chapter
-
Understanding of network development status and importance (understanding)
-
Current status and problems of network information security (understand)
-
Basic attributes of network information security (must master)
-
Network information security goals and functions (currently understood, functions must be mastered)
-
Basic technical requirements for network information security (familiar)
-
Network information security management content and methods (familiar)
-
Network Information Security Law and Policy Documents (Familiarity)
-
Network information security technology information acquisition (familiarity)
Network development status and importance understanding*
-
**"Digitalization, networking, and intelligence"** have become the main characteristics of the information society, and the era of "Internet of Everything" has arrived.
-
Network information security in a narrow sense refers specifically to the fact that each component of the network information system meets the requirements of security attributes, namely "confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation, and controllability"**.
-
Network information security in a broad sense is "big security" involving national security, urban security, economic security, social security, production safety, personal safety, etc.
-
Focusing on network security issues, the object content, concepts, methods, and duration of ensuring network information security are constantly evolving. The new changes are reflected in three aspects:
-
First, the guarantee content has changed from single dimension to multi-dimensional. The dimensions of guarantee include cyberspace domain, physical space domain and social space domain.
-
Second, network information security measures have evolved from single (technology) to comprehensive (law, policy, technology, management, industry, education);
-
Third, the guarantee time dimension requires covering the entire life cycle of the network system, and the guarantee response speed requirements continue to shorten. Network information security is not divided into wartime and peacetime, but all the time.
-
In 2016, the country released the National Cyberspace Security Strategy, and relevant cybersecurity laws, regulations and policies were also introduced one after another.
-
The "Cybersecurity Law of the People's Republic of China" has been implemented on June 1, 2017. In order to strengthen network security education, cyberspace security has been added as a first-level subject.
Current status and problems of network information security*
-
According to statistics from the National Information Security Vulnerability Sharing Platform (as of May 2020), there are tens of thousands of operating system vulnerability entries, more than 7,000 network equipment vulnerability entries, and more than 2,000 database vulnerability entries.
-
In 2018, national information security vulnerability sharing. The platform collected 14,201 new vulnerabilities, including 4,898 high-risk vulnerabilities.
-
Network information security is an unavoidable and important task in network informatization. The main network security issues are:
-
Strong network dependence and network security-related risks are highlighted
-
Network information product supply chain and security quality risks
-
Technical homogeneity of network information products and risk of technology abuse
-
Unbalanced and inadequate development of network security construction and management risks
-
Network data security risks
-
Advanced persistent threat risk
-
Malicious code risk
-
Software code and security vulnerability risks
-
Cyber security awareness risks of personnel
-
Network information technology complexity and operational security risks
-
Economic risks of underground black industry on the Internet
-
Cyber espionage and cyber warfare risks
Basic attributes of network information security
Basic attributes of network information security-CIA security attributes***
Common basic network security attributes include confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation, and controllability. In addition, there are authenticity, timeliness, compliance, privacy, compliance, fairness, reliability, and accountability. survivability.
❝
The core content of "CIA's Three Attributes" :
"Confidentiality" : refers to the "not leaking" of network information to unauthorized users, entities or programs, which can prevent unauthorized persons from obtaining information.
"Integrity" : refers to the characteristic that network information or systems cannot be changed without authorization. ( "Not tampered with" )
"Availability" : refers to the characteristic that legally permitted users can "timely obtain" network information or services. ( "Ready to use" )
❞
Non-repudiation: refers to the characteristic of "preventing" network information system-related "users from denying" their activities. ( "Non-repudiation" )
Controllability: refers to the "attribute of the responsible party of the network information system that has the ability to manage and control" it, and can effectively control and control the system according to authorization rules, so that managers can effectively control the behavior of the system and the use of information, in line with System operation target.
Basic attributes of network information security-other security attributes**
| Other features | concept |
|---|---|
| authenticity | It refers to the "consistency" between cyberspace information and the objective facts of actual physical space and social space** |
| Timeliness | It refers to the ability of cyberspace information, services and systems to meet the **"time constraints"** requirements |
| Compliance | It means that network information, services and systems comply with **"laws and regulations"** policies, standards and other requirements |
| fairness | It refers to the characteristic requirement that the relevant entities of the network information system are in **"equal status"** to handle related tasks, and neither party has an advantage. |
| reliability | It refers to the characteristics of a network information system that can "effectively complete" predetermined system functions under specified conditions and time. |
| survivability | It refers to the security features of the network information system that provide minimal and necessary service functions and can "support the continued operation of the business" when the security of the network information system is compromised. |
| Privacy | Refers to the security attribute of sensitive personal information** "not disclosed to the public"** |
Network information security goals and functions
Network Information Security Objectives and Functions—Network Information Security Objectives*
-
Network security goals can be divided into "macro" network security goals and "micro" network security goals.
