linux network service NFS
1. Introduction to NFS
NFS (Network File Service)
- NFS is a network file system protocol based on tcp/ip transmission, originally opened by sun
- By using the NFS protocol, the client can access the shared resources in the remote server as if accessing the local directory
- Features:
- Using tcp/ip to transfer network files
- low security
- easy to operate
- Suitable for LAN environment
Two. NFS principle

Three. NFS advantages
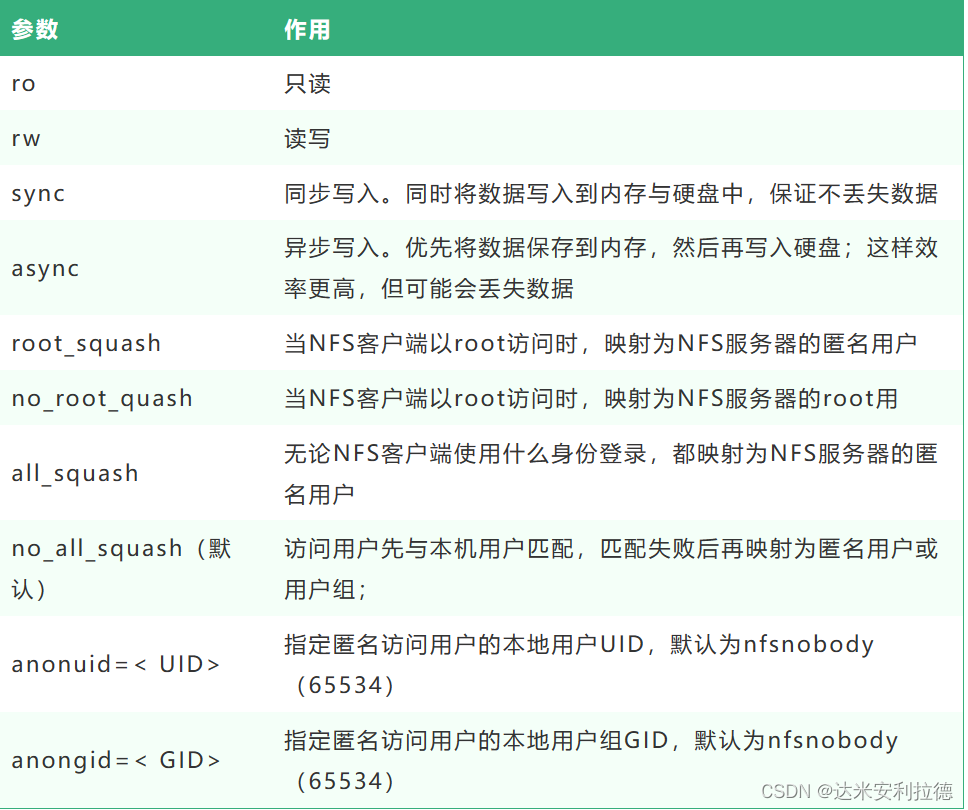
package
- nfs-utils (nfs port number 2049/tcp)
- rpcbind (rpc port number 111/tcp
NFS main process - rpm.nfsd is the most important NFS process, whether the management client can log in
- rpm.mountd mounts and unmounts NFS file systems, including permission management
- rpm.lockd is not necessary, manage file locks to avoid simultaneous errors
