1 Introduction
In the previous chapters, we learned [Android Framework Series] Chapter 5 AMS Startup Process and [Android Framework Series] Chapter 6 AMS Principle Launcher Startup Process , and roughly understood AMSthe principle and startup process. In this chapter, we use reflection and dynamic AMSProxy for different Android versions Hook, 实现登录页面的跳转.
Here we only briefly introduce the ideas and key codes of HookAMS. If you need to know more, please go to the project address at the end of the article to download and view.
1.1 Realize opening the unified login page
In our Android APP, there is usually a login status. If you are not logged in, except for the splash screen page and the login page, you need to log in first to open other pages. Often the login status also has a term of validity. If the validity period expires, we need to jump to the login page instead of continuing to open the page. In this case, we can achieve it through HookAMS.
1.2 Realize opening the dynamic plug-in delivery page
In addition, HookAMSthe function of dynamically delivering plug-ins can also be realized through the method. For example, if the dynamically delivered plug- Activityin AndroidManifest.xmlis not registered, if you want to open it, you need to HookAMSuse the proxy page to AndroidManifest.xmlregister, and dynamically switch to the delivered plug-in when jumping InsideActivity
2 achieve
2.1 Implementation ideas
Through the way of dynamic proxy, the AMSmiddle startActivitymethod is intercepted, and the intention to jump is replaced with the one we want to open Activity. Since the source codes of different Androidversions AMSare different, here we distinguish SDK<=23, SDK<=28, and SDK>28these three situations for HookAMSadaptation. Let's take a look at the project structure
2.2 Project structure
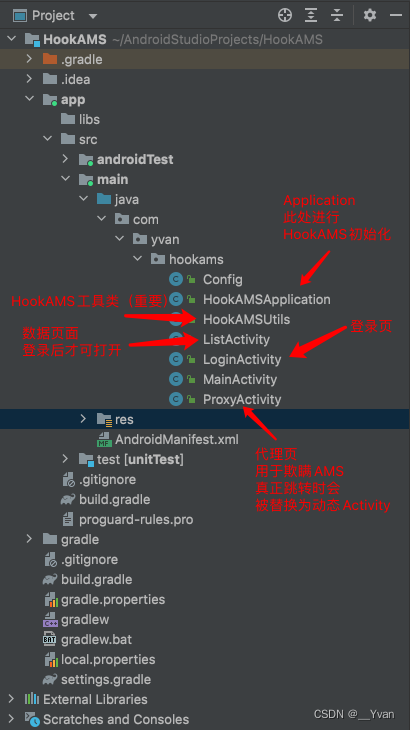
In the figure above, we can see that the project structure is as follows:
// Config 常量配置类
// HookAMSApplication Application进行HookAMS初始化
// HookAMSUtils HookAMS工具类,主要的Hook逻辑
// ListActivity 数据页面,登录后才可打开
// LoginActivity 登录页
// MainActivity 首页,这里打开数据页面
// ProxyActivity 代理页,用于欺瞒AMS,跳转时动态替换为真正Activity
