First of all we need to know that is what is RAID Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive (Independent) Disks, Chinese as cheap redundant disk arrays, by 1988 the University of California at Berkeley (University of California-Berkeley) "A Case for Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks" proposed multiple disks into one "array" to provide better performance, redundancy, or both, provided, it has been more widely used. RAID disk array technology allows a series of packets, in order to achieve data redundancy protection necessary data, and a data read section for improving the performance of the band profile is formed. With the rapid development of computer technology, RAID technology more and more common, and now, in the home computer motherboard, RAID controller chip also can be seen everywhere.

RAID level is divided into 0, 1,2,4,5, the most commonly used is 0, 1, 3, 5 four levels. Others include 6, 7, 10, etc.
In recent years, storage vendors continue to introduce such RAID7, RAID10 / 01, RAID50, RAID53, RAID100 such as RAID level, but there is no uniform standard. The industry accepted standards is RAID0 ~ RAID5, four levels except RAID2 outside the box is defined as an industry standard, and most used RAID level in the field of practical application is RAID0, RAID1, RAID3, RAID5, RAID6 and RAID10.
From the implementation point of view, RAID is divided into software RAID, hardware RAID and hard and soft Hybrid RAID three. Software RAID has all the features of the operating system and CPU to complete, no separate RAID controller / processing chip and I / O processing chip, efficiency of natural low. Hardware RAID equipped with a special RAID control / processing chip and I / O buffer and an array processing chip, no CPU resources, but the cost is high. RAID controller includes hardware and software RAID mixing / processing chip, but the lack of I / O processing chip, CPU and the driver needs to accomplish, performance and cost between the soft and hard RAID in RAID.
RAID characteristics:
1. Low cost, low power consumption, high transmission rate. In RAID, you can make a lot of disk drive while transferring data, and these disk drives are logically is a disk drive, so the use of RAID can achieve a single disk drive several times, several times or even hundred times the rate. This is the first RAID want to solve the problem. CPU speed because it was growing rapidly, and the data transfer rate of the disk drive can not be a substantial increase, so the need for a solution to the conflict between the two. The RAID finally succeeded.
2. Can provide fault tolerance, which is the most second reason for using RAID. Because, ordinary disk drives can not provide fault tolerance, if not included on the disk write CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) code words. RAID and fault tolerance is built on a hardware fault tolerance of each disk drive, so it can provide better security.
3. RAID compared to traditional large-diameter disk drives in the same capacity, the price is much lower.
4. Increase IO capability
Disk read-write parallel
5. improve durability
Disk redundancy is achieved
6. Level: multiple disks grouped together work differently
7.RAID the way to achieve
External disk arrays: adaptation capabilities provided by the expansion card
The explanation RAID: front onboard RAID controller, mounted in the BIOS, OS configuration
Software RAID: OS achieved through
RAID 0:
RAID 0 is also called a data block, i.e., the data is divided into a plurality of pieces of equal size, and write them to a different hard disk array, this technique is also called "Stripping" (forthcoming data striping). The data is distributed over a plurality of disks, each hard disk during read and write operations are simultaneously parallel manner. Theoretically, the capacity and data transfer rate which is N times that of a single disk. N is the total number of a hard disk RAID0. Of course, if the hard disk array controller has a plurality of channels, the plurality of channels on the hard disk RAID0 operation, I / O performance will be higher.
RAID 0 characteristics:
Reading and writing performance of free space: N * min (S1, S2, ...) without the fault tolerance of the minimum number of disks: 2, 2+
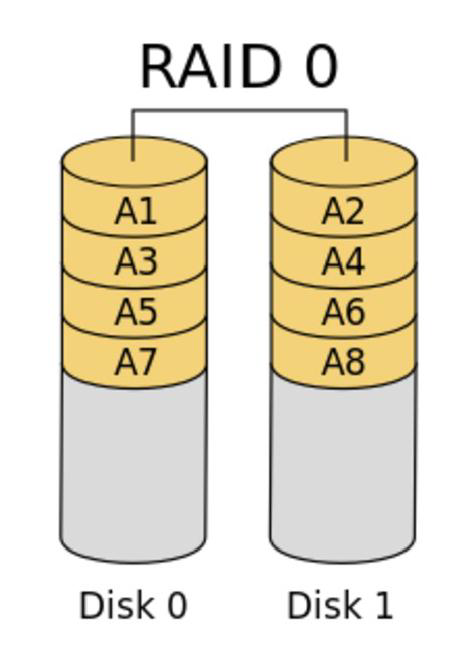
RAID 1:
RAID 1 is also known as mirrored RAID (Disk Mirroring), because the data on one disk is copied to another disk entirely. Data loss and system if a data disk error, or hard disk have bad, then back to another hard disk failure can be remedied caused interruption. In addition, RAID 1 can achieve duplex - that can copy the entire controller, so that when a disk failure or controller failure occurs, your data can be protected.