- rpm.statd is not necessary, check the consistency of the file, and can repair the file
Four. Configuration file
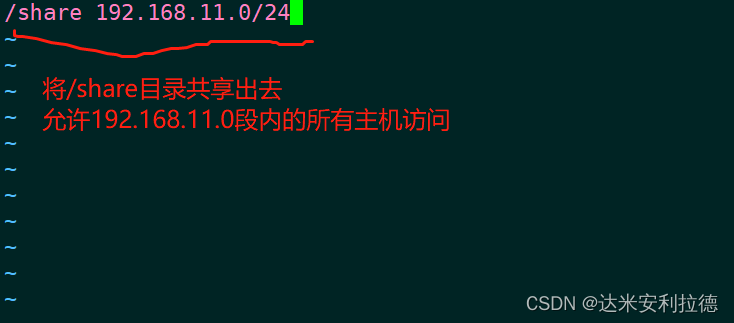
Configuration file location: /etc/exports
5. Operation steps of NFS shared storage service
Experimental environment:
server; 192.168.11.11
Client: 192.168.11.12
Experimental steps:
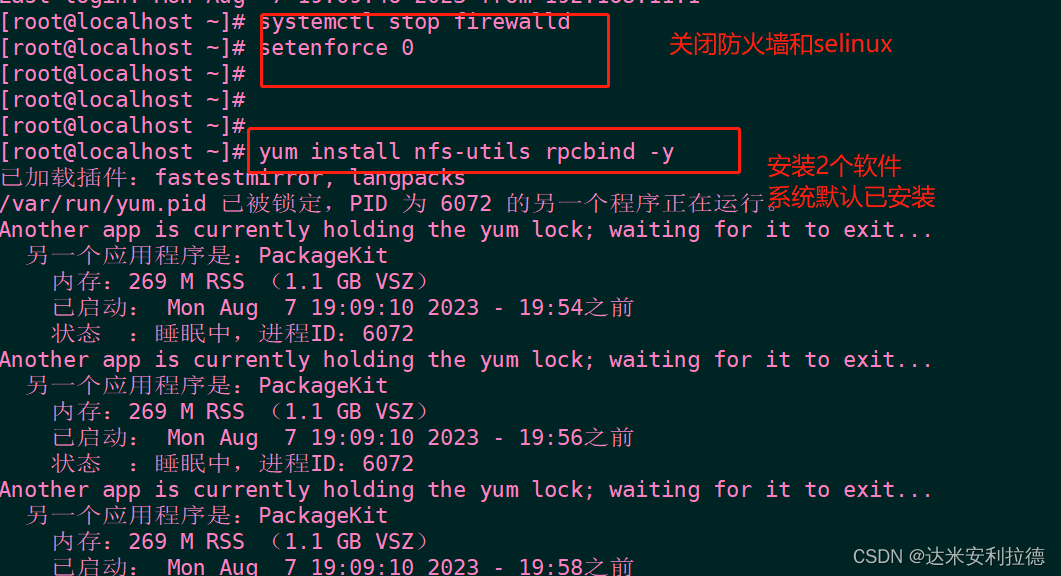
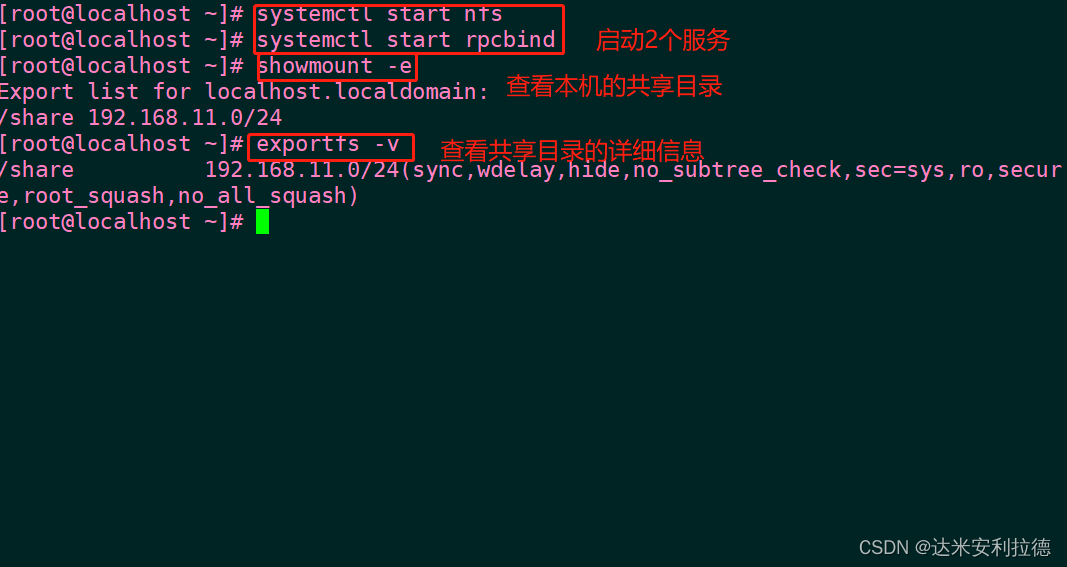
1. Server settings

2. Client settings
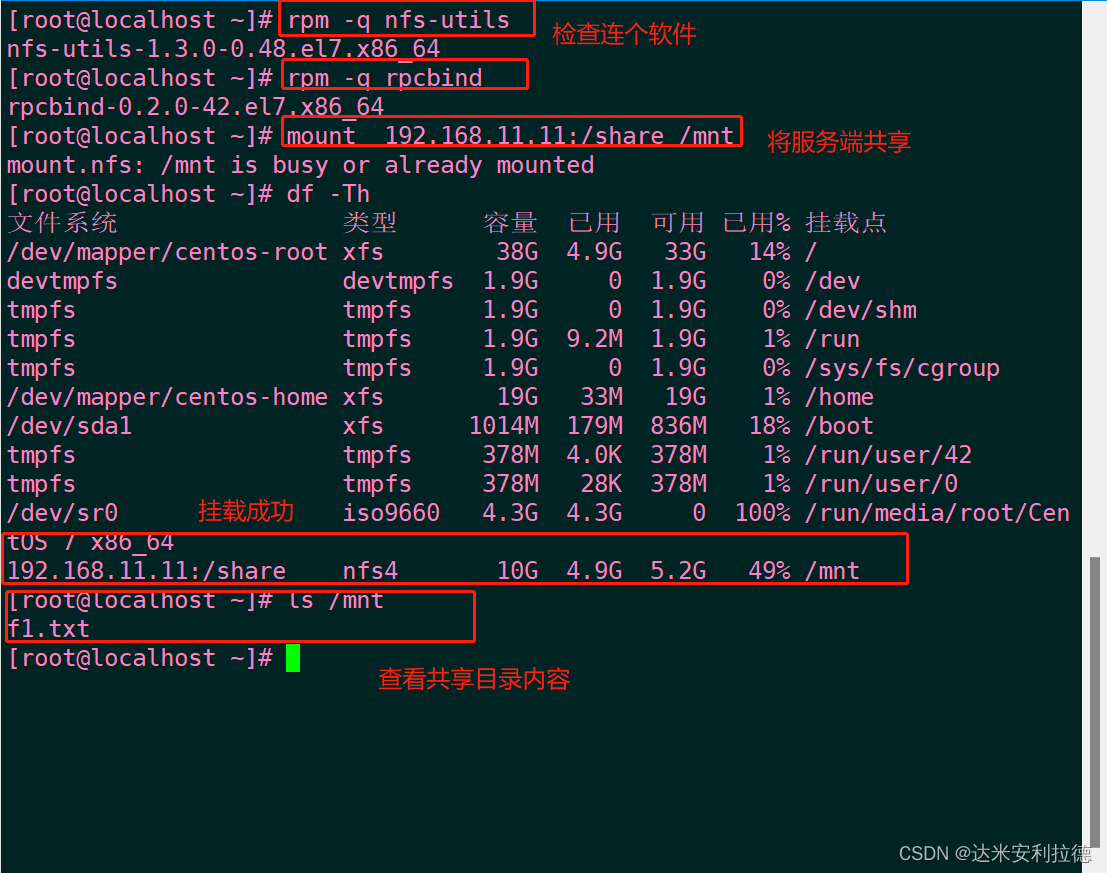
1.1 After starting the service, you can use the "ss -ntuap | grep 111" command to check whether the port is enabled, so as to confirm whether the service is started normally.
1.2 Use the mount command to mount temporarily. If you want to permanently mount the NFS shared directory locally, you need to modify the configuration file /etc/fstab. The mount parameters are: defaults,_netdev.
