1. Brief description
Commercial password
Commercial encryption is the general name for a series of encryption technologies and encryption products used by the government of the People's Republic of China to protect non-state confidential information. The related technologies are state secrets . The research, development and use of commercial cryptography are under the unified management of the State Cryptozoology Administration .
National secret algorithm
The national secret algorithm refers to the cryptographic algorithm standard independently designed and used by China. Its purpose is to protect information security and national interests. At present, the national secret algorithm includes the following major cryptographic algorithms:
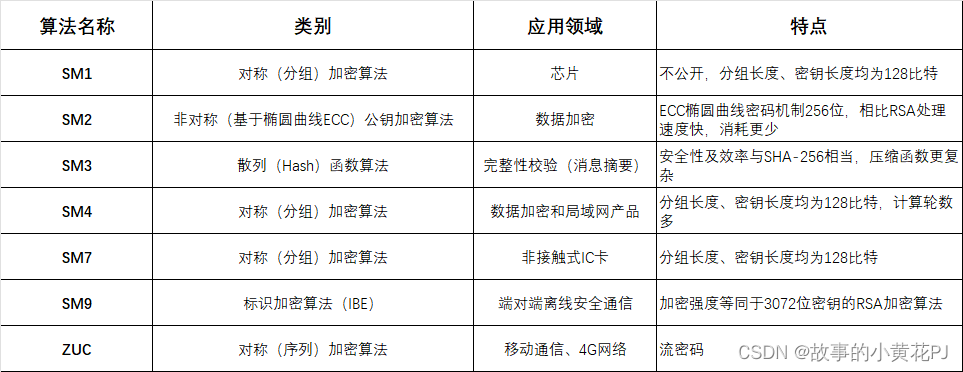
2. SM1 block encryption algorithm
SM1 is a block encryption algorithm, symmetric encryption, the block length and key length are both 128 bits. Therefore, when encrypting and decrypting messages, if the message length is too long, it needs to be grouped, and if the message length is not enough, it needs to be padded. The security and confidentiality strength of the algorithm and the implementation performance of related software and hardware are equivalent to AES. The algorithm is not public and only exists in the chip in the form of IP core. When calling the algorithm, it needs to be called through the interface of the encryption chip. Already developed using this algorithm A series of security products such as chips, smart IC cards, smart password keys, encryption cards, and encryption machines are widely used in various application fields of e-government, e-commerce, and the national economy (including important fields such as national government affairs and police communications).
3. SM2 Elliptic Curve Public Key Encryption Algorithm
SM2 is an elliptic curve public key cryptography algorithm released by the State Cryptography Administration on December 17, 2010.
This algorithm is an asymmetric key algorithm based on the ECC algorithm. Its encryption strength is 256 bits. Its security has obvious advantages compared with the currently used RSA1024.

The SM2 algorithm and the RSA algorithm are both public key cryptography algorithms. The SM2 algorithm is a more advanced and secure algorithm and is used to replace the RSA algorithm in our country's commercial cryptography system .
With the development of cryptography and computer technology, the currently commonly used 1024-bit RSA algorithm faces serious security threats. After research, our national cryptography management department decided to use the SM2 elliptic curve algorithm to replace the RSA algorithm .
Comparison between SM2 algorithm and RSA algorithm
SM2 has better performance and security: high password complexity, fast processing speed, and smaller machine performance consumption.
| SM2 |
RSA | |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm structure |
Elementary Elliptic Curve (ECC) |
Based on special reversible modular exponentiation operation |
| Computational complexity |
Completely exponential |
sub-exponential |
| storage |
192-256bit |
2048-4096bit |
| Key generation speed |
More than a hundred times faster than the RSA algorithm |
slow |
| Decryption encryption speed |
faster |
generally |
4. SM3 hash algorithm
SM3 is a cryptographic hash function standard adopted by the country and was released by the State Cryptozoological Administration on December 17, 2010. The relevant standard is "GM/T 0004-2012 "SM3 Cryptographic Hash Algorithm".
This algorithm is also called cryptographic hash algorithm, which is a type of hash (digest) algorithm. The hash value is 256 bits and was announced together with the SM2 algorithm. The function is the same as MD5, SHA-1. Produces a 256-bit encoding. This algorithm is an irreversible algorithm. The specific algorithm is also confidential.
