The function of spatial pyramid pooling is to solve the defects caused by different sizes of input images and at the same time increase the accuracy in target recognition. Spatial pyramid pooling can convert feature maps of any size into fixed-size feature vectors. Here is an inventory of some typical spatial pyramids.
Some pictures are from blog:Spatial Pyramid Pooling Improvement SPP / SPPF / SimSPPF / ASPP / RFB / SPPCSPC / SPPCSPC_Pyramid Pooling Module-CSDN Blog< a i=2>, intrusion and deletion
(1)SPP, Spatial Pyramid Pooling
paper:Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep ConvolutionalNetworks for Visual Recognition
paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.4729
repo link: https://github.com/yifanjiang19/sppnet-pytorch
main idea
Introducing the classic pyramid pooling structure Spatial Pyramid Pooling into CNN, so that CNN can process images of any size
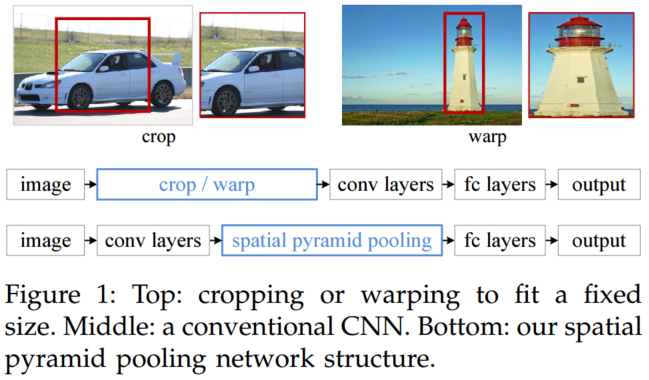
frame
Network structure with spatial pyramid pooling layers. Here 256 is the number of convolution kernels in the conv5 layer, and conv5 is the last convolution layer.
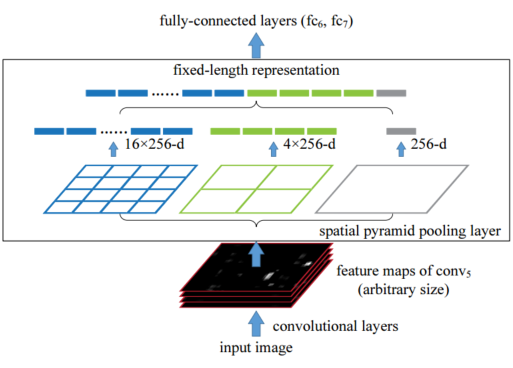
code_pytorch
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import init
import functools
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
class SPP_NET(nn.Module):
'''
A CNN model which adds spp layer so that we can input multi-size tensor
'''
def __init__(self, opt, input_nc, ndf=64, gpu_ids=[]):
super(SPP_NET, self).__init__()
self.gpu_ids = gpu_ids
self.output_num = [4,2,1]
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.BN1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.BN2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4)
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.BN3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8)
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 64, 4, 1, 0, bias=False)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(10752,4096)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(4096,1000)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.LReLU1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.leaky_relu(self.BN1(x))
x = self.conv3(x)
x = F.leaky_relu(self.BN2(x))
x = self.conv4(x)
# x = F.leaky_relu(self.BN3(x))
# x = self.conv5(x)
spp = spatial_pyramid_pool(x,1,[int(x.size(2)),int(x.size(3))],self.output_num)
# print(spp.size())
fc1 = self.fc1(spp)
fc2 = self.fc2(fc1)
s = nn.Sigmoid()
output = s(fc2)
return output
def spatial_pyramid_pool(self,previous_conv, num_sample, previous_conv_size, out_pool_size):
'''
previous_conv: a tensor vector of previous convolution layer
num_sample: an int number of image in the batch
previous_conv_size: an int vector [height, width] of the matrix features size of previous convolution layer
out_pool_size: a int vector of expected output size of max pooling layer
returns: a tensor vector with shape [1 x n] is the concentration of multi-level pooling
'''
# print(previous_conv.size())
for i in range(len(out_pool_size)):
# print(previous_conv_size)
h_wid = int(math.ceil(previous_conv_size[0] / out_pool_size[i]))
w_wid = int(math.ceil(previous_conv_size[1] / out_pool_size[i]))
h_pad = (h_wid*out_pool_size[i] - previous_conv_size[0] + 1)/2
w_pad = (w_wid*out_pool_size[i] - previous_conv_size[1] + 1)/2
maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d((h_wid, w_wid), stride=(h_wid, w_wid), padding=(h_pad, w_pad))
x = maxpool(previous_conv)
if(i == 0):
spp = x.view(num_sample,-1)
# print("spp size:",spp.size())
else:
# print("size:",spp.size())
spp = torch.cat((spp,x.view(num_sample,-1)), 1)
return spp(2)SPPF(Spatial Pyramid Pooling -Fast)
paper: Since SPPF was proposed by the author yolov5 based on SPP, there is no paper source.