First let's see how HookAMSApplication:
2.3 HookAMSApplication
package com.yvan.hookams;
import android.app.Application;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Looper;
/**
* @author yvan
* @date 2023/7/28
* @description
*/
public class HookAMSApplication extends Application {
private final Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
handler.post(this::hookAMS);
}
public void hookAMS() {
try {
HookAMSUtils hookUtils = new HookAMSUtils(this, ProxyActivity.class);
hookUtils.hookAms();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
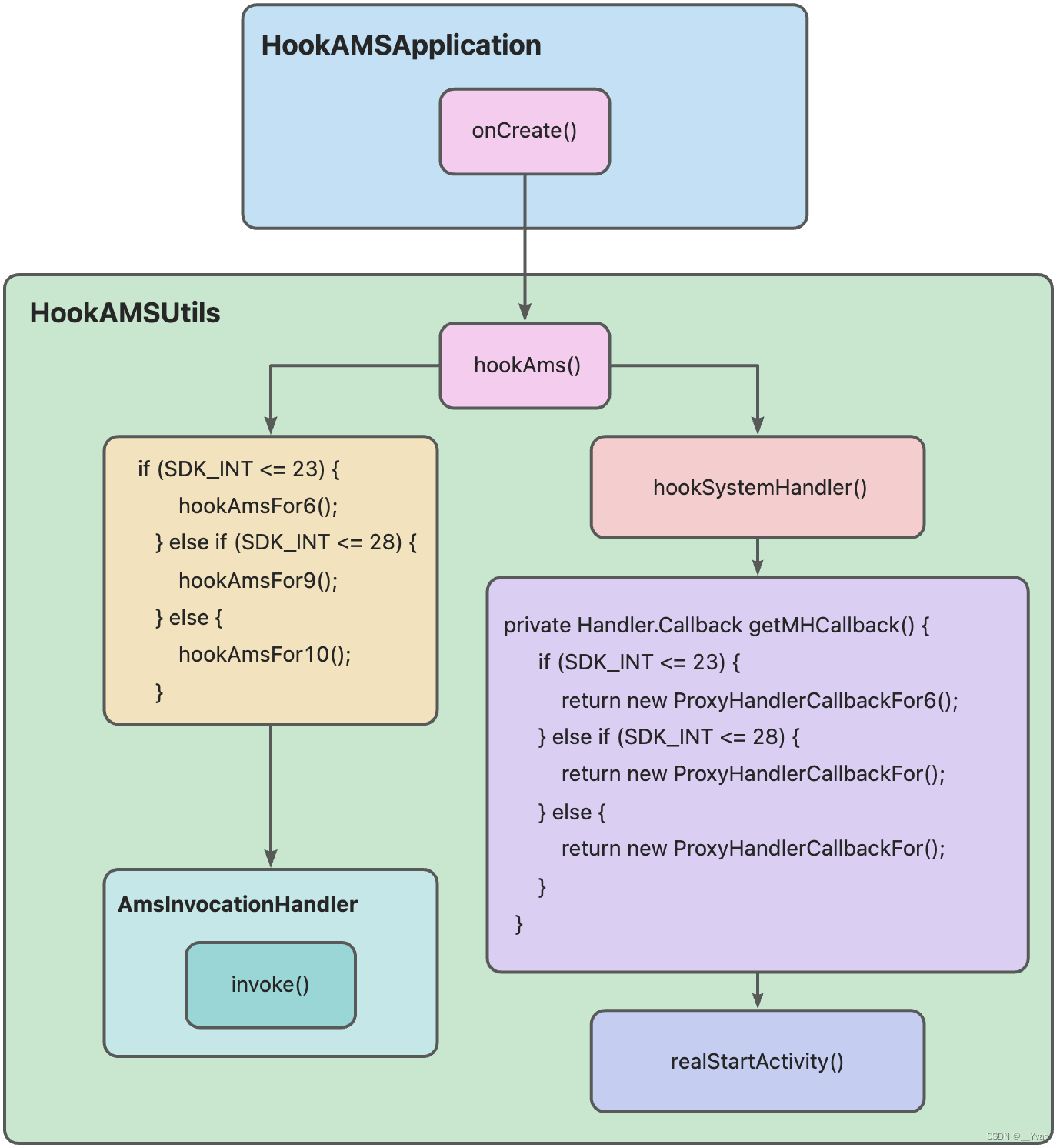
When the App starts, Applicationthe method passed onCreate()in the method calls the method of the class . Why use Handler? The initialization of the initialization has not been completed, and the direct call method will crash. Here, post is added to add the task to the queue of the main thread, so that there will be no crash exception.HandlerpostHookAMSUtilshookAms()ApplicationonCreate()hookAms()
Let's continue to look at HookAMSUtilsthe class:
2.4 HookAMSUtils
package com.yvan.hookams;
import static android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author yvan
* @date 2023/7/28
* @description Hook AMS工具类
*/
public class HookAMSUtils {
private static final String TAG = HookAMSUtils.class.getSimpleName();
private Context context;
private Class<?> proxyActivity;
/**
* proxyActivity 传入一个有注册在AndroidManifest的就行
*
* @param context
* @param proxyActivity
*/
public HookAMSUtils(Context context, Class<?> proxyActivity) {
this.context = context;
this.proxyActivity = proxyActivity;
}
public void hookAms() throws Exception {
if (SDK_INT <= 23) {
hookAmsFor6();
} else if (SDK_INT <= 28) {
hookAmsFor9();
} else {
hookAmsFor10();
}
hookSystemHandler();
}
public void hookAmsFor10() throws Exception {
Class<?> iActivityManagerClazz = Class.forName("android.app.IActivityTaskManager");
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityTaskManager");
Field singletonField = clazz.getDeclaredField("IActivityTaskManagerSingleton");
singletonField.setAccessible(true);
Object singleton = singletonField.get(null);
