I. Introduction
Recently, I have been doing work related to polygons, which involves a lot of related algorithms. Let’s summarize it for everyone’s convenience.如果帮到您,记得点赞!
2. Demonstration
【Online demo】
【Source code gitee】
Three, use
All core algorithms are in utils.js, including parameter descriptions, if you don’t understand, you can see the use of the demo.
3.1 Polygon scaling
3.1.1 Algorithms
Reference: https://blog.csdn.net/sun_and_breeze/article/details/107517088
Reference: https://blog.csdn.net/shyjhyp11/article/details/126396170
3.1.2 Use:
需配合‘顺时针判断’方法一起使用
const polygon = [
{
x: 314, y: 61 },
{
x: 385, y: 128 },
{
x: 496, y: 35 },
{
x: 390, y: 182 },
];
// 多边形放大5个单位
const zoomInPolygon = scalePolygon(polygon, 5); // 返回放大后多边形坐标集合
// 多边形缩小5个单位
const zoomOutPolygon = scalePolygon(polygon, -5); // 返回缩小后多边形坐标集合
3.1.3 Demonstration:
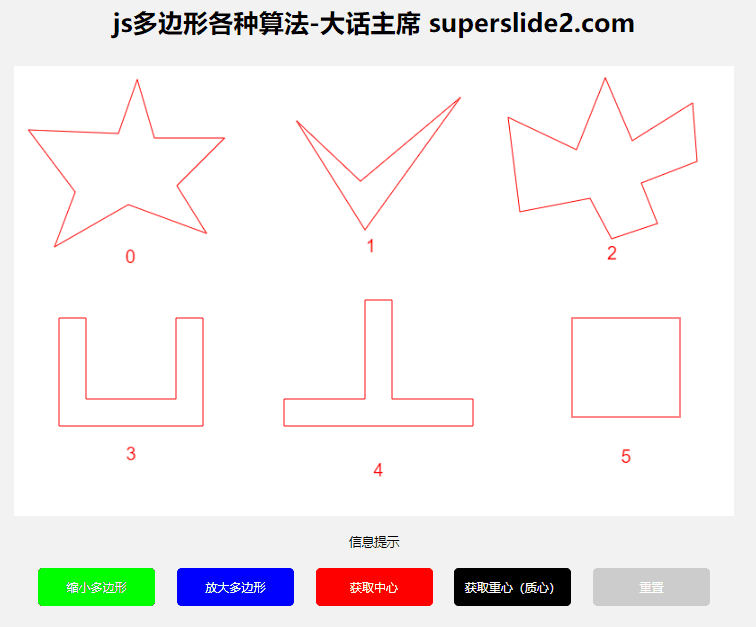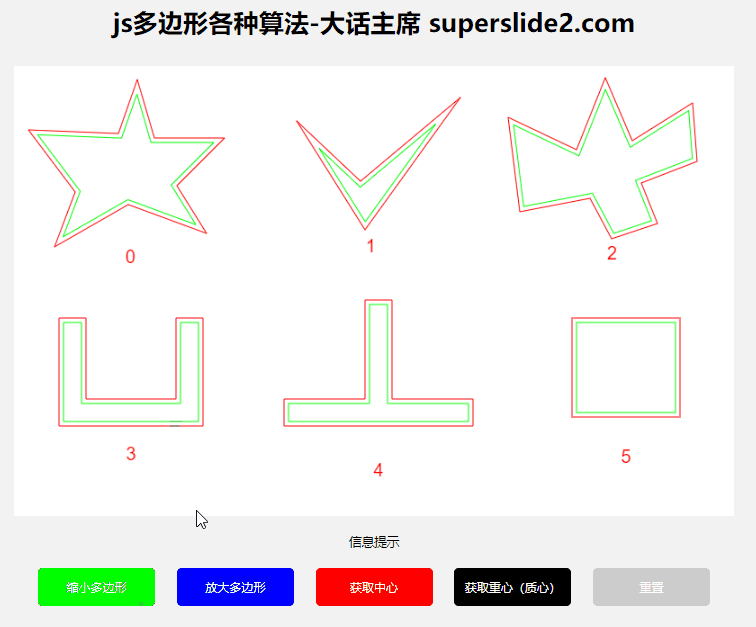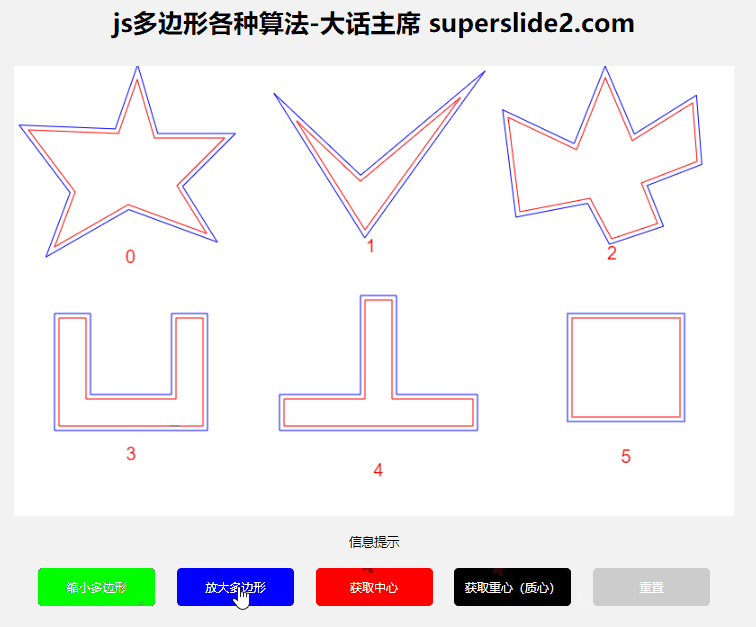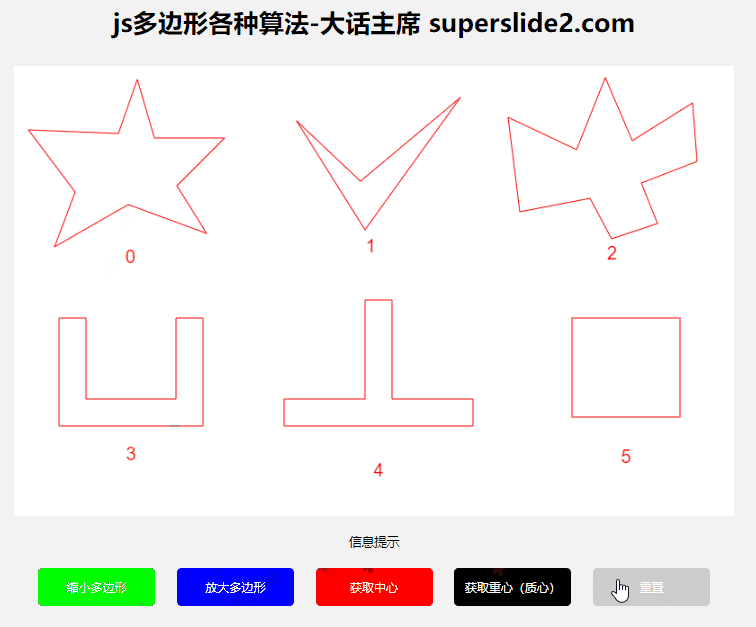
3.2 Get polygon center, center of gravity/centroid
The polygon center and the center of gravity are different. If it is a regular polygon, it is the same. If it is a concave polygon, the center will be outside the graph in many cases, so you need to choose the center or the center of gravity according to the actual situation.
3.2.1 Algorithm
Center algorithm: relatively simple, that is, to add up all coordinate points and calculate the average.