yolov5 link: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
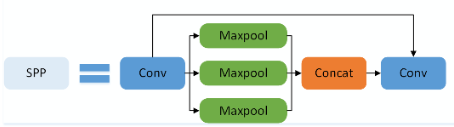

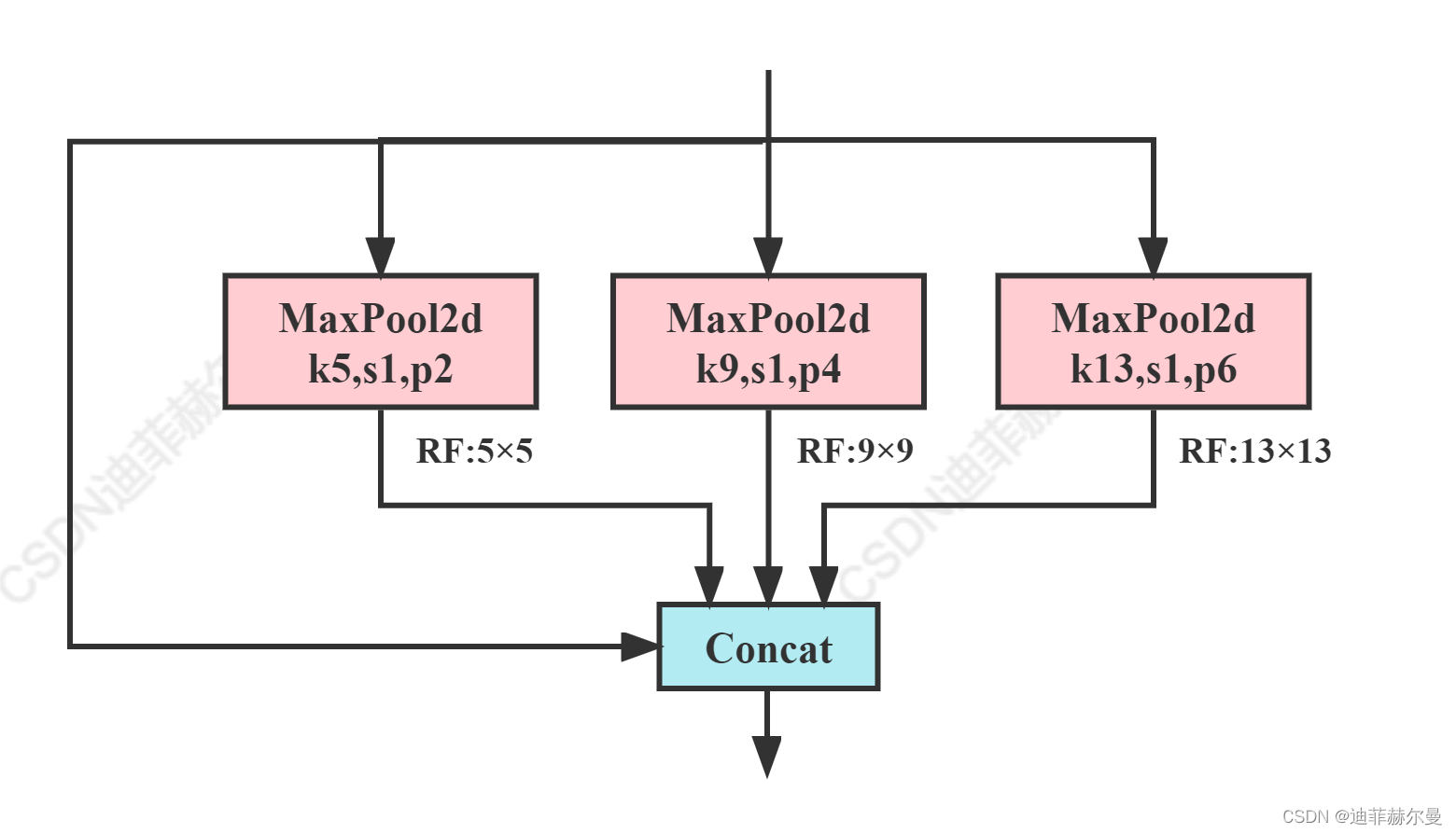
code_pytorch
class SPPF(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat((x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)), 1))(3)ASPP(Simplified SPPF)
paper: DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs
paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.00915.pdf
repo link: https://github.com/kazuto1011/deeplab-pytorch
main idea
Asymmetric spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) is proposed to robustly segment objects at multiple scales. ASPP uses filters to probe incoming convolutional feature layers at multiple sampling rates and effective fields of view, thereby capturing object and image context at multiple scales.