Class<?> singletonClass = Class.forName("android.util.Singleton");
Field mInstanceField = singletonClass.getDeclaredField("mInstance");
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
final Object mInstance = mInstanceField.get(singleton);
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()
, new Class[]{
iActivityManagerClazz}, new AmsInvocationHandler(mInstance));
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
mInstanceField.set(singleton, proxyInstance);
}
public void hookAmsFor9() throws Exception {
// 1.反射获取类>ActivityTaskManager,这个就是AMS实例
Class ActivityManagerClz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityManager");
// 2.获取IActivityManagerSingleton,并设置访问权限
Field iActivityManagerSingletonFiled = ActivityManagerClz.getDeclaredField("IActivityManagerSingleton");
iActivityManagerSingletonFiled.setAccessible(true);
// 因为是静态变量,所以获取的到的是默认值
final Object iActivityManagerSingletonObj = iActivityManagerSingletonFiled.get(null);
// 3.现在创建我们的AMS实例
// 由于IActivityManager是一个接口,那么其实我们可以使用Proxy类来进行代理对象的创建
// 结果被摆了一道,IActivityManager这玩意居然还是个AIDL,动态生成的类,编译器还不认识这个类,怎么办?反射咯
// 反射创建一个Singleton的class
Class SingletonClz = Class.forName("android.util.Singleton");
Field mInstanceField = SingletonClz.getDeclaredField("mInstance");
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
// 4.获取AMS Proxy
Object iActivityManagerObj = mInstanceField.get(iActivityManagerSingletonObj);
// 5.获取需要实现的接口IActivityManager实现类
Class iActivityManagerClz = Class.forName("android.app.IActivityManager");
// 6.动态生成接口对象
// 构建代理类需要两个东西用于创建伪装的Intent
// 拿到AMS实例,然后用代理的AMS换掉真正的AMS,代理的AMS则是用 假的Intent骗过了 activity manifest检测.
Object proxyIActivityManager = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{
iActivityManagerClz}, new AmsInvocationHandler(iActivityManagerObj));
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
// 7.替换掉系统的变量
mInstanceField.set(iActivityManagerSingletonObj, proxyIActivityManager);
}
public void hookAmsFor6() throws Exception {
//1.反射获取类>ActivityManagerNative
Class ActivityManagerClz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityManagerNative");
//2.获取变量>gDefault
Field IActivityManagerSingletonFiled = ActivityManagerClz.