-
Macroscopic network security goals refer to network information systems that meet national security needs and comply with national laws, regulations and policy requirements, such as network sovereignty, network compliance, etc.
-
Micro network security goals refer to the specific security requirements of network information systems.
-
The specific goal of network security is to "protect network information and related information systems from network security threats". The relevant protection objects meet the basic attribute requirements of network security, user network behavior complies with national laws and regulations, and the network information system can support business Safe and continuous operations, data security is effectively protected.
Network Information Security Goals and Functions—Network Information Security Functions**
To achieve the basic goals of network information security, the network should have basic functions such as "defense" , "monitoring" , "emergency" and "recovery". ( "Defense Monitoring, Emergency Recovery" )
| security function | content |
|---|---|
| defense | It refers to the adoption of various means and measures to enable the network system to "have the function of preventing and resisting various known network security threats"** |
| monitor | It refers to the function of adopting various means and measures to "detect and discover various known or unknown network security threats"** |
| emergency | It refers to taking various means and measures to respond to emergencies in the network system and "having the function of promptly responding to and handling network attacks"** |
| recover | It refers to taking various means and measures to "have the function of restoring network system operation" in response to network disaster events that have occurred. |
Nineteen aspects of basic technical requirements for network information security*
| skills requirement | content |
|---|---|
| Physical environment security | It refers to the overall security of all hardware that supports the operation of the network system, including the environment, equipment and recording media. It is the "basic guarantee for the safe, reliable and uninterrupted operation of the network system. " Physical security requirements mainly include "environmental security, equipment security, and storage media security"**. |
| Network Information Security Certification | It is **"the premise and basis for realizing network resource access control and an important technical method to effectively protect network management objects"**. The function of network authentication is to identify and verify the authenticity of network resource visitors and prevent users from accessing network resources by impersonating their identities. |
| Network information access control | It is a key technical method to effectively protect network management objects from threats. Its main goals are two: "(1) Restrict illegal users from obtaining or using network resources; (2) Prevent legitimate users from abusing their permissions and accessing network resources beyond their authority." |
| Network security and confidentiality | The purpose of network security and confidentiality is to "prevent unauthorized users from accessing online information or network equipment"**. |
| Network information security vulnerability scanning | Intruders usually use some programs to detect security vulnerabilities in network systems, and then use corresponding techniques to attack through the discovered security vulnerabilities. Therefore, the network system needs to be equipped with a weakness or vulnerability scanning system to detect whether there are security vulnerabilities in the network, so that network security administrators can develop appropriate vulnerability management methods based on the vulnerability detection report. |
| Malicious code protection | The Internet is one of the best and fastest ways for viruses, worms, Trojans and other malicious codes to spread. Malicious code can enter personal computers or servers through online file downloads, emails, web pages, file sharing and other propagation methods. Therefore, "preventing malicious code is an essential security requirement for network systems . " |
| Network information content security | It means that the information and data carried by relevant network information systems comply with legal and regulatory requirements and prevent the spread of bad information and junk information. Relevant network information content security technologies mainly include "spam filtering, IP address/URL filtering, natural language analysis and processing", etc. |
| Network information security monitoring and early warning | Network systems face different levels of threats, and network security operation is a complex task. The role of network security monitoring is to discover intrusion activities in integrated network systems and check the effectiveness of security protection measures, so as to promptly alert the network security administrator, take effective measures against intruders, prevent the spread of harm and adjust security policies |
| Network information security emergency response | Security threats encountered by network systems are often difficult to predict. Although some network security precautions have been taken, "network information security incidents will still inevitably occur due to human or technical flaws . " Since network information security incidents cannot be completely eliminated, some measures must be taken to ensure the normal operation of the network system in the event of an accident. At the same time, electronic evidence collection is conducted for cyber attacks to combat cyber criminal activities. |
Network information security management content and methods
Contents and methods of network information security management - Network information security management*
-
Network information security management refers to **"taking appropriate security measures for network assets to ensure the availability, integrity, controllability and non-repudiation of network assets"**, etc., and does not cause network equipment, network communication protocols, network Services and network management are harmed by human and natural factors, resulting in network interruption, information leakage or destruction.