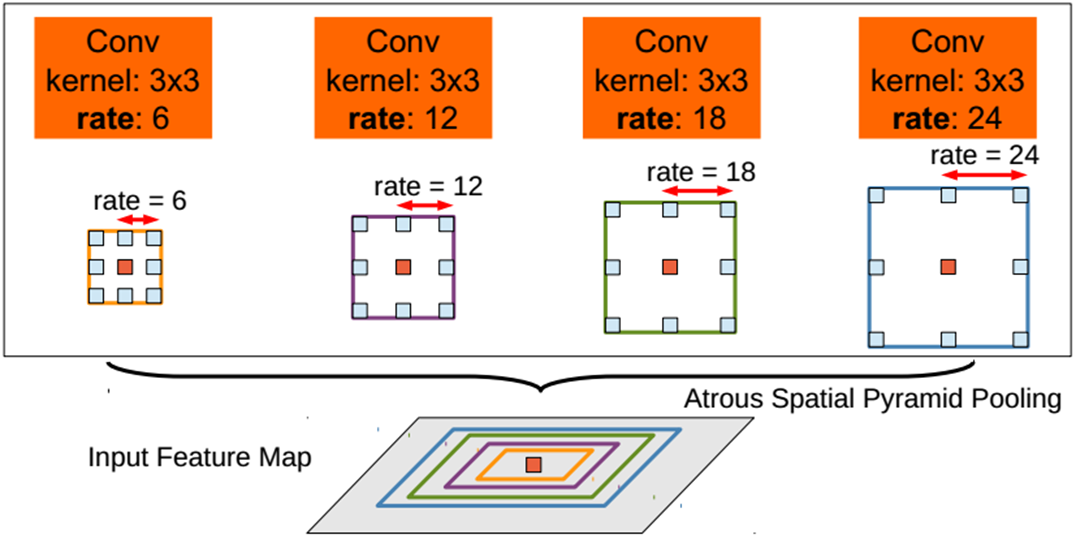
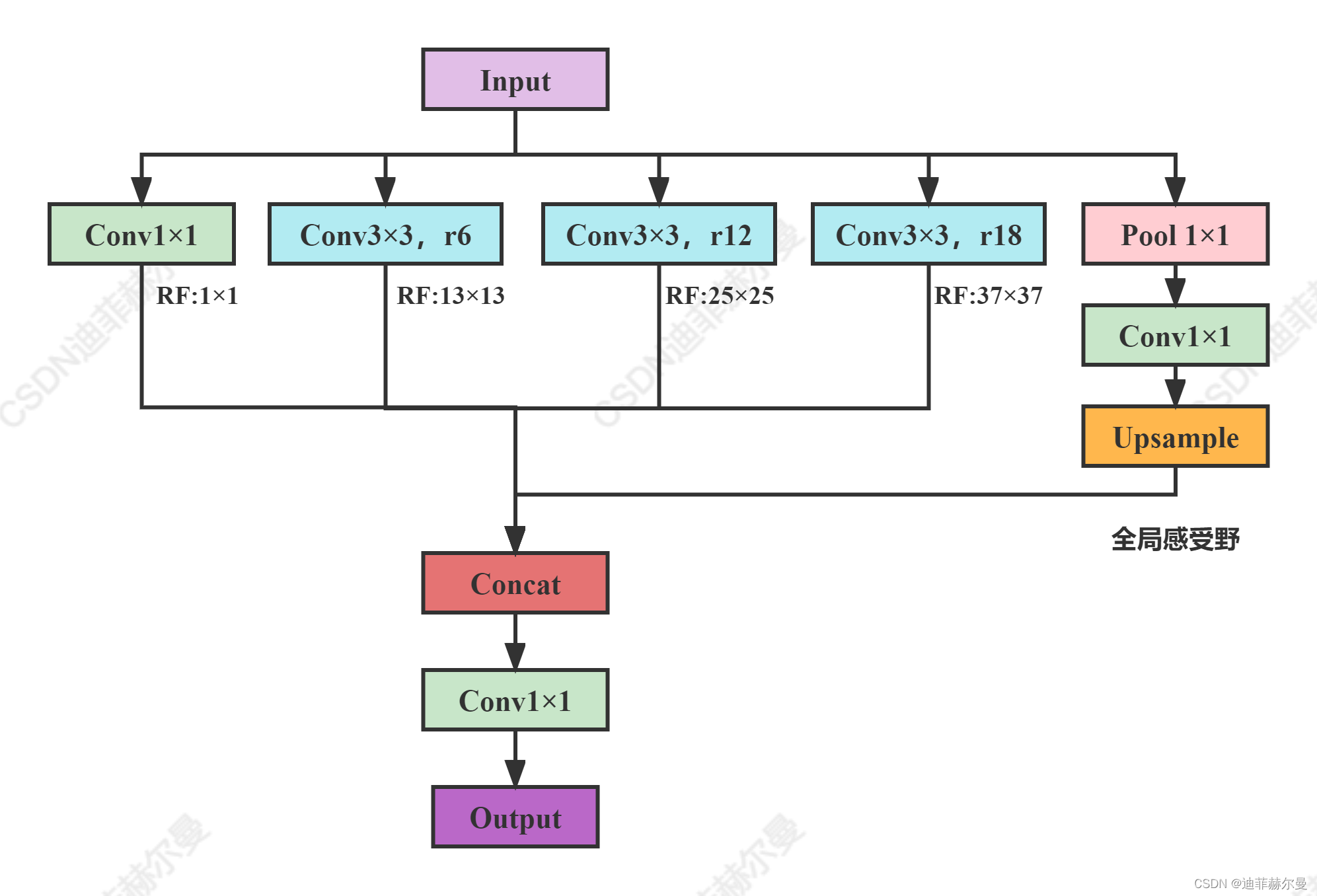
code_pytorch
class _ASPP(nn.Module):
"""
Atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP)
"""
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch, rates):
super(_ASPP, self).__init__()
for i, rate in enumerate(rates):
self.add_module(
"c{}".format(i),
nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, 3, 1, padding=rate, dilation=rate, bias=True),
)
for m in self.children():
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0, std=0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