getDeclaredField("gDefault");
//2.1 设置访问权限
IActivityManagerSingletonFiled.setAccessible(true);
//3. 获取变量的实例值
Object IActivityManagerSingletonObj = IActivityManagerSingletonFiled.get(null);
//4.获取mInstance
Class SingletonClz = Class.forName("android.util.Singleton");
Field mInstanceField = SingletonClz.getDeclaredField("mInstance");
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
//5.获取AMS Proxy
Object AMSProxy = mInstanceField.get(IActivityManagerSingletonObj);
//6.由于不能去手动实现IActivityManager实现类,
// 所以只能通过动态代理去动态生成实现类
//6.1 获取需要实现的接口
Class IActivityManagerClz = Class.forName("android.app.IActivityManager");
//6.2 动态生成接口对象
Object proxyIActivityManager = Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
new Class[]{
IActivityManagerClz}, new AmsInvocationHandler(AMSProxy));
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
//7.替换掉系统的变量
mInstanceField.set(IActivityManagerSingletonObj, proxyIActivityManager);
}
private class AmsInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object iActivityManagerObject;
public AmsInvocationHandler(Object iActivityManagerObject) {
this.iActivityManagerObject = iActivityManagerObject;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("startActivity".contains(method.getName())) {
Intent intent = null;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
Object arg = args[i];
if (arg instanceof Intent) {
intent = (Intent) args[i]; // 原意图,过不了安检
index = i;
break;
}
}
Intent proxyIntent = new Intent();
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(context, proxyActivity);
proxyIntent.setComponent(componentName);
proxyIntent.putExtra("realIntent", intent);
//替换原有的intent为我们自己生成的,为了骗过PMS
//为跳到我们的传入的proxyActivity
args[index] = proxyIntent;
}
return method.invoke(iActivityManagerObject, args);
}
}
//上面的主要是替换成我们自己的intent,骗过系统
//下面的主要是将我们上面替换的intent中,取出我们真正的意图(也就是正在要启动的Activity)
//
//下面是为了拿到mH对象,但是mH是一个非static 的值,那我们就只能拿到他的持有对象,也就是ActivityThread
//正好发现在ActivityThread类中有一个static变量sCurrentActivityThread值可以拿到ActivityThread类,那我们就从他入手
public void hookSystemHandler() throws Exception {
//1.反射ActivityThread
Class ActivityThreadClz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
//2. 获取sCurrentActivityThread 是一个static变量
Field field = ActivityThreadClz.getDeclaredField("sCurrentActivityThread");
field.setAccessible(true);
//3.获取ActivityThread对象
Object ActivityThreadObj = field.get(null);
//4.通过ActivityThreadObj获取到mH变量
Field mHField = ActivityThreadClz.getDeclaredField("mH");
mHField.setAccessible(true);
//5.获取到mH的对象
Handler mHObj = (Handler) mHField.get(ActivityThreadObj);//ok,当前的mH拿到了
//到这里,获取到mH的对象了,那我们怎么去监听他的方法调用呢?
//能不能通过动态代理?不能,因为它不是个接口
//由于在Handler的源码中,我们知道如果mCallback如果不等于空,就会调用mCallback的handleMessage方法。
//6.获取mH的mCallback
Field mCallbackField = Handler.class.getDeclaredField("mCallback");
mCallbackField.setAccessible(true);
//7.创建我们自己的Callback,自己处理handleMessage
Handler.Callback proxyMHCallback = getMHCallback();
//8.给系统的mH(Handler)的mCallback设值(proxyMHCallback)
mCallbackField.set(mHObj, proxyMHCallback);
}
private Handler.Callback getMHCallback() {
if (SDK_INT <= 23) {
return new ProxyHandlerCallbackFor6();
} else if (SDK_INT <= 28) {
return new ProxyHandlerCallbackFor();
} else {
return new ProxyHandlerCallbackFor();
}
}
private class ProxyHandlerCallbackFor6 implements Handler.Callback {
private int LAUNCH_ACTIVITY = 100;
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what == LAUNCH_ACTIVITY) {
try {
Class ActivityClientRecord = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread$ActivityClientRecord");
//判断传过来的值(msg.obj)是不是ClientTransaction对象
if (!ActivityClientRecord.isInstance(msg.obj)) return false;
//获取ActivityClientRecord的intent变量
Field intentField = ActivityClientRecord.getDeclaredField("intent");
intentField.setAccessible(true);
if (intentField == null) return false;
Intent mIntent = (Intent) intentField.get(msg.obj);
if (mIntent == null) return false;