Center of gravity/centroid algorithm reference: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43847416/article/details/95781817
3.2.2 Use
const polygon = [
{
x: 314, y: 61 },
{
x: 385, y: 128 },
{
x: 496, y: 35 },
{
x: 390, y: 182 },
];
// 获取多边形中心
const center = getPolygonCenter(polygon); // 返回坐标点
// 获取多边形重心/质心
const baryCenter = getPolygonBaryCenter(polygon); // 返回坐标点
3.2.3 Demonstration
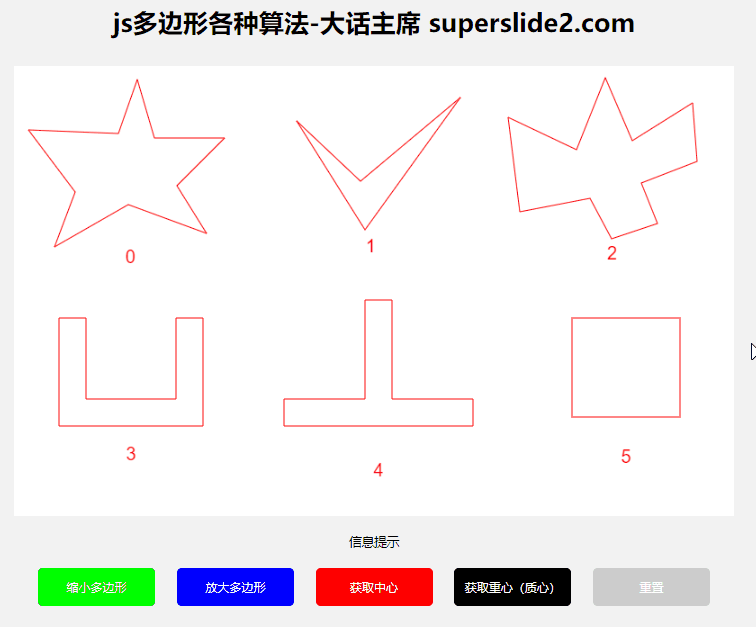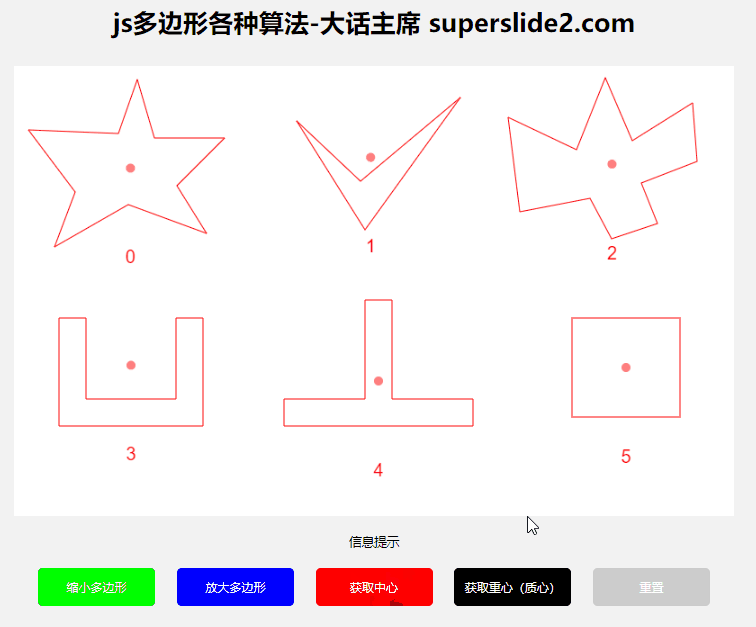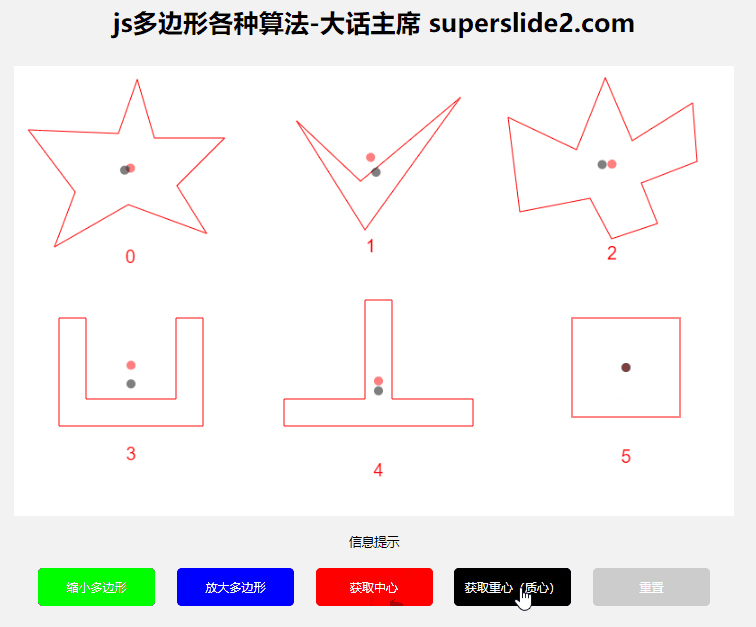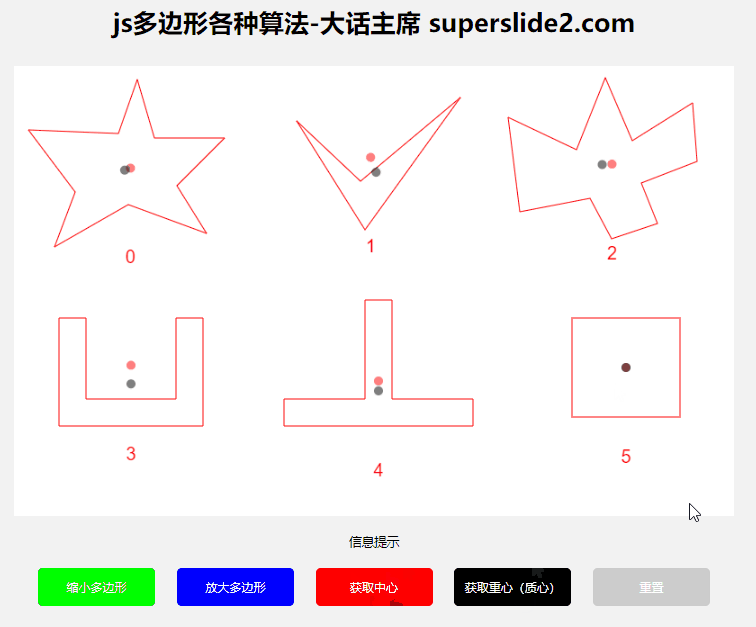