return sum([stage(x) for stage in self.children()])(4)RFB
paper: Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection
paper link: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ECCV_2018/papers/Songtao_Liu_Receptive_Field_Block_ECCV_2018_paper.pdf
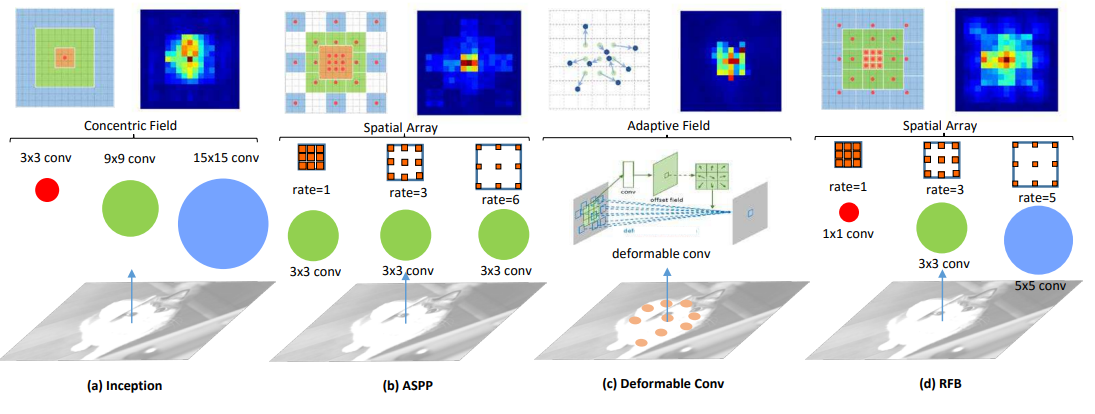
main idea
Inspired by the structure of the receptive field (RF), we propose a new RF Block (RFB) module that considers the relationship between the size and eccentricity of the RF to enhance the discriminability and robustness of features .