In commercial cryptography systems, SM3 is mainly used for digital signatures and verification, message authentication code generation and verification, random number generation, etc. Its algorithm is public. According to the State Cryptozoology Administration, its security and efficiency are equivalent to SHA-256.
cryptographic hash function
Cryptographic hash function (English: Cryptographic hash function), also translated as cryptographic hash function , cryptographic hash function , is a type of hash function . It is considered a one-way function , which means that it is extremely difficult to deduce the result output by the hash function back to what the input data was. Such one-way functions are known as the "work horses of modern cryptography". The input data of this hash function is often called a message , and its output is often called a message digest or digest .
In information security , there are many important applications that use cryptographic hash functions, such as digital signatures and message authentication codes .
characteristic
An ideal cryptographic hash function should have four main properties:
-
For any given message, it is easy to calculate the hash value.
-
It is difficult to deduce the original message from a known hash value.
-
It is not feasible to modify the message content without changing the hash value.
-
It cannot give the same hash value to two different messages.
5. SM4 block encryption algorithm
SM4.0 (formerly known as SMS4.0) is a block cipher standard adopted by the country and was released by the State Cryptozoology Administration on March 21, 2012. The relevant standard is "GM/T 0002-2012 "SM4 Block Cipher Algorithm" (formerly SMS4 Block Cipher Algorithm)".
This algorithm is a symmetric encryption algorithm, which was announced together with the WAPI standard, and its encryption strength is 128 bits. This algorithm is a grouping algorithm used in wireless LAN products. The block length of this algorithm is 128 bits, and the key length is 128 bits. Both the encryption algorithm and the key expansion algorithm adopt a 32-round nonlinear iteration structure. The decryption algorithm has the same structure as the encryption algorithm, except that the round keys are used in the opposite order. The decryption round key is the reverse order of the encryption round key.
In the commercial cryptography system, SM4 is mainly used for data encryption . Its algorithm is public. The block length and key length are both 128 bits. Both the encryption algorithm and the key expansion algorithm adopt a 32-round nonlinear iteration structure. The S box is fixed at 8 bits. Input 8-bit output.
The instruction length in SM4.0 has been increased to a level greater than 64K (i.e. 64×1024), which is 128 times the SM 3.0 specification (the rendering instruction length is allowed to be greater than 512).
Related concepts
In cryptography , block cipher (English: Block cipher ), also known as block cipher or block cipher , is a symmetric key algorithm. It divides the plaintext into multiple equal-length modules (blocks), and uses a certain algorithm and symmetric key to encrypt and decrypt each group separately. Block encryption is an extremely important encryption protocol. Typical ones such as DES and AES are standard encryption algorithms approved by the US government, and their applications range from email encryption to bank transaction transfers.
6. SM7 block encryption algorithm
SM7 algorithm is a block cipher algorithm with a block length of 128 bits and a key length of 128 bits. SM7 is suitable for contactless IC cards. Its applications include identity recognition applications (access control cards, work passes, participation passes), ticketing applications (tickets for large events, exhibition tickets), payment and card applications (points consumption cards, campus cards). , enterprise card, etc.).
Features
Security features of SM7 national secret algorithm
1. True random number generator
2. Use SM7 national secret algorithm to encrypt and protect the security of data interaction.
3. Adopt SM7 national secret algorithm triple mutual security authentication mechanism
4. It has 8 independent 128-bit passwords and supports one card, one password and one card for multiple purposes.
5. Each card has a 4-byte unique serial number
application
SM7 is suitable for contactless IC card applications, including identity recognition applications (access control cards, work passes, participation passes), ticketing applications (tickets for large events, exhibition tickets), payment and card applications (point consumption cards, campus cards, enterprise cards) All-in-one card, all-in-one bus card).
7. SM9 logo encryption algorithm
SM9 is an identification password standard adopted by the country. It was released by the State Cryptography Administration on March 28, 2016. The relevant standard is "GM/T 0044-2016 SM9 identification password algorithm".
SM9 is a pair-based identity encryption algorithm, similar to SM2, including four parts: general principles, digital signature algorithm, key exchange protocol, key encapsulation mechanism and public key encryption algorithm. In these algorithms, the pair on the elliptic curve is used, which is different from the SM2 algorithm in the traditional sense. It can realize the identity-based cryptosystem, that is, the public key is related to the user's identity information, that is, the identity, so that it is more complex than the traditional SM2 algorithm. The public key cryptography system has many advantages, eliminating the need for certificate management, etc.