RAID 1 Features
Read performance, write performance declined slightly, the available space: 1 * min (S1, S2, ...), there is redundancy, the minimum number of disks: 2, 2N
RAID1 and RAID0 is just the opposite, in order to enhance data security so that two fully mirrored disk data presented, so as to achieve security is good, technology is simple, easy to manage. RAID1 has the ability to completely fault-tolerant, but the high implementation costs. RAID1 applied to sequential read and write data on the high performance requirements and application of paramount concern, such as protection of the data messaging system.

RAID 2:
RAID2 称为纠错海明码磁盘阵列,其设计思想是利用海明码实现数据校验冗余。海明码是一种在原始数据中加入若干校验码来进行错误检测和纠正的编码技术,其中第 2n 位( 1, 2, 4, 8, … )是校验码,其他位置是数据码。因此在 RAID2 中,数据按位存储,每块磁盘存储一位数据编码,磁盘数量取决于所设定的数据存储宽度,可由用户设定。图 4 所示的为数据宽度为 4 的 RAID2 ,它需要 4 块数据磁盘和 3 块校验磁盘。如果是 64 位数据宽度,则需要 64 块 数据磁盘和 7 块校验磁盘。可见, RAID2 的数据宽度越大,存储空间利用率越高,但同时需要的磁盘数量也越多。
海明码的数据冗余开销太大,而且 RAID2 的数据输出性能受阵列中最慢磁盘驱动器的限制。再者,海明码是按位运算, RAID2 数据重建非常耗时。由于这些显著的缺陷,再加上大部分磁盘驱动器本身都具备了纠错功能,因此 RAID2 在实际中很少应用,没有形成商业产品,目前主流存储磁盘阵列均不提供 RAID2 支持。
RAID 3 :
RAID3 是使用专用校验盘的并行访问阵列,它采用一个专用的磁盘作为校验盘,其余磁盘作为数据盘,数据按位可字节的方式交叉存储到各个数据盘中。RAID3 至少需要三块磁盘,不同磁盘上同一带区的数据作 XOR 校验,校验值写入校验盘中。 RAID3 完好时读性能与 RAID0 完全一致,并行从多个磁盘条带读取数据,性能非常高,同时还提供了数据容错能力。向 RAID3 写入数据时,必须计算与所有同条带的校验值,并将新校验值写入校验盘中。一次写操作包含了写数据块、读取同条带的数据块、计算校验值、写入校验值等多个操作,系统开销非常大,性能较低。RAID3中某一磁盘出现故障,不会影响数据读取,可以借助校验数据和其他完好数据来重建数据。