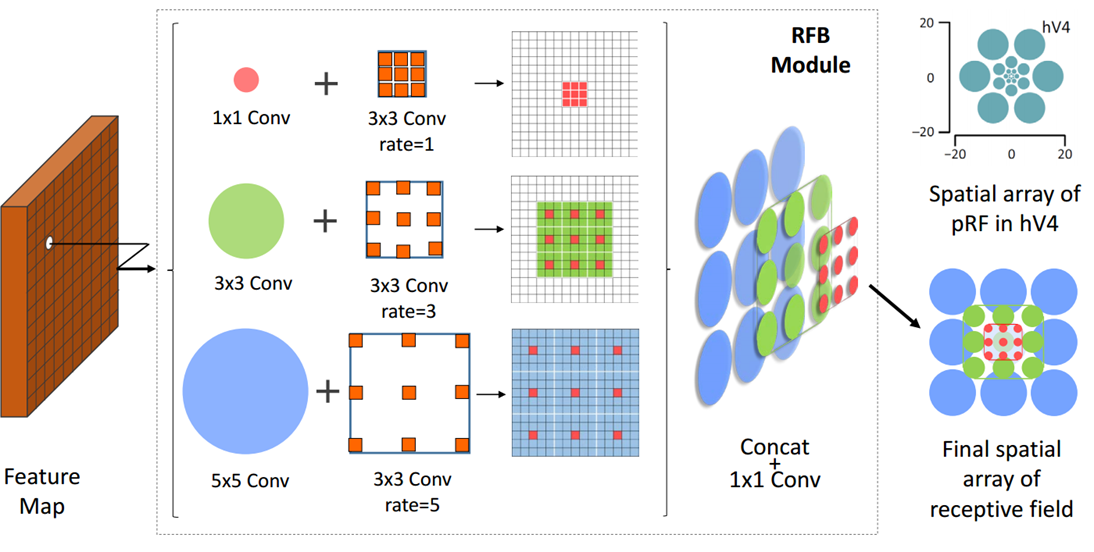

Code_Pytorch
class BasicRFB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, scale = 0.1, visual = 1):
super(BasicRFB, self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
self.out_channels = out_planes
inter_planes = in_planes // 8
self.branch0 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride),
BasicConv(2*inter_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=visual, dilation=visual, relu=False)
)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
BasicConv(inter_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=stride, padding=(1,1)),
BasicConv(2*inter_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=visual+1, dilation=visual+1, relu=False)
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
BasicConv(inter_planes, (inter_planes//2)*3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv((inter_planes//2)*3, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1),
BasicConv(2*inter_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2*visual+1, dilation=2*visual+1, relu=False)
)
self.ConvLinear = BasicConv(6*inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, relu=False)
self.shortcut = BasicConv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, relu=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
def forward(self,x):
x0 = self.branch0(x)
x1 = self.branch1(x)
x2 = self.branch2(x)
out = torch.cat((x0,x1,x2),1)
out = self.ConvLinear(out)
short = self.shortcut(x)
out = out*self.scale + short
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class BasicRFB_a(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, scale = 0.1):
super(BasicRFB_a, self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
self.out_channels = out_planes
inter_planes = in_planes //4
self.branch0 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,relu=False)
)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=(3,1), stride=1, padding=(1,0)),
BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=3, dilation=3, relu=False)
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=(1,3), stride=stride, padding=(0,1)),
BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=3, dilation=3, relu=False)
)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes//2, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
BasicConv(inter_planes//2, (inter_planes//4)*3, kernel_size=(1,3), stride=1, padding=(0,1)),
BasicConv((inter_planes//4)*3, inter_planes, kernel_size=(3,1), stride=stride, padding=(1,0)),
BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=5, dilation=5, relu=False)
)
self.ConvLinear = BasicConv(4*inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, relu=False)
self.shortcut = BasicConv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, relu=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
def forward(self,x):
x0 = self.branch0(x)
x1 = self.branch1(x)
x2 = self.branch2(x)
x3 = self.branch3(x)
out = torch.cat((x0,x1,x2,x3),1)
out = self.ConvLinear(out)
short = self.shortcut(x)
out = out*self.scale + short
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class RFBNet(nn.Module):
"""RFB Net for object detection
The network is based on the SSD architecture.
Each multibox layer branches into
1) conv2d for class conf scores
2) conv2d for localization predictions
3) associated priorbox layer to produce default bounding
boxes specific to the layer's feature map size.
See: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.07767.pdf for more details on RFB Net.
Args:
phase: (string) Can be "test" or "train"
base: VGG16 layers for input, size of either 300 or 512
extras: extra layers that feed to multibox loc and conf layers
head: "multibox head" consists of loc and conf conv layers
"""
def __init__(self, phase, size, base, extras, head, num_classes):
super(RFBNet, self).__init__()
self.phase = phase
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.size = size
if size == 300:
self.indicator = 3
elif size == 512:
self.indicator = 5
else:
print("Error: Sorry only SSD300 and SSD512 are supported!")
return
# vgg network
self.base = nn.ModuleList(base)
# conv_4
self.Norm = BasicRFB_a(512,512,stride = 1,scale=1.0)
self.extras = nn.ModuleList(extras)
self.loc = nn.ModuleList(head[0])
self.conf = nn.ModuleList(head[1])
if self.phase == 'test':
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x):
"""Applies network layers and ops on input image(s) x.
Args:
x: input image or batch of images. Shape: [batch,3*batch,300,300].