-
Network information security management objects mainly include the sum of all software and hardware that support the operation of network systems, including network equipment, network communication protocols, network operating systems, network services, secure network management, etc. Network information security involves **"physical security, network communication security, operating system security, network service security, network operation security and personnel security"**.
-
The goal of network information security management is to ensure the operational safety and information security of the network through appropriate security precautions, and to meet the security requirements for online business development.
-
Network security management methods mainly include "risk management, hierarchical protection, defense in depth, hierarchical protection, emergency response, and PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act, Deming cycle)" methods.
-
The elements of network information security management are composed of **"network management objects, network threats, network vulnerabilities, network risks, and network protection measures"**.
-
Network information security management objects are assets that companies and institutions have directly given value to and need to be protected. Its existence forms include tangible and intangible. For example, network equipment hardware and software documents are tangible, while service quality and network bandwidth are intangible.
-
According to the natural attributes of the threat subject, it can be divided into "natural threats and man-made threats" . Natural threats include "earthquakes, lightning strikes, floods, fires, static electricity, rodents and power failures" . According to the classification of threat objects, it can be divided into "physical security threats, network communication threats, network service threats, and network management threats"**.
-
Vulnerability refers to the state or error in the computing system that conflicts with the security policy, which will lead to unauthorized access by attackers, impersonation of users to perform operations, and denial of service. The CC standard states that "the existence of vulnerabilities will lead to risks, and threat actors use vulnerabilities to create risks . "
-
Protective measures refer to the collective term for the various practices, procedures and mechanisms implemented to counter cybersecurity threats, reduce vulnerabilities, limit the impact of unexpected events, detect unexpected events and facilitate disaster recovery.
-
Network information security management assessment refers to the evaluation of network information security management capabilities and whether management work conforms to specifications. Common network information security management assessments include network security level protection assessment, information security management system certification (ISMS for short), system security engineering capability maturity model (SSE-CMM for short), etc.
Network information security management content and methods - Network information security risks**
Network information security risk refers to the possibility that specific threats exploit the vulnerabilities of network management objects, causing the value of network management objects to be damaged or lost. Simply put, "Cyber risk is the product of the probability of a cyber threat occurring and the impact caused . "
Network security management actually controls the risks of network management objects in the network system:
| risk control | content |
|---|---|
| avoid risk | Separate the internal network and the external network through physical isolation devices to avoid attacks from the external network |
| transfer risk | Purchase a business insurance plan or security outsourcing |
| reduce threats | Install anti-virus software packages to prevent virus attacks |
| Eliminate vulnerabilities | Patch operating systems or enhance security awareness among staff |
| Reduce the impact of threats | Use multiple communication lines for backup or develop emergency plans |
| risk monitoring | Regularly conduct risk analysis on the security status of network systems and monitor potential threatening behaviors |
Network information security management content and methods - Network information security management process**
- Network information security management generally follows the following workflow:
-
"Determine" network information security management "object"
-
"Assess" the "value" of network information security management objects
-
"Identify" "threats" to network information security management objects
-
"Identify" the "vulnerabilities" of network information security management objects
-
"Determine" the "risk level" of network information security management objects
-
"Develop" network information security "prevention system and preventive measures"
-
"Implement" and implement network information security "preventive measures"
-
"Operation/Maintenance" Network Information "Security Equipment, Configuration"
( "Determine the object-assess the value-identify the threat-identify the vulnerability-determine the level-formulate measures-implement measures-operation configuration" )
Network Information Security Law and Policy Document**
-
The "Cybersecurity Law of the People's Republic of China" will come into effect on June 1, 2017.
-
The "Cryptozoology Law of the People's Republic of China" (hereinafter referred to as the Cryptozoology Law) will be implemented on January 1, 2020.
-
Take technical measures to monitor and record network operating status and network security events, and retain relevant network logs **"not less than six months"** in accordance with regulations.
-
The main work of network security level protection can be summarized as **"rating, filing, construction and rectification, rating evaluation, operation and maintenance"** (supervision and management).
-
The grading work is to confirm the grading objects, determine the appropriate level, and pass expert review and review by the competent department.
