Django learning record: a preliminary understanding of django and the realization of the front-end and back-end development of a simple web login page
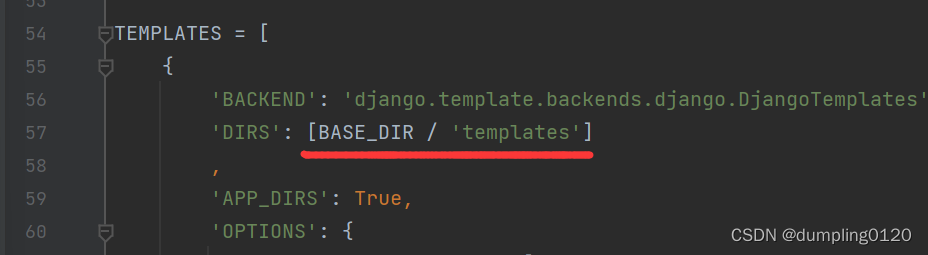
1. You can delete the template folder first, and delete this line in the setting
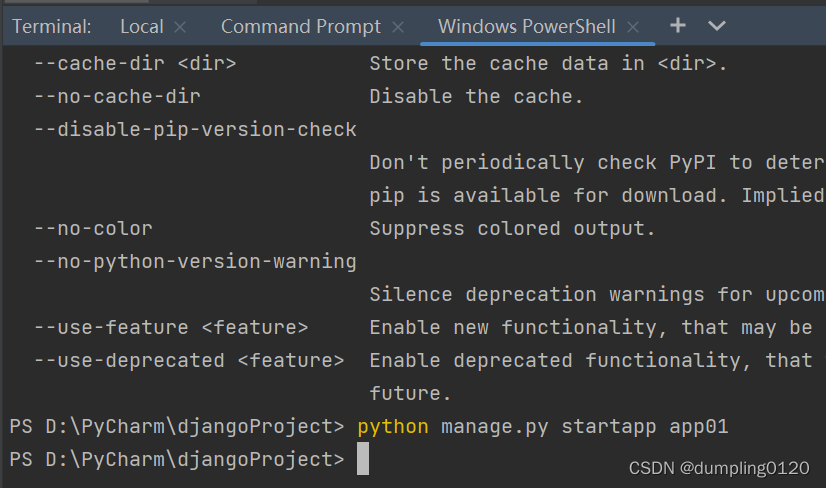
2. Create app in pycharm:
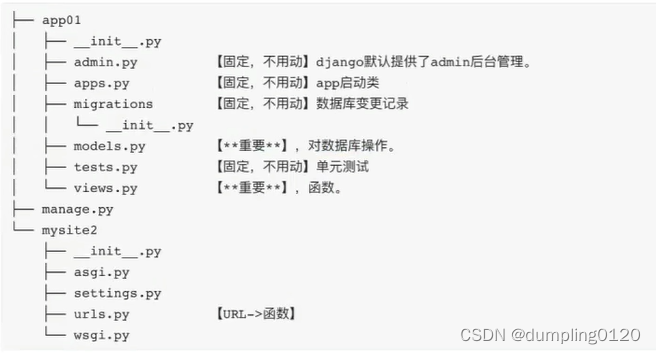
3. Start the app: Write the relationship between the URL and the view function [urls.py]
Writing view functions [views.py]
Start the pycharm project