RAID3 只需要一个校验盘,阵列的存储空间利用率高,再加上并行访问的特征,能够为高带宽的大量读写提供高性能,适用大容量数据的顺序访问应用,如影像处理、流媒体服务等。目前, RAID5 算法不断改进,在大数据量读取时能够模拟 RAID3 ,而且 RAID3 在出现坏盘时性能会大幅下降,因此常使用 RAID5 替代 RAID3 来运行具有持续性、高带宽、大量读写特征的应用。
RAID 4:
RAID4 在不同磁盘上的同级数据块同样使用 XOR 校验,结果存储在校验盘中。写入数据时, RAID4 按这种方式把各磁盘上的同级数据的校验值写入校验 盘,读取时进行即时校验。因此,当某块磁盘的数据块损坏, RAID4 可以通过校验值以及其他磁盘上的同级数据块进行数据重建。
RAID4 提供了 非常好的读性能,但单一的校验盘往往成为系统性能的瓶颈。对于写操作, RAID4 只能一个磁盘一个磁盘地写,并且还要写入校验数据,因此写性能比较差。而且随着成员磁盘数量的增加,校验盘的系统瓶颈将更加突出。正是如上这些限制和不足, RAID4 在实际应用中很少见,主流存储产品也很少使用 RAID4 保护。
RAID 5:
RAID5 应该是目前最常见的 RAID 等级,它的原理与 RAID4 相似,区别在于校验数据分布在阵列中的所有磁盘上,而没有采用专门的校验磁盘。对于数据和校验数据,它们的写操作可以同时发生在完全不同的磁盘上。因此, RAID5 不存在 RAID4 中的并发写操作时的校验盘性能瓶颈问题。另外, RAID5 还具备很好的扩展性。当阵列磁盘 数量增加时,并行操作量的能力也随之增长,可比 RAID4 支持更多的磁盘,从而拥有更高的容量以及更高的性能。
RAID5的磁盘上同时存储数据和校验数据,数据块和对应的校验信息存保存在不同的磁盘上,当一个数据盘损坏时,系统可以根据同一条带的其他数据块和对应的校验数据来重建损坏的数据。与其他 RAID 等级一样,重建数据时, RAID5 的性能会受到较大的影响。
RAID5 兼顾存储性能、数据安全和存储成本等各方面因素,它可以理解为 RAID0 和 RAID1 的折中方案,是目前综合性能最佳的数据保护解决方案。 RAID5 基本上可以满足大部分的存储应用需求,数据中心大多采用它作为应用数据的保护方案。
RAID5特点:
读、写性能提升,可用空间:(n-1)*min(S1,S2,...),有容错能力:允许最多1块磁盘损坏,最少磁盘数:3 ,3+

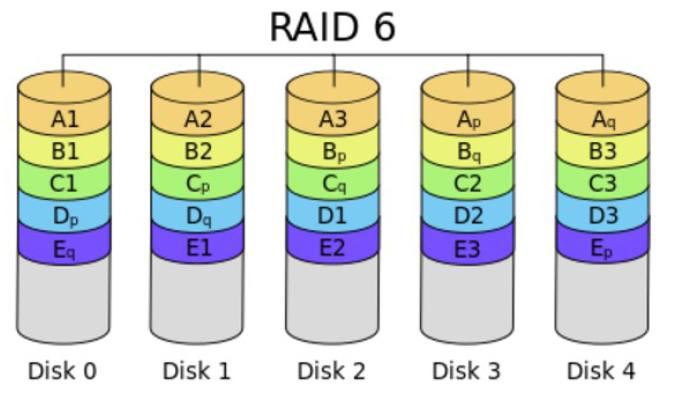
RAID 6:
RAID引入双重校验的概念,它可以保护阵列中同时出现两个磁盘失效时,阵列仍然能够继续工作,不会发生数据丢失。RAID6等级是在RAID5基础上为了进一步增强数据保护而设计的一种RAID方式,它可以看做是一种扩展的RAID5等级。
RAID6 不仅要支持数据的恢复,还要支持校验数据的恢复,因此实现代价很高,控制器的设计也比其他等级更复杂、更昂贵。 RAID6 具有快速的读取性能、更高的容错能力。但是,它的成本要高于 RAID5 许多,写性能也较差,并有设计和实施非常复杂。因此, RAID6 很少得到实际应用,主要用于对数据安全等级要求非常高的场合。它一般是替代 RAID10 方案的经济性选择。
RAID6特点:
读、写性能提升,可用空间:(N-2)*min(S1,S2,...),有容错能力:允许最多2块磁盘损坏,最少磁盘数:4, 4+
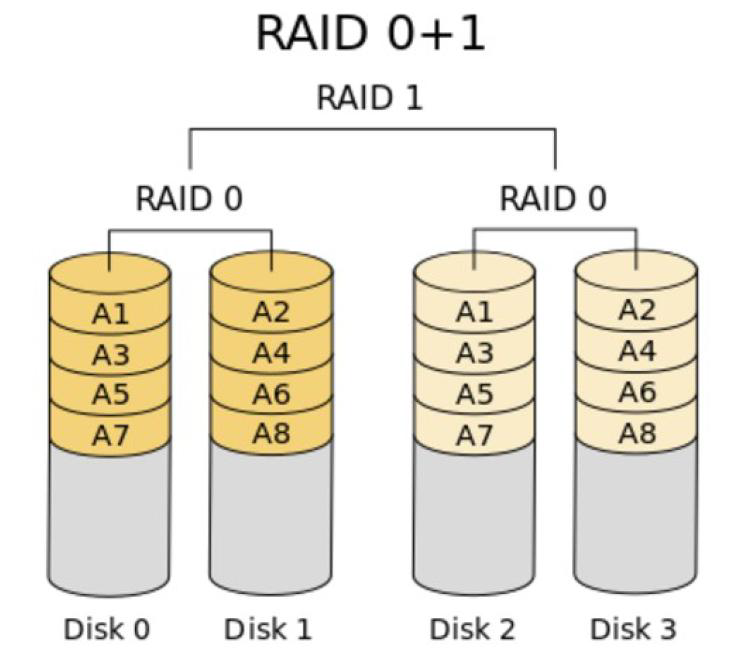
RAID 01和RAID 10:
