1. KITTI data set preparation
DAMO-YOLO supports COCO format data sets. Before training KITTI, the annotations of KITTI need to be converted to KITTI format. KITTI is determined by labeling each file, that is, one picture corresponds to one label file. The following is the first annotation file of the KITTI 3D target detection training set: 000000.txt
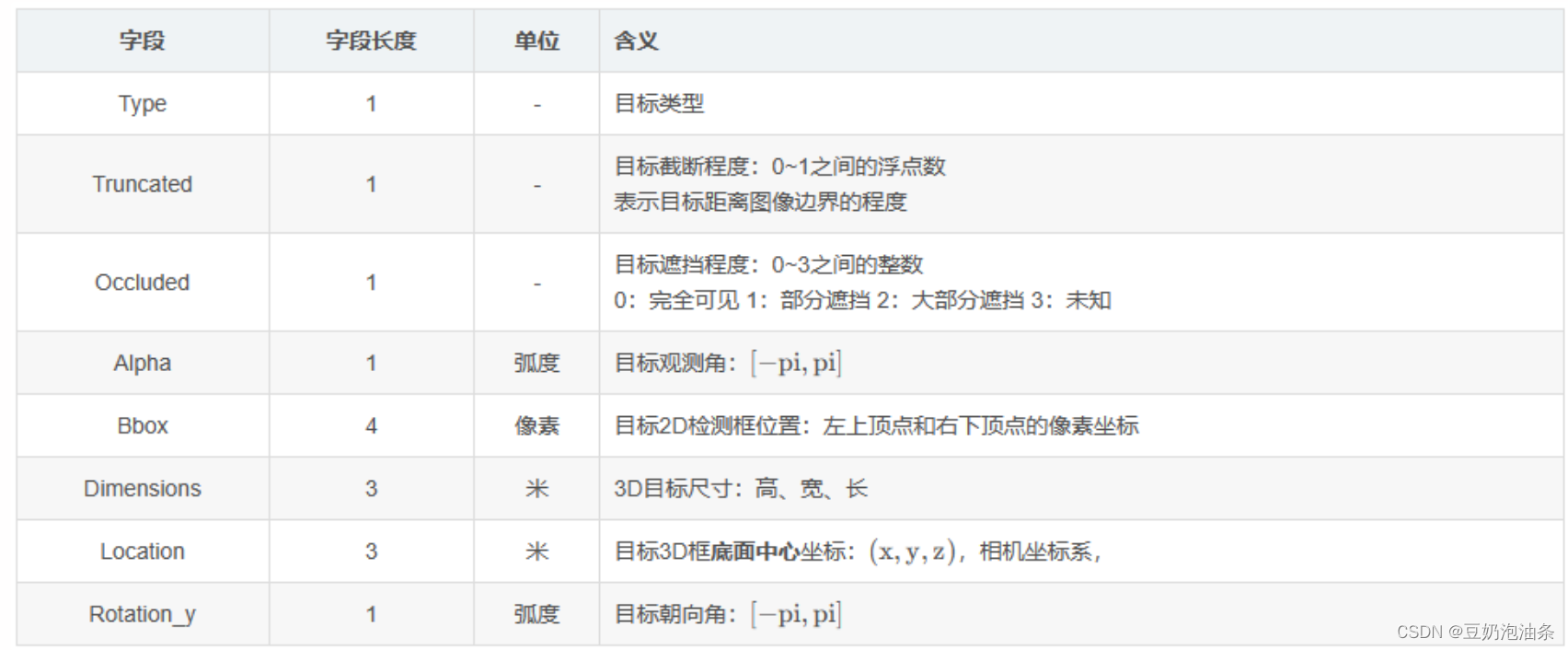
Pedestrian 0.00 0 -0.20 712.40 143.00 810.73 307.92 1.89 0.48 1.20 1.84 1.47 8.41 0.01
I won’t explain them one by one. Please refer to the table of KITTI 3D target detection data set analysis (full version)_kitti data set structure-CSDN blog . You can take a look at the detailed explanation of this article.