-
The filing work is to prepare filing materials in accordance with the regulations on graded protection management, and submit them to the local public security agency for filing and review;
-
建设整改工作是指依据相应等级要求对当前保护对象的实际情况进行差距分析,针对不符合项结合行业要求对保护对象进行整改,建设符合等级要求的安全技术和管理体系
-
等级测评工作是指等级保护测评机构依据相应等级要求,对定级的保护对象进行测评,并出具相应的等级保护测评证书
-
运营维护(监督管理)工作是指等级保护运营主体按照相应等级要求,对保护对象的安全相关事宜进行监督管理。
-
「中国网络安全审查技术与认证中心(CCRC」,原中国信息安全认证中心)是负责实施网络安全审查和认证的专门机构。
-
域名服务是网络基础服务。该服务主要是指从事域名根服务器运行和管理、顶级域名运行和管理、域名注册、域名解析等活动。域名系统出现网络与信息安全事件时,应当在**「24小时内」**向电信管理机构报告。域名是政府网站的基本组成部分和重要身份标识。
-
国家计算机网络应急技术处理协调中心(简称’'国家互联网应急中心",英文缩写为CNCERT或CNCERT/CC)是中国计算机网络应急处理体系中的牵头单位,是国家级应急中心。CNCERT的主要职责是:按照**「积极预防、及时发现、快速响应、力保恢复」**的方针,开展互联网网络安全事件的预防、发现、预警和协调处置等工作,维护公共互联网安全,保障关键信息基础设施的安全运行。
网络信息安全科技信息获取*
-
网络信息安全科技信息获取来源主要有**「网络安全会议、网络安全期刊、网络安全网站、网络安全术语」**等。
-
网络信息安全领域"四大"顶级学术会议是S&P、CCS、NDSS、USENIX Security。
-
网络信息安全术语是获取网络安全知识和技术的重要途径,常见的网络安全术语可以分成基础技术类、风险评估技术类、防护技术类、检测技术类、响应恢复技术类、测评技术类等。
-
基础技术类术语常见的是密码。常见的密码术语如加密(encryption)、解密(decryption)、、非对称加密算法 (asymmetric cryptographic algorithm) 、公钥加密算法 (public key cryptographic algorithm) 、公钥 (public key)等。
-
风险评估技术类术语包括拒绝服务 (Denial of Service) 、分布式拒绝服务 (Distributed Denial of Service) 、网页篡改 (Website Distortion) 、网页仿冒 (Phishing) 、网页挂马( Website Malicious Code) 、域名劫持 (DNS Hijack) 、路由劫持 (Routing Hijack) 、垃圾邮件 (Spam) 、恶意代码 (Malicious Code) 、特洛伊木马 (Trojan Horse) 、网络蠕虫 (Network Worm) 、僵尸网络 CBotNet) 等。
-
检测技术类术语包括入侵检测(IntrusionDetection)、漏洞扫描(VulnerabilityScanning)等。
-
防护技术类术语包括访问控制 (Access Control )防火墙 (Firewall) 、入侵防御系统 (Intrusion Prevention System) 等。
-
检测技术类术语包括入侵检测 (Intrusion Detection) 、漏洞扫描 (Vulnerability Scanning) 等。
-
响应/恢复技术类术语包括应急响应(Emergency Response )灾难恢复(Disaster Recovery) 备份 (Backup) 等。
-
测评技术类术语包括黑盒测试 (Black Box Testing) 、白盒测试 (White Box Testing) 、灰 盒测试 (Gray Box Testing) 、渗透测试 (Penetration Testing) 、模糊测试 (Fuzz Testing)。
练习
1、()不是网络信息安全的CIA安全属性?
A、机密性
B、可用性
C、可控性
D、完整性
2、()是指网络信息系统相关主体处于同等地位处理相关任务,任何一方不占据优势的特性要求?
A、真实性
B、公平性
C、可靠性
D、可生存性
3、网络信息安全功能不包括()?
A、防御
B、监测
C、应急
D、识别
4、网络信息安全威胁从威胁对象来分类,以下不正确的是()?
A、物理安全威胁
B、网络通信威胁
C、网络服务威胁
D、网络数据威胁
5、某企业采取多条通信线路进行备份或制定应急预案,此措施属于()?
A、避免风险
B、转移风险
C、减少威胁
D、减少威胁的影响
6、()是中国计算机网络应急处理体系中的牵头单位?