Return:
Depending on phase:
test:
list of concat outputs from:
1: softmax layers, Shape: [batch*num_priors,num_classes]
2: localization layers, Shape: [batch,num_priors*4]
3: priorbox layers, Shape: [2,num_priors*4]
train:
list of concat outputs from:
1: confidence layers, Shape: [batch*num_priors,num_classes]
2: localization layers, Shape: [batch,num_priors*4]
3: priorbox layers, Shape: [2,num_priors*4]
"""
sources = list()
loc = list()
conf = list()
# apply vgg up to conv4_3 relu
for k in range(23):
x = self.base[k](x)
s = self.Norm(x)
sources.append(s)
# apply vgg up to fc7
for k in range(23, len(self.base)):
x = self.base[k](x)
# apply extra layers and cache source layer outputs
for k, v in enumerate(self.extras):
x = v(x)
if k < self.indicator or k%2 ==0:
sources.append(x)
# apply multibox head to source layers
for (x, l, c) in zip(sources, self.loc, self.conf):
loc.append(l(x).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous())
conf.append(c(x).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous())
#print([o.size() for o in loc])
loc = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in loc], 1)
conf = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in conf], 1)
if self.phase == "test":
output = (
loc.view(loc.size(0), -1, 4), # loc preds
self.softmax(conf.view(-1, self.num_classes)), # conf preds
)
else:
output = (
loc.view(loc.size(0), -1, 4),
conf.view(conf.size(0), -1, self.num_classes),
)
return output
def load_weights(self, base_file):
other, ext = os.path.splitext(base_file)
if ext == '.pkl' or '.pth':
print('Loading weights into state dict...')
self.load_state_dict(torch.load(base_file))
print('Finished!')
else:
print('Sorry only .pth and .pkl files supported.')
# This function is derived from torchvision VGG make_layers()
# https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/models/vgg.py(5)SPPCSPC
paper: YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors
paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2207.02696v1.pdf