4. Reference static files
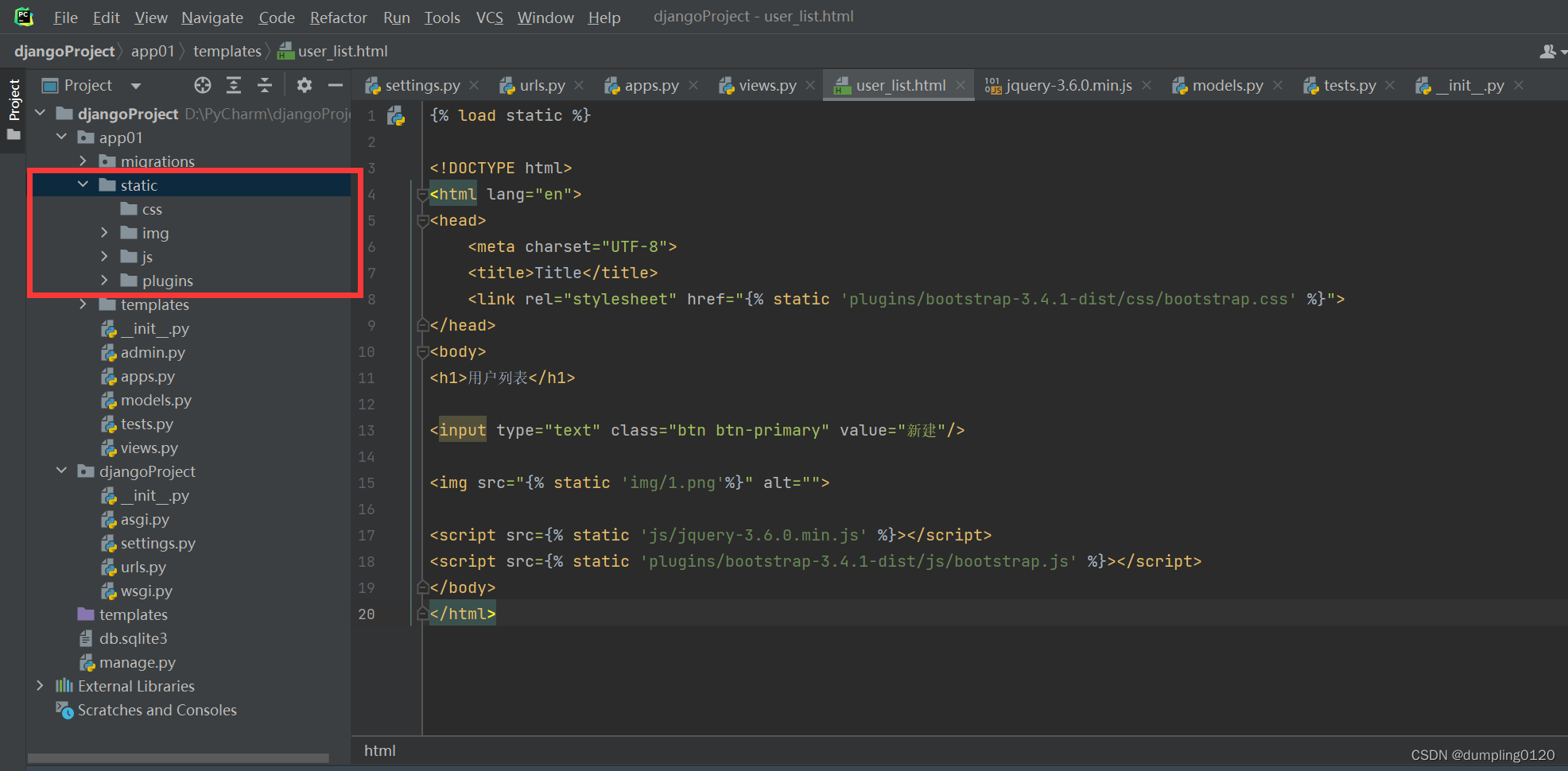
There are two imports of files: (jquery and bootstrap)
jquery: https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js can be copied directly to create a notepad, save it and change it to a js file to use.
bootstrap: https://v3.bootcss.com/getting-started/#download can be downloaded directly from this website, but the download end is on github. (You can also send me a private message if necessary)
template syntax
Inside the render function of the view function:
1. Read HTML files containing template syntax
2. Render internally (template syntax execution and replace data), and finally get a string containing only HTML tags.
3. Return the string that renders (replaces) the Great Wall to the user's browser
Code under views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
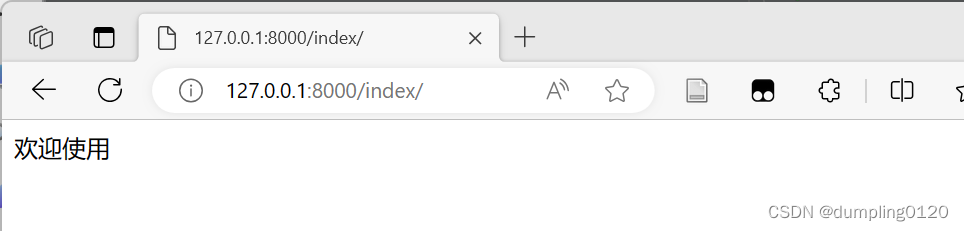
def index(request):
return HttpResponse("欢迎使用")
def user_list(request):
# 1.如果未删除默认setting中dirs那行代码,则有限去项目根目录的templates中寻找(提前先配置)【不配置就是无效】
# 2.根据app的注册顺序,在每个app下的templates目录中寻找【更改设置后】
return render(request, "user_list.html")
def user_add(request):
return render(request, "user_add.html")
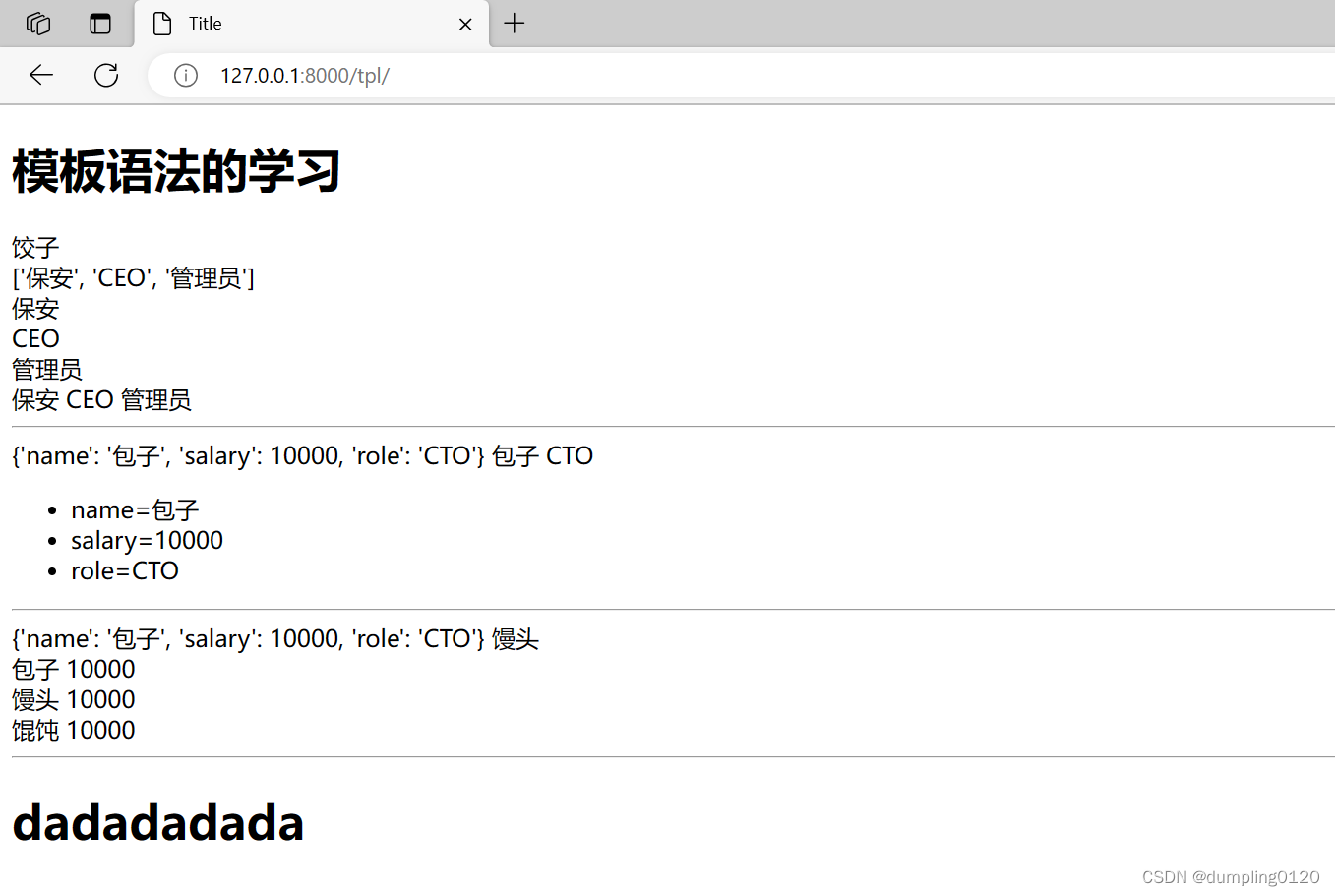
def tpl(request):
name = "饺子"
# 列表,元组与列表相同
role =["保安","CEO","管理员"]
# 字典
user_info={
"name":"包子","salary":10000,"role":"CTO"}
data_list=[
{
"name": "包子", "salary": 10000, "role": "CTO"},
{
"name": "馒头", "salary": 10000, "role": "CTO"},
{
"name": "馄饨", "salary": 10000, "role": "CTO"},
]
return render(request, "tpl.html", {
"n1":name, "n2":role,"n3":user_info,"n4":data_list})
Code under tpl.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>模板语法的学习</h1>
<div>{
{ n1 }}</div>
<div>{
{ n2 }}</div>
<div>{
{ n2.0 }}</div>
<div>{
{ n2.1 }}</div>
<div>{
{ n2.2 }}</div>
<div>
{% for item in n2 %}
<span>{
{ item }}</span>
{% endfor %}
</div>
<hr/>
{
{ n3 }}
{
{ n3.name }}
{
{ n3.role }}
<ul>
{% for k,v in n3.items %}
<li>{
{ k }}={
{ v }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<hr/>
{
{ n4.0 }}
{
{ n4.1.name }}
{% for item in n4 %}
<div>{
{ item.name }} {
{ item.salary }}</div>
{% endfor %}
<hr/>
{% if n1 == "饺子" %}