RAID01 是先做条带化再作镜像,本质是对物理磁盘实现镜像;而 RAID10 是先做镜像再作条带化,是对虚拟磁盘实现镜像。相同的配置下,通常 RAID01 比 RAID10 具有更好的容错能力。
RAID01 兼备了 RAID0 和 RAID1 的优点,它先用两块磁盘建立镜像,然后再在镜像内部做条带化。 RAID01 的数据将同时写入到两个磁盘阵列中,如果其中一个阵列损坏,仍可继续工作,保证数据安全性的同时又提高了性能。 RAID01 和 RAID10 内部都含有 RAID1 模式,因此整体磁盘利用率均仅为 50% 。

RAID 50:
多块磁盘先实现RAID5,再组合成RAID0

RAID 7:
RAID7 的全称是最优化的异步高 I/O 速率和高数据传输率,它与其他 RAID 等级有着明显区别。它不仅仅是一种技术,它还是一个独立存储计算机,自身带的操作系统和管理工具,完全可以独立运行。
RAID7 的存储计算机操作系统是一套实时事件驱动操作系统,其主要用来进行系统初始化和安排 RAID7 磁盘阵列的所有数据传输,并把它们转换到相应的物理存储驱动器上。 RAID7 通过自身系统中的专用控制板来控制读写速度,存储计算机操作系统可使主机 I/O 传递性能达到最佳。如果一个磁盘出现故障, RAID7 还能够自动执行恢复操作,并可管理备份磁盘的重建过程。
RAID7 突破了以往 RAID 标准的技术架构,采用了非同步访问,极大地减轻了数据写瓶颈,提高了 I/O 速度。 RAID7 系统内置实时操作系统还可自动对主机发送过来的读写指令进行优化处理,以智能化方式将可能被读取的数据预先读入快速缓存中,从而大大减少了磁头的转动次数,提高存储系统的 I/O 速度。
软RAID
软 RAID 没有专用的控制芯片和 I/O 芯片,完全由操作系统和 CPU 来实现所的 RAID 的功能。现代操作系统基本上都提供软 RAID 支持,通过在磁盘设备驱动程序上添加一个软件层,提供一个物理驱动器与逻辑驱动器之间的抽象层。目前,操作系统支持的最常见的 RAID 等级有 RAID0 、 RAID1 、 RAID10 、 RAID01 和 RAID5 等。比如, Windows Server 支持 RAID0 、 RAID1 和 RAID5 三种等级, Linux 支持 RAID0 、 RAID1 、 RAID4 、 RAID5 、 RAID6 等, Mac OS X Server 、 FreeBSD 、 NetBSD 、 OpenBSD 、 Solaris 等操作系统也都支持相应的 RAID 等级。
软 RAID 的配置管理和数据恢复都比较简单,但是 RAID 所有任务的处理完全由 CPU 来完成,如计算校验值,所以执行效率比较低下,这种方式需要消耗大量的运算资源,支持 RAID 模式 较少,很难广泛应用。
硬RAID:
硬 RAID 拥有自己的 RAID 控制处理与 I/O 处理芯片,甚至还有阵列缓冲,对 CPU 的占用率和整体性能是三类实现中最优的,但实现成本也最高的。硬 RAID 通常都支持热交换技术,在系统运行下更换故障磁盘。
硬 RAID 包含 RAID 卡和主板上集成的 RAID 芯片, 服务器平台多采用 RAID 卡。 RAID 卡由 RAID 核心处理芯片( RAID 卡上的 CPU )、端口、缓存和电池 4 部分组成。其中,端口是指 RAID 卡支持的磁盘接口类型,如 IDE/ATA 、 SCSI 、 SATA 、 SAS 、 FC 等接口。