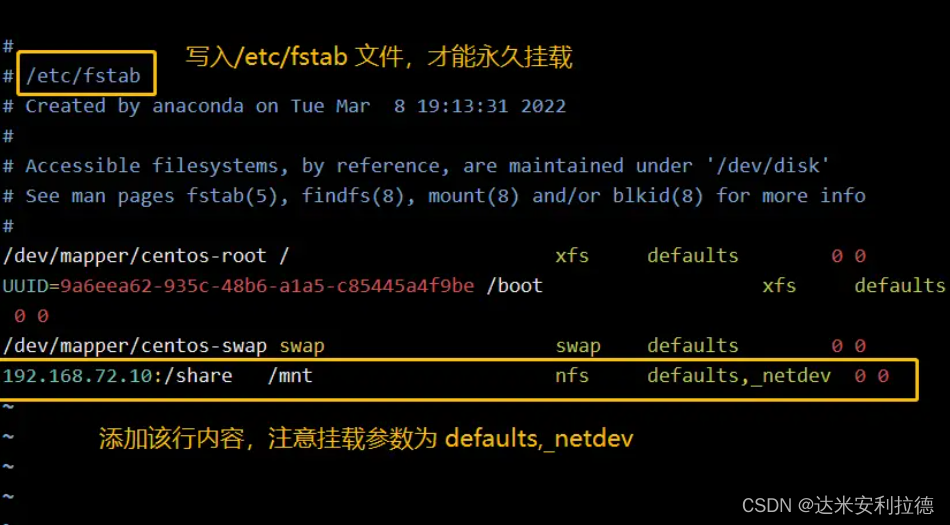
1.3 However, if a permanent mount is written in the local configuration file /etc/fstab, and then the server cancels the NFS share to the local machine, then a "CRTL-D" error will appear when the machine restarts, and you need to enter the but In user mode, edit /etc/fstab to delete the mount information of the NFS shared directory.
1.4 Forcibly unmount NFS: umount -lf mount device/mount point
- If the server-side NFS service suddenly stops, while the client is mounting and using it, the execution of the df -h command will freeze on the client. At this time, it is not possible to directly use the umount command to unmount directly, and the -lf option needs to be added to unmount.