3.3 Determine whether the point is within the polygon
3.3.1 Algorithms
This example uses the "ray method"
reference: https://blog.csdn.net/WilliamSun0122/article/details/77994526
3.3.2 Use
const point = {
x: 322, y: 90 };
const polygon = [
{
x: 314, y: 61 },
{
x: 385, y: 128 },
{
x: 496, y: 35 },
{
x: 390, y: 182 },
];
// 判断点是否在多边形内部
const isIn = isInPolygon(point,polygon); // true or false
3.3.3 Demonstration
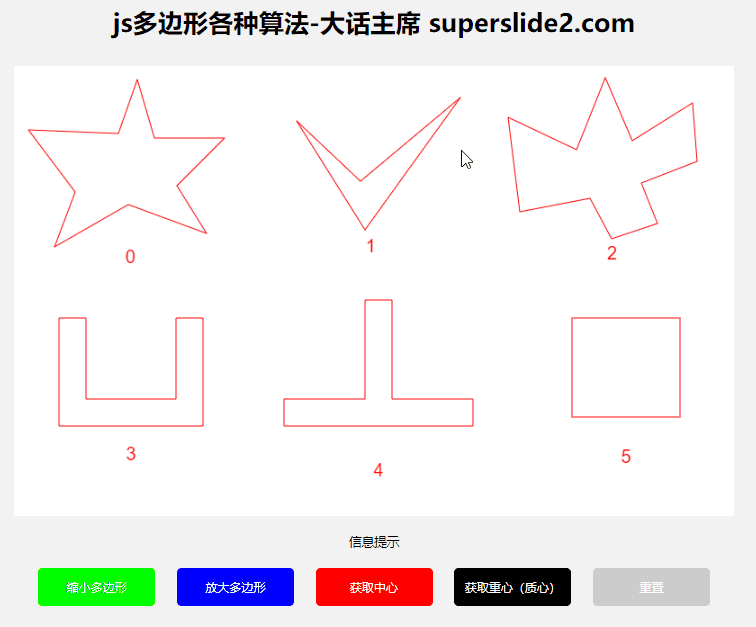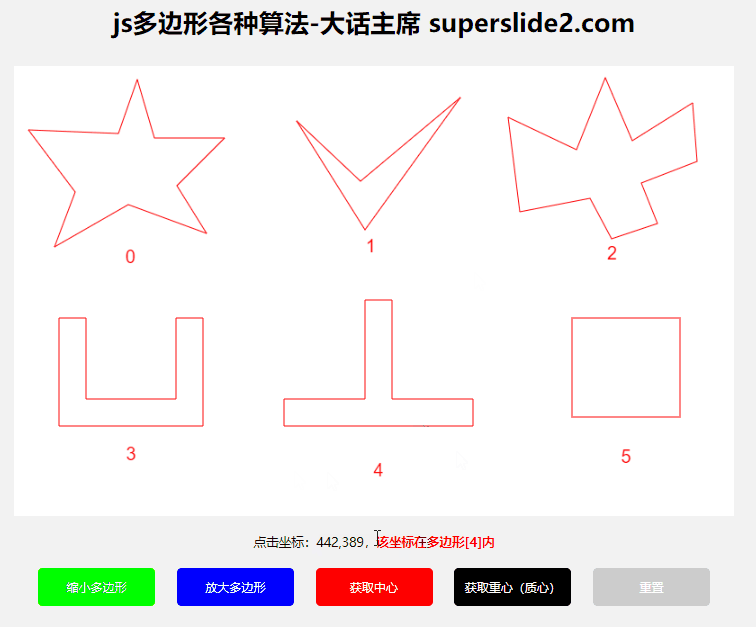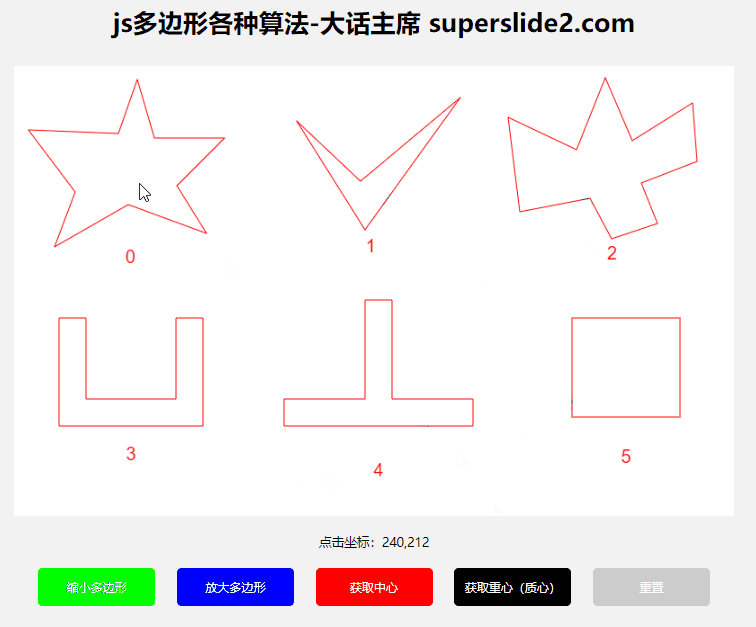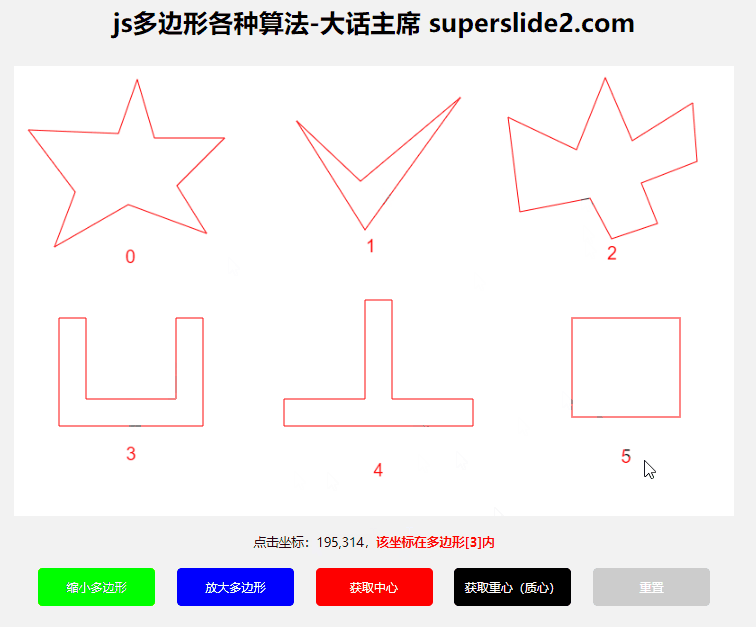
3.4 Determine whether the polygon is clockwise
3.4.1 Algorithms
Reference: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34447899/article/details/93991335
3.4.1 Use
const polygon = [
{
x: 314, y: 61 },
{
x: 385, y: 128 },
{
x: 496, y: 35 },
{
x: 390, y: 182 },
];
// 判断多边形坐标是否顺时针
const isClock = isClockwise(polygon); // true or false
3.4.2 Demonstration
I won't demonstrate here
4. Core code
/*
* @Author: 大话主席 superslide2.com
* @Description: 多边形核心算法
*/
/**
* 获取多边形中心点
* @param {Point[]} points 点坐标数组 [{x:0,y:0}...]