<h1>dadadadada</h1>
{% else %}
<h1>dududududu</h1>
{% endif %}
</body>
</html>
The web page displays:
request and response
def sth(request):
# request是一个对象,封装了用户发送过来的所有请求相关数据
# 1.获取请求方式 GET/POST
print(request.method)
# 2.在URL上传递值(即在网址后面添加:/sth/?n1=123&n2=999,则会传回n1,n2对应的值)
print(request.GET)
# 3.在请求体中提交数据
print(request.POST)
# 4. (响应)HttpResponse("返回内容"),内容字符串内容返回给请求者
# return HttpResponse("返回内容")
# 5.(响应)读取HTML的内容 + 渲染(替换) —> 字符串,返回给用户浏览器
# return render(request,'sth.html',{"title":"来了"})
# 6.(响应)让浏览器重定向到其他的页面
return redirect("http://www.baidu.com")
Writing the login interface
def login(requset):
if requset.method == "GET":
return render(requset, "login.html")
# 如果是POST请求,获取用户提交的数据
# print(requset.POST)
username = requset.POST.get("user")
password = requset.POST.get("pwd")
if username == 'root' and password == "123":
# return HttpResponse("登陆成功")
return redirect("https://www.bbac.com.cn/cn/")
# 可删去else,以省略嵌套。
else:
# return HttpResponse("登陆失败")
return render(requset, 'login.html', {
"error_msg": "用户名或密码错误"})
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>用户登录</h1>
<form method="post" action = "/login/">
{% csrf_token %}
<input type = "text" name = "user" placeholder="用户名">
<input type = "password" name = "pwd" placeholder="密码">
<input type = "submit" value="提交">
<span style="color:red;"> {
{ error_msg }}</span>
</form>
</body>
</html>
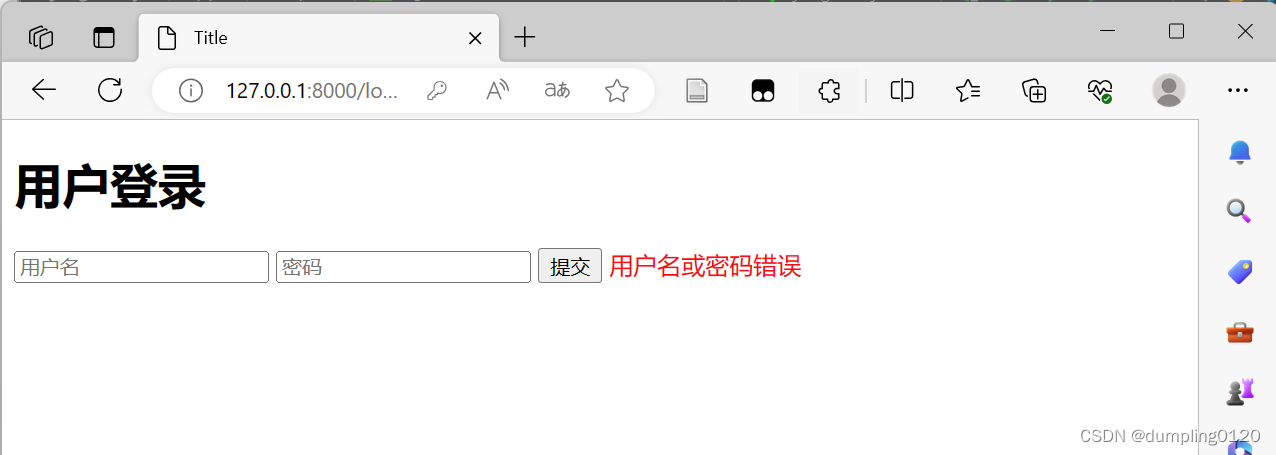
If the login fails: the interface is as follows; if the login is successful, the page will be redirected.
Course source:
The most detailed django3 tutorial at station B in 2022 (django from entry to practice)