Information security: principles and applications of authentication technology.
The authentication mechanism is the basic protection measure of network security and the premise of implementing access control. Authentication is the process by which an entity proves its claimed identity to another entity. During the authentication process, the entity that needs to be verified is the claimant, and the entity responsible for checking and confirming the claimant is the verifier.
Authentication generally consists of two parts: Identification and Authentication.
Identification: The identity mark used to represent entity objects (such as personnel, equipment, data, services, applications), to ensure the uniqueness and identifiability of entities, and to have a strong relationship with entities. Identification is generally represented by a name and an identifier (ID).
Authentication: Generally, it is the process of identifying and verifying the attributes claimed by an entity by using relevant digital credentials such as passwords, electronic signatures, digital certificates, tokens, biometrics, and behavioral performance.
Table of contents:
Information security: principles and applications of authentication technology.
Certification overview:
(1) Certification basis:
(2) Certification principle:
Certification type and certification process:
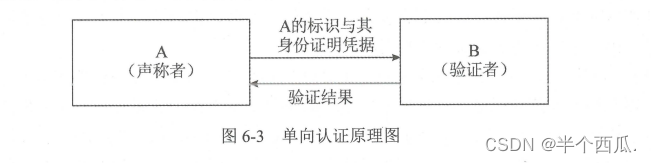
(1) One-way authentication:
(2) Two-way authentication:
(3) Third-party certification:
Certification technical methods:
(1) Password authentication technology:
(2) Smart card technology:
(3) Based on biometric authentication technology:
(4) Kerberos authentication technology:
(5) Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) technology:
(6) Single sign-on:
(7) Basic man-machine identification and authentication technology:
(8) Multi-factor authentication technology:
(9) Identity authentication technology based on thousands of behaviors:
(10) Fast online authentication (FIDO):
Main certified products and technical indicators:
(1) Main certified products:
(2) Main technical indicators:
Certification technology applications:
Certification overview:
(1) Certification basis:
◆ Known secret information: secret information held by the entity (claimant), such as user passwords, verification codes, etc.
◆ Possessed physical certificates: unforgeable physical devices held by the entity (claimant), such as smart cards, U-shields, etc.
◆ Possessed biological characteristics: biological characteristics possessed by the entity (claimant), such as fingerprints, voice, iris, face, etc.
◆ Behavioral characteristics displayed : Behavioral characteristics displayed by the entity (claimant), such as mouse usage habits, keyboard keystroke intensity, geographical location, etc.
(2) Certification principle:
◆ Authentication mechanism: composed of verification object, authentication protocol, and authentication entity .
◆ Verification object: the entity (claimer) that needs to be authenticated.
◆ Authentication protocol: the rules to be followed for authentication information exchange between the verification object and the authentication entity (verifier) . ◆ Authentication entity: according to the authentication basis provided by the verification object , give Judging the authenticity or attributes of identity .
◆ According to the number of types of authentication credentials , authentication can be divided into: single-factor authentication, two-factor authentication, and multi-factor authentication .
◆ According to the length of time used for authentication , authentication can be divided into : one-time password, continuous authentication.
▶ One-time password: OTP for short, used to protect password security and prevent password reuse attacks . A common authentication example for OTP is the use of short message verification codes .
▶ Continuous authentication: refers to the continuous provision of identity confirmation. Its technical principle is to continuously monitor the characteristic behavior of the user throughout the session and continuously verify the characteristics of the user;
The identification factors used in continuous certification are mainly: cognitive factors, physical factors, and contextual factors;
Certification type and certification process:
(1) One-way authentication:
◆ One-way authentication means that during the authentication process, the verifier conducts unilateral identification of the claimant, and the claimant does not need to identify and verify
identity of the witness.
◆ There are two technical methods to achieve one-way authentication : based on shared secret and based on challenge response.

(2) Two-way authentication:
◆ Two-way authentication means that the verifier unilaterally identifies the claimant during the authentication process, and at the same time, the claimant also confirms the
identity of the verifier, and the two entities participating in the authentication are mutually verifiers.
(3) Third-party certification:
◆ Third-party authentication: The two entities are authenticated through a trusted third party during the authentication process . The third party shares the secret with each authenticated entity, with which entity A and entity B respectively share the secret key KPA KPB. When entity A initiates an authentication request, entity A applies to a trusted third party to obtain the key KAB of entity A and entity B, and then entity A and entity B use KAB to encrypt and protect the authentication messages of both parties.


Certification technical methods:
(1) Password authentication technology:
◆ Password authentication: Authentication technology based on secrets known to the user . It is a common identity authentication method on the Internet .
◆ Password authentication: Generally, both parties involved in the authentication are required to follow the pre-agreed rules , the user initiates a service request, and then the user is required to provide the user ID and user password to the service entity , and the service entity verifies its correctness. If the verification passes, the user is allowed to access .