*/
function getPolygonCenter(points) {
if (!Array.isArray(points) || points.length < 3) {
console.error("多边形坐标集合不能少于3个");
return;
}
const result = {
x: 0, y: 0 };
points.forEach((p) => {
result.x += p.x;
result.y += p.y;
});
result.x /= points.length;
result.y /= points.length;
return result;
}
/**
* 获取多边形重心(质心)
* @param {Point[]} points 点坐标数组 [{x:0,y:0}...]
*/
function getPolygonBaryCenter(points) {
if (!Array.isArray(points) || points.length < 3) {
console.error("多边形坐标集合不能少于3个");
return;
}
const result = {
x: 0, y: 0 };
let area = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= points.length; i++) {
const curX = points[i % points.length].x;
const curY = points[i % points.length].y;
const nextX = points[i - 1].x;
const nextY = points[i - 1].y;
const temp = (curX * nextY - curY * nextX) / 2;
area += temp;
result.x += (temp * (curX + nextX)) / 3;
result.y += (temp * (curY + nextY)) / 3;
}
result.x /= area;
result.y /= area;
return result;
}
/**
* 判断点是否在多边形内部
* @param {Point} point 点坐标
* @param {Point[]} points 点坐标数组 [{x:0,y:0}...]
* @returns
*/
function isInPolygon(point, points) {
if (!Array.isArray(points) || points.length < 3) {
console.error("多边形坐标集合不能少于3个");
return;
}
const n = points.length;
let nCross = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const p1 = points[i];
const p2 = points[(i + 1) % n];
// 求解 y=p.y 与 p1 p2 的交点
// p1p2 与 y=p0.y平行
if (p1.y === p2.y) continue;
// 交点在p1p2延长线上
if (point.y < Math.min(p1.y, p2.y)) continue;
// 交点在p1p2延长线上
if (point.y >= Math.max(p1.y, p2.y)) continue;
// 求交点的 X 坐标
const x = ((point.y - p1.y) * (p2.x - p1.x)) / (p2.y - p1.y) + p1.x;
// 只统计单边交点
if (x > point.x) nCross++;
}
return nCross % 2 === 1;
}
/**
* 缩放多边形坐标
* @decoration 需配合顺时针判断方法一起使用
* @param {Point[]} points 点坐标数组 [{x:0,y:0}...]