The bilinear property of bilinear pairing is based on the identification cipher of the pair. The general rules in SM2 are also applicable to SM9, because the relevant theory and implementation basis applicable to pairs are added in the general rules of SM9.
In commercial cryptography systems, SM9 is mainly used for user identity authentication. According to a public report by Xinhuanet, the encryption strength of SM9 is equivalent to the RSA encryption algorithm with a 3072-bit key .
8. ZUC Zu Chong’s Algorithm
ZUC is a stream cipher algorithm, symmetric encryption. This confidentiality algorithm can be applied to encryption and decryption in 3GPP LTE communication. The algorithm includes Zu Chongzhi algorithm (ZUC), confidentiality algorithm (128-EEA3) and integrity algorithm (128-EIA3 ) three parts. It has been recommended by the international organization 3GPP as a candidate algorithm for the third set of international encryption and integrity standards for 4G wireless communications.
It is understood that at the 53rd 3GPP System Architecture Group Meeting held in Fukuoka, Japan , China's Zu Chongzhi Cryptographic Algorithm (ZUC) was approved as an international standard for a new generation of broadband wireless mobile communication system (LTE). The name of Zu Chongzhi's encryption algorithm comes from Zu Chongzhi, an ancient Chinese mathematician. Zu Chongzhi's algorithm set is an encryption and integrity algorithm independently designed by Chinese scholars. It is a stream cipher. It is the core of two new LTE algorithms, encryption algorithm 128-EEA3 and integrity algorithm 128-EIA3. The ZUC algorithm consists of three basic parts, in order: 1. Bit reorganization; 2. Nonlinear function F; 3. Linear feedback shift register (LFSR).
Relevant people believe that ZUC's becoming an international standard has improved my country's status and influence in the field of mobile communications, and has great and far-reaching significance for the development of my country's mobile communications industry and commercial encryption industry.
It is reported that Zu Chongzhi's encryption algorithm is the first time that my country's commercial encryption algorithm has gone abroad to participate in the international standard competition, which has expanded the scope of public evaluation of Zu Chongzhi's algorithm.
9. Comparison of Several Algorithms
Symmetric/reversible
| algorithm name | Is it reversible? | Is it symmetrical? |
|---|---|---|
| SM2 | reversible | asymmetric |
| SM2 signature | irreversible | symmetry |
| SM3 signature | irreversible | - |
| SM4 | reversible | symmetry |
| SM9 | reversible | symmetry |
| SM9 signature | irreversible | - |
Key length
| algorithm name | Key length |
|---|---|
| SM2 | 256 bits (64-bit hexadecimal number) |
| SM2 signature | 256 bits (64-bit hexadecimal number) |
| SM3 signature | - |
| SM4 | 128 bits (32-bit hexadecimal number) |
| SM9 | not limited |
| SM9 signature | not limited |
Plain/ciphertext length
| algorithm name | algorithm pattern | Whether to make up (isPadding) | length relationship |
|---|---|---|---|
| SM2 reversible | - | - | M=(m-1)/3*8+202 |
| SM2 signature | - | - | M=140/142/144 |
| SM3 signature | - | - | M=64 |
| SM4 | ECB | yes | When m<10, M=32; when m>=10, M=[(m-10)/12+2]*32 |
| SM4 | ECB | no | M=[(m-1)/12+1]*32 |
| SM4 | CBC | - | When m<10, M=32; when m>=10, M=[(m-10)/12+2]*32 |
Algorithm mode column: -indicates no correlation
. Complementary column: -indicates no such parameter.
Length relationship column: Mindicates 密文长度, mindicates明文长度
advantage analysis
As the recommended encryption algorithm, the National Secret Algorithm has its own advantages compared with other algorithms:
Compared with RSA, SM2 has a higher password strength. Since the SM2 algorithm is based on the logarithm problem of discrete point groups on the elliptic curve, the 256-bit SM2 password strength is already higher than the 2048-bit RSA password strength;
Compared with MD5 and SHA-1, SM3 produces a different hash value length. The output length of SM3 is 256 bits, MD5 is 128 bits, and SHA-1 is 160 bits. As a hash algorithm, the higher the hash value, the higher the security. Therefore, the SM3 algorithm is more secure than the MD5 algorithm and SHA-1 algorithm;
Compared with 3DES, SM4 and AES have the same key length (when the AES key length is 128 bits) and packet length, so SM4 security is significantly higher than 3DES.