A、CCRC
B、CNCERT
C、国家网信办
D、国家应急管理局
7、以下哪项不是信息化社会的主要特征()
A、数字化
B、虚拟化
C、网络化
D、智能化
8、狭义上的网络安全指的是()
A、网络信息系统的各组成要素符合安全属性的要求。
B、涉及国家安全、城市安全、经济安全、社会安全、生产安全、人身安全在内的安全。
C、网络信息系统运行环境、软件、硬件、运行维护安全。
D、网络信息系统开发生命周期的安全
9、以下哪项不是网络安全问题的新的变化()
A、保证内容从单维度向多维度转变
B、保障措施从单一性向综合性转变
C、保证时间维度要求涵盖网络系统的整个生命周期,保障响应速度要求不断缩短
D、保证空间范围从局部向全局转变
10、未授权的实体得到了数据的访问权,这属于对安全的()的破坏
A、机密性
B、完整性
C、合法性
D、可用性
11、()是指采取各种手段和措施,使得网络系统具备阻止、抵御各种己知网络安全威胁的功能。
A、防御
B、预防
C、监测
D、阻断
12、《中华人民共和国密码法》于()起实施。
A、2018年1月1目
B、2019年1月1日
C、2020年1月1目
D、2021年1月1日
13、以下关于CNCERT(国家互联网应急中心)的主要职责描述错误的是()
A、积极预防
B、定期发现
C、快速响应
D、力保恢复
14、网络信息安全术语是获取网络安全知识和技术的重要途径,以下()是风险评估技术类。
A、加密
B、风险监测
C、防火墙
D、拒绝服务
15、简述网络信息安全的CIA属性内容?(简答题)
16、简述常见的网络安全风险控制的措施有哪些?(简答题)
17、简述网络信息安全管理遵循的一般流程?(简答题)
题外话
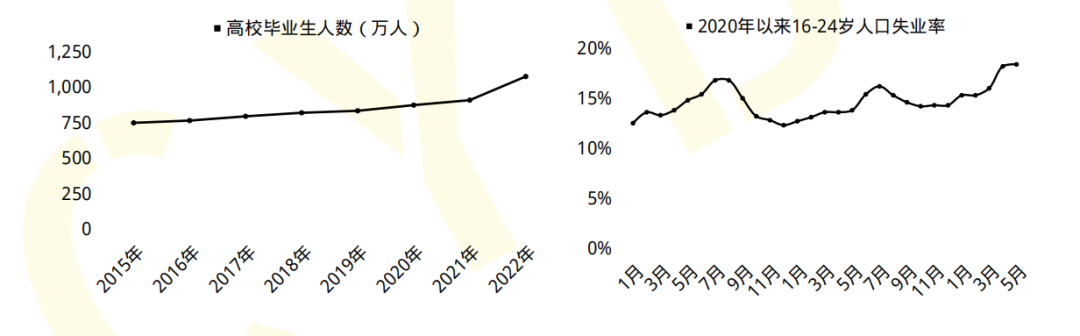
初入计算机行业的人或者大学计算机相关专业毕业生,很多因缺少实战经验,就业处处碰壁。下面我们来看两组数据:
-
2023届全国高校毕业生预计达到1158万人,就业形势严峻;
-
国家网络安全宣传周公布的数据显示,到2027年我国网络安全人员缺口将达327万。
一方面是每年应届毕业生就业形势严峻,一方面是网络安全人才百万缺口。
6月9日,麦可思研究2023年版就业蓝皮书(包括《2023年中国本科生就业报告》《2023年中国高职生就业报告》)正式发布。
2022届大学毕业生月收入较高的前10个专业
本科计算机类、高职自动化类专业月收入较高。2022届本科计算机类、高职自动化类专业月收入分别为6863元、5339元。其中,本科计算机类专业起薪与2021届基本持平,高职自动化类月收入增长明显,2022届反超铁道运输类专业(5295元)排在第一位。
具体看专业,2022届本科月收入较高的专业是信息安全(7579元)。对比2018届,电子科学与技术、自动化等与人工智能相关的本科专业表现不俗,较五年前起薪涨幅均达到了19%。数据科学与大数据技术虽是近年新增专业但表现亮眼,已跻身2022届本科毕业生毕业半年后月收入较高专业前三。五年前唯一进入本科高薪榜前10的人文社科类专业——法语已退出前10之列。

“没有网络安全就没有国家安全”。当前,网络安全已被提升到国家战略的高度,成为影响国家安全、社会稳定至关重要的因素之一。
网络安全行业特点
1、就业薪资非常高,涨薪快 2021年猎聘网发布网络安全行业就业薪资行业最高人均33.77万!