The COCO format will not be explained in detail. You can take a look at this article COCO data set (target detection task json file content summary . To summarize, the COCO format requires a large json file, which contains the path and comments of each image, bbox It is given in the form of center coordinates and width and height.
Therefore, to convert KITTI format to COCO, you need to read txt files one by one, perform coordinate conversion and write them into json. The code is as follows, based on the annotation of converting TXT into COCO jason format_D_galaxy's blog-CSDN blog modification:
import cv2
from math import *
import numpy as np
import os, random, shutil
import glob as gb
from time import sleep
import copy
import json
def copyFile2Folder(srcfile, dstfolder):
'''
复制文件到指定文件夹,名字和以前相同
Args:
srcfile: '/home/wsd/***/yolov5/data/PCB_DATASET/labels/Spur/04_spur_06.txt' 文件的绝对路径
dstfile: '/home/wsd/***/yolov5/data/PCB_DATASET/train/labels' 文件夹
Returns:
'''
if not os.path.isfile(srcfile):
print("%s not exist!" % (srcfile))
else:
src_fpath, src_fname = os.path.split(srcfile) # 分离文件名和路径
if not os.path.exists(dstfolder):
os.makedirs(dstfolder) # 创建路径dst_file
dst_file = os.path.join(dstfolder, src_fname)
shutil.copyfile(srcfile, dst_file) # 复制文件
print("copy %s -> %s" % (srcfile, dst_file))
return dst_file
class cocoJsaon(object):
'''
coco 的json 的文件格式类
'''
def __init__(self, categories):
self.info = {
'description': 'PCB DATASET',
'url': 'DLH',
'version': '1.0',
'year': 2021,
'contributor': 'DLHgroup',
'date_created': '2021-01-12 16:11:52.357475'
}
self.license = {
"url": "none",
"id": 1,
"name": "Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License"}
self.images = None
self.annotations = None
self.category = categories
self.cocoJasonDict = {
"info": self.info, "images": self.images, "annotations": self.annotations,
"licenses": self.license, 'categories': self.category}
def getDict(self):
'''
Returns: 返回 格式的字典化
'''
self.cocoJasonDict = {
"info": self.info, "images": self.images, "annotations": self.annotations,
"licenses": self.license, 'categories': self.category}
return self.cocoJasonDict
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 文件原本:
'''
root: /home/dlh/opt/***/PCB_DATASET
------------------->labels/ # 原本的所有目标检测框的 *.txt
------------------->images/ # *.jpg 所有的图片
------------------->ImageSets/ # train.txt 和 val.txt
------------------->annotations / 存放 labels 下所有对应的train.json
最终:
root: /home/dlh/opt/***/PCB_DATASET/PCB
------------------->images/ # *.jpg 所有的图片
------------------->annotations / instances_train_set_name.json # 存放 labels 下所有对应的train.json
/ instances_val_set_name.json # 存放 labels val.json
'''
# 写入的train 还是Val
wrtie_str = 'train'
train_path = '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/training/'
# 存放 train.txt 和 val.txt 的绝对地址 (修改)
Imageset = '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/ImageSets/' + wrtie_str + '.txt'
# 存放 即将所有的原本图片 保存到 该地址 临时 (修改)
tarset = '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/training/image_2/' + wrtie_str + '_set_name'
# 下面是更改 json 文件 的
tempDir = Imageset.replace('txt', 'json')
tempDir = tempDir.replace('ImageSets', 'annotations')
jsonFile = tempDir.replace(wrtie_str, 'instances_' + wrtie_str + '_set_name')
jasonDir, _ = os.path.split(jsonFile)
# 告诉你 最新的Jason 文件保存到了那里
print(f'jsonFile saved {
jsonFile}')
# 检查目标文件夹是否存在
if not os.path.exists(tarset):
os.makedirs(tarset)