* @param {number} extra 外延大小。为正: 向外扩; 为负: 向内缩
* @return {Point[]} 扩展或缩小后的多边形点坐标数组
*/
function scalePolygon(points, extra) {
if (!Array.isArray(points) || points.length < 3) {
console.error("多边形坐标集合不能少于3个");
return;
}
const ps = points;
// 通过顺时针判断取正值还是负值
const extra0 = isClockwise(ps) ? -extra : extra;
const norm = (x, y) => Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
const len = ps.length;
const polygon = [];
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const point = ps[i];
const point1 = ps[i === 0 ? len - 1 : i - 1];
const point2 = ps[i === len - 1 ? 0 : i + 1];
// 向量PP1
const vectorX1 = point1.x - point.x; // 向量PP1 横坐标
const vectorY1 = point1.y - point.y; // 向量PP1 纵坐标
const n1 = norm(vectorX1, vectorY1); // 向量的平方根 为了对向量PP1做单位化
let vectorUnitX1 = vectorX1 / n1; // 向量单位化 横坐标
let vectorUnitY1 = vectorY1 / n1; // 向量单位化 纵坐标
// 向量PP2
const vectorX2 = point2.x - point.x; // 向量PP2 横坐标
const vectorY2 = point2.y - point.y; // 向量PP2 纵坐标
const n2 = norm(vectorX2, vectorY2); // 向量的平方根 为了对向量PP1做单位化
let vectorUnitX2 = vectorX2 / n2; // 向量单位化 横坐标
let vectorUnitY2 = vectorY2 / n2; // 向量单位化 纵坐标
// PQ距离
const vectorLen =
-extra0 /
Math.sqrt(
(1 - (vectorUnitX1 * vectorUnitX2 + vectorUnitY1 * vectorUnitY2)) / 2
);
// 根据向量的叉乘积来判断角是凹角还是凸角
if (vectorX1 * vectorY2 + -1 * vectorY1 * vectorX2 < 0) {
vectorUnitX2 *= -1;
vectorUnitY2 *= -1;
vectorUnitX1 *= -1;
vectorUnitY1 *= -1;
}
// PQ的方向
const vectorX = vectorUnitX1 + vectorUnitX2;
const vectorY = vectorUnitY1 + vectorUnitY2;
const n = vectorLen / norm(vectorX, vectorY);
const vectorUnitX = vectorX * n;
const vectorUnitY = vectorY * n;
const polygonX = vectorUnitX + point.x;
const polygonY = vectorUnitY + point.y;
polygon[i] = {
x: polygonX, y: polygonY };
}
return polygon;
}
/**
* 判断坐标数组是否顺时针(默认为false)
* @param {Point[]} points 点坐标数组 [{x:0,y:0}...]
* @returns {boolean} 是否顺时针
*/
function isClockwise(points) {
// 三个点可以判断矢量是顺时针旋转还是逆时针旋转的,但由于可能存在凹边,所以并不是任意三点都可以正确反映多边形的走向
// 因此需要取多边形中绝对是凸边的点来判断,
// 多边形中的极值点(x最大或x最小或y最大或y最小)它与相邻两点构成的边必然是凸边,因此我们先取出多边形中的极值点,再由极值点和其前后两点去判断矢量的走向,从而判断出多边形的走向。
if (!Array.isArray(points) || points.length < 3) {
console.error("多边形坐标集合不能少于3个");
return false;
}
let coords = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(points));
if (coords[0] === coords[coords.length - 1]) {
coords = coords.slice(0, coords.length - 1);
}
coords = coords.reverse();
let maxXIndex = 0;
let maxX = parseFloat(coords[maxXIndex].x);
let c1;
let c2;
let c3;
for (let i = 0; i < coords.length; i++) {
if (parseFloat(coords[i].x) > maxX) {
maxX = parseFloat(coords[i].x);
maxXIndex = i;
}
}
if (maxXIndex === 0) {
c1 = coords[coords.length - 1];
c2 = coords[maxXIndex];
c3 = coords[maxXIndex + 1];
} else if (maxXIndex === coords.length - 1) {
c1 = coords[maxXIndex - 1];
c2 = coords[maxXIndex];
c3 = coords[0];
} else {
c1 = coords[maxXIndex - 1];
c2 = coords[maxXIndex];
c3 = coords[maxXIndex + 1];
}
const x1 = parseFloat(c1.x);
const y1 = parseFloat(c1.y);
const x2 = parseFloat(c2.x);
const y2 = parseFloat(c2.y);
const x3 = parseFloat(c3.x);
const y3 = parseFloat(c3.y);
const s = (x1 - x3) * (y2 - y3) - (x2 - x3) * (y1 - y3);
return s < 0;
}
5. Like
如果帮到您,点个赞再走!