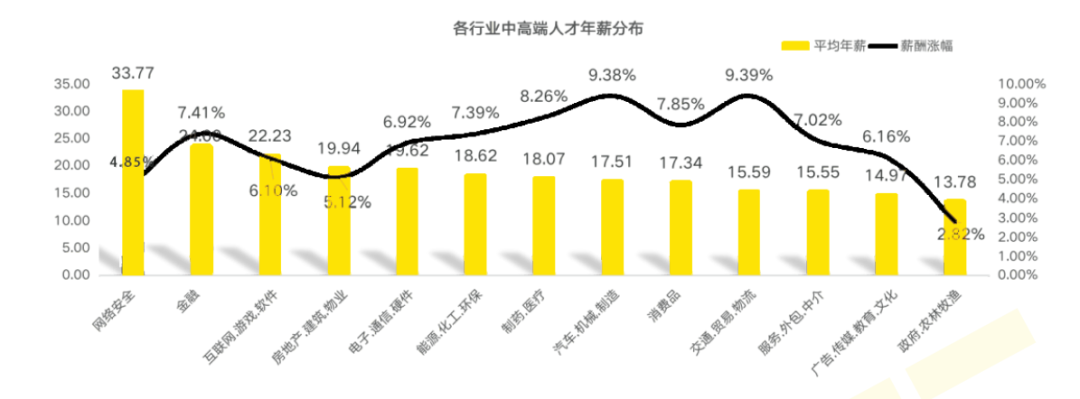
2、人才缺口大,就业机会多
2019年9月18日《中华人民共和国中央人民政府》官方网站发表:我国网络空间安全人才 需求140万人,而全国各大学校每年培养的人员不到1.5W人。猎聘网《2021年上半年网络安全报告》预测2027年网安人才需求300W,现在从事网络安全行业的从业人员只有10W人。
行业发展空间大,岗位非常多
网络安全行业产业以来,随即新增加了几十个网络安全行业岗位︰网络安全专家、网络安全分析师、安全咨询师、网络安全工程师、安全架构师、安全运维工程师、渗透工程师、信息安全管理员、数据安全工程师、网络安全运营工程师、网络安全应急响应工程师、数据鉴定师、网络安全产品经理、网络安全服务工程师、网络安全培训师、网络安全审计员、威胁情报分析工程师、灾难恢复专业人员、实战攻防专业人员…
职业增值潜力大
网络安全专业具有很强的技术特性,尤其是掌握工作中的核心网络架构、安全技术,在职业发展上具有不可替代的竞争优势。
随着个人能力的不断提升,所从事工作的职业价值也会随着自身经验的丰富以及项目运作的成熟,升值空间一路看涨,这也是为什么受大家欢迎的主要原因。
从某种程度来讲,在网络安全领域,跟医生职业一样,越老越吃香,因为技术愈加成熟,自然工作会受到重视,升职加薪则是水到渠成之事。
黑客&网络安全如何学习
今天只要你给我的文章点赞,我私藏的网安学习资料一样免费共享给你们,来看看有哪些东西。
1.学习路线图
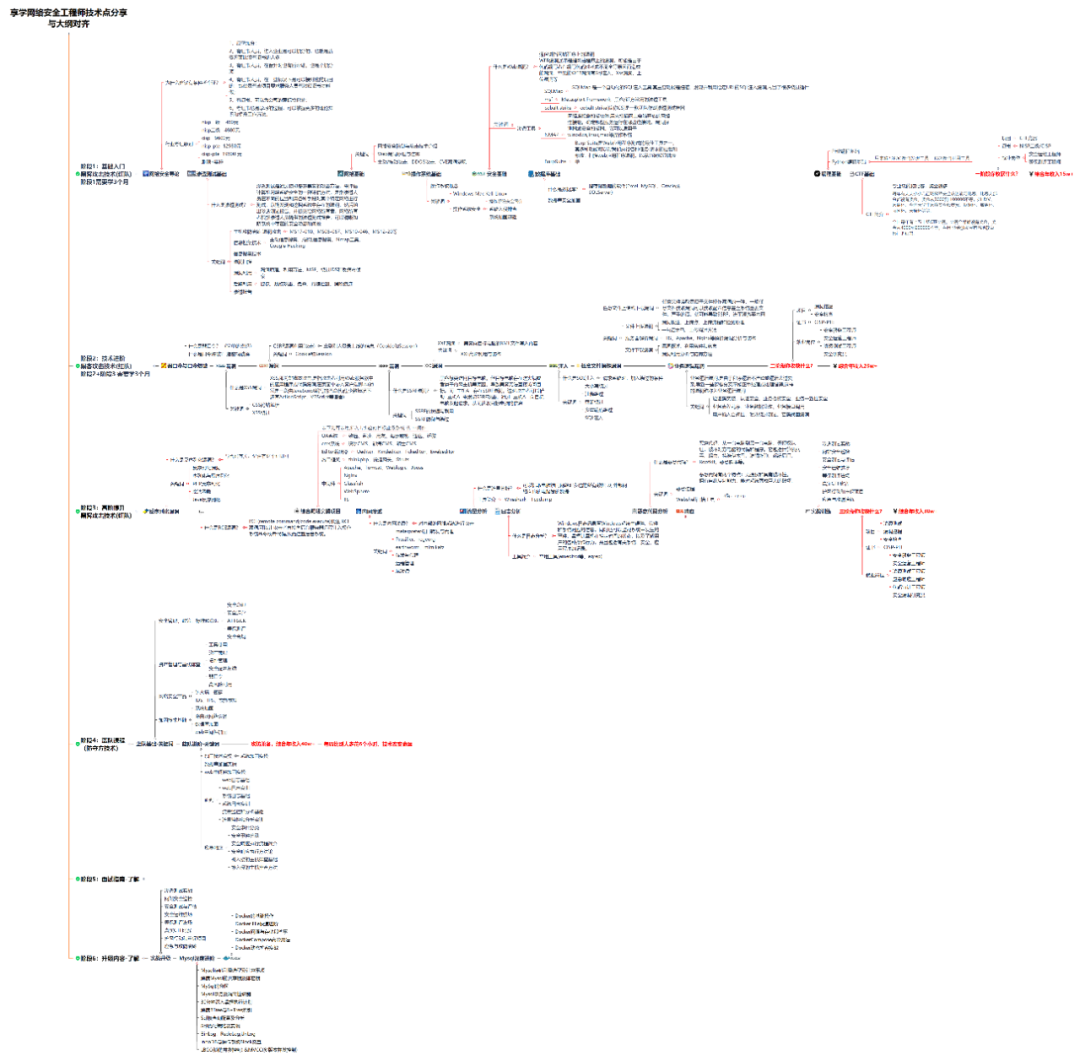
攻击和防守要学的东西也不少,具体要学的东西我都写在了上面的路线图,如果你能学完它们,你去就业和接私活完全没有问题。
2.视频教程
网上虽然也有很多的学习资源,但基本上都残缺不全的,这是我自己录的网安视频教程,上面路线图的每一个知识点,我都有配套的视频讲解。
内容涵盖了网络安全法学习、网络安全运营等保测评、渗透测试基础、漏洞详解、计算机基础知识等,都是网络安全入门必知必会的学习内容。
(都打包成一块的了,不能一一展开,总共300多集)