if not os.path.exists(jasonDir):
os.makedirs(jasonDir)
# images 段 的字典模板
images = {
"license": 3,
"file_name": "COCO_val2014_000000391895.jpg",
"coco_url": "",
"height": 360, "width": 640, "date_captured": "2013-11-14 11:18:45",
"id": 0}
# annotation 段 的字典模板
an = {
"segmentation": [],
"iscrowd": 0,
"keypoints": 0,
"area": 10.0,
"image_id": 0, "bbox": [], "category_id": 0,
"id": 0}
# categories 段 的字典模板
cate_ = {
'id': 0,
'name': 'a',
}
# 用来保存目标类的 字典
cate_list = []
# 你的目标类有几个 (修改)
className = ['Pedestrian', 'Car', 'Cyclist', 'DontCare']
carName = ['Car', 'Van', 'Truck', 'Tram'] # 车的类型,最终会归一成car
personName = ['Pedestrian', 'Person_sitting'] # 人员类型,最终归一为Pedestrian
dontCare = ['Misc', 'DontCare'] # 杂物,归一为DontCare
temId = 0
for idName in className:
tempCate = cate_.copy()
tempCate['id'] = temId
temId += 1
tempCate['name'] = idName
cate_list.append(tempCate)
# print(cate_list)
# 创建coco json 的类 实例
js = cocoJsaon(cate_list)
image_lsit = []
annoation_list = []
# 打开 train。txt
with open(Imageset, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
# print(f'imageset lines:{lines}')
img_id = 0
bbox_id = 0
# 按值去打开图片
for path in lines:
# 我的train.txt 是按照绝对路径保存的,各位需要的根据自己的实际情况来修改这里的代码
# 去出 \n 之类的空格
path = path.lstrip().rstrip()
# 得到图像文件路径
img_path = train_path + 'image_2/' + path + '.png'
# print(f'path:{path}')
# 打开图片
image = cv2.imread(img_path)
# 将这个图片副知道新的文件夹 (以实际情况 修改)
copyFile2Folder(img_path, tarset)
# 得到宽高
(height, width) = image.shape[:2]
# (height, width) = 375, 1242
# 得到文件名子
_, fname = os.path.split(img_path)
# print(f'_ and name:{_, fname}')
# 图像对应的txt 文件路径
txtPath = train_path + 'label_2/' + path + '.txt'
# print(f'txtPath:{txtPath}')
# 复制images 的字典的复制
image_temp = images.copy()
image_temp['file_name'] = fname
image_temp['height'] = height
image_temp['width'] = width
image_temp['id'] = img_id
# 将其放入到集合中
image_lsit.append(image_temp)
# 打开图片的对应的txt 目标文件的txt
# print(f'txt path:{txtPath}')
with open(txtPath, 'r') as re:
txtlines = re.readlines()
for txtline in txtlines:
# 去出 \n 之类的空格
temp = txtline.rstrip().lstrip().split(' ')
# print(f'temp:{temp}')
# 分别的到 目标的类 中心值 xy 和 该检测框的宽高
if temp[0] in carName:
classid = className.index('Car')
elif temp[0] in personName:
classid = className.index('Pedestrian')
elif temp[0] in dontCare:
classid = className.index('DontCare')
else:
classid = className.index('Cyclist')
# classid = className.index(temp[0]) # 获取id
# 计算宽高及中心
w = float(temp[6]) - float(temp[4])
h = float(temp[7]) - float(temp[5])
x = (float(temp[6]) + float(temp[4]))/2
y = (float(temp[7]) + float(temp[5]))/2
iscrowd = int(temp[2])
# 判断是否遮挡
if iscrowd != 0:
iscrowd = 1
# 计算面积
area = w * h
# 复制annotation 的字典
temp_an['area'] = area
temp_an = an.copy()
temp_an['image_id'] = img_id
temp_an['bbox'] = [x, y, w, h]
temp_an['iscrowd'] = iscrowd
temp_an['category_id'] = classid
temp_an['id'] = bbox_id
bbox_id += 1 # 这个是 这个annotations 的id 因为一个图像可能对应多个 目标的id
annoation_list.append(temp_an)
# 图像的id
img_id += 1
# print(js.getDict())
# print('***********************************************************************\n\n')
# 将json 的实例 中images 赋值
js.images = image_lsit
# 将json 的实例 annotations 赋值
js.annotations = annoation_list
# 写入文件
json_str = json.dumps(js.getDict())
with open(jsonFile, 'w+') as ww:
ww.write(json_str)
print('finished')
For the above code, you only need to change the sum at the beginning of the main function wrtie_str. train_pathThe code is not difficult to understand.