//获取我们之前传入的realIntent,也就是我们真正要打开的Activity
Intent realIntent = mIntent.getParcelableExtra("realIntent");
if (realIntent == null) {
return false;
}
realStartActivity(mIntent, realIntent);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
}
private class ProxyHandlerCallbackFor implements Handler.Callback {
private int EXECUTE_TRANSACTION = 159;
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what == EXECUTE_TRANSACTION) {
try {
Class ClientTransactionClz = Class.forName("android.app.servertransaction.ClientTransaction");
//判断传过来的值(msg.obj)是不是ClientTransaction对象
if (!ClientTransactionClz.isInstance(msg.obj)) return false;
Class LaunchActivityItemClz = Class.forName("android.app.servertransaction.LaunchActivityItem");
//获取ClientTransaction的mActivityCallbacks变量
Field mActivityCallbacksField = ClientTransactionClz
.getDeclaredField("mActivityCallbacks");//ClientTransaction的成员
//设值成
mActivityCallbacksField.setAccessible(true);
//获取到ASM传递过来的值(ClientTransaction对象)里的mActivityCallbacks变量
Object mActivityCallbacksObj = mActivityCallbacksField.get(msg.obj);
List list = (List) mActivityCallbacksObj;
if (list.size() == 0) return false;
Object LaunchActivityItemObj = list.get(0);
if (!LaunchActivityItemClz.isInstance(LaunchActivityItemObj)) return false;
//获取mIntent变量
Field mIntentField = LaunchActivityItemClz.getDeclaredField("mIntent");
mIntentField.setAccessible(true);
//获取mIntent对象
Intent mIntent = (Intent) mIntentField.get(LaunchActivityItemObj);
//获取我们之前传入的realIntent,也就是我们真正要打开的Activity
Intent realIntent = mIntent.getParcelableExtra("realIntent");
if (realIntent == null) {
return false;
}
realStartActivity(mIntent, realIntent);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
}
private void realStartActivity(Intent mIntent, Intent realIntent) {
//登录判断
SharedPreferences share = context.getSharedPreferences(Config.SP_NAME,
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
if (share.getBoolean(Config.SP_KEY_LOGIN, false)) {
mIntent.setComponent(realIntent.getComponent());
} else {
Log.i(TAG, "handleLauchActivity: " + realIntent.getComponent().getClassName());
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(context, LoginActivity.class);
mIntent.putExtra("extraIntent", realIntent.getComponent()
.getClassName());
mIntent.setComponent(componentName);
}
}
}
From the above code we can see:
hookAms()The methods are SDK<=23, SDK<=28, and SDK>28 to carry out HookAMS, but they are all similar. In fact, the object is obtainedIActivityManager, through the dynamic proxyProxy.newProxyInstance()Hook to all its methods, and throughAmsInvocationHandlerthe callback of the method call.hookSystemHandler()The methodhookAms()is executed immediately after the method is called, and the properties and instancesandroid.app.ActivityThreadof the class object are obtained through reflection , and the callback method of the Handler is intercepted. According to the different situations of SDK<=23, SDK<=28, and SDK>28, it is handled differently.sCurrentActivityThreadHandlermHhandleMessage()- In 1,
AmsInvocationHandlerit is responsiblehookAms()for the processing of the method call from the Hook. IfHookit isCallbackjudged asstartActivity()a method, it will be intercepted, and the Activity intent we really want to jump will be stored in the Extra. Since the real Activity intent is hidden in the original Intent, So you just need to take out the real intent and replace itsIntentintent with the one you want to openActivity. - In 2 , the method
handleMessage()is actuallystartActivity()intercepted, and if it is judged that it is not logged in, it will take out the actual jumpActivityfromExtrathe inside and jump, and if it is logged in, it will not replace the Intent intent to jump.
3 summary
The article only HookAMSanalyzes the core code ideas. Here is the project address . Friends can download and view it by themselves. Don’t forget to click Star, thank you! !