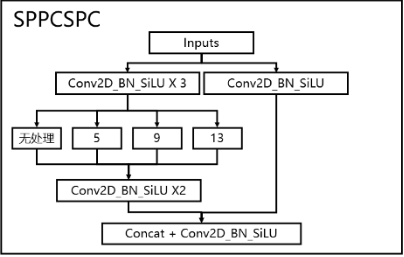
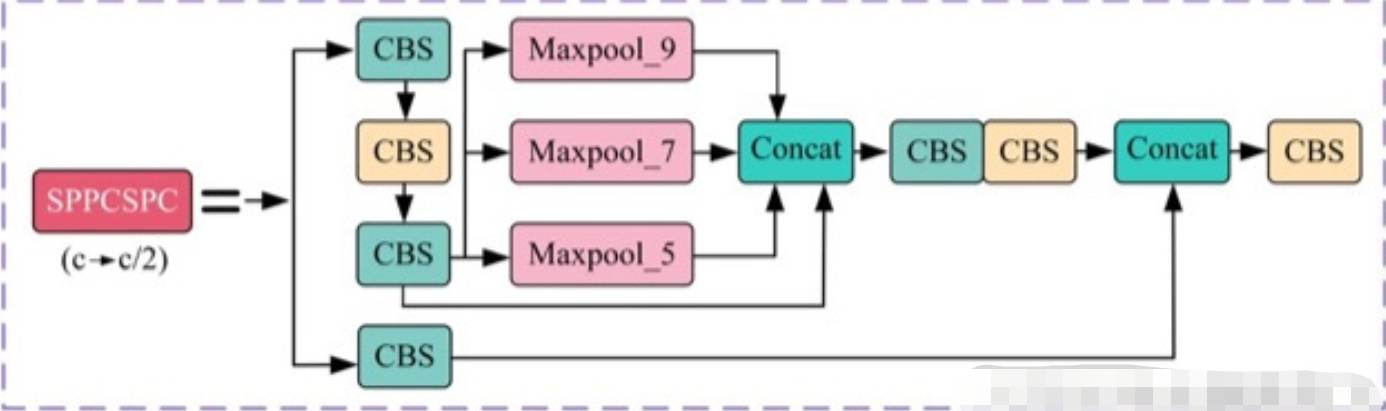
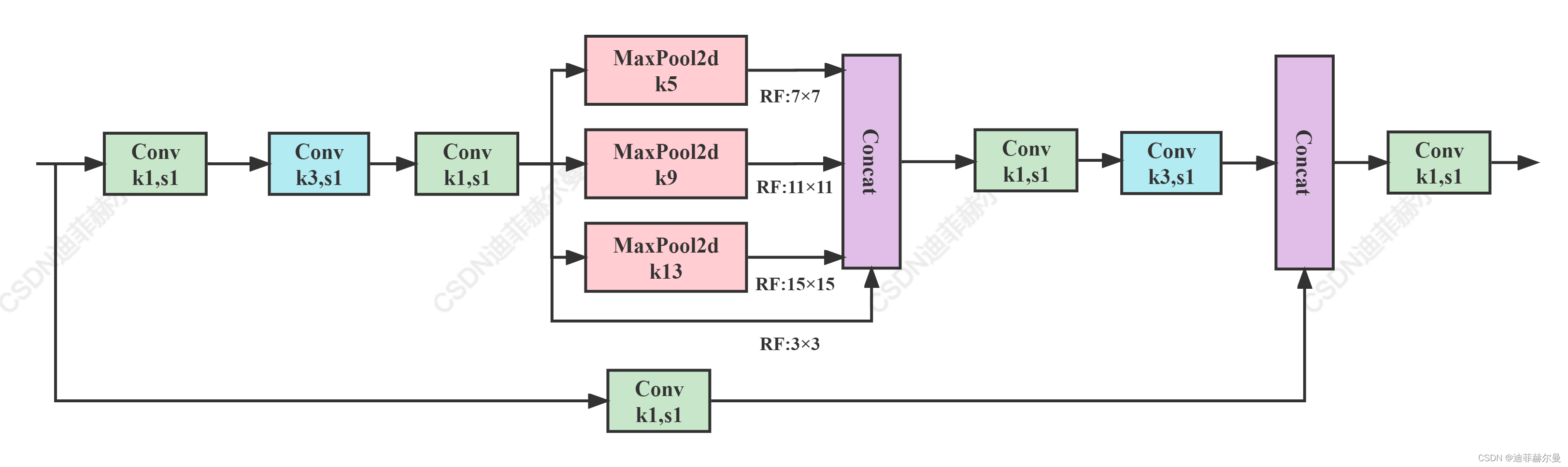
code_pytorch
class SPPCSPC(nn.Module):
# CSP https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super(SPPCSPC, self).__init__()
c_ = int(2 * c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv4 = Conv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
self.cv5 = Conv(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv6 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv7 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))
y1 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat([x1] + [m(x1) for m in self.m], 1)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv7(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))(6) SimCSPSPPF
paper: YOLOv6 v3.0: A Full-Scale Reloading
paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.05586
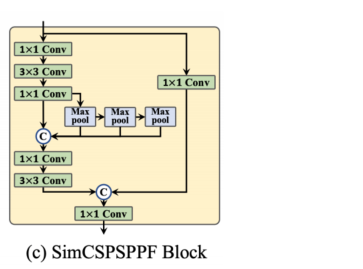
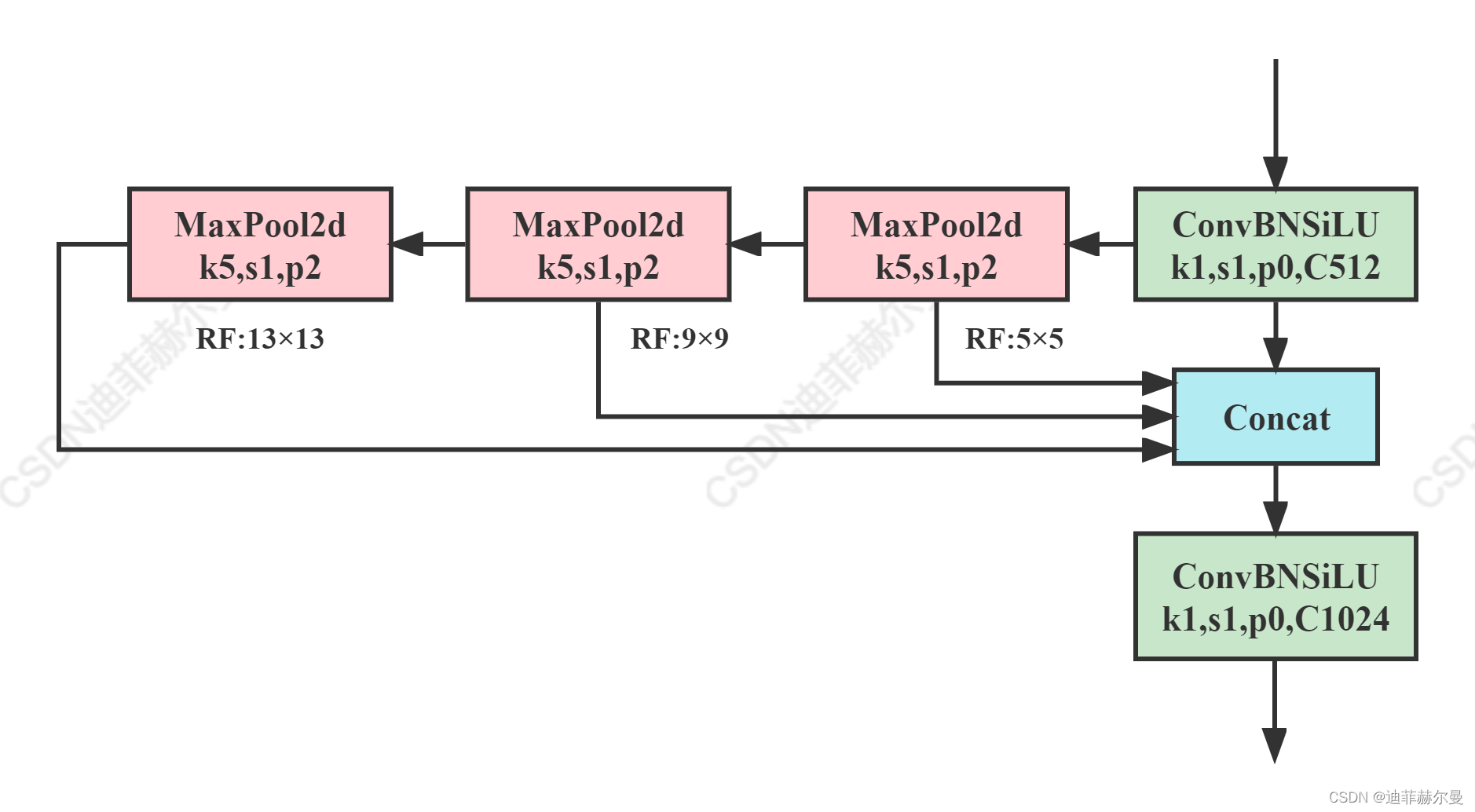
This article simplifies SPPF into SimCSPSPF blocks, which brings performance gains with negligible speed degradation.
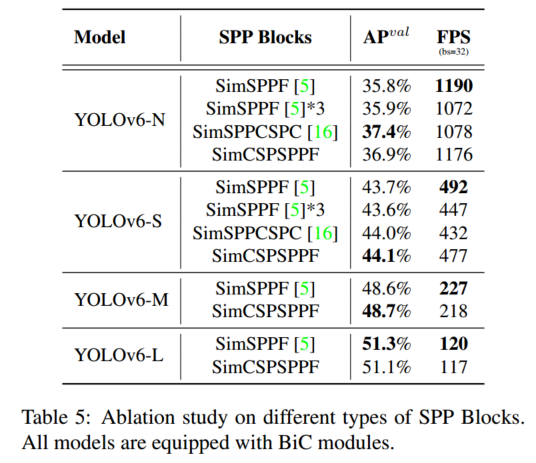
Furthermore, the impact of different types of SPP blocks is explored, including simplified variants of SPPF and SPPCSPC (denoted as SimSPPF and SimSPPCSPC, respectively) and the SimCSPSPF block, and the performance is compared as follows.
code_pytorch
class SPPFModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, block=ConvBNReLU):
super().__init__()
c_ = in_channels // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = block(in_channels, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = block(c_ * 4, out_channels, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=kernel_size // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1))
class SimSPPF(nn.Module):
'''Simplified SPPF with ReLU activation'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, block=ConvBNReLU):
super().__init__()