2. Modify the configuration file of DAMO-YOLO
- Modify
damo/config/paths_catalog.py, modify the related paths ofcoco_2017_trainandcoco_2017_val
# Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
# Copyright (C) Alibaba Group Holding Limited. All rights reserved.
"""Centralized catalog of paths."""
import os
class DatasetCatalog(object):
DATA_DIR = 'datasets'
DATASETS = {
'coco_2017_train': {
'img_dir': '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/training/image_2',
'ann_file': '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/annotations/instances_train_set_name.json' # 第一步生成的json文件
},
'coco_2017_val': {
'img_dir': '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/training/image_2',
'ann_file': '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/annotations/instances_val_set_name.json'
},
'coco_2017_test_dev': {
'img_dir': '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/training/image_2',
'ann_file': '/home/wistful/Datasets/KITTI/annotations/instances_val_set_name.json'
},
}
@staticmethod
def get(name):
if 'coco' in name:
data_dir = DatasetCatalog.DATA_DIR
attrs = DatasetCatalog.DATASETS[name]
args = dict(
root=os.path.join(data_dir, attrs['img_dir']),
ann_file=os.path.join(data_dir, attrs['ann_file']),
)
return dict(
factory='COCODataset',
args=args,
)
else:
raise RuntimeError('Only support coco format now!')
return None
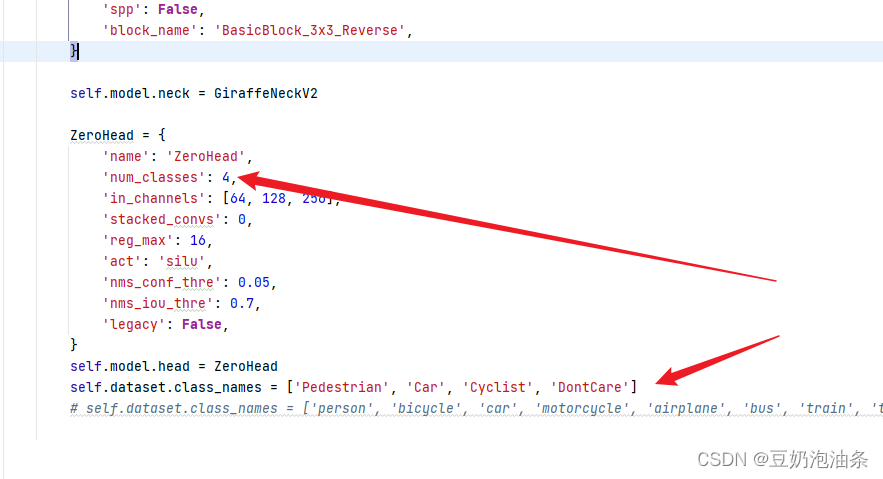
- Modify the configuration file
ZeroHeadandself.dataset.class_names
- Importing pre-training weights and modifying the number of training rounds are available in the official GitHub repository, so I won’t introduce them here.
3.Training
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=2 tools/train.py -f configs/damoyolo_tinynasL20_T.py
2 refers to the number of gpu, -f is followed by the configuration file