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
CSDN大礼包:《黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包》免费分享
3.技术文档和电子书
技术文档也是我自己整理的,包括我参加大型网安行动、CTF和挖SRC漏洞的经验和技术要点,电子书也有200多本,由于内容的敏感性,我就不一一展示了。
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
CSDN大礼包:《黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包》免费分享
4.工具包、面试题和源码
“工欲善其事必先利其器”我为大家总结出了最受欢迎的几十款款黑客工具。涉及范围主要集中在 信息收集、Android黑客工具、自动化工具、网络钓鱼等,感兴趣的同学不容错过。
还有我视频里讲的案例源码和对应的工具包,需要的话也可以拿走。
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
CSDN大礼包:《黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包》免费分享
最后就是我这几年整理的网安方面的面试题,如果你是要找网安方面的工作,它们绝对能帮你大忙。
这些题目都是大家在面试深信服、奇安信、腾讯或者其它大厂面试时经常遇到的,如果大家有好的题目或者好的见解欢迎分享。
参考解析:深信服官网、奇安信官网、Freebuf、csdn等
内容特点:条理清晰,含图像化表示更加易懂。
内容概要:包括 内网、操作系统、协议、渗透测试、安服、漏洞、注入、XSS、CSRF、SSRF、文件上传、文件下载、文件包含、XXE、逻辑漏洞、工具、SQLmap、NMAP、BP、MSF…

因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取