Hello, this is the Network Technology Alliance site.
In today's digital world, cloud computing has become the preferred way for enterprises and organizations to process data and deploy applications. The four main forms of cloud computing—public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and multicloud—each have their own characteristics and advantages. This article will analyze these four forms of cloud computing in detail to help readers understand their concepts and their respective applicable scenarios.

Article directory
public cloud
Public cloud is the most common form of cloud computing. In a public cloud, third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure make the hardware, software, and supporting infrastructure available to users over the Internet.
Diversity of public cloud providers
Alibaba Cloud, AWS, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud and Microsoft Azure are currently the largest public cloud providers, providing a wide range of cloud services around the world. These providers have a strong presence in different geographies and sectors, each with a unique set of features and benefits to meet a variety of customer needs.
On-premises public cloud
General public cloud providers have begun to provide cloud services in customers' on-premises data centers. This model is often referred to as "private cloud in public cloud" or "cloud edge computing". This approach enables organizations to run cloud workloads on their on-premises infrastructure while still benefiting from the elasticity and services of the public cloud.
Cloud partitioning and tenant isolation
Ensuring partitioning and tenant isolation of cloud environments is critical to the security of public clouds. This ensures that resources and data between different tenants do not interfere with each other. This is a key responsibility of public cloud providers to ensure the privacy and security of customer data.
Billing structure diversity
Public cloud providers have begun to offer more flexible billing models to meet the needs of different customers. This includes pay-as-you-go, subscription models, stored-value cards, and free tiers, among others. This variety helps customers choose the billing method that works best for them based on their budget and usage.
IT infrastructure abstraction
Public cloud providers have abstracted the underlying IT infrastructure and offered it as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) or Platform as a Service (PaaS). This allows developers to focus more on application development without having to worry about the management of hardware and underlying infrastructure.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantages of this model are:
- No large initial investment is required. Users only need to pay according to actual usage, which greatly reduces the initial cost.
- There is no need to maintain and upgrade hardware and software, and users can focus on their core business.
- Usage can be easily scaled up or down to meet changes in business needs.
However, public clouds also have some disadvantages. For example, data security and privacy may not be as high as private clouds, and if users use a large amount of resources, they may be more expensive in the long run.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a cloud environment customized specifically for a single organization or enterprise. It can be deployed in an organization's internal data center or hosted by a third-party provider.
Location and ownership are no longer defining criteria
Today's private clouds no longer have to rely on on-premises IT infrastructure. Enterprises can choose to build a private cloud in a leased, vendor-owned external data center, a model often referred to as an "external private cloud." This trend allows organizations to more flexibly deploy and manage private cloud environments without bearing the full cost of hardware and facilities.
Subcategories of Private Cloud
Private cloud encompasses several subcategories, including hosted private cloud and dedicated cloud. Managed private clouds are private clouds that are deployed, configured, and managed by a third-party provider and are suitable for businesses that may be short-staffed or under-skilled. A private cloud is a private cloud environment deployed on a public cloud or private cloud for a specific department or user group. These different subcategories allow organizations to choose the appropriate private cloud model based on their needs and resources.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantages of private cloud are:
- High level of security and control. Organizations can control their hardware, software and network environments to better protect sensitive data.
- Can be customized to meet an organization's specific needs.
However, the disadvantage of a private cloud is that it requires more initial investment, as well as ongoing maintenance and management costs.
hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud combines the characteristics of public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to flow between the two.

The Variety of Hybrid Clouds
Hybrid cloud can be composed of a variety of environments, including private cloud, public cloud, LAN, WAN, VPN, etc. These different components can work together in a unified IT environment that looks like a single environment but actually covers multiple different resources and connections.
How to Build a Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds can be built in many ways, one of which is connecting at least one private cloud with at least one public cloud. It is also possible to build a hybrid cloud with multiple interconnected private clouds or multiple public clouds. This diversity allows organizations to create custom hybrid cloud environments based on their specific needs and resources.
Environment portability
A key feature of hybrid cloud is the portability of its environment. This means applications can be easily moved between different cloud environments without the need for massive refactoring. This flexibility enables organizations to better respond to changing needs and conditions.
Integration and Management
To effectively manage hybrid cloud environments, organizations often need to use an integrated management and orchestration platform. These tools allow different cloud environments to be managed and monitored as a single environment, simplifying operations and maintenance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantages of this model are:
- Flexibility: Workloads can be moved as needed to the environment that best suits them.
- Keep sensitive data secure while enjoying the flexibility and scalability of the public cloud.
The challenge with hybrid cloud is the complex data management and integration required between the two cloud environments.
partly cloudy
Multicloud is a strategy that uses two or more public clouds, typically to avoid reliance on a single vendor or to meet specific business needs.
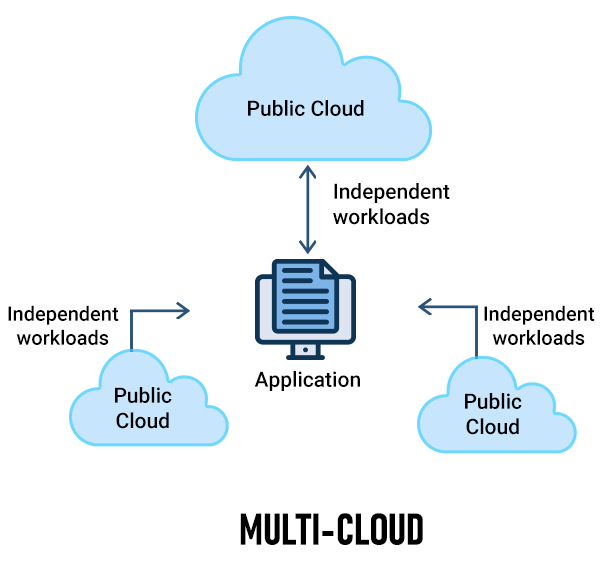
The relationship between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud
Multi-cloud is a broader concept that refers to leveraging cloud services from multiple cloud providers to build a combined cloud environment. These cloud services can include public, private, or hybrid clouds. Hybrid cloud is a subset of multi-cloud, typically consisting of private and public clouds, with unified management of resources through integration or orchestration.
multi-cloud uses
Multi-cloud environments can serve different purposes, including improving security, performance and disaster recovery. For example, organizations may choose to use multiple cloud providers to better spread risk, or use different cloud environments to store sensitive data to increase security.
Shadow IT and multi-cloud
Shadow IT refers to the procurement and use of cloud services by internal departments or individuals within an organization without approval from the IT department. The emergence of a multi-cloud environment may be due to different departments or individuals choosing different cloud providers, resulting in the emergence of multi-cloud situations.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantages of multi-cloud are:
- Avoid vendor lock-in and choose the cloud provider that's best suited for your specific workloads.
- You can take advantage of different cloud service providers.
The challenge with multi-cloud is the need to manage multiple vendor relationships and manage data across different cloud environments.
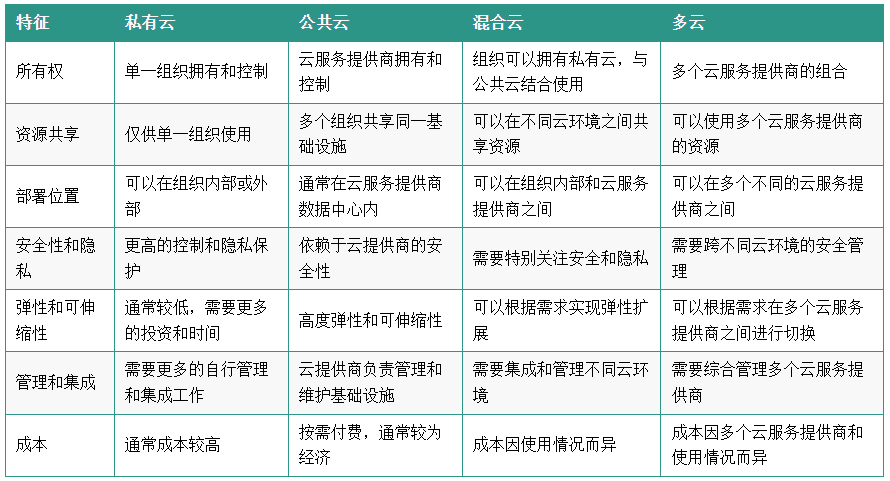
The difference between private cloud, public cloud, hybrid cloud and multi-cloud
| feature | Private Cloud | public cloud | hybrid cloud | partly cloudy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ownership | Owned and controlled by a single organization | Cloud service provider owned and controlled | Organizations can have private clouds, combined with public clouds | A combination of multiple cloud service providers |
| Resource Sharing | For use by a single organization only | Multiple organizations share the same infrastructure | Resources can be shared between different cloud environments | Can use resources from multiple cloud service providers |
| Deployment location | Can be internal or external to the organization | Typically within a cloud service provider data center | Can be used within an organization and between cloud service providers | Can be used across multiple different cloud service providers |
| Security and privacy | Greater control and privacy protection | Rely on cloud provider for security | Special attention needs to be paid to security and privacy | Requires security management across different cloud environments |
| Elasticity and scalability | Usually lower and requires more investment and time | Highly elastic and scalable | Elastic expansion can be achieved according to needs | Can switch between multiple cloud service providers as needed |
| Management and integration | Requires more self-management and integration work | The cloud provider manages and maintains the infrastructure | Need to integrate and manage different cloud environments | Requires comprehensive management of multiple cloud service providers |
| cost | Usually more costly | Pay as you go, often economical | Cost varies by usage | Costs vary across multiple cloud providers and usage |
How to Choose the Appropriate Cloud Model
Choosing the appropriate cloud model depends on your organization's specific needs and goals. Here are some considerations:
-
Business needs : First, an organization should understand its business needs, such as performance, availability, security, and compliance requirements. This will help determine which cloud model is best suited to meet these needs.
-
Cost Budget : Cost is an important consideration. If an organization has a limited budget, the public cloud may be an attractive option because it can reduce hardware and facility costs.
-
Security and compliance requirements : If your organization handles sensitive data or needs to meet specific compliance requirements, a private or hybrid cloud may be a better fit as they offer greater control and privacy.
-
Flexibility and scalability : If an organization needs to scale up or down its resources quickly, hybrid or multi-cloud may be a better choice as they offer greater flexibility.
-
Vendor Selection : Organizations should carefully consider the strengths and weaknesses of different cloud providers to determine which provider best suits their needs.
in conclusion
Public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and multi-cloud all have their advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the appropriate model should be based on your organization's specific circumstances and strategic goals. Sometimes, organizations may choose to combine multiple cloud models to meet different needs to achieve the best business results. Whichever cloud model is chosen, careful planning, management, and monitoring are required to ensure efficient utilization and security of resources.