foreword
When we want to store the spatial point information in the database in our work, we generally use the following statement to achieve
INSERT INTO `test-point` ( point,text ) VALUES ( st_GeomFromText ( 'POINT(1 1)' ),'第1个点');
update `test-point` set point=st_PointFromText('POINT(5 5)') where id =10;
But it is very troublesome to write new and edited sql statements every time, which does not reflect the convenience of mybatisplus, so you can add GeometryTypeHandler to splice the st_GeomFromText () function into the sql statement when mybatisplus generates new edit statements, which is more Convenient
1. Preparations
- First add dependencies to the project:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.vividsolutions</groupId>
<artifactId>jts</artifactId>
<version>1.13</version>
</dependency>
- Add GeometryTypeHandler to the project
package com.sinosoft.springbootplus.lft.business.dispatch.map.common;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Geometry;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.GeometryFactory;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.PrecisionModel;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.io.*;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.MappedJdbcTypes;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.MappedTypes;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@MappedTypes({
String.class})
@MappedJdbcTypes({
JdbcType.OTHER})
@Slf4j
public class GeometryTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<String> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i, String s, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
try{
//String转Geometry
Geometry geo = new WKTReader(new GeometryFactory(new PrecisionModel())).read(s);
// Geometry转WKB
byte[] geometryBytes = new WKBWriter(2, ByteOrderValues.LITTLE_ENDIAN, false).write(geo);
// 设置SRID为mysql默认的 0
byte[] wkb = new byte[geometryBytes.length+4];
wkb[0] = wkb[1] = wkb[2] = wkb[3] = 0;
System.arraycopy(geometryBytes, 0, wkb, 4, geometryBytes.length);
preparedStatement.setBytes(i,wkb);
}catch (ParseException e){
log.error("坐标转换异常:【{}】",e.getMessage(),e);
}
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, String s){
try(InputStream inputStream = resultSet.getBinaryStream(s)){
Geometry geo = getGeometryFromInputStream(inputStream);
if(geo != null){
return geo.toString();
}
}catch(Exception e){
log.error("坐标转换异常:【{}】",e.getMessage(),e);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, int i){
try(InputStream inputStream = resultSet.getBinaryStream(i)){
Geometry geo = getGeometryFromInputStream(inputStream);
if(geo != null){
return geo.toString();
}
}catch(Exception e){
log.error("坐标转换异常:【{}】",e.getMessage(),e);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
return "";
}
/**
* 流 转 geometry
* */
private Geometry getGeometryFromInputStream(InputStream inputStream) throws Exception {
Geometry dbGeometry = null;
if (inputStream != null) {
// 二进制流转成字节数组
byte[] buffer = new byte[255];
int bytesRead;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((bytesRead = inputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
// 得到字节数组
byte[] geometryAsBytes = baos.toByteArray();
// 字节数组小于5 异常
if (geometryAsBytes.length < 5) {
throw new RuntimeException("坐标异常");
}
//字节数组前4个字节表示srid 去掉
byte[] sridBytes = new byte[4];
System.arraycopy(geometryAsBytes, 0, sridBytes, 0, 4);
boolean bigEndian = (geometryAsBytes[4] == 0x00);
// 解析srid
int srid = 0;
if (bigEndian) {
for (byte sridByte : sridBytes) {
srid = (srid << 8) + (sridByte & 0xff);
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < sridBytes.length; i++) {
srid += (sridBytes[i] & 0xff) << (8 * i);
}
}
WKBReader wkbReader = new WKBReader();
// WKBReader 把字节数组转成geometry对象。
byte[] wkb = new byte[geometryAsBytes.length - 4];
System.arraycopy(geometryAsBytes, 4, wkb, 0, wkb.length);
dbGeometry = wkbReader.read(wkb);
dbGeometry.setSRID(srid);
}
return dbGeometry;
}
}
Two. Use
Find the corresponding spatial point field and add a comment:
@TableField(typeHandler = GeometryTypeHandler.class)
as shown in the figure below
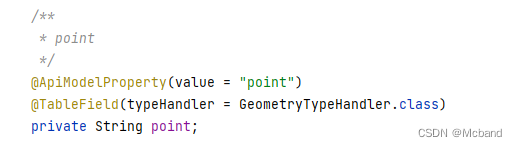
. In this case, the field content point (1 2) is normally passed in. When adding and editing, mybatisplus will automatically splice st_GeomFromText () to realize the entry and editing of spatial point data.