self.sppf = SPPFModule(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, block)
def forward(self, x):
return self.sppf(x)
class SPPF(nn.Module):
'''SPPF with SiLU activation'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, block=ConvBNSiLU):
super().__init__()
self.sppf = SPPFModule(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, block)
def forward(self, x):
return self.sppf(x)
class CSPSPPFModule(nn.Module):
# CSP https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, e=0.5, block=ConvBNReLU):
super().__init__()
c_ = int(out_channels * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = block(in_channels, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = block(in_channels, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = block(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv4 = block(c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=kernel_size // 2)
self.cv5 = block(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv6 = block(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv7 = block(2 * c_, out_channels, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))
y0 = self.cv2(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
y1 = self.m(x1)
y2 = self.m(y1)
y3 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat([x1, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1)))
return self.cv7(torch.cat((y0, y3), dim=1))
class SimCSPSPPF(nn.Module):
'''CSPSPPF with ReLU activation'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, e=0.5, block=ConvBNReLU):
super().__init__()
self.cspsppf = CSPSPPFModule(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, e, block)
def forward(self, x):
return self.cspsppf(x)
class CSPSPPF(nn.Module):
'''CSPSPPF with SiLU activation'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, e=0.5, block=ConvBNSiLU):
super().__init__()
self.cspsppf = CSPSPPFModule(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, e, block)
def forward(self, x):
return self.cspsppf(x)