◆ Advantages of password authentication : simple and easy to implement . When a user wants to access the system, the user is required to enter a " username and password "
◆ Shortcomings of password authentication : It is vulnerable to attacks . The main attack methods include eavesdropping, replay, man-in-the-middle attack, password guessing, etc. Therefore, to achieve password authentication security, at least the following conditions should be met:
▶
Password information should be safely encrypted and stored ;
▶
Password information must be transmitted securely ;
▶
The password authentication protocol must resist attacks and comply with security protocol design requirements;
▶
Password selection requires avoiding weak passwords ;
(2) Smart card technology:
◆ Smart card is an integrated circuit card with memory and microprocessor , which can safely store authentication information and has certain computing power .
◆ In challenge/response authentication, the user provides a smart card, which displays a number that changes over time .
(3) Based on biometric authentication technology:
◆ The disadvantage of using passwords for authentication is that the password information is easily leaked, and the smart card may be lost or forged . Biometric authentication uses human biometrics for verification . Currently, biometric information such as fingerprints, faces, retinas, and voices can be used for identity authentication.
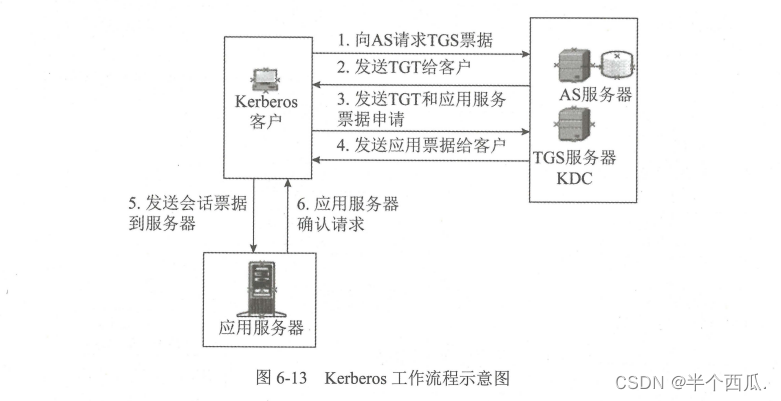
(4) Kerberos authentication technology:
◆ Kerberos is a network authentication protocol whose goal is to provide strong authentication for client/server applications using key encryption.
Authentication.
◆Technical principle: It uses symmetric encryption technology (DES)
◆ Use a trusted third party to provide authentication services for the application server and establish a secure channel between the user and the server.
A Kerberos system involves four basic entities :
▶ Kerberos client , used by users to access server devices;
▶ AS (authentication server) , identifies user identity and provides TGS session key;
▶ TGS (ticket issuance server) , which issues tickets to users who apply for services;
▶ Application server , a device or system that provides services to users;
◆ The Kerberos protocol requires users to undergo double authentication of AS and TGS . There are two main advantages .
▶ It can significantly reduce the exposure times of the ciphertext of the user key , which can reduce the accumulation of the ciphertext of the user key by the attacker.
▶ The Kerberos authentication process has the advantage of single sign-on . As long as the user obtains the TGT and the TGT has not expired, the user can use the TGT to complete the authentication process to any server through TGS without having to re-enter the password.
◆ Kerberos also has shortcomings . The Kerberos authentication system requires solving host node time synchronization issues and resisting denial of service attacks.
(5) Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) technology:
◆ The public key cryptography system can not only realize encryption services, but also provide identification and authentication services. In addition to confidentiality, trusted distribution of public key cryptography is also a problem faced by it, that is, the authenticity and ownership of the public key . To solve this problem, people use the method of "public key certificate" , similar to ID cards and passports.
◆ Public key certificate: Binds an entity to a public key and allows other entities to verify this binding relationship. To this end, a trusted third party is needed to guarantee the identity of the entity. This third party is called a certification authority , referred to as CA (Certification Authority). The CA is responsible for issuing certificates. The certificate contains the entity name, public key and other identity information of the entity .
◆ PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) is the security service facility related to the hardware, software, personnel, policies and processes required to create, manage, store, distribute and revoke public key certificates . PKI provides a systematic, scalable, unified, and easily controlled public key distribution method.
◆ The main security services based on PKI include identity authentication, integrity protection, digital signature, session encryption management, and key recovery. Generally speaking, PKI involves negotiations and operations between multiple entities. The main entities include CA, RA, terminal entities, clients, and directory servers.
◆ The functions of each PKI entity are described as follows:
▶ CA ( Certificate Authority ): mainly for the issuance, revocation and renewal of certificates; the certification authority is responsible for issuing, managing and revoking a group of end-user certificates.
