--monitor Keep listening for events forever. Without
this option, inotifywait will exit after one
event is received.
-d|--daemon Same as --monitor, except run in the background
logging events to a file specified by --outfile.
Implies --syslog.
-r|--recursive Watch directories recursively.
--fromfile <file>
Read files to watch from <file> or `-' for stdin.
-o|--outfile <file>
Print events to <file> rather than stdout.
-s|--syslog Send errors to syslog rather than stderr.
-q|--quiet Print less (only print events).
-qq Print nothing (not even events).
--format <fmt> Print using a specified printf-like format
string; read the man page for more details.
--timefmt <fmt> strftime-compatible format string for use with
%T in --format string.
-c|--csv Print events in CSV format.
-t|--timeout <seconds>
When listening for a single event, time out after
waiting for an event for <seconds> seconds.
If <seconds> is 0, inotifywait will never time out.
-e|--event <event1> [ -e|--event <event2> ... ]
Listen for specific event(s). If omitted, all events are
listened for.
Exit status:
0 - An event you asked to watch for was received.
1 - An event you did not ask to watch for was received
(usually delete_self or unmount), or some error occurred.
2 - The --timeout option was given and no events occurred
in the specified interval of time.
Events:
access file or directory contents were read
modify file or directory contents were written
attrib file or directory attributes changed
close_write file or directory closed, after being opened in
writeable mode
close_nowrite file or directory closed, after being opened in
read-only mode
close file or directory closed, regardless of read/write mode
open file or directory opened
moved_to file or directory moved to watched directory
moved_from file or directory moved from watched directory
move file or directory moved to or from watched directory
create file or directory created within watched directory
delete file or directory deleted within watched directory
delete_self file or directory was deleted
unmount file system containing file or directory unmounted
English level good point, I believe to see the above help documentation no pressure, then practically speaking common knowledge.
A Chinese translation attached
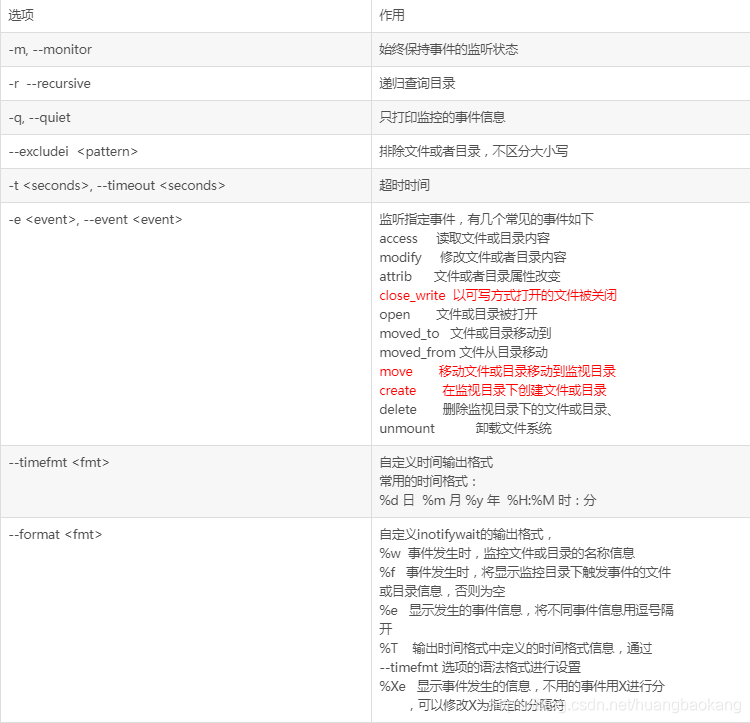
Monitoring events
For the experiment, we monitor / root / hbk / test directory, test for the new empty directory, we monitor the new files in this directory, rename files, delete files, modify files, and so
as we monitor new and delete events
[root@localhost test]# /usr/local/bin/inotifywait -mrq --format '%Xe %w%f' -e create,delete /root/hbk/test
Execute the above command, is blocked, runs in the background, we need to open a separate window for Shell / root / hbk / test new directories, files, delete and other operations
[root@localhost test]# mkdir images
[root@localhost test]# touch index.html
[root@localhost test]# rm -rf index.html
You can see the log output is as follows:
CREATEXISDIR /root/hbk/test/images
CREATE /root/hbk/test/index.html
DELETE /root/hbk/test/index.html
We can write a loop, using awk take full path to the file from the log output, and then with the rsync command to synchronize and achieve real-time synchronization file.
inotifywatch Command
command format:
inotifywatch [-hvzrqf] [-e <event> ] [-t <seconds> ] [-a <event> ] [-d <event> ] <file> [ ...]
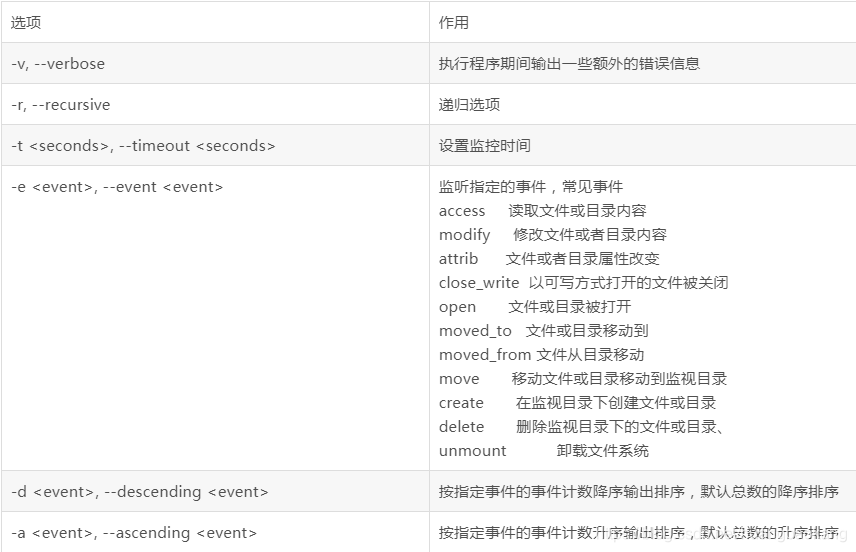
Example:
Statistics events occurring within one hour / root / hbk under / test directory.
[root@localhost test]# /usr/local/bin/inotifywatch -v -t 3600 -r /root/hbk/test
Note the number of seconds does not support the calculation, the following is wrong
[root@localhost test]# /usr/local/bin/inotifywatch -v -t 60*60 -r /root/hbk/test
'60*60' is not a valid timeout value.