▶ RA ( certificate registration authority ): link the public key with the identity and other attributes of the corresponding certificate holder for registration and guarantee; RA can act as an intermediate entity between the CA and its end users, assisting the CA to complete Most other certificate processing functions.
▶ Directory server: CA usually uses a directory server to provide certificate management and distribution services .
▶ Terminal entity: refers to the object that requires authentication , such as: server, printer, user, etc.
▶ Client: refers to users who need PKI-based security services , including users, service processes, etc.
(6) Single sign-on:
◆ Single sign-on: When a user accesses different systems, he only needs to perform identity authentication once, and he can access authorized resources according to the authentication identity of this login .
(7) Basic man-machine identification and authentication technology:
◆ Based on the human-computer identification authentication, the difficulty of solving problems by computers is used to distinguish between computer and human operations , and to prevent malicious operations of computer programs, such as malicious registration and brute-force guessing of passwords.
(8) Multi-factor authentication technology:
◆ Multi-factor authentication technology uses a variety of identification information to combine to enhance the security strength of authentication.
(9) Identity authentication technology based on thousands of behaviors:
◆ Behavior-based identity authentication is an identity authentication technology based on user behavior and risk level . By analyzing the user's basic information, obtain the user's individual portrait, and then dynamically monitor the user's status to determine the user's identity , and prevent counterfeit user login or key operation errors.
(10) Fast online authentication (FIDO):
◆ FIDO uses standard public key encryption technology to provide strong authentication . FIDO is designed to protect user privacy by not providing information that tracks users, and user biometric information does not leave the user's device.
▶ Registration: The user creates a new public and private key pair . Among them, the private key is retained in the user device , and only the public key is registered to the online service . The public key is sent to the online service and associated with the user's account. The private key and any information about the local authentication method ( such as biometric measurements or templates) never leave the local device.
▶ Login and use: When a user uses FIDO to log in to an online service, the online service prompts the user to log in using a previously registered device.
Main certified products and technical indicators:
(1) Main certified products:
◆ The main product types of authentication technology include: system security enhancement, biometric authentication, electronic authentication service, network access control and identity authentication gateway .
▶
System security enhancement:
The technical feature of system security enhancement products is to use multi-factor authentication technology to enhance
the authentication security strength of operating systems
, database systems, websites, etc. The multi-factor authentication technologies used are usually U
disk + password, smart card + password, biometric information + password, etc. Product application scenarios include U disk login to computer, online banking U- shield authentication, fingerprint login to computer/website/email, etc.
▶
Biometric authentication:
The technical feature of biometric authentication products is to use biological information such as fingerprints, faces, and voices to identify people's identities. The products currently
on the market include smart terminals for verification, fingerprint
disks, face recognition access control, fingerprint collectors, and fingerprint comparison engines.
Automatic face recognition platform.
▶
Electronic certification services:
The technical characteristics of electronic certification service products are that electronic certification service agencies use
PKI
technology
, cryptographic algorithms, etc. Comprehensive services of trusted identity, trusted
time and trusted behavior.
▶
Network access control:
The technical feature of network access control products is to use
authentication related technologies such as
802.lX protocol, Radius protocol, VPN , etc., to link with network switches, routers, security gateways and other equipment to control network access equipment ( Such as hosts, mobile PCs , smartphones, etc.) for identity authentication and security compliance verification to prevent non-security devices from accessing the internal network.
▶
Identity Authentication Gateway:
The technical feature of identity authentication gateway products is to use digital certificates, data synchronization, network service redirection and other technologies to provide centralized and unified authentication services to form an identity authentication center, with single sign-on, security audit and other security services Function.
(2) Main technical indicators:
◆ The evaluation indicators of certified technology products can be divided into three categories , namely safety function requirements , performance requirements and safety assurance requirements . The main technical indicators of certified technology products are as follows:
▶ Cryptographic algorithm support: Authentication technology mainly relies on cryptographic technology. Therefore, the cryptographic algorithm in authentication products is an important factor in security. Common cryptographic algorithm types include DES/3DES, AES, SHA-1, RSA, SM1/SM2/SM3/SM4;
▶ Certification accuracy: the fake recognition rate and authenticity rejection rate of certified products;
▶Number of users supported: The maximum number of users that the certified product can support;
▶ Security assurance level: security assurance measures, safety and reliability, ability to resist attacks, etc. of certified products;
Certification technology applications:
◆ Authentication technology is the basic technology for network security and is widely used in the protection of network information systems . Common application scenarios of authentication technology are as follows:
▶ User authentication: Verify the identity of visitors to network resources and provide support services for network system access authorization.
▶ Information source verification: Verify the authenticity of the sender and receiver of network information to prevent counterfeiting.
▶ Information security protection: Protect the confidentiality and integrity of network information through authentication technology to prevent leakage, tampering, replay or delay.
Study books: Information